Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L03 Cell Strucure Mdefied
6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L03 Cell Strucure Mdefied
Uploaded by
WafaaFarouk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views14 pagesOriginal Title
6-8A_CNLAEPN693330_U01L03 cell strucure mdefied
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views14 pages6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L03 Cell Strucure Mdefied
6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L03 Cell Strucure Mdefied
Uploaded by
WafaaFaroukCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
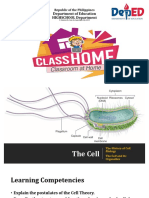
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
Being Eu-nique
What are the characteristics of
eukaryotic cells?
• Eukaryotic cells differ from each other depending
on their structure and function.
• Structure is the arrangement of parts. Function is
the activity the parts carry out.
• All eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, membrane-
bound organelles, and parts that protect and
support the cell.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
What are the characteristics of
eukaryotic cells?
• The cell membrane protects the cell and regulates
what enters and leaves the cell.
• Throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells is a
cytoskeleton, or network of protein filaments
that gives shape and support to cells.
• The cytoskeleton also helps in cell division and in
movement.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
What are the characteristics of
eukaryotic cells?
• The nucleus is an organelle that contains the cell’s
genetic material or DNA.
• Instructions for making proteins are stored in DNA
and sent out of the nucleus through pores in the
nuclear membrane.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
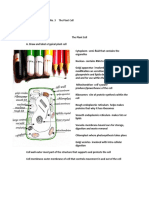
Part-iculars
What organelles are found in plant and
animal cells?
• Cellular respiration is the process by which cells
get energy by breaking down food.
• Mitochondrion is an organelle where cellular
respiration occurs.
• Mitochondria have their own DNA and two
membranes.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
What organelles are found in plant and
animal cells?
• Ribosomes are organelles that make proteins by
putting together chains of amino acids.
• Ribosomes are not enclosed in a membrane.
• Some ribosomes are free, and others are attached
to an organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
What organelles are found in plant and
animal cells?
• The endoplasmic reticulum, or ER, assists in the
production, processing, and transport of proteins
and in the production of lipids.
• Rough ER has ribosomes attached to its membrane.
• Smooth ER makes lipids and breaks down toxins.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
What organelles are found in plant and
animal cells?
• The Golgi complex is a system of flattened
membrane sacs. It packages and distributes
materials in a cell.
• Lipids and proteins from the ER are delivered to the
Golgi complex to be modified for different jobs.
• Vesicles of pinched-off Golgi complex membrane
carry products out of the cell or to other parts of the
cell.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
What organelles are found in plant and
animal cells?
• Describe the functions of the organelles in the
image below.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
Now Showing: The Plant Cell
What additional parts are found in
plant cells?
• In plants, the cell wall is a rigid structure that
surrounds the cell membrane, providing support
and protection to the cell.
• Some fungi, archaea, bacteria, and protists also
have cell walls.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
What additional parts are found in
plant cells?
• A vacuole is a fluid-filled vesicle found in the cells
of most animals, plants, and fungi.
• A vacuole may contain enzymes, nutrients, water,
or wastes.
• Plant cells have large central vacuoles that store
water and help support the cell.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
What additional parts are found in
plant cells?
• A chloroplast is an organelle where
photosynthesis occurs.
• Photosynthesis is the process by which cells use
sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make sugar
and oxygen.
• Chloroplasts are green because of green pigment
called chlorophyll, which absorbs solar energy.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
What additional parts are found in
plant cells?
• How does a chloroplast make food for a plant cell?
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 3 Cell Structure and Function
Introducing: The Animal Cell
What additional part is found in animal
cells?
• Lysosomes are organelles in animal cells that
contain digestive enzymes.
• These enzymes break down damaged organelles,
waste material, and foreign invaders in the cell.
• Some of these materials are collected in vacuoles.
A lysosome attaches to the vacuole and releases
the digestive enzymes inside.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
You might also like
- Cytogenetics Report For G-Banded KaryotypeDocument3 pagesCytogenetics Report For G-Banded Karyotypeapi-3823725640% (1)
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (4)
- Cell BiologyDocument76 pagesCell BiologyDave Arthur Robledo92% (12)
- Chapter 1 BC SC Probe 8Document36 pagesChapter 1 BC SC Probe 8api-265180883No ratings yet
- Organelle TableDocument2 pagesOrganelle Tablejamkulit29No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function - 2Document14 pagesCell Structure and Function - 2Richard LindemannNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument56 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKENT GARCIA100% (1)
- Sec 3Document28 pagesSec 3Jana Moataz Mohamed G02No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document44 pagesChapter 3Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- CH 7 3 Structures and Organelles ..Document31 pagesCH 7 3 Structures and Organelles ..ghalia.amkNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 2. Exploring The CellDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 2. Exploring The CellArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Animal Plant CellsDocument15 pagesAnimal Plant CellsMarilou TagarinoNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 9 and 10 Revision Short NotesDocument17 pagesBiology Grade 9 and 10 Revision Short Notesdawitdesta2022No ratings yet
- Classroom at Home: Department of Education HIGHSCHOOL DepartmentDocument33 pagesClassroom at Home: Department of Education HIGHSCHOOL DepartmentKrystin DiamosNo ratings yet
- Activity: "Comparing Plant and Animal Cells"Document39 pagesActivity: "Comparing Plant and Animal Cells"criselNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Del Tema 5Document44 pagesEjercicios Del Tema 5Natalia Ricoy CallejaNo ratings yet
- The Living Cell: by Faith and RoxanneDocument11 pagesThe Living Cell: by Faith and RoxanneFaith SolomonNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - CellDocument4 pagesIGCSE - CellSamer AwwadNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument16 pagesChapter - 5 The Fundamental Unit of Lifekarunadawar.11No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Organisation of The OrganismDocument49 pagesChapter 2 Organisation of The Organismjzdf2d9nnvNo ratings yet
- Quipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellDocument17 pagesQuipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellPhil Christian MerinoNo ratings yet
- HSB Session 1Document14 pagesHSB Session 1Akedah MurrienNo ratings yet
- 01 Living ThingsDocument32 pages01 Living Thingsapi-632307358No ratings yet
- Module 1Document19 pagesModule 1pohv22csNo ratings yet
- Biology - Cell Structure OrganizationDocument42 pagesBiology - Cell Structure OrganizationzubairNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallDocument5 pagesCell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallAsad MasoodNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer The CellDocument28 pagesBiology Reviewer The CellAndrea Grace Bayot AdanaNo ratings yet
- Cell and TransportDocument77 pagesCell and TransportEugenie Francisco100% (1)
- Earth Life Science Module 5Document15 pagesEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- K G K SCH YnplbWFuQGVtdWZzZC5vcmc Study Guide For Cells TestDocument8 pagesK G K SCH YnplbWFuQGVtdWZzZC5vcmc Study Guide For Cells TestRachael SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesChapter 03 - Cell Structure and FunctionMaryam Ali100% (1)
- The Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of BiologyDocument6 pagesThe Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of Biologyhendrix obciana100% (1)
- Lecture 1Document39 pagesLecture 1Mohammed SindiNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document2 pagesActivity 1Ryan Lee DelremedioNo ratings yet
- Cell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceDocument48 pagesCell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Sample AssignmentDocument4 pagesSample Assignmentmuhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - The Characteristics of CellsDocument12 pagesLesson 1 - The Characteristics of CellsJohny Cristian Mamani ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument21 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsNoemi DenostaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure-WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesCell Structure-WPS OfficeyennaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument27 pagesCellTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeDocument39 pagesLesson 5.1 Cell The Basic Unit of LifeMarjorie CaneteNo ratings yet
- 2nd Q CEellDocument30 pages2nd Q CEellDeserie ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Study of Life: Dr. Sajeela AhmedDocument32 pagesWelcome To The Study of Life: Dr. Sajeela AhmedMohammad NaqashNo ratings yet
- W1 Bio 1Document4 pagesW1 Bio 1Joven J. AndohoyanNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument27 pagesGen BioAeron Kurt AcuñaNo ratings yet
- The Building Blocks of LifeDocument105 pagesThe Building Blocks of LifePradhees BtechNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function: Chapter 4 Part 1Document56 pagesCell Structure and Function: Chapter 4 Part 1Sampaguita LacernaNo ratings yet
- Cell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaDocument10 pagesCell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Structure of CellsDocument14 pagesStructure of CellsTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- 1SS - Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems - Notes B2Document7 pages1SS - Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems - Notes B2Gavin Ng100% (1)
- Lesson - 4 - Structures - and - Organelles W6Document24 pagesLesson - 4 - Structures - and - Organelles W6jansameh16No ratings yet
- 1.1.1. ADocument24 pages1.1.1. Ayishan.miao427No ratings yet
- Gen Bio Group 2 0.2Document42 pagesGen Bio Group 2 0.2clintmonevaeduNo ratings yet
- Plants and Animal CellsDocument24 pagesPlants and Animal CellsJen NyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa BiologyDocument6 pagesReviewer Sa BiologyKate ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie Jaiswal100% (1)
- Act 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportDocument7 pagesAct 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- Module 1-2Document21 pagesModule 1-2Edel Ruth Pal-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cells and StructureDocument17 pagesCells and StructurekayleenerikaNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell Structure - A 2019Document88 pages2 Cell Structure - A 2019Isworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument30 pagesCell Structuremazura100% (1)
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - The Cellular Level of OrganizationChristina MarkwartNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. ZoologyDocument21 pagesM.Sc. ZoologySabyasachi DasNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument68 pagesFungillccdd100% (17)
- 4.1 CellcraftDocument2 pages4.1 CellcraftMia RicaurteNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument52 pagesBiology Notessree220100% (1)
- Nature 2018 555 300Document3 pagesNature 2018 555 300Hinathitha AndaluzNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesCell Structure and Functionapi-217439283No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument25 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- BCH 201 General - Biochemistry 1 - Farid2 PDFDocument103 pagesBCH 201 General - Biochemistry 1 - Farid2 PDFOgunsina olabode100% (1)
- SCIENCE 7 2nd Periodical TestDocument2 pagesSCIENCE 7 2nd Periodical TestAngelica BacolodNo ratings yet
- Q3 Week 1 Stem G11 General Biology Las W1Document13 pagesQ3 Week 1 Stem G11 General Biology Las W1John Erniest Tabungar AustriaNo ratings yet
- Glossary For BiologyDocument18 pagesGlossary For BiologyPershernNo ratings yet
- Npa1 Lab StudentDocument99 pagesNpa1 Lab StudentJanssen BendanaNo ratings yet
- Cell Class 9 Question PDFDocument8 pagesCell Class 9 Question PDFJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Organisation (Biology) : Year 9 Topic 2Document10 pagesCell Structure and Organisation (Biology) : Year 9 Topic 2Aidah JasniNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: An Evolving ScienceDocument26 pagesMicrobiology: An Evolving ScienceHong Quang Pham56% (9)
- 10.3 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes - Introduction To Life Science - University of TokyoDocument4 pages10.3 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes - Introduction To Life Science - University of Tokyokondaveeti sreenivasulu NaiduNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument39 pagesBiology NotesdarakhshanNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Term 1 Week 1 - 2021Document4 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Term 1 Week 1 - 2021Lucky Jr MonobeNo ratings yet
- GenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Document20 pagesGenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Ethan Erika BionaNo ratings yet
- Is The Mitochondrion A Good Malaria Drug Target?: OpinionDocument9 pagesIs The Mitochondrion A Good Malaria Drug Target?: OpinionShashank SharanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure GizmoDocument3 pagesCell Structure GizmoNatalie Bonsu100% (1)
- General BiologyDocument82 pagesGeneral BiologyNanashiNo ratings yet
- 1-Chapter 1 Introduction To BiochemistryDocument53 pages1-Chapter 1 Introduction To BiochemistryFarhana Mohd Hatta100% (1)
- Topic 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument6 pagesTopic 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationAdeyinka OluyoleNo ratings yet
- Cells TissuesDocument7 pagesCells TissuesNisha ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Art Dynamic Morphology and Embryology PDFDocument42 pagesArt Dynamic Morphology and Embryology PDFimageorge13No ratings yet