Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L04 Levels of Cellular
6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L04 Levels of Cellular
Uploaded by
WafaaFarouk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views14 pagesOriginal Title
6-8A_CNLAEPN693330_U01L04 levels of cellular
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views14 pages6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L04 Levels of Cellular
6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L04 Levels of Cellular
Uploaded by
WafaaFaroukCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
Body Building
How are living things organized?
• An organism is a living thing that can carry out
life processes by itself.
• Unicellular organisms are made up of just one cell
that performs all the functions necessary for life.
• Unicellular organisms do not have levels of
organization.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
How are living things organized?
• Unicellular organisms need fewer resources and
some can live in harsh conditions.
• They are very small and are easily eaten by other
organisms.
• If the single cell dies, the entire organism dies.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
How are living things organized?
• Multicellular organisms have multiple cells that are
grouped into different levels of organization.
• Multicellular organisms are larger, more efficient,
and have a longer lifespan than unicellular
organisms.
• Multicellular organisms need more resources than
unicellular organisms.
• The cells are specialized and must depend on each
other for survival of the organism.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
How are living things organized?
• A tissue is a group of similar cells that perform a
common function.
• Humans and other animals are made up of
nervous, epithelial, connective, and muscle tissues.
• Plants have transport, protective, and ground
tissues.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
How are living things organized?
• An organ is a structure made up of a collection of
tissues that carries out a specialized function.
• Different tissues can work together to accomplish a
function, such as digesting food.
• Plants have organs such as leaves, stems, and
roots.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
How are living things organized?
• An organ system is a group of organs that work
together to perform body functions.
• Each organ system in the body has a specific job to
do for the organism.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
How are living things organized?
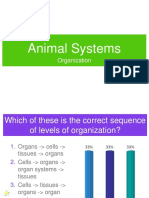
• What are the levels of organization in this tree?
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
What’s Your Function?
What is the connection between
structure and function?
• Cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems make up
the structure of a multicellular organism.
• Structure is the arrangement of parts in an
organism or object.
• Function is the activity of each part in an
organism.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
What is the connection between
structure and function?
• Tiny air sacs in the lung are called alveoli. What is
the structure and function of alveoli?
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
Odd Bodies
• Different organisms develop many different kinds
of body structures.
• The spiny katydid has spines to protect it from
being eaten.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
Odd Bodies
• The longhorn cowfish has a puckered mouth to
blow away sand on the shallow ocean floor to find
and feed on tiny organisms.
• The tarsier has huge eyes to give it better night
vision for finding insects to eat. It also has long
fingers to help it grasp branches.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
Systems at Work
What tasks do systems perform to
meet the needs of cells?
• A unicellular organism must perform all functions
necessary for life.
• A multicellular organism has specialized cells,
tissues, organs, and organ systems that perform
specific functions.
• Some plants have a vascular system that
transports water and nutrients to and from cells
throughout the plant.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 1 Lesson 4 Levels of Cellular Organization
What tasks do systems perform to
meet the needs of cells?
• Food is broken down by the digestive system.
Nutrients are delivered to cells via the circulatory
system.
• Oxygen is taken in by the respiratory system. This
oxygen is carried to cells via the circulatory
system.
• Wastes are removed from the body by the skin,
lungs, digestive system, and kidneys.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
You might also like
- Cracker Book For Bank (IBPS - SBI - RRB PO - Clerk) Mains ExamsDocument338 pagesCracker Book For Bank (IBPS - SBI - RRB PO - Clerk) Mains ExamsManish Kumar100% (2)
- F.E. Campbell - Fetters Are Forever - HIT 180Document160 pagesF.E. Campbell - Fetters Are Forever - HIT 180HokusLocus63% (8)
- Trailblazer 2019Document75 pagesTrailblazer 2019Georgiana CiaraNo ratings yet
- EnvSci CH 4 PPT Organization of LifeDocument49 pagesEnvSci CH 4 PPT Organization of LifeChristine Sena0% (1)
- Lesson 1 - The Characteristics of CellsDocument12 pagesLesson 1 - The Characteristics of CellsJohny Cristian Mamani ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organization PPT - 1314Document9 pagesLevels of Organization PPT - 1314HafserhNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument40 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeRenu SekaranNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Lesson 20 - Classsification of Living ThingsDocument19 pages7th Grade Lesson 20 - Classsification of Living ThingsPamela Ribeiro Gonçalves100% (1)
- Levels of OrganiztionDocument21 pagesLevels of OrganiztionSahar HassanNajadNo ratings yet
- Ana Lect & Lab ReviewerDocument11 pagesAna Lect & Lab ReviewerLora Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Cell To Organism NoteDocument3 pagesCell To Organism NoteIshani Anushika JayakodyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Life Science, Earth and LifeDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Life Science, Earth and Lifejoel TorresNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Life Science, Earth and LifeDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Life Science, Earth and Lifejoel Torres100% (2)
- Final Levels of Organization 2024 (Lecture)Document26 pagesFinal Levels of Organization 2024 (Lecture)rk4876001No ratings yet
- Sturcture and Function of AnimalsDocument78 pagesSturcture and Function of AnimalsElvin H. JunsayNo ratings yet
- 4 - Levels of Organization of Living ThingsDocument20 pages4 - Levels of Organization of Living ThingsFrancisco jezziel dominguez fernandezNo ratings yet
- 6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L03 Cell Strucure MdefiedDocument14 pages6-8A - CNLAEPN693330 - U01L03 Cell Strucure MdefiedWafaaFaroukNo ratings yet
- Introduction On LifeDocument33 pagesIntroduction On LifeKeren Joy WiganNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Lesson 25 Introduction To AnimalsDocument21 pages7th Grade Lesson 25 Introduction To AnimalsPamela Ribeiro GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Noteserika sabelNo ratings yet
- APEX The Organ SystemsDocument171 pagesAPEX The Organ Systemsjt100% (2)
- Levels of OrganizationDocument12 pagesLevels of OrganizationMa Reana Ortega VillarealNo ratings yet
- Basic Defining Characteristics of LifeDocument5 pagesBasic Defining Characteristics of LifeBry Raf100% (1)
- Unit 1 Organization of LifeDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Organization of LifeIrma Sri SusantiNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument22 pagesCharacteristics of Living ThingsNinia Dabu LoboNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument2 pagesLevels of OrganizationSospeter NgociNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. The Eartha Planet Full of LifeDocument110 pagesUnit 6. The Eartha Planet Full of LifePika PiNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument11 pagesLevels of OrganizationLeo Cambaya Lascuña Jr.No ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument24 pagesLevels of OrganizationJhen BonNo ratings yet
- I.C. The Connections and Interactions Among Living ThingsDocument23 pagesI.C. The Connections and Interactions Among Living ThingsDarwin Nool100% (1)
- General Physiology Introduction To Human Physiology: By: Dr. Hamza Al-TradDocument10 pagesGeneral Physiology Introduction To Human Physiology: By: Dr. Hamza Al-TradibrahimNo ratings yet
- What Is Biology?: Section 4Document13 pagesWhat Is Biology?: Section 4rumpyhw100% (2)
- Lesson 4 Characteristics of LifeDocument29 pagesLesson 4 Characteristics of Liferosie sialanaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive and Excretory SystemDocument16 pagesThe Digestive and Excretory SystemMiguel Angel Loor MolinaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Unit 5 Study GuideDocument15 pagesScience 7 Unit 5 Study GuideMae RicañaNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document72 pagesWeek 1joshuafababier9No ratings yet
- IGCSE Student Revision Power Point Topic 1 - 複本Document37 pagesIGCSE Student Revision Power Point Topic 1 - 複本yt kNo ratings yet
- bWVJC0O1J5 Handouts 90598Document16 pagesbWVJC0O1J5 Handouts 90598SAAD UR REHMANNo ratings yet
- Animal Systems: OrganizationDocument23 pagesAnimal Systems: OrganizationEugine QuirozNo ratings yet
- Model of CellsDocument54 pagesModel of CellsTNANo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological Organization: Here Starts The Lesson!Document18 pagesLevels of Biological Organization: Here Starts The Lesson!Marievic DavidNo ratings yet
- BIO121 Chapter 1 The Science of BiologyDocument45 pagesBIO121 Chapter 1 The Science of BiologyggttettanNo ratings yet
- Cell-Unicellular and Multicellular OrganismsDocument12 pagesCell-Unicellular and Multicellular OrganismsPalden KuengaNo ratings yet
- The 7 Characteristics of LifeDocument3 pagesThe 7 Characteristics of LifeGu Jun PyoNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument17 pagesLevels of OrganizationYsabelle Bea ManaguelodNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument10 pagesLevels of OrganizationMOYA SOLIS CELSONo ratings yet
- Living Systems: A Molecule Is A Basic Unit of MatterDocument3 pagesLiving Systems: A Molecule Is A Basic Unit of MatterKristinaNo ratings yet
- Unicellular Organisms Multicellular OrganismsDocument5 pagesUnicellular Organisms Multicellular OrganismsDeasserei TatelNo ratings yet
- BIOL-101 - Chapter 1 SummaryDocument3 pagesBIOL-101 - Chapter 1 SummaryOmar BadaamNo ratings yet
- Lower Secondary BIOLOGY NOTESDocument19 pagesLower Secondary BIOLOGY NOTESmamboian01No ratings yet
- W5-DLL 2-Els-Jan 4-5 2023Document5 pagesW5-DLL 2-Els-Jan 4-5 2023Anne Rivero100% (1)
- Bio MergedDocument366 pagesBio MergedReshab Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument22 pagesCellcmizalpccfuNo ratings yet
- Organ System of Representative AnimalsDocument8 pagesOrgan System of Representative AnimalsMARIA LOURDES MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human BiologyDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Human BiologyWael AbdelAzim AbdelAzimNo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology Lesson 1Document26 pagesHuman and Social Biology Lesson 1alferoz zabarNo ratings yet
- Bio 103-L1Document24 pagesBio 103-L1Nahid Sagar 1812889042No ratings yet
- 1 Cell OrganizationDocument27 pages1 Cell OrganizationLawrence RayappenNo ratings yet
- 1 Organization of Living ThingsDocument2 pages1 Organization of Living ThingscarlNo ratings yet
- 1 General Biology 1 - IntroductionDocument6 pages1 General Biology 1 - IntroductionKay JusonNo ratings yet
- Classifying Living Things: Similarities and Differences Among OrganismsDocument15 pagesClassifying Living Things: Similarities and Differences Among Organismslachel joy tahinayNo ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Acclimatisation Healthy in High HimalayasDocument32 pagesAcclimatisation Healthy in High HimalayasNiti Ranjan DasNo ratings yet
- Zoonotic DiseasesDocument13 pagesZoonotic Diseasesapi-533975734No ratings yet
- NSTSE Class 4 SolutionDocument4 pagesNSTSE Class 4 SolutionMota Chashma100% (1)
- Operant ConditioningDocument18 pagesOperant Conditioningkariverma100% (2)
- Antibiotics in The Swine IndustryDocument10 pagesAntibiotics in The Swine IndustryCameronNo ratings yet
- Keyura, Kankana, Katisutra) and An Yajnopavitha Across His ChestDocument4 pagesKeyura, Kankana, Katisutra) and An Yajnopavitha Across His ChestPrantik GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2804env s2846207 LitreviewDocument10 pages2804env s2846207 Litreviewapi-267781539No ratings yet
- Hyena Feeding Ne Nader Tha Ls 2014Document36 pagesHyena Feeding Ne Nader Tha Ls 2014Davide MargaritoraNo ratings yet
- Lovecraft, H.P. - Selected WritingsDocument823 pagesLovecraft, H.P. - Selected WritingsSantiagoDiazNo ratings yet
- Human Kindnes - Bhandu Daya KriyaDocument2 pagesHuman Kindnes - Bhandu Daya KriyaFelipe OliverNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Pat 7 TH.21Document20 pagesLatihan Soal Pat 7 TH.21Fairuza AchmadNo ratings yet
- Delilah PedigreeDocument1 pageDelilah Pedigreeapi-241037643No ratings yet
- Pediatric RadiologyDocument82 pagesPediatric Radiologyabakferro0% (1)
- NARRATIVE TEXT FABLE - MicroteachingDocument13 pagesNARRATIVE TEXT FABLE - MicroteachingfadivnizarulNo ratings yet
- Word Parts Dictionary ADocument27 pagesWord Parts Dictionary AJosh Flynn100% (1)
- Finding The Main IideaDocument2 pagesFinding The Main IideaJonna May Delgaco-MotaNo ratings yet
- Module 26 - EditedDocument30 pagesModule 26 - EditedLu LuNo ratings yet
- Success in Science Revision Notes Year 7: EurekaDocument19 pagesSuccess in Science Revision Notes Year 7: EurekaToby D. AdamsNo ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata FishesDocument92 pagesPhylum Chordata FishesSoumen ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- B01 MDJDVDocument16 pagesB01 MDJDVInn Dye ToryoNo ratings yet
- Questions-Biological Science DavaoDocument10 pagesQuestions-Biological Science DavaoMARY ANN TIONGSONNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneum of CinderDocument36 pagesMiscellaneum of CinderjrientsNo ratings yet
- Hair Salon & Spa RequirementsDocument5 pagesHair Salon & Spa RequirementsHNN100% (1)
- 1 - Gulfstream Park RETROSPECTODocument9 pages1 - Gulfstream Park RETROSPECTOajimenezn_0412No ratings yet
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAEDocument23 pagesENTEROBACTERIACEAEapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Aconitum NapellusDocument18 pagesAconitum NapellusRaveendra MungaraNo ratings yet
- Donkey Fromnt Teeth - Google Search PDFDocument1 pageDonkey Fromnt Teeth - Google Search PDFasma abdiNo ratings yet