Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 12 - Green Economy in The Context of Sustainable Development
Chapter 12 - Green Economy in The Context of Sustainable Development
Uploaded by
SAIPRASAD MOHAPATRACopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Neft Challan CanaraDocument1 pageNeft Challan Canarasrivenkateshwaracoirs250564% (11)
- Sustainability in Construction (CIOB PDF)Document11 pagesSustainability in Construction (CIOB PDF)avinine86100% (4)
- Pixonix Inc - Currency Exposure Session IXDocument3 pagesPixonix Inc - Currency Exposure Session IXshiv50% (2)
- Eco AssignmentDocument2 pagesEco AssignmentMehul BariNo ratings yet
- Porter's Diamond Model (Analysis of Competitiveness) ...Document2 pagesPorter's Diamond Model (Analysis of Competitiveness) ...BobbyNicholsNo ratings yet
- Alfred-Marshall UpdatedDocument7 pagesAlfred-Marshall UpdatedChristina AureNo ratings yet
- Why We Need Sustainable Development Goals: ES FRDocument6 pagesWhy We Need Sustainable Development Goals: ES FRAbhishek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- GSDR 2023 Key Messages - 1Document4 pagesGSDR 2023 Key Messages - 1Ani MeqvabishviliNo ratings yet
- Abdul Bari Khan SST ProjectDocument20 pagesAbdul Bari Khan SST ProjectAbdul Bari KhanNo ratings yet
- MCN-201 - Sustainable EngineeringDocument40 pagesMCN-201 - Sustainable EngineeringMuhammed SaalimNo ratings yet
- Eco AssignmentDocument2 pagesEco AssignmentMehul BariNo ratings yet
- UKAD Guidance Sustainability - 2019Document5 pagesUKAD Guidance Sustainability - 2019Alexander MartinezNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Outline (A Strategy and Action For Sustainable Living and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGroup 7 Outline (A Strategy and Action For Sustainable Living and Developmenttadioaneljo159No ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Concept: Yolanda Wirawan (1510534028) Vidia Ferila (1510534026) Tefi Putri Meliska (1510534023)Document15 pagesSustainable Development Concept: Yolanda Wirawan (1510534028) Vidia Ferila (1510534026) Tefi Putri Meliska (1510534023)Bertha Muhammad SyahNo ratings yet
- Issues, and Challenges of Green Economics: Dr. Naresh Chandra Sahu School of HSS&M IIT BhubaneswarDocument39 pagesIssues, and Challenges of Green Economics: Dr. Naresh Chandra Sahu School of HSS&M IIT BhubaneswarVIVEK SINGHNo ratings yet
- 16.0 ConclusionsDocument6 pages16.0 ConclusionsMansi bhagatNo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument21 pagesSustainable DevelopmentAmaan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Unit V (Sustainable Developmen) - Dr. Suvendu BarikDocument37 pagesUnit V (Sustainable Developmen) - Dr. Suvendu BarikTECH TUBENo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument20 pagesSustainable DevelopmentJennifer Mayano75% (4)
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument21 pagesSustainable DevelopmentMarjorie EbiteNo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument21 pagesSustainable DevelopmentAryan SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Economics of SustainableDocument2 pagesThe Economics of Sustainabledheeraj.linkupNo ratings yet
- Achieving Green Growth Transformation ReportDocument24 pagesAchieving Green Growth Transformation ReporthumejraNo ratings yet
- SF Zero Draft Submission - FINALDocument19 pagesSF Zero Draft Submission - FINALMarc Gloria StevensNo ratings yet
- Week12 - 56 To 61Document103 pagesWeek12 - 56 To 61Khushboo chauhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-1Document36 pagesUnit 1-1Arpit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development DefinitionDocument31 pagesSustainable Development DefinitionAnisha KumariNo ratings yet
- Bel 47Document7 pagesBel 47Db DbNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document4 pagesUnit 1jaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Updated PCTP SBP 23Document154 pagesUpdated PCTP SBP 23Precious Onyeka OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development IntroductionDocument24 pagesSustainable Development IntroductionKoteswararao GundaboluNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World (Gec 8)Document4 pagesContemporary World (Gec 8)Sanchez MikeryanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development: Economics and The EnvironmentDocument59 pagesSustainable Development: Economics and The EnvironmentAikansh JainNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev ReportDocument16 pagesEcon Dev ReportNic NicNo ratings yet
- National Action Plan On Climate ChangeDocument56 pagesNational Action Plan On Climate ChangeHussainNo ratings yet
- Systemic Approach To Sustainable Development Strategies and Food SecurityDocument26 pagesSystemic Approach To Sustainable Development Strategies and Food SecuritykuganatsukiNo ratings yet
- V1.3 Zero Policy Draft - 31-05-2023Document12 pagesV1.3 Zero Policy Draft - 31-05-2023rishiputraNo ratings yet
- Hackfest 2024Document18 pagesHackfest 2024anujgupta9278No ratings yet
- Pias Development AssignmentDocument31 pagesPias Development Assignmentpias azmirNo ratings yet
- ' ''ShivanshuDocument12 pages' ''ShivanshuShivanshu RajputNo ratings yet
- Sustainable 123 PPTDocument21 pagesSustainable 123 PPTyuvrajchoudhary135No ratings yet
- Sustainable Principles and Practices: Introduction To The Ideas, Issues and Concepts of Sustainable DevelopmentDocument7 pagesSustainable Principles and Practices: Introduction To The Ideas, Issues and Concepts of Sustainable Developmentanubhav dasguptaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 Role of Government & International BodiesDocument30 pagesLECTURE 3 Role of Government & International Bodiesn0195520kNo ratings yet
- 14 Chapter 11 ConclusionDocument5 pages14 Chapter 11 ConclusionSustainable Neighbourhoods NetworkNo ratings yet
- Climate Change GovernanceDocument26 pagesClimate Change GovernanceKaab RanaNo ratings yet
- Off Wizballs InnitDocument8 pagesOff Wizballs Innitpratik.jha0208No ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument20 pagesSustainable DevelopmentTanay KhemaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 2022Document26 pagesLecture 3 2022NURUL YAHSIFAH SYQELLA BINTI YAHYA BK21110100No ratings yet
- How Is A Green Economy Defined?Document22 pagesHow Is A Green Economy Defined?Anya Scott SorrorityNo ratings yet
- Government of India: National Action Plan On Climate ChangeDocument62 pagesGovernment of India: National Action Plan On Climate ChangePrashant PalNo ratings yet
- GEC State of The World FinalDocument17 pagesGEC State of The World Finalvivek0724bryantNo ratings yet
- SustainableDocument6 pagesSustainableMaryGrace LagamiaNo ratings yet
- ECO-City Planning Methods and ToolsDocument19 pagesECO-City Planning Methods and ToolsStefan Pallantzas67% (3)
- Research Methodology and TechniquesDocument71 pagesResearch Methodology and TechniquesVinod TyagiNo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument26 pagesSustainable DevelopmentCëz PäscuälNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development: San Carlos CollegeDocument13 pagesSustainable Development: San Carlos CollegeArya Guzman82% (11)
- Sustainable Development PDFDocument27 pagesSustainable Development PDFKartik guliaNo ratings yet
- Key Elements of A Global DealDocument56 pagesKey Elements of A Global DealANDI Agencia de Noticias do Direito da InfanciaNo ratings yet
- Economic Globalization and SustainabilityDocument15 pagesEconomic Globalization and SustainabilityPrincess Dungca FloresNo ratings yet
- WDR10 Main MessagesDocument2 pagesWDR10 Main Messagesfaizan25No ratings yet
- Sustinibilty and Ui Green Metric RankingDocument34 pagesSustinibilty and Ui Green Metric RankingEslam Alaa100% (1)
- Global Devt and DivideDocument15 pagesGlobal Devt and DivideJinalyn NacuspagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Sustainability-A New Direction For DevelopmentDocument10 pagesChapter 3 - Sustainability-A New Direction For DevelopmentSAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Making Cities More SustainableDocument14 pagesChapter 10 - Making Cities More SustainableSAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Energy For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument11 pagesChapter 9 - Energy For Sustainable DevelopmentSAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Module 1: Demand and Supply Analysis: IIM Bodhgaya Tamali ChakrabortyDocument15 pagesModule 1: Demand and Supply Analysis: IIM Bodhgaya Tamali ChakrabortySAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - From Global Concern To Local ActionDocument10 pagesChapter 8 - From Global Concern To Local ActionSAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - The Private Sector - Business and Civil SocietyDocument10 pagesChapter 7 - The Private Sector - Business and Civil SocietySAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Analysis (Lecture 1 and 2)Document21 pagesDemand and Supply Analysis (Lecture 1 and 2)SAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Afar10joint ArrangementDocument8 pagesAfar10joint ArrangementJohn DomingoNo ratings yet
- SABMiller: Strategic Position in 2007 and Its' Future ImplicationsDocument16 pagesSABMiller: Strategic Position in 2007 and Its' Future ImplicationsTom Jacob100% (8)
- Effect of Leadership On Organisational PerformanceDocument21 pagesEffect of Leadership On Organisational PerformanceRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Municipal Social Welfare and Development Office Social Case StudyDocument2 pagesMunicipal Social Welfare and Development Office Social Case StudyHannah Naki MedinaNo ratings yet
- Eco Sem 1Document5 pagesEco Sem 1Tutul BiswasNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Club Pilates - 2015-10-28 - FDD - Xponential FitnessDocument233 pagesClub Pilates - 2015-10-28 - FDD - Xponential FitnessFuzzy PandaNo ratings yet
- Lifting of Corporate VeilDocument8 pagesLifting of Corporate VeilPratulNo ratings yet
- Final Requirements: Logistics Management BA-519Document5 pagesFinal Requirements: Logistics Management BA-519GINANo ratings yet
- Fn5623-Fn6623-Assignment: International DiversificationDocument7 pagesFn5623-Fn6623-Assignment: International DiversificationJoyce WanguiNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Review QuestionsDocument12 pagesCost Accounting Review QuestionsYckzCasera100% (9)
- Business2018 4 21401210Document12 pagesBusiness2018 4 21401210Sri PraveenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Encouraging Entrepreneurship in The Philippines: Name: Renelle Habac SECTION: CBET-01-401PDocument4 pagesChapter 9: Encouraging Entrepreneurship in The Philippines: Name: Renelle Habac SECTION: CBET-01-401PRenelle HabacNo ratings yet
- Relationship Marketing An Important Tool For Succe PDFDocument11 pagesRelationship Marketing An Important Tool For Succe PDFSimon Malou Manyang MangethNo ratings yet
- Aorpc3601a 2023Document4 pagesAorpc3601a 2023radhikaenterprises106057No ratings yet
- How To Develop New Profit Centers: Mike Pownall, DVMDocument2 pagesHow To Develop New Profit Centers: Mike Pownall, DVMAditya Pratama SarwonoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Set 1 Dividend Discount ModelsDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Set 1 Dividend Discount ModelsNick HaldenNo ratings yet
- Balco Employees Union (Regd.) v. Union of IndiaDocument34 pagesBalco Employees Union (Regd.) v. Union of IndiaAnonymous XuOGlMiNo ratings yet
- Financial Profit & Loss KPI Dashboard: Open Index Income StatementDocument30 pagesFinancial Profit & Loss KPI Dashboard: Open Index Income StatementMohannad100% (2)
- Shree MaheshwariDocument69 pagesShree Maheshwarixc123544No ratings yet
- Fpu Budgeting FormsDocument11 pagesFpu Budgeting FormsKelvinNo ratings yet
- Homework 4題目Document2 pagesHomework 4題目劉百祥No ratings yet
- Business Plan ExampleDocument11 pagesBusiness Plan ExampleNichol CorderoNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy of Nishat Textile Mills Assignment IIDocument8 pagesMarketing Strategy of Nishat Textile Mills Assignment IINaureen AyubNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Concept Adoption On Customer Satisfaction - Customers PerspectiveDocument171 pagesThe Effect of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Concept Adoption On Customer Satisfaction - Customers PerspectiveMaheenNo ratings yet
- 5P ModelDocument2 pages5P ModelShella AzizahNo ratings yet
Chapter 12 - Green Economy in The Context of Sustainable Development
Chapter 12 - Green Economy in The Context of Sustainable Development
Uploaded by
SAIPRASAD MOHAPATRAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 12 - Green Economy in The Context of Sustainable Development
Chapter 12 - Green Economy in The Context of Sustainable Development
Uploaded by
SAIPRASAD MOHAPATRACopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 12 - Green Economy in the
Context of Sustainable Development
Overview
• About Green Economy (GE) in Relation to SD
• Key Development Parameters
• Good Life Within Planetary Boundaries
• General GE Strategies
• Key Enabling Conditions
• Four Visions of GE
• Landmarks on the GE Road
About Green Economy in Relation
to SD
• Green economy: A series of co-ordinated policy changes affecting key
development parameters that make up the core of the country
strategy for SD
• Sustainable development: A type of development that meets the
needs of the present generation without compromising the
possibilities of future generations to meet their needs
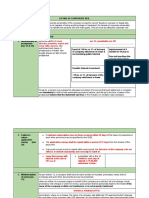
Key Development Parameters
• Institutions whose characteristics have important impacts on the
incentive structures for development stakeholders
Examples:
o Tariff systems for basic goods and services, such as water, energy and public transport
(flat rate or per unit; degree of cost coverage; and adjustment for inflation)
o Tax bases, structures and rates (does the system tax good things and subsidise
pollution or vice versa?)
o Temporary or permanent subsidies
Good Life Within Planetary Boundaries
General GE Strategies
• Reduction in environmental pollution and ecosystem degradation Strongly benefits the
poor who suffered more
• Gradual recovery of ecosystems and their services to humans, for instance, degraded
lands and forests
• Growth in the number and quality of jobs in sustainable businesses, for instance, in
renewable energy
• Increase in numbers of people having access to renewable energy services
• More energy- and water-efficient infrastructure and buildings in expanding cities
• Access to sustainably produced food for the poor in DCs
Key Enabling Conditions
• SD as a long-term investment goal of public and private sector
• Effective policy co-ordination between government agencies (both levels and
policy areas)
• Fair public awareness of environment and development issues, which
accepts/supports GE/SD policy rationales
• Customers and citizens willing to accept sustainable options, for instance,
improved public transport and paid parking
• Interests opposing the challenge to their business and short-term profitability
unable to block SD changes
• Improved monitoring and law enforcement
Four Visions of GE
• Bio-environmentalist: The food system has increased its own financial result by putting burdens on
people and the environment; fair trade over free trade; support biological farming; promote
vegetarian and vegan alternatives
• Institutionalist: Focus on constant productivity increases has led to a system that exhausts soil and
pollutes water with pesticide leftovers; support the shift of public funds to ecological forms of
agriculture
• Market-liberal: IFIs imposed conditions on poor country lenders to minimise regulation, reduce
trade barriers, and privatise technical and market advisory services and cheap lending facilities
• Social Green: Smallholder farmers are business people, educators and stewards of the land; must
have our support against extortive practices by powerful investors (TNCs) from rich countries;
against GMO food
Landmarks on the GE Road
• Pioneer countries in high-, middle- and low-income country groups that try out the
new concept
• Co-ordinate policies and resources from international donors (development banks)
• Dialogues with stakeholder groups in order to explore common interests and
strengths and inform new priorities
• Mobilise and exchange knowledge on technology and systems in order to improve
planning, measure progress and avoid mistakes that could derail the GE venture
• Gather and analyse statistical and qualitative information about GE initiatives to
promote fast learning
End of Chapter 12 Green Economy is a starter and
sustainable Development
somehow an end stage of the
journey for a good life within
planetary boundaries.
Nevertheless, ongoing
development of a sustainable
nature will take place, preferably
on the basis of a social contract
between leaders and the
community.
You might also like
- Neft Challan CanaraDocument1 pageNeft Challan Canarasrivenkateshwaracoirs250564% (11)
- Sustainability in Construction (CIOB PDF)Document11 pagesSustainability in Construction (CIOB PDF)avinine86100% (4)
- Pixonix Inc - Currency Exposure Session IXDocument3 pagesPixonix Inc - Currency Exposure Session IXshiv50% (2)
- Eco AssignmentDocument2 pagesEco AssignmentMehul BariNo ratings yet
- Porter's Diamond Model (Analysis of Competitiveness) ...Document2 pagesPorter's Diamond Model (Analysis of Competitiveness) ...BobbyNicholsNo ratings yet
- Alfred-Marshall UpdatedDocument7 pagesAlfred-Marshall UpdatedChristina AureNo ratings yet
- Why We Need Sustainable Development Goals: ES FRDocument6 pagesWhy We Need Sustainable Development Goals: ES FRAbhishek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- GSDR 2023 Key Messages - 1Document4 pagesGSDR 2023 Key Messages - 1Ani MeqvabishviliNo ratings yet
- Abdul Bari Khan SST ProjectDocument20 pagesAbdul Bari Khan SST ProjectAbdul Bari KhanNo ratings yet
- MCN-201 - Sustainable EngineeringDocument40 pagesMCN-201 - Sustainable EngineeringMuhammed SaalimNo ratings yet
- Eco AssignmentDocument2 pagesEco AssignmentMehul BariNo ratings yet
- UKAD Guidance Sustainability - 2019Document5 pagesUKAD Guidance Sustainability - 2019Alexander MartinezNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Outline (A Strategy and Action For Sustainable Living and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGroup 7 Outline (A Strategy and Action For Sustainable Living and Developmenttadioaneljo159No ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Concept: Yolanda Wirawan (1510534028) Vidia Ferila (1510534026) Tefi Putri Meliska (1510534023)Document15 pagesSustainable Development Concept: Yolanda Wirawan (1510534028) Vidia Ferila (1510534026) Tefi Putri Meliska (1510534023)Bertha Muhammad SyahNo ratings yet
- Issues, and Challenges of Green Economics: Dr. Naresh Chandra Sahu School of HSS&M IIT BhubaneswarDocument39 pagesIssues, and Challenges of Green Economics: Dr. Naresh Chandra Sahu School of HSS&M IIT BhubaneswarVIVEK SINGHNo ratings yet
- 16.0 ConclusionsDocument6 pages16.0 ConclusionsMansi bhagatNo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument21 pagesSustainable DevelopmentAmaan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Unit V (Sustainable Developmen) - Dr. Suvendu BarikDocument37 pagesUnit V (Sustainable Developmen) - Dr. Suvendu BarikTECH TUBENo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument20 pagesSustainable DevelopmentJennifer Mayano75% (4)
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument21 pagesSustainable DevelopmentMarjorie EbiteNo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument21 pagesSustainable DevelopmentAryan SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Economics of SustainableDocument2 pagesThe Economics of Sustainabledheeraj.linkupNo ratings yet
- Achieving Green Growth Transformation ReportDocument24 pagesAchieving Green Growth Transformation ReporthumejraNo ratings yet
- SF Zero Draft Submission - FINALDocument19 pagesSF Zero Draft Submission - FINALMarc Gloria StevensNo ratings yet
- Week12 - 56 To 61Document103 pagesWeek12 - 56 To 61Khushboo chauhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-1Document36 pagesUnit 1-1Arpit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development DefinitionDocument31 pagesSustainable Development DefinitionAnisha KumariNo ratings yet
- Bel 47Document7 pagesBel 47Db DbNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document4 pagesUnit 1jaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Updated PCTP SBP 23Document154 pagesUpdated PCTP SBP 23Precious Onyeka OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development IntroductionDocument24 pagesSustainable Development IntroductionKoteswararao GundaboluNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World (Gec 8)Document4 pagesContemporary World (Gec 8)Sanchez MikeryanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development: Economics and The EnvironmentDocument59 pagesSustainable Development: Economics and The EnvironmentAikansh JainNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev ReportDocument16 pagesEcon Dev ReportNic NicNo ratings yet
- National Action Plan On Climate ChangeDocument56 pagesNational Action Plan On Climate ChangeHussainNo ratings yet
- Systemic Approach To Sustainable Development Strategies and Food SecurityDocument26 pagesSystemic Approach To Sustainable Development Strategies and Food SecuritykuganatsukiNo ratings yet
- V1.3 Zero Policy Draft - 31-05-2023Document12 pagesV1.3 Zero Policy Draft - 31-05-2023rishiputraNo ratings yet
- Hackfest 2024Document18 pagesHackfest 2024anujgupta9278No ratings yet
- Pias Development AssignmentDocument31 pagesPias Development Assignmentpias azmirNo ratings yet
- ' ''ShivanshuDocument12 pages' ''ShivanshuShivanshu RajputNo ratings yet
- Sustainable 123 PPTDocument21 pagesSustainable 123 PPTyuvrajchoudhary135No ratings yet
- Sustainable Principles and Practices: Introduction To The Ideas, Issues and Concepts of Sustainable DevelopmentDocument7 pagesSustainable Principles and Practices: Introduction To The Ideas, Issues and Concepts of Sustainable Developmentanubhav dasguptaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 Role of Government & International BodiesDocument30 pagesLECTURE 3 Role of Government & International Bodiesn0195520kNo ratings yet
- 14 Chapter 11 ConclusionDocument5 pages14 Chapter 11 ConclusionSustainable Neighbourhoods NetworkNo ratings yet
- Climate Change GovernanceDocument26 pagesClimate Change GovernanceKaab RanaNo ratings yet
- Off Wizballs InnitDocument8 pagesOff Wizballs Innitpratik.jha0208No ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument20 pagesSustainable DevelopmentTanay KhemaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 2022Document26 pagesLecture 3 2022NURUL YAHSIFAH SYQELLA BINTI YAHYA BK21110100No ratings yet
- How Is A Green Economy Defined?Document22 pagesHow Is A Green Economy Defined?Anya Scott SorrorityNo ratings yet
- Government of India: National Action Plan On Climate ChangeDocument62 pagesGovernment of India: National Action Plan On Climate ChangePrashant PalNo ratings yet
- GEC State of The World FinalDocument17 pagesGEC State of The World Finalvivek0724bryantNo ratings yet
- SustainableDocument6 pagesSustainableMaryGrace LagamiaNo ratings yet
- ECO-City Planning Methods and ToolsDocument19 pagesECO-City Planning Methods and ToolsStefan Pallantzas67% (3)
- Research Methodology and TechniquesDocument71 pagesResearch Methodology and TechniquesVinod TyagiNo ratings yet
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument26 pagesSustainable DevelopmentCëz PäscuälNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development: San Carlos CollegeDocument13 pagesSustainable Development: San Carlos CollegeArya Guzman82% (11)
- Sustainable Development PDFDocument27 pagesSustainable Development PDFKartik guliaNo ratings yet
- Key Elements of A Global DealDocument56 pagesKey Elements of A Global DealANDI Agencia de Noticias do Direito da InfanciaNo ratings yet
- Economic Globalization and SustainabilityDocument15 pagesEconomic Globalization and SustainabilityPrincess Dungca FloresNo ratings yet
- WDR10 Main MessagesDocument2 pagesWDR10 Main Messagesfaizan25No ratings yet
- Sustinibilty and Ui Green Metric RankingDocument34 pagesSustinibilty and Ui Green Metric RankingEslam Alaa100% (1)
- Global Devt and DivideDocument15 pagesGlobal Devt and DivideJinalyn NacuspagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Sustainability-A New Direction For DevelopmentDocument10 pagesChapter 3 - Sustainability-A New Direction For DevelopmentSAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Making Cities More SustainableDocument14 pagesChapter 10 - Making Cities More SustainableSAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Energy For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument11 pagesChapter 9 - Energy For Sustainable DevelopmentSAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Module 1: Demand and Supply Analysis: IIM Bodhgaya Tamali ChakrabortyDocument15 pagesModule 1: Demand and Supply Analysis: IIM Bodhgaya Tamali ChakrabortySAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - From Global Concern To Local ActionDocument10 pagesChapter 8 - From Global Concern To Local ActionSAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - The Private Sector - Business and Civil SocietyDocument10 pagesChapter 7 - The Private Sector - Business and Civil SocietySAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Analysis (Lecture 1 and 2)Document21 pagesDemand and Supply Analysis (Lecture 1 and 2)SAIPRASAD MOHAPATRANo ratings yet
- Afar10joint ArrangementDocument8 pagesAfar10joint ArrangementJohn DomingoNo ratings yet
- SABMiller: Strategic Position in 2007 and Its' Future ImplicationsDocument16 pagesSABMiller: Strategic Position in 2007 and Its' Future ImplicationsTom Jacob100% (8)
- Effect of Leadership On Organisational PerformanceDocument21 pagesEffect of Leadership On Organisational PerformanceRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Municipal Social Welfare and Development Office Social Case StudyDocument2 pagesMunicipal Social Welfare and Development Office Social Case StudyHannah Naki MedinaNo ratings yet
- Eco Sem 1Document5 pagesEco Sem 1Tutul BiswasNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Club Pilates - 2015-10-28 - FDD - Xponential FitnessDocument233 pagesClub Pilates - 2015-10-28 - FDD - Xponential FitnessFuzzy PandaNo ratings yet
- Lifting of Corporate VeilDocument8 pagesLifting of Corporate VeilPratulNo ratings yet
- Final Requirements: Logistics Management BA-519Document5 pagesFinal Requirements: Logistics Management BA-519GINANo ratings yet
- Fn5623-Fn6623-Assignment: International DiversificationDocument7 pagesFn5623-Fn6623-Assignment: International DiversificationJoyce WanguiNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Review QuestionsDocument12 pagesCost Accounting Review QuestionsYckzCasera100% (9)
- Business2018 4 21401210Document12 pagesBusiness2018 4 21401210Sri PraveenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Encouraging Entrepreneurship in The Philippines: Name: Renelle Habac SECTION: CBET-01-401PDocument4 pagesChapter 9: Encouraging Entrepreneurship in The Philippines: Name: Renelle Habac SECTION: CBET-01-401PRenelle HabacNo ratings yet
- Relationship Marketing An Important Tool For Succe PDFDocument11 pagesRelationship Marketing An Important Tool For Succe PDFSimon Malou Manyang MangethNo ratings yet
- Aorpc3601a 2023Document4 pagesAorpc3601a 2023radhikaenterprises106057No ratings yet
- How To Develop New Profit Centers: Mike Pownall, DVMDocument2 pagesHow To Develop New Profit Centers: Mike Pownall, DVMAditya Pratama SarwonoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Set 1 Dividend Discount ModelsDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Set 1 Dividend Discount ModelsNick HaldenNo ratings yet
- Balco Employees Union (Regd.) v. Union of IndiaDocument34 pagesBalco Employees Union (Regd.) v. Union of IndiaAnonymous XuOGlMiNo ratings yet
- Financial Profit & Loss KPI Dashboard: Open Index Income StatementDocument30 pagesFinancial Profit & Loss KPI Dashboard: Open Index Income StatementMohannad100% (2)
- Shree MaheshwariDocument69 pagesShree Maheshwarixc123544No ratings yet
- Fpu Budgeting FormsDocument11 pagesFpu Budgeting FormsKelvinNo ratings yet
- Homework 4題目Document2 pagesHomework 4題目劉百祥No ratings yet
- Business Plan ExampleDocument11 pagesBusiness Plan ExampleNichol CorderoNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy of Nishat Textile Mills Assignment IIDocument8 pagesMarketing Strategy of Nishat Textile Mills Assignment IINaureen AyubNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Concept Adoption On Customer Satisfaction - Customers PerspectiveDocument171 pagesThe Effect of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Concept Adoption On Customer Satisfaction - Customers PerspectiveMaheenNo ratings yet
- 5P ModelDocument2 pages5P ModelShella AzizahNo ratings yet