Professional Documents
Culture Documents
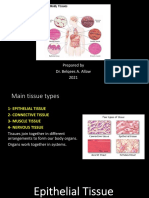
Animal Tissues
Animal Tissues
Uploaded by
Alanie Rakim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesSimple squamous epithelium lines cavities like the mouth and blood vessels. Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in glands and kidney tubules. Simple columnar epithelium lines the stomach and intestines. Glandular epithelium cells secrete substances like enzymes and hormones. Connective tissues include ligaments connecting bones, cartilages in joints, tendons connecting muscle to bone, and adipose tissue. Epithelial tissues perform several functions including protection, sensation, secretion, absorption, excretion, diffusion, cleaning, and reducing friction.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSimple squamous epithelium lines cavities like the mouth and blood vessels. Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in glands and kidney tubules. Simple columnar epithelium lines the stomach and intestines. Glandular epithelium cells secrete substances like enzymes and hormones. Connective tissues include ligaments connecting bones, cartilages in joints, tendons connecting muscle to bone, and adipose tissue. Epithelial tissues perform several functions including protection, sensation, secretion, absorption, excretion, diffusion, cleaning, and reducing friction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesAnimal Tissues
Animal Tissues
Uploaded by
Alanie RakimSimple squamous epithelium lines cavities like the mouth and blood vessels. Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in glands and kidney tubules. Simple columnar epithelium lines the stomach and intestines. Glandular epithelium cells secrete substances like enzymes and hormones. Connective tissues include ligaments connecting bones, cartilages in joints, tendons connecting muscle to bone, and adipose tissue. Epithelial tissues perform several functions including protection, sensation, secretion, absorption, excretion, diffusion, cleaning, and reducing friction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
Animal Tissues
Simple Squamous Epithelium
• Squamous cells have
the appearance of
thin, flat plates. They
form the lining of
cavities such as the
mouth, blood
vessels, heart and
lungs and make up
the outer layers of
the skin.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
• Cube like cells.
• found in glands and in
the lining of the kidney
tubules as well as in the
ducts of the glands..
Simple Columnar Epithelium
• Columnar epithelium are
elongated.
• forms the lining of the
stomach and intestines.
Glandular epithelium
• Columnar and cuboidal
epithelial cells often
become specialized as
gland cells which are
capable of synthezising
and secreting certain
substances such as
enzymes, hormones,
milk, mucus, sweat, wax
and saliva.
Functions of Epithelium
• Protection Epithelial cells from the skin protect underlying
tissue from mechanical injury, harmful chemicals, invading
bacteria and from excessive loss of water.
• Sensation Sensory stimuli penetrate specialized epithelial cells.
Specialised epithelial tissue containing sensory nerve endings
is found in the skin, eyes, ears, nose and on the tongue.
• Secretion In glands, epithelial tissue is specialized to secrete
specific chemical substances such as enzymes, hormones and
lubricating fluids.
• Absorption Certain epithelial cells lining the small intestine
absorb nutrients from the digestion of food.
Functions of Epithelium
• Excretion Epithelial tissues in the kidney excrete waste
products from the body and reabsorb needed materials from
the urine. Sweat is also excreted from the body by epithelial
cells in the sweat glands.
• Diffusion Simple epithelium promotes the diffusion of gases,
liquids and nutrients. Because they form such a thin lining,
they are ideal for the diffusion of gases (eg. walls of capillaries
and lungs).
• Cleaning Ciliated epithelium assists in removing dust particles
and foreign bodies which have entered the air passages.
• Reduces Friction The smooth, tightly-interlocking, epithelial
cells that line the entire circulatory system reduce friction
between the blood and the walls of the blood vessels.
Connective Tissues
• Ligaments
• Ligament – connects two
bones together
Cartilages
Cartilage is usually found in
close association with bone
in the body. It is a type of
connective tissue which is
tough, semi-transparent,
elastic and flexible. The
matrix or ground substance
of cartilage consists mainly
of glyco-protein material,
chondroitin.
Hyaline cartilage
• Hyaline cartilage occurs
in trachea, the larynx,
the tip of the nose, in
the connection between
the ribs and the
breastbone and also the
ends of bone where they
form joints.
Fibrocartilage
• Fibrocartilage is found as discs between the vertebrae
between the pubic bones in front of the pelvic girdle
and around the edges of the articular cavities such as
the glenoid cavity in the shoulder joint.
Elastic Cartilage
• This type of cartilage is
found in the lobe of the
ear, the epiglottis and in
parts of the larynx.
Tendon
• Connects muscle to bone
Adipose tissues
You might also like
- Instant Download Basic Applied Concepts of Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 4th Edition Ebook PDF PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Basic Applied Concepts of Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 4th Edition Ebook PDF PDF Scribdmark.gallo26898% (53)
- Hemorrhage ShockDocument17 pagesHemorrhage ShockgrizzlovNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Diseases of The NewbornDocument9 pagesHemolytic Diseases of The NewbornLekshmi Manu100% (3)
- Epithelial TissuesDocument14 pagesEpithelial TissuesJhunelyn100% (2)
- Epithelial TissueDocument35 pagesEpithelial TissueSamreen RashidNo ratings yet
- SpecializedcellsDocument17 pagesSpecializedcellspewdiefannn3No ratings yet
- Epithelia CellsDocument18 pagesEpithelia CellsmohamadNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesRafael SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- Biology NinaDocument6 pagesBiology NinaadlinaarrifNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument3 pagesBiologyLuisa PalomoNo ratings yet
- Eptihelial NLDocument30 pagesEptihelial NLSalon LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Tissue: Physiology: Controlling & Coordinating SystemsDocument30 pagesTissue: Physiology: Controlling & Coordinating Systemsdibya patraNo ratings yet
- CH-6 TISSUES - Aug 4,2021Document9 pagesCH-6 TISSUES - Aug 4,2021selvasaku1964No ratings yet
- Lecture-1 With AnnonationDocument39 pagesLecture-1 With AnnonationShaily NainNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument47 pagesAnimal TissueJoshua Verzosa PalconitNo ratings yet
- Epithelial HighlightedDocument33 pagesEpithelial HighlightedharizgaleonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture NotesDocument94 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notesbiddyusmc100% (2)
- Tissues: Prepared By: Arthur Christian B. Mangio, PTRPDocument80 pagesTissues: Prepared By: Arthur Christian B. Mangio, PTRPjm fabellar100% (1)
- Ep It HeliumDocument75 pagesEp It HeliumSahin mollickNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument28 pagesEpithelial TissuesHamza SultanNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument80 pagesTissueskrmgxc8p4fNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: Dr. Bhuvaneswari CDocument23 pagesEpithelium: Dr. Bhuvaneswari CAjinkya AravindNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Classification of ElementsDocument24 pagesCH 3 Classification of Elementssachin aggarwal100% (1)
- Human Cell TypesDocument75 pagesHuman Cell Typesmegamemory14No ratings yet
- DR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesDocument49 pagesDR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesAnnie Khan100% (1)
- L13-Tissues-20201 2Document22 pagesL13-Tissues-20201 22szrc2wkhtNo ratings yet
- EpithelialDocument48 pagesEpithelialMbali MazongweNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument80 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument91 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsDivya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument105 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- 2.animal TissuesDocument50 pages2.animal TissuesAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Epithelia DR - RaviDocument60 pagesEpithelia DR - Ravi安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument68 pagesEpithelial TissueJASMEEN RAVALNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument33 pagesEpithelial TissueStnrhalizaNo ratings yet
- Dilek Akakin Epithelial TissueDocument65 pagesDilek Akakin Epithelial TissueErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Dilek Akakin Epithelial TissueDocument65 pagesDilek Akakin Epithelial TissueErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- ch-6 PPT 1Document17 pagesch-6 PPT 1UtkarshNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial Tissuebenrz1234No ratings yet
- Histology Lecture Chapter 3 PrelimDocument8 pagesHistology Lecture Chapter 3 PrelimFRANCESCA ALEXANDRIA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissues: StructureDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissues: StructureKristine JamilleNo ratings yet
- Xi New Zoo-Chapt - 3-Tissue Level OrganisationDocument45 pagesXi New Zoo-Chapt - 3-Tissue Level Organisationbalasubash1977No ratings yet
- Histology-The Study of TissuesDocument63 pagesHistology-The Study of Tissueshuguetteigiraneza9No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument26 pagesEpithelial Tissueaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Histology Lab GITDocument44 pagesHistology Lab GITkedas70No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesKenken MijaresNo ratings yet
- Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument68 pagesTissue Level of OrganizationCecil AlbaNo ratings yet
- 4b Epithelial TissueallDocument43 pages4b Epithelial Tissueallapi-159564163No ratings yet
- Tissues 4Document65 pagesTissues 4marianisie448100% (3)
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueReshmi SanjayNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands and MembranesDocument68 pagesTissues, Glands and MembranesMerrylFrancisco100% (1)
- Yy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYDocument64 pagesYy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYsreedam100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue: Workgroup Khiana Vélez Yoenys Casadiegos Magda Paola Jenny Julieth VillalobosDocument13 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Workgroup Khiana Vélez Yoenys Casadiegos Magda Paola Jenny Julieth VillalobosYoenys Casadiegos DuarteNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Animal TissuesDocument68 pagesPhysiology of Animal TissuesSudheera SemasingheNo ratings yet
- Zoology 15mo Lecture 1 RecordedDocument85 pagesZoology 15mo Lecture 1 RecordedyannolerouxNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- HistologyDocument5 pagesHistologySNo ratings yet
- Tissue Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument35 pagesTissue Anatomy and Physiologysnp88100% (1)
- TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATIONDocument8 pagesTISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATIONMaria MaeNo ratings yet
- HMM1414 Chapter 5 Part 1Document56 pagesHMM1414 Chapter 5 Part 1Luqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueSofia LiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and BiotechniquesDocument8 pagesMicrobiology and BiotechniquesAlanie RakimNo ratings yet
- Mendelian LawsDocument41 pagesMendelian LawsAlanie RakimNo ratings yet
- PLANTSDocument39 pagesPLANTSAlanie RakimNo ratings yet
- Bio Sci Final CoachingDocument16 pagesBio Sci Final CoachingAlanie RakimNo ratings yet
- An Aggregation of Similarly Specialized Cells Which Together Perform Specialized Functions Are CalledDocument44 pagesAn Aggregation of Similarly Specialized Cells Which Together Perform Specialized Functions Are CalledAlanie RakimNo ratings yet
- Critical Limits TableDocument2 pagesCritical Limits TableheidyNo ratings yet
- Sop For Immediate Spin Crossmatch Ver2Document9 pagesSop For Immediate Spin Crossmatch Ver2huangc17No ratings yet
- HELLP SyndromeDocument29 pagesHELLP SyndromeJames Jayson LibertoNo ratings yet
- Four Types of Animal TissuesDocument8 pagesFour Types of Animal TissuesAngel IgarNo ratings yet
- Thrombocytosis, Thrombocytopenia & Related Dissoders: Marshell Tendean, DPCP Department of Internal MedicineDocument29 pagesThrombocytosis, Thrombocytopenia & Related Dissoders: Marshell Tendean, DPCP Department of Internal MedicineAdit PrayogaNo ratings yet
- BIO 2311 Test #2 Study GuideDocument1 pageBIO 2311 Test #2 Study GuideAnnabell CheungNo ratings yet
- Blood PhysiologyDocument35 pagesBlood PhysiologyShane Margauxh AlabastroNo ratings yet
- Grafik QC Hematologi 2023 BaruDocument125 pagesGrafik QC Hematologi 2023 BaruSyifa nurfitriNo ratings yet
- Idexx Lasercyte Dx/Idexx Lasercyte Hematology Analyzer Operator'S GuideDocument34 pagesIdexx Lasercyte Dx/Idexx Lasercyte Hematology Analyzer Operator'S GuideCharity WesleyNo ratings yet
- Rodaks 6th Ed. Hema Lab Midterm ReviewerDocument30 pagesRodaks 6th Ed. Hema Lab Midterm ReviewerGerald SorianoNo ratings yet
- Tissue BiochemistryDocument40 pagesTissue BiochemistryZahid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- 11 Anti-Coagulants & FibrinolyticsDocument52 pages11 Anti-Coagulants & FibrinolyticsUmmuShefaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyTyrNo ratings yet
- Solubility Test For Sickle CellDocument14 pagesSolubility Test For Sickle CellChristian OranzaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood: February 2021Document23 pagesPhysiology of Blood: February 2021miknayrb galdianoNo ratings yet
- IMDC Anatomy Mock Test 1b-1-1Document4 pagesIMDC Anatomy Mock Test 1b-1-1Tofunmi AdegokeNo ratings yet
- Hematology Blood Test Results Manuel Garcia ColindresDocument7 pagesHematology Blood Test Results Manuel Garcia ColindresJUAN PABLO SOLISNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Paparan Suhu Dingin Terhadap Perubahan Tekanan Darah Sebelum Dan Sesudah BekerjaDocument4 pagesHubungan Paparan Suhu Dingin Terhadap Perubahan Tekanan Darah Sebelum Dan Sesudah BekerjaRomydaQurrotinA'yuniNo ratings yet
- RADHEDocument4 pagesRADHENeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications: A New Era in Cell CountingDocument2 pagesTechnical Specifications: A New Era in Cell CountingDinil KannurNo ratings yet
- Avian HematologyDocument16 pagesAvian HematologyNatalie Woodward100% (1)
- Biomechanics of Peripheral and Spinal Nerve RootsDocument86 pagesBiomechanics of Peripheral and Spinal Nerve RootsJawad HassanNo ratings yet
- Erythropoiesis: Staff NameDocument36 pagesErythropoiesis: Staff NameShresthaNo ratings yet
- Crossmatch Technique Indirect Coombs Anti Globulin TestDocument4 pagesCrossmatch Technique Indirect Coombs Anti Globulin TestMai ÜüNo ratings yet
- ABO Incompatible Platelets: Risks Versus Benefit: ReviewDocument5 pagesABO Incompatible Platelets: Risks Versus Benefit: Reviewmy accountNo ratings yet
- BB Lec FinalsDocument28 pagesBB Lec Finalsimbendo.cvtNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument57 pagesEpithelial TissuePreet Kaur100% (1)