Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types
Types
Uploaded by
CHAITANYA SAHU0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views24 pagesThe document describes 4 levels of information systems:
1) Operational systems support daily transactions and operations.
2) Knowledge systems help workers discover and organize knowledge.
3) Management systems provide reports for middle managers.
4) Strategic systems help senior leadership with long-term issues.
The levels vary in their structure, timeframes, and use of internal vs. external data.
Original Description:
Original Title
types
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes 4 levels of information systems:
1) Operational systems support daily transactions and operations.
2) Knowledge systems help workers discover and organize knowledge.
3) Management systems provide reports for middle managers.
4) Strategic systems help senior leadership with long-term issues.
The levels vary in their structure, timeframes, and use of internal vs. external data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views24 pagesTypes
Types
Uploaded by
CHAITANYA SAHUThe document describes 4 levels of information systems:
1) Operational systems support daily transactions and operations.
2) Knowledge systems help workers discover and organize knowledge.
3) Management systems provide reports for middle managers.
4) Strategic systems help senior leadership with long-term issues.
The levels vary in their structure, timeframes, and use of internal vs. external data.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 24
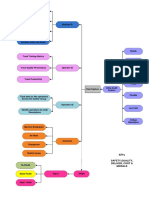
Information Systems
4 Levels of Information System
Operational-level Systems
Knowledge-level Systems
Management-level Systems
Strategic-level Systems
Operational-level Systems
Support operational managers by keeping track of the
elementary activities and transactions of the
organization.
The principle purpose of systems at this level is to
answer routine questions and track the flow of
transactions through the organization.
Covers things such as sales, receipts, cash deposits,
payroll, credit decisions, flow of materials.
Knowledge-level Systems
Support knowledge and data workers in an
organization.
The purpose of these systems is to help the
organization discover, organize and integrate
new and existing knowledge into the business,
and to help control the flow of paperwork.
These systems, specially in the form of
collaboration tools, workstations, and office
systems, are the fastest growing applications in
business today.
Management-level Systems
Designed to serve the monitoring, controlling,
decision-making, and administrative activities
of middle managers.
These systems typically provide periodic
reports rather than instant information on
operations.
Some of these systems support non-routine
decision-making, focusing on less-structured
decisions for which information requirements
are not always clear. This will often require
information from normal operational-level data.
Strategic-level Systems
Help senior management tackle and address
strategic issues and long-term trends, both
within the organisation and in the external
environment.
Principal concern is matching organizational
capability to changes, and opportunities,
occurring in the medium to long term (i.e. 5 -
10 years) in the external environment.
Typically, an organization might have
operational, knowledge, management and
strategic level systems for each functional area
within the organisation.
Operational-level Systems
Transaction-Processing Systems (TPS)
Basic business systems
Perform daily routine transactions necessary for
business functions
At the operational level, tasks, resources and
goals are predefined and highly structured
Generally, five functional categories are
identified, as shown in the diagram.
Knowledge-level Systems
Office Automation Systems (OAS)
Targeted at meeting the knowledge needs of
data workers within the organization
Data workers tend to process rather than create
information. Primarily involved in information
use, manipulation or dissemination.
Typical OAS handle and manage documents,
scheduling and communication.
Knowledge Work Systems (KWS)
Targeted at meeting the knowledge needs of
knowledge workers within the organization
In general, knowledge workers hold degree-
level professional qualifications (e.g. engineers,
scientists, lawyers), their jobs consist primarily
in creating new information and knowledge
KWS, such as scientific or engineering design
workstations, promote the creation of new
knowledge, and its dissemination and
integration throughout the organization.
Management-level Systems
Management Information Systems (MIS)
MIS provide managers with reports and, in
some cases, on-line access to the organization’s
current performance and historical records
Typically these systems focus entirely on
internal events, providing the information for
short-term planning and decision making.
MIS summarise and report on the basic
operations of the organisation, dependent on the
underlying TPS for their data.
Decision-Support Systems (DSS)
As MIS, these serve the needs of the
management level of the organization
Focus on helping managers make decisions that
are semi-structured, unique, or rapidly
changing, and not easily specified in advance
Use internal information from TPS and MIS,
but also information from external sources
Greater analytical power than other systems,
incorporate modelling tools, aggregation and
analysis tools, and support what-if scenarios
Voyage-estimating Decision Support System
Strategic-level Systems
Executive Support/Information Systems
(ESS/EIS)
Serve the strategic level of the organization
ESS/EIS address unstructured decisions and create
a generalized computing and communications
environment, rather than providing any fixed
application or specific capability.
Such systems are not designed to solve specific
problems, but to tackle a changing array of
problems
ESS/EIS are designed to incorporate data about
external events, such as new tax laws or
competitors, and also draw summarised
information from internal MIS and DSS
These systems filter, compress, and track critical
data, emphasising the reduction of time and effort
required to obtain information useful to executive
management
ESS/EIS employ advanced graphics software to
provide highly visual and easy-to-use
representations of complex information and
current trends, but they tend not to provide
analytical models
Inter-relationships and inter-dependencies between IS types
SYSTEM FROM A FUNCTIONAL PERSPECTIVE
Information system can be classified by specific organizational
function they serve as well as by organizational level.
Sales and Marketing System
The sales and marketing function is responsible for selling
organization’s products or services. Marketing is concerned
with identifying customers for the firm’s product or service,
determining what customer need, planning and developing
products and services to meet their needs, and advertising
and promoting these products and services. Sales is
concerned with contacting customers, selling the product and
services, taking orders, and following up on sales. Sales and
marketing information system support these activities.
At the Strategic level, Sales and marketing Monitor trends
affecting new products and sales opportunities, support
planning for new products and services, monitor the
performance of competitors.
At Management level, sales and marketing system support
market research, advertising and promotional campaigns,
and pricing decision. They analyze sales performance and
performance of sales staff.
At Operational level, sales and marketing system assist in
locating and contacting prospective customer, tackling
sales, processing orders and providing customer service
support.
Manufacturing and Production system
The manufacturing and production system is responsible for
actually producing the firm’s goods and services. manufacturing
and production system deals with planning, development and
maintenance of production facilities; the establishment of
production goals; the acquisition , storage, and availability of
production, and material; and the scheduling of equipments,
facilities, materials, and labor required to fashion finished
products. Manufacturing and production system support these
activities.
At Strategic level, manufacturing system deals with firms long-term
manufacturing goals, such as where to locate new plants or whether to
invest in new manufacturing technology.
At Management level, manufacturing and production system
analyze and monitor manufacturing and production cost and
resources.
At Operational level, manufacturing and production system deals
with status of production task.
Product Life Cycle Management [PLM] systems
You might also like
- Unit 6 Managing A Successful Computing Project 2021Document62 pagesUnit 6 Managing A Successful Computing Project 2021ishan maduahanka0% (2)
- Management Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4From EverandManagement Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4No ratings yet
- Notes CH 1 2 Revision For Mid 1Document13 pagesNotes CH 1 2 Revision For Mid 1juhanaNo ratings yet
- Six Major Types of Information SystemsDocument8 pagesSix Major Types of Information SystemsCharmaine Magtangob100% (1)
- Information Systems in The EnterpriseDocument7 pagesInformation Systems in The EnterpriseLeading UniversityNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Management Information System: 1. Office Automation System (OAS)Document13 pagesTopic 2: Management Information System: 1. Office Automation System (OAS)Hildah JJNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Overview of Information SystemsDocument7 pagesUnit 2 - Overview of Information SystemsJason Jay MillerNo ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration Semester II MB0047 - Management Information Systems Assignment Set-1Document51 pagesMaster of Business Administration Semester II MB0047 - Management Information Systems Assignment Set-1drew54321No ratings yet
- The Main Kinds of Information Systems in Business Are Described Briefly BelowDocument11 pagesThe Main Kinds of Information Systems in Business Are Described Briefly BelowDrPallati SujendraNo ratings yet
- Questions For MISDocument11 pagesQuestions For MISKaran ShahNo ratings yet
- MIS (Final)Document24 pagesMIS (Final)sharath pNo ratings yet
- Ism 1Document38 pagesIsm 1Neha KanojiaNo ratings yet
- INFS1602 - Week 5 NotesDocument8 pagesINFS1602 - Week 5 NotesUnswlegendNo ratings yet
- Anderson DSSDocument7 pagesAnderson DSSMiraculous MiracleNo ratings yet
- NCRD'S Sterling Institute of Management Studies: Subject:-Management Information System Assignment No.: - 1, 2, 3Document13 pagesNCRD'S Sterling Institute of Management Studies: Subject:-Management Information System Assignment No.: - 1, 2, 3Nishita ShivkarNo ratings yet
- Full Set-Management Information SystemDocument13 pagesFull Set-Management Information SystemmaiNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemsDocument3 pagesDecision Support SystemsAyesha SiddiqaNo ratings yet
- BBA MIS ch4Document62 pagesBBA MIS ch4FrankNo ratings yet
- Models of Decision Making MISDocument27 pagesModels of Decision Making MISAnish Padhi100% (1)
- 6 Categories of Information SystemDocument10 pages6 Categories of Information SystemCharmaine MagtangobNo ratings yet
- Ipm - CH 3Document41 pagesIpm - CH 3Kidus AbebeNo ratings yet
- MaterialDocument11 pagesMaterialch meghanaNo ratings yet
- Management Information Syste1Document9 pagesManagement Information Syste1DerickMwansaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 02 - Business Processes and Information Systems (Handout 2020)Document4 pagesLesson 02 - Business Processes and Information Systems (Handout 2020)AnuNo ratings yet
- Information SystemsDocument4 pagesInformation Systemssha chandraNo ratings yet
- MIS, DSS and ERPDocument7 pagesMIS, DSS and ERPNaveen SarmaNo ratings yet
- Roles Types IsDocument23 pagesRoles Types IsDindo 2037No ratings yet
- Ae 23 It Application Tools in Business Pre FinalDocument3 pagesAe 23 It Application Tools in Business Pre FinalNina Mae DiazNo ratings yet
- Q1 Short Note On Information System: RelevanceDocument13 pagesQ1 Short Note On Information System: RelevanceAkriti ShahNo ratings yet
- Information Systems: Instructor University of Agriculture, Faisalabad Sub-Campus Burewala/Vehari, PakistanDocument23 pagesInformation Systems: Instructor University of Agriculture, Faisalabad Sub-Campus Burewala/Vehari, PakistantwinklenoorNo ratings yet
- Structure of MIS: Decision Support SystemDocument19 pagesStructure of MIS: Decision Support SystemAnkur RajputNo ratings yet
- Types of Information Systems Serve Each Level?Document9 pagesTypes of Information Systems Serve Each Level?nepalmanindjnkNo ratings yet
- CAPE Information Technology Unit 1: Module 2 Topic: Information SystemsDocument5 pagesCAPE Information Technology Unit 1: Module 2 Topic: Information SystemsblueboyNo ratings yet
- Infoormation System,,,,typesDocument7 pagesInfoormation System,,,,typesyonasminbiyewNo ratings yet
- Information System in The Enterprise.: 2.1 Types of Information SystemsDocument38 pagesInformation System in The Enterprise.: 2.1 Types of Information SystemsParul RathvaNo ratings yet
- Information System Applications Unit IIIDocument18 pagesInformation System Applications Unit IIIHrithick BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Management Information System in IndiaDocument5 pagesManagement Information System in IndiaAnkur TripathiNo ratings yet
- DPB1033 Management Information System: Information Systems and Organization StrategyDocument20 pagesDPB1033 Management Information System: Information Systems and Organization StrategyNur AdreanaNo ratings yet
- Information System: Operational-Level Systems Support Operational Managers by Keeping TrackDocument17 pagesInformation System: Operational-Level Systems Support Operational Managers by Keeping TrackAvreile RabenaNo ratings yet
- Major Types of Systems in OrganizationsDocument10 pagesMajor Types of Systems in OrganizationsRifat M. MustafizNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions Review QuestionsDocument8 pagesTutorial Questions Review QuestionsJing HangNo ratings yet
- Tactical and Operational Level of ManagementDocument5 pagesTactical and Operational Level of ManagementJowanna Burce100% (6)
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument3 pagesTransaction Processing SystemParteek SidhuNo ratings yet
- Information SystemDocument13 pagesInformation SystemAkhil James XaiozNo ratings yet
- MIS Notes ConsolidatedDocument13 pagesMIS Notes ConsolidatedShivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Computing, Library and Information Science Department of Library and Information ScienceDocument6 pagesFaculty of Computing, Library and Information Science Department of Library and Information ScienceNiyonzimaNo ratings yet
- 02 ITF Tutorial Review QuestionsDocument7 pages02 ITF Tutorial Review Questionsahmedsalem2012No ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument10 pagesManagement Information SystemPankaj Kr LakraNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument13 pagesManagement Information SystemnorizaNo ratings yet
- Review Questions: ISYS104 Tutorial - Week 3Document8 pagesReview Questions: ISYS104 Tutorial - Week 3Amy AungNo ratings yet
- Types of Information System ApplicationsDocument6 pagesTypes of Information System ApplicationsJoyce FererNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Is in The EnterpriseDocument44 pagesLecture 2 Is in The EnterpriseAludahNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument18 pagesManagement Information SystemHaqiqat AliNo ratings yet
- Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument80 pagesGlobal E-Business and CollaborationB.L. Siam100% (1)
- PGDM, II Semester, Jan-2009 Institute of Technology & Science Mohan Nagar, GhaziabadDocument72 pagesPGDM, II Semester, Jan-2009 Institute of Technology & Science Mohan Nagar, GhaziabadRashi GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document29 pagesChapter 3HaRsHa VaRdHaNNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document24 pagesChapter 2Rojesh BasnetNo ratings yet
- BCM 2208 Management Information Systems Lecture IIDocument14 pagesBCM 2208 Management Information Systems Lecture IIHillary OdungaNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument106 pagesManagement Information SystemAbdelrhman AhmedNo ratings yet
- BUS 516 - Chapter 2 - Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument50 pagesBUS 516 - Chapter 2 - Global E-Business and CollaborationArju LubnaNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: Impact of Information System On Organization's PerformanceDocument19 pagesManagement Information System: Impact of Information System On Organization's PerformanceAbhishek SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Smart Textilesnew - BackupDocument15 pagesSmart Textilesnew - BackupCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Smart TextilesDocument15 pagesSmart TextilesCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Coe Scope DocumentDocument17 pagesCoe Scope DocumentCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Ride Details Bill Details: Thanks For Travelling With Us, ChaitanyaDocument3 pagesRide Details Bill Details: Thanks For Travelling With Us, ChaitanyaCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Notice Inviting Expressions of InterestDocument7 pagesNotice Inviting Expressions of InterestCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Expressions of Interest: Writing For SuccessDocument2 pagesExpressions of Interest: Writing For SuccessCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Foshan Nanhai Landieyu Hardware Products Etc. U.S. Trademark Application No. 87777398 - Yhb - N/A 2/1/2019 5:55:20 PM Ecom115@Uspto - GovDocument7 pagesFoshan Nanhai Landieyu Hardware Products Etc. U.S. Trademark Application No. 87777398 - Yhb - N/A 2/1/2019 5:55:20 PM Ecom115@Uspto - GovCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Ride Details Bill Details: Thanks For Travelling With Us, ChaitanyaDocument3 pagesRide Details Bill Details: Thanks For Travelling With Us, ChaitanyaCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Ride Details Bill Details: Thanks For Travelling With Us, ChaitanyaDocument3 pagesRide Details Bill Details: Thanks For Travelling With Us, ChaitanyaCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Self-Declaration by Resident Individual For Release of Foreign Exchange Under LRSDocument2 pagesSelf-Declaration by Resident Individual For Release of Foreign Exchange Under LRSCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- KPI's Safety, Quality, Deliver, Cost & MoraleDocument1 pageKPI's Safety, Quality, Deliver, Cost & MoraleCHAITANYA SAHUNo ratings yet
- Project Planning Appraisal and Control PDFDocument217 pagesProject Planning Appraisal and Control PDFGodfrey Mkandala80% (5)
- 0quiz CH 1-3Document20 pages0quiz CH 1-3rajlaxmi1001100% (1)
- Epm - Topic 2 - Zoom Class Notes - Nov 2021Document9 pagesEpm - Topic 2 - Zoom Class Notes - Nov 2021kitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- Case 3 PDFDocument3 pagesCase 3 PDFBilawal Ali100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Modern Project ManagementDocument49 pagesChapter 1 - Modern Project ManagementDr. Shuva Ghosh100% (1)
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocument4 pagesCustomer Relationship ManagementadnanNo ratings yet
- Motion Control NC82 Complete English 2022 01Document260 pagesMotion Control NC82 Complete English 2022 01NhatQuangNguyenNo ratings yet
- AEC Standard 4Document447 pagesAEC Standard 4Giles EvansNo ratings yet
- 2021 - Digital Twin A State of The Art Review of Its Enabling Technologies, Applications and ChallengesDocument34 pages2021 - Digital Twin A State of The Art Review of Its Enabling Technologies, Applications and ChallengesTAWHIDNo ratings yet
- IEEE 12207 - SW Process Improvement Working Group2Document40 pagesIEEE 12207 - SW Process Improvement Working Group2Prudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- Virgo - Product and ProfileDocument8 pagesVirgo - Product and ProfilepsyclonesesNo ratings yet
- Pegasystems Pega 7Document41 pagesPegasystems Pega 7SunnyNo ratings yet
- Siemens PLM Wieland Electric Cs Z3Document3 pagesSiemens PLM Wieland Electric Cs Z3rasgeetsinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Assignment - ERDocument2 pagesUnit 4 Assignment - EREstefany Carolina RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Virtual SimutechDocument2 pagesVirtual SimutechRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- CSI PresentationDocument29 pagesCSI PresentationAdneya AudhiNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Roadmap Approach For Integrating BIM Into Lifecycle Project ManagementDocument11 pagesConceptual Framework and Roadmap Approach For Integrating BIM Into Lifecycle Project ManagementZina ibraheemNo ratings yet
- Strong Points and Weak Points For Paper ReviewDocument4 pagesStrong Points and Weak Points For Paper ReviewKanagala Raj ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Sae J1211-2012Document126 pagesSae J1211-2012seenudesignNo ratings yet
- Catia v5 - Biw Welding Fixture DesignDocument5 pagesCatia v5 - Biw Welding Fixture Designचन्दनप्रसादNo ratings yet
- OMF551 Unit 1 & 2Document77 pagesOMF551 Unit 1 & 2Bharath JbNo ratings yet
- Erp Life Cycle PDFDocument2 pagesErp Life Cycle PDFCarlaNo ratings yet
- CATIA V5 Interview Question and AnswersDocument67 pagesCATIA V5 Interview Question and Answerssuresh051No ratings yet
- Twelve Systems Engineering RolesDocument12 pagesTwelve Systems Engineering RolesioanchiNo ratings yet
- Siemens PLM Ducati Cs Z8Document4 pagesSiemens PLM Ducati Cs Z8rasgeetsinghNo ratings yet
- A Product of PTC PLM SoftwareDocument9 pagesA Product of PTC PLM SoftwareNguyên TrươngNo ratings yet
- Development of A Lean Enterprise Transformation Maturity ModelDocument17 pagesDevelopment of A Lean Enterprise Transformation Maturity Modelshekharbiswas60No ratings yet
- Pharma 4.0: Your Roadmap To Digital Manufacturing in Regulated IndustriesDocument35 pagesPharma 4.0: Your Roadmap To Digital Manufacturing in Regulated IndustriesBambangIrawan48No ratings yet
- Business AnalyticsDocument35 pagesBusiness Analyticsish tandonNo ratings yet