Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsMyfile
Myfile
Uploaded by
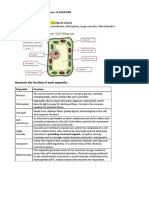
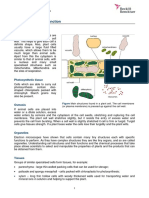
Odell FosterLeaves are specially adapted organs for photosynthesis. They have large surface areas and thin structures to maximize light absorption and diffusion of carbon dioxide. Chloroplasts containing chlorophyll absorb sunlight while stomata and internal air spaces aid gas exchange. Veins transport water, minerals, and the sugar sucrose produced during photosynthesis, which plants use for growth, respiration, energy, starch storage, and developing stems, leaves and reproductive structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology 1Document60 pagesPlant Anatomy and Physiology 1keron100% (1)
- MyfileDocument3 pagesMyfileOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION - RegDocument35 pagesNUTRITION - Regwairimucarren77No ratings yet
- L6.3 Laef StructureDocument19 pagesL6.3 Laef StructureDima ArafatNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument9 pagesPlant Nutritionakshai.ar13No ratings yet
- B3 Plant Biology IntroductionDocument10 pagesB3 Plant Biology Introductionyungl3No ratings yet
- Lesson 19 PlantsDocument23 pagesLesson 19 Plantstupapaentanga.172312No ratings yet
- 4-Plant Structure and FunctionDocument7 pages4-Plant Structure and FunctionfebrimetrinNo ratings yet
- Describe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaDocument16 pagesDescribe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaStudy's AnayNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science C1Document44 pagesYear 9 Science C1Ventus TanNo ratings yet
- Plant GrowthDocument90 pagesPlant GrowthDans DansNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition PresentationDocument22 pagesPlant Nutrition PresentationRaquel ColladoNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument31 pagesPlant NutritionAbhay BhingradiaNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavessssfiresssNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Plant Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Plant Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSE PDFHmael AsifNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Plant Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Plant Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEStudy GuyNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition & TransportDocument21 pagesPlant Nutrition & TransportKim-Elaine Pohatu100% (1)
- Notes - Photosynthesis & Transport System in Plants - P6Document11 pagesNotes - Photosynthesis & Transport System in Plants - P6Erlangga PanjiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument8 pagesNutrition in PlantsSweet HomeNo ratings yet
- Preig Point 8 Unit1Document30 pagesPreig Point 8 Unit1myatthirisan2010No ratings yet
- Leaf Structure Plant NutritionDocument5 pagesLeaf Structure Plant NutritionShahed Bulbul PaponNo ratings yet
- Introduction Class: Plant Morphology, Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument29 pagesIntroduction Class: Plant Morphology, Anatomy and PhysiologykerryNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument44 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISsuggaballNo ratings yet
- Ivory Brown Vintage Old Daily NotesDocument3 pagesIvory Brown Vintage Old Daily NotesPrajvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition.Document16 pagesPlant Nutrition.zena mohamedNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionsarNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Biology Anatomy and Physiology SPU 2024 Notes 1Document44 pagesAgricultural Biology Anatomy and Physiology SPU 2024 Notes 1Gift ThobaneNo ratings yet
- BE-Ch03 Basic Aspect of Vegetation-StDocument52 pagesBE-Ch03 Basic Aspect of Vegetation-StPradeep ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Combined Science Study PackDocument6 pagesForm 1 Combined Science Study PackMarylyn Ace TeeNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesDocument50 pagesAlwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Green Plants - 2Document11 pagesGreen Plants - 2Catherine Dharshini LabrooyNo ratings yet
- Plant NutirionDocument29 pagesPlant NutirionRaidioactiveguyNo ratings yet
- The Leaf As An OrganDocument11 pagesThe Leaf As An OrganAlana DariesNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science NotesDocument115 pagesIntegrated Science Notesserene munga100% (1)
- Biology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?Document11 pagesBiology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?rickyNo ratings yet
- 9B Summary SheetsDocument5 pages9B Summary SheetsNafiul Munsur Year 7No ratings yet
- The Leaf OrganDocument12 pagesThe Leaf OrganGEN EL NISSI SUELTONo ratings yet
- Dioxide and Water Using Energy From Sunlight: ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-21 Notes CH: 1 Photosynthesis Grade: 8 Subject: BiologyDocument7 pagesDioxide and Water Using Energy From Sunlight: ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-21 Notes CH: 1 Photosynthesis Grade: 8 Subject: Biologyanish kanthethiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Plant TissuesDocument20 pagesWeek 2 Plant Tissueskevin愛No ratings yet
- Biology Module 4 NotesDocument5 pagesBiology Module 4 Notescjmonkey182No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument36 pagesLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- How Plants SurviveDocument25 pagesHow Plants SurviveAnna Mae MarconNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition NoteDocument5 pagesPlant Nutrition NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- LeavezDocument6 pagesLeavezLenovoNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Plant PPT PresentationDocument20 pagesParts of The Plant PPT PresentationMaricris OpamilNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and Function PDFDocument2 pagesPlant Structure and Function PDFPT.Susan Angwyn Gemilang 8No ratings yet
- Nmhs Horticulture I - 3Document47 pagesNmhs Horticulture I - 3api-279806117No ratings yet
- C6 - Plant NutritionDocument5 pagesC6 - Plant NutritionThet Htar ZawNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Unit B Unit ReviewDocument16 pagesSci7 Unit B Unit Reviewapi-242221534No ratings yet
- Pamuzinda Science Notes in PDFDocument113 pagesPamuzinda Science Notes in PDFSillolwazi BroughNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Note FotosintesisDocument4 pagesTeacher's Note Fotosintesisbijaksains2018No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and ATP Synthesis Part 1Document39 pagesPhotosynthesis and ATP Synthesis Part 1Andy100% (1)
- SG-Life of Plants 2012Document39 pagesSG-Life of Plants 2012niku007No ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument7 pagesNUTRITIONTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Module 21 - Principles of Plant Growth - 230508 - 161625Document59 pagesModule 21 - Principles of Plant Growth - 230508 - 161625ralobekwalelentleNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- Adaptation of The LeavesDocument17 pagesAdaptation of The LeavesKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Hydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeFrom EverandHydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeNo ratings yet
- Do Plants Eat Sunlight? Biology Textbook for Young Learners | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandDo Plants Eat Sunlight? Biology Textbook for Young Learners | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- MyfileDocument3 pagesMyfileOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- MyfileDocument4 pagesMyfileOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- Worms Move Downwards in The SoilDocument2 pagesWorms Move Downwards in The SoilOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- Birds That Flew The SameDocument2 pagesBirds That Flew The SameOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- The Yellow Road of GraceDocument2 pagesThe Yellow Road of GraceOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- Silent Night Dreams of YouDocument2 pagesSilent Night Dreams of YouOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- MyfileDocument2 pagesMyfileOdell FosterNo ratings yet
Myfile
Myfile
Uploaded by
Odell Foster0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views6 pagesLeaves are specially adapted organs for photosynthesis. They have large surface areas and thin structures to maximize light absorption and diffusion of carbon dioxide. Chloroplasts containing chlorophyll absorb sunlight while stomata and internal air spaces aid gas exchange. Veins transport water, minerals, and the sugar sucrose produced during photosynthesis, which plants use for growth, respiration, energy, starch storage, and developing stems, leaves and reproductive structures.
Original Description:
create fod
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLeaves are specially adapted organs for photosynthesis. They have large surface areas and thin structures to maximize light absorption and diffusion of carbon dioxide. Chloroplasts containing chlorophyll absorb sunlight while stomata and internal air spaces aid gas exchange. Veins transport water, minerals, and the sugar sucrose produced during photosynthesis, which plants use for growth, respiration, energy, starch storage, and developing stems, leaves and reproductive structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views6 pagesMyfile
Myfile
Uploaded by
Odell FosterLeaves are specially adapted organs for photosynthesis. They have large surface areas and thin structures to maximize light absorption and diffusion of carbon dioxide. Chloroplasts containing chlorophyll absorb sunlight while stomata and internal air spaces aid gas exchange. Veins transport water, minerals, and the sugar sucrose produced during photosynthesis, which plants use for growth, respiration, energy, starch storage, and developing stems, leaves and reproductive structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
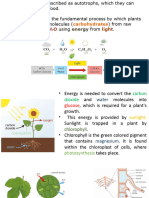
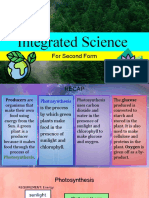
Photosynthesis?
• The leaf is the organ in a plant specially adapted for photosynthesis
• Leaves are adapted for photosynthesis and gaseous exchange. The
function of a leaf is photosynthesis, to absorb light and carbon dioxide
to produce glucose (food).
The adaptations of leaf for photosynthesis
are:
• Large surface area for maximum light absorption.
• The presence of chlorophyll containing chloroplast (mesophyll cells and
guard cells contain many chloroplasts) to absorb sunlight
• Thin structure– Short distance for carbon dioxide to diffuse into leaf cells
• The stomata that allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf and oxygen
to diffuse out
• A large network of veins to support the leaf and transport water, mineral
ions and sucrose (sugar)
• Air Spaces – to reduce distance for carbon dioxide to diffuse and to
increase the surface area of the gas exchange surface inside the leaf
How the plants use the food they made?
● Plants use it in the process for respiration to release energy for
growth
● Plants use it to form starch, which is stored in leaves and other
storage organs, such as tubers example irish potato and seeds
● Plants use it so that they can grow in height and width
developing stems, leaves and reproductive structures.
How are leaves adapted for
photosynthesis
• The leaf is the organ in a plant specially adapted for photosynthesis
• Leaves are adapted for photosynthesis and gaseous exchange. The
function of a leaf is photosynthesis, to absorb light and carbon dioxide
to produce glucose (food).
You might also like
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology 1Document60 pagesPlant Anatomy and Physiology 1keron100% (1)
- MyfileDocument3 pagesMyfileOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION - RegDocument35 pagesNUTRITION - Regwairimucarren77No ratings yet
- L6.3 Laef StructureDocument19 pagesL6.3 Laef StructureDima ArafatNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument9 pagesPlant Nutritionakshai.ar13No ratings yet
- B3 Plant Biology IntroductionDocument10 pagesB3 Plant Biology Introductionyungl3No ratings yet
- Lesson 19 PlantsDocument23 pagesLesson 19 Plantstupapaentanga.172312No ratings yet
- 4-Plant Structure and FunctionDocument7 pages4-Plant Structure and FunctionfebrimetrinNo ratings yet
- Describe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaDocument16 pagesDescribe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaStudy's AnayNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science C1Document44 pagesYear 9 Science C1Ventus TanNo ratings yet
- Plant GrowthDocument90 pagesPlant GrowthDans DansNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition PresentationDocument22 pagesPlant Nutrition PresentationRaquel ColladoNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument31 pagesPlant NutritionAbhay BhingradiaNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavessssfiresssNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Plant Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Plant Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSE PDFHmael AsifNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Plant Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 Plant Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEStudy GuyNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition & TransportDocument21 pagesPlant Nutrition & TransportKim-Elaine Pohatu100% (1)
- Notes - Photosynthesis & Transport System in Plants - P6Document11 pagesNotes - Photosynthesis & Transport System in Plants - P6Erlangga PanjiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument8 pagesNutrition in PlantsSweet HomeNo ratings yet
- Preig Point 8 Unit1Document30 pagesPreig Point 8 Unit1myatthirisan2010No ratings yet
- Leaf Structure Plant NutritionDocument5 pagesLeaf Structure Plant NutritionShahed Bulbul PaponNo ratings yet
- Introduction Class: Plant Morphology, Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument29 pagesIntroduction Class: Plant Morphology, Anatomy and PhysiologykerryNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument44 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISsuggaballNo ratings yet
- Ivory Brown Vintage Old Daily NotesDocument3 pagesIvory Brown Vintage Old Daily NotesPrajvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition.Document16 pagesPlant Nutrition.zena mohamedNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionsarNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Biology Anatomy and Physiology SPU 2024 Notes 1Document44 pagesAgricultural Biology Anatomy and Physiology SPU 2024 Notes 1Gift ThobaneNo ratings yet
- BE-Ch03 Basic Aspect of Vegetation-StDocument52 pagesBE-Ch03 Basic Aspect of Vegetation-StPradeep ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Combined Science Study PackDocument6 pagesForm 1 Combined Science Study PackMarylyn Ace TeeNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesDocument50 pagesAlwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Green Plants - 2Document11 pagesGreen Plants - 2Catherine Dharshini LabrooyNo ratings yet
- Plant NutirionDocument29 pagesPlant NutirionRaidioactiveguyNo ratings yet
- The Leaf As An OrganDocument11 pagesThe Leaf As An OrganAlana DariesNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science NotesDocument115 pagesIntegrated Science Notesserene munga100% (1)
- Biology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?Document11 pagesBiology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?rickyNo ratings yet
- 9B Summary SheetsDocument5 pages9B Summary SheetsNafiul Munsur Year 7No ratings yet
- The Leaf OrganDocument12 pagesThe Leaf OrganGEN EL NISSI SUELTONo ratings yet
- Dioxide and Water Using Energy From Sunlight: ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-21 Notes CH: 1 Photosynthesis Grade: 8 Subject: BiologyDocument7 pagesDioxide and Water Using Energy From Sunlight: ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-21 Notes CH: 1 Photosynthesis Grade: 8 Subject: Biologyanish kanthethiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Plant TissuesDocument20 pagesWeek 2 Plant Tissueskevin愛No ratings yet
- Biology Module 4 NotesDocument5 pagesBiology Module 4 Notescjmonkey182No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument36 pagesLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- How Plants SurviveDocument25 pagesHow Plants SurviveAnna Mae MarconNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition NoteDocument5 pagesPlant Nutrition NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- LeavezDocument6 pagesLeavezLenovoNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Plant PPT PresentationDocument20 pagesParts of The Plant PPT PresentationMaricris OpamilNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and Function PDFDocument2 pagesPlant Structure and Function PDFPT.Susan Angwyn Gemilang 8No ratings yet
- Nmhs Horticulture I - 3Document47 pagesNmhs Horticulture I - 3api-279806117No ratings yet
- C6 - Plant NutritionDocument5 pagesC6 - Plant NutritionThet Htar ZawNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Unit B Unit ReviewDocument16 pagesSci7 Unit B Unit Reviewapi-242221534No ratings yet
- Pamuzinda Science Notes in PDFDocument113 pagesPamuzinda Science Notes in PDFSillolwazi BroughNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Note FotosintesisDocument4 pagesTeacher's Note Fotosintesisbijaksains2018No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and ATP Synthesis Part 1Document39 pagesPhotosynthesis and ATP Synthesis Part 1Andy100% (1)
- SG-Life of Plants 2012Document39 pagesSG-Life of Plants 2012niku007No ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument7 pagesNUTRITIONTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Module 21 - Principles of Plant Growth - 230508 - 161625Document59 pagesModule 21 - Principles of Plant Growth - 230508 - 161625ralobekwalelentleNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- Adaptation of The LeavesDocument17 pagesAdaptation of The LeavesKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Hydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeFrom EverandHydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeNo ratings yet
- Do Plants Eat Sunlight? Biology Textbook for Young Learners | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandDo Plants Eat Sunlight? Biology Textbook for Young Learners | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- MyfileDocument3 pagesMyfileOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- MyfileDocument4 pagesMyfileOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- Worms Move Downwards in The SoilDocument2 pagesWorms Move Downwards in The SoilOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- Birds That Flew The SameDocument2 pagesBirds That Flew The SameOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- The Yellow Road of GraceDocument2 pagesThe Yellow Road of GraceOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- Silent Night Dreams of YouDocument2 pagesSilent Night Dreams of YouOdell FosterNo ratings yet
- MyfileDocument2 pagesMyfileOdell FosterNo ratings yet