Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 viewsRailway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 3 To 5
Railway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 3 To 5
Uploaded by
Civil RguktThe aviation history of India began in 1911 with the first airmail service. Regular airmail services were established in the 1920s. The Department of Civil Aviation was set up in 1927. Major developments included JRD Tata obtaining a pilot's license in 1929 and the founding of Air India in 1946. Currently, India has 137 operational airports and is the 9th largest aviation market globally. The Airport Authority of India manages these airports. Key components of airports include runways, taxiways, terminals, control towers, and hangars. Wind rose diagrams are used to determine optimal runway orientation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- BS en 2583Document26 pagesBS en 2583Kevin Lee50% (2)
- CSR of Air IndiaDocument25 pagesCSR of Air IndiaKomal0% (2)
- WIPP (Sultan M Badaruddin II) : General InfoDocument10 pagesWIPP (Sultan M Badaruddin II) : General InfoM Ananda TNo ratings yet
- Egll KJFKDocument3 pagesEgll KJFKBoba FettNo ratings yet
- Project (Air India)Document81 pagesProject (Air India)Amulay Oberoi100% (2)
- Novas - Aeronaves 2020 TM 09Document7 pagesNovas - Aeronaves 2020 TM 09evdNo ratings yet
- Viation Sector in India: Presented By-Swapnilkumar Pawar (13253)Document39 pagesViation Sector in India: Presented By-Swapnilkumar Pawar (13253)Mohammed BilalNo ratings yet
- AAI Training ReportDocument64 pagesAAI Training ReportAkshta Kaushal0% (1)
- Air India ProjectDocument48 pagesAir India ProjectApoorva Sharma100% (4)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentPranav Manohar DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Intro To AviationDocument64 pagesIntro To AviationMahesh GorijavoluNo ratings yet
- Air IndiaDocument3 pagesAir IndiaZamora Enguerra EmmalyneNo ratings yet
- Project AirsiaDocument81 pagesProject AirsiaShreyas Js100% (1)
- Jetlite Vs Kingfisher AirlinesDocument19 pagesJetlite Vs Kingfisher AirlinesPramod P NairNo ratings yet
- Final Training ReportDocument66 pagesFinal Training ReportNimit JainNo ratings yet
- Indira Gandhi International AirportDocument14 pagesIndira Gandhi International AirportSumit Nautiyal100% (1)
- Airport Planning and DesigningDocument78 pagesAirport Planning and Designingayoushika abrolNo ratings yet
- Company Profile AaiDocument11 pagesCompany Profile AaijijomuraliNo ratings yet
- Abstract Versions 8Document39 pagesAbstract Versions 8K ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Indian Airlines IndustryDocument6 pagesIndian Airlines IndustrySandeep ShahNo ratings yet
- The History of Civil Aviation in India Began in December 1912Document8 pagesThe History of Civil Aviation in India Began in December 1912donNo ratings yet
- Indira Gandhi International Airport Business AnalyisDocument10 pagesIndira Gandhi International Airport Business AnalyisRenjitha rajuNo ratings yet
- Ad8 Research PrelimDocument11 pagesAd8 Research PrelimQuinn HarloweNo ratings yet
- Development of Air Transportation in India and CurrentDocument31 pagesDevelopment of Air Transportation in India and CurrentKishore100% (2)
- Airport Planning and DesignDocument203 pagesAirport Planning and DesignSushant SauravNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Aviation SectorDocument3 pagesLiterature Review Aviation SectorabhinavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4Ajay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- The Indian Aviation IndustryDocument24 pagesThe Indian Aviation IndustryNaresh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies,: "Airline Industry - Changing Times"Document36 pagesNarsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies,: "Airline Industry - Changing Times"Uma Shankar AravapalliNo ratings yet
- Rise and Fall of Air IndiaDocument39 pagesRise and Fall of Air IndianARAYANNo ratings yet
- Rise and Fall of Air IndiaDocument44 pagesRise and Fall of Air IndianARAYANNo ratings yet
- Principles of Airline and Airport ManagementDocument118 pagesPrinciples of Airline and Airport ManagementShreyas JsNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Aviation SectorDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Aviation SectorAlok Agarwal80% (5)
- Air India IPTDocument22 pagesAir India IPTRaj KiranNo ratings yet
- Aviation Management - Sae1403Document80 pagesAviation Management - Sae1403Pongsiri KamkankaewNo ratings yet
- Blackbook ProjectDocument37 pagesBlackbook ProjectShruti MhatreNo ratings yet
- Airports Veer Savarkar International AirportDocument73 pagesAirports Veer Savarkar International AirportsharlinsdgmailcomNo ratings yet
- Civil Aviation in IndiaDocument10 pagesCivil Aviation in IndiashyamNo ratings yet
- Indira Gandhi International AirportDocument28 pagesIndira Gandhi International AirportRenjitha raju0% (1)
- Chapter - I IntroductionDocument38 pagesChapter - I IntroductionKirti JindalNo ratings yet
- Trivandrum International Airport Since 1932Document64 pagesTrivandrum International Airport Since 1932Varun sam jacobNo ratings yet
- Apd PPT Ver1Document203 pagesApd PPT Ver1Rutvik100% (1)
- Kingfisher Airlines - Business StartegyDocument16 pagesKingfisher Airlines - Business Startegymakann1100% (1)
- CASE STUDY of Air IndiaDocument10 pagesCASE STUDY of Air IndiasonaljimsNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Introduction To Airline IndustryDocument55 pages1st Sem Introduction To Airline IndustryK ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Airports: by Mahesh RamtekeDocument55 pagesAirports: by Mahesh RamtekeMahesh RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Airport and Plane Runaway in INDIADocument9 pagesAirport and Plane Runaway in INDIATomi ZuhriNo ratings yet
- Aanchal Final MRPDocument101 pagesAanchal Final MRPGaurav GagwaniNo ratings yet
- FINAL Project Presentation Islamabad International Airport: Group # 1 Afzal Ahmed 21015Document10 pagesFINAL Project Presentation Islamabad International Airport: Group # 1 Afzal Ahmed 21015Aamir YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Aviation Sector in IndiaDocument66 pagesAviation Sector in Indiasrpvicky100% (1)
- Airport Planning and Design: by SrinivasDocument55 pagesAirport Planning and Design: by SrinivasSaketSinghNo ratings yet
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj International Airport - WikipediaDocument27 pagesChhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj International Airport - WikipediaSelvakumar ChinnaduraiNo ratings yet
- Mini Project On Airport Planning and Design: Ce - 1308 (Transportation Engineering-Ii)Document29 pagesMini Project On Airport Planning and Design: Ce - 1308 (Transportation Engineering-Ii)Pradeepta DeyNo ratings yet
- AAI Project ReportDocument45 pagesAAI Project Reportmanav rahejaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Industry Profile: History of Civil AviationDocument54 pagesChapter - 1 Industry Profile: History of Civil AviationsilkysilverNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Strategic ManagementDocument12 pagesAssignment On Strategic ManagementAshok Nigam0% (1)
- History: Size of TheindustryDocument38 pagesHistory: Size of TheindustryDikshit KothariNo ratings yet
- Air India: "Your Palace in The SkyDocument21 pagesAir India: "Your Palace in The SkyRashi ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Air Port - 6th SemDocument35 pagesAir Port - 6th SemSayantan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Air IndiaDocument12 pagesAir IndiaRahul GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Dubai International AirportDocument19 pagesDubai International AirportelcivilengNo ratings yet
- Trusses, Frames & MachinesDocument55 pagesTrusses, Frames & MachinesCivil RguktNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Civil Engineering: Unit - 1Document51 pagesIntroduction To Civil Engineering: Unit - 1Civil RguktNo ratings yet
- Durability of Concrete (Affecting Factors and Measures To Control)Document42 pagesDurability of Concrete (Affecting Factors and Measures To Control)Civil RguktNo ratings yet
- Railway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 1 & 2Document95 pagesRailway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 1 & 2Civil RguktNo ratings yet
- Cockpit Voice Recorder Inspection CheckDocument2 pagesCockpit Voice Recorder Inspection CheckEleazarNo ratings yet
- La 5 InstructionsDocument10 pagesLa 5 InstructionsAbel MongelosNo ratings yet
- Htza PDFDocument2 pagesHtza PDFМистермарк МистерклимюкNo ratings yet
- Hurricane 25 - Team 3 TranscriptDocument2 pagesHurricane 25 - Team 3 Transcriptdoquocviet0505No ratings yet
- CS-26 Easy Access Rules For Additional Airworthiness Specifications (Jan 2018)Document28 pagesCS-26 Easy Access Rules For Additional Airworthiness Specifications (Jan 2018)Ferhan SadikogluNo ratings yet
- GTE B1 2019 All SessionDocument17 pagesGTE B1 2019 All SessionChalla Amarsrinu100% (1)
- HW 2 Isd 520Document3 pagesHW 2 Isd 520HemaNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Practice: P. Pounds, R. Mahony, P. CorkeDocument9 pagesControl Engineering Practice: P. Pounds, R. Mahony, P. CorkeKhalil HsaineNo ratings yet
- Course Introduction To Database: PROJECT: Airplane Ticket Buying Management SystemDocument21 pagesCourse Introduction To Database: PROJECT: Airplane Ticket Buying Management SystemHamim hasan HimuNo ratings yet
- AerodynamicsDocument42 pagesAerodynamicsFreda FungNo ratings yet
- 3504 S 63 Rev 0 ENDocument2 pages3504 S 63 Rev 0 ENIbrahim AsifNo ratings yet
- At-38B Phase ManualDocument189 pagesAt-38B Phase ManualTate100% (2)
- Homework Unit 8, NovDocument5 pagesHomework Unit 8, NovAlbert Miguelangel HernandezNo ratings yet
- OPLADocument47 pagesOPLAsohaib arifNo ratings yet
- Beechcraft King Air 350 SME ConfigurationDocument1 pageBeechcraft King Air 350 SME ConfigurationNudin SeninNo ratings yet
- Air Frame & Aircraft System 2 1Document16 pagesAir Frame & Aircraft System 2 1Alpha DeltaNo ratings yet
- 17 - Propellers Cat ADocument335 pages17 - Propellers Cat AFitrianisutantiNo ratings yet
- EASA-TCDS A 439 DV20 Issue 03Document10 pagesEASA-TCDS A 439 DV20 Issue 03Dennis HNo ratings yet
- Nothing by ChanceDocument3 pagesNothing by ChanceDarjan SušaNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Better PilotDocument48 pagesHow To Be A Better PilotAntonio Pereira95% (19)
- Future of Air Traffic ManagementDocument12 pagesFuture of Air Traffic ManagementHamza MughalNo ratings yet
- Robert M Pimpsner - Orbital Debris Mitigation - ENS 100Document18 pagesRobert M Pimpsner - Orbital Debris Mitigation - ENS 100RobertMPimpsnerNo ratings yet
- Test Plan Votv-FimpDocument4 pagesTest Plan Votv-FimpNagarjuna Reddy TNo ratings yet
- GMX 200 InstalDocument100 pagesGMX 200 InstalLaboratorio01 AvionicsNo ratings yet
- 10, Zara Rutherford - WikipediaDocument6 pages10, Zara Rutherford - WikipediaGost hunterNo ratings yet
- Ho 49Document68 pagesHo 49Lavern P. SipinNo ratings yet
Railway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 3 To 5
Railway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 3 To 5
Uploaded by
Civil Rgukt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views30 pagesThe aviation history of India began in 1911 with the first airmail service. Regular airmail services were established in the 1920s. The Department of Civil Aviation was set up in 1927. Major developments included JRD Tata obtaining a pilot's license in 1929 and the founding of Air India in 1946. Currently, India has 137 operational airports and is the 9th largest aviation market globally. The Airport Authority of India manages these airports. Key components of airports include runways, taxiways, terminals, control towers, and hangars. Wind rose diagrams are used to determine optimal runway orientation.
Original Description:
Original Title
Airport Engineering
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe aviation history of India began in 1911 with the first airmail service. Regular airmail services were established in the 1920s. The Department of Civil Aviation was set up in 1927. Major developments included JRD Tata obtaining a pilot's license in 1929 and the founding of Air India in 1946. Currently, India has 137 operational airports and is the 9th largest aviation market globally. The Airport Authority of India manages these airports. Key components of airports include runways, taxiways, terminals, control towers, and hangars. Wind rose diagrams are used to determine optimal runway orientation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views30 pagesRailway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 3 To 5
Railway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 3 To 5
Uploaded by
Civil RguktThe aviation history of India began in 1911 with the first airmail service. Regular airmail services were established in the 1920s. The Department of Civil Aviation was set up in 1927. Major developments included JRD Tata obtaining a pilot's license in 1929 and the founding of Air India in 1946. Currently, India has 137 operational airports and is the 9th largest aviation market globally. The Airport Authority of India manages these airports. Key components of airports include runways, taxiways, terminals, control towers, and hangars. Wind rose diagrams are used to determine optimal runway orientation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 30
RAILWAY & AIRPORT
ENGINEERING
UNIT – 3 to 5
SIRAM VENKAT RAMANA
AVIATION HISTORY OF INDIA
The world’s first airmail service was started in India at Allahabad; on 18th Feb 1911 the
occasion of Kumbh mela. This in turn led the beginning of civil aviation in India. On the
special day Henry Piquet carried 6500 mails on a Humber biplane from Allahabad to Naini,
covering almost a distance of 10km
The first International flight to and from India was introduced in December 1912 over the
route, London-Karachi-Delhi with the collaboration of Indian state air services and UK based
imperial airways.
Regular airmail services were started by Tata Sons Ltd, between Karachi and Madrasand.
On 24th Jan 1920 Royal airforce started regular airmail services between Karachi and Bombay.
Construction of airports in India started at Dum Dum in Calcutta, Bamrauli in Allahabad
and Gillbert hill of Bombay in 1924.
Separate Department of civil aviation was set up in April 1927.Also, Aero club of India was
established the same year.
JRD Tata became the first person to be awarded with pilot license by
Aeronautique International on behalf of Aero club of India and Burma in Feb 1929.
Tata Airlines became a division of Tata Sons Limited in 1932.It started Air Mail services on
the Karachi, Ahmedabad, Bombay, Bellary, Madras routes on 15 October.
AVIATION HISTORY OF INDIA
In 1945 the Deccan Airways was founded – jointly owned by the Nizam of Hyderabad
and Tata. Its first flight began in July 1946.
In 1946 ‘Air India’ came into being when Tata Airlines changed its name to Air India.
At present India holds the 9th largest aviation market in the world with 137 operational
airports, 735 aircraft. The number of air passengers travelling in India is expected to cross 50
million this year(2022).
There are 34 operational International Airports in India. Of which Indira Gandhi
International Airport is the largest International airport constructed in 5495 acres. It is also
the busiest airport in India followed by the Chatrapati Shivaji International Airport.
Cochin International Airport, Kerala is the first international airport in India developed
under PPP- Public-Private Partnership Model.
Calicut International Airport, Kerala is recently added to the list of International Airports
in India.
Juhu Aerodrome, Mumbai is the first and oldest Airport in India founded in 1928.
Airport of Trichy is the smallest airport in India.
Kushok Bakula Rimpochee, Ladhak is the 23rd highest commercial airport in the world at
3256 meters elevation.
AIRPORT AUTHORITY OF INDIA
The Airport Authority of India is the body
that manages both the International Airports in
India as well as the Domestic Airports in India.
Airports Authority of India (AAI) manages a
total of 137 Airports, which includes 103
Domestic Airports, 24 International Airports,
and 10 Customs Airports. AAI is responsible
for creating, maintaining, upgrading, and
managing civil aviation infrastructure in India
and works under the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
OBJECTIVES OF CIVIL AVIATION MINISTRY
MAJOR INTERNATIONAL AIRPORTS IN INDIA
DOMESTIC AIRPORTS IN INDIA
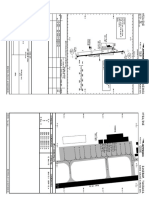
COMPONENTS OF AIRPORT
Runway
Taxiway
Apron
Terminal building
Control tower
Hanger
Parking
Hanger Apron
Control Tower
Terminal Building Taxiway
COMPONENTS OF AIRPORT
Runway is a paved land strip on which
landing and takeoff operations of aircrafts
takes place. It is in leveled position without
any obstructions on it.
COMPONENTS OF AIRPORT
COMPONENTS OF AIRPORT
COMPONENTS OF AIRPORT
Hanger
Hangars are buildings in which airplanes are repaired or serviced . Most airlines
have their own hangars, in which they can park many jets at the same time.
Most hangars are far away from terminals and runways so that they do not
interfere with airport traffic.
Taxiway connects the hanger with runway so, when a repair needed for an
aircraft it can be moved to hanger easily.
AIRCRAFT COMPONENTS
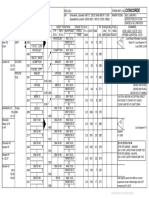
WIND ROSE DIAGRAMS
WIND ROSE:
The wind data direction, duration and intensity are graphically represented by a diagram
called wind rose.
The wind data should usually be collected for a period of at least 5 years and preferably
of 10 years so as to obtain an average data with sufficient accuracy.
Wind rose plays a key role in deciding the orientation of runway of Airport.
Wind rose diagrams can be plotted in two types
1. showing direction and duration of wind. (TYPE-I)
2. Showing direction duration and intensity of wind. (TYPE-II)
WIND ROSE DIAGRAMS TYPE-I
WIND ROSE DIAGRAM TYPE-I:
Wind rose diagram can be plotted by type-I, showing direction and duration of wind.
In the wind rose diagram plotted by type-I, the radial lines represents the wind direction
and each concentric circle indicate the duration of wind to certain scale.
Total percentage of wind blowing in north is taken from the collected value of wind data
and this point is marked along north direction.
The best direction of runway is shown along the direction of the longest line on the wind
rose diagram.
WIND ROSE DIAGRAM TYPE-II
WIND ROSE DIAGRAM TYPE-II:
Wind rose diagram can be plotted by type-II, showing Direction, Duration and intensity
of wind.
Each circle represents the wind intensity to some scale. The values entered in each
segment represent the percentage of time in a year during which the wind having a
particular intensity blows from the respective direction.
You might also like
- BS en 2583Document26 pagesBS en 2583Kevin Lee50% (2)
- CSR of Air IndiaDocument25 pagesCSR of Air IndiaKomal0% (2)
- WIPP (Sultan M Badaruddin II) : General InfoDocument10 pagesWIPP (Sultan M Badaruddin II) : General InfoM Ananda TNo ratings yet
- Egll KJFKDocument3 pagesEgll KJFKBoba FettNo ratings yet
- Project (Air India)Document81 pagesProject (Air India)Amulay Oberoi100% (2)
- Novas - Aeronaves 2020 TM 09Document7 pagesNovas - Aeronaves 2020 TM 09evdNo ratings yet
- Viation Sector in India: Presented By-Swapnilkumar Pawar (13253)Document39 pagesViation Sector in India: Presented By-Swapnilkumar Pawar (13253)Mohammed BilalNo ratings yet
- AAI Training ReportDocument64 pagesAAI Training ReportAkshta Kaushal0% (1)
- Air India ProjectDocument48 pagesAir India ProjectApoorva Sharma100% (4)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentPranav Manohar DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Intro To AviationDocument64 pagesIntro To AviationMahesh GorijavoluNo ratings yet
- Air IndiaDocument3 pagesAir IndiaZamora Enguerra EmmalyneNo ratings yet
- Project AirsiaDocument81 pagesProject AirsiaShreyas Js100% (1)
- Jetlite Vs Kingfisher AirlinesDocument19 pagesJetlite Vs Kingfisher AirlinesPramod P NairNo ratings yet
- Final Training ReportDocument66 pagesFinal Training ReportNimit JainNo ratings yet
- Indira Gandhi International AirportDocument14 pagesIndira Gandhi International AirportSumit Nautiyal100% (1)
- Airport Planning and DesigningDocument78 pagesAirport Planning and Designingayoushika abrolNo ratings yet
- Company Profile AaiDocument11 pagesCompany Profile AaijijomuraliNo ratings yet
- Abstract Versions 8Document39 pagesAbstract Versions 8K ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Indian Airlines IndustryDocument6 pagesIndian Airlines IndustrySandeep ShahNo ratings yet
- The History of Civil Aviation in India Began in December 1912Document8 pagesThe History of Civil Aviation in India Began in December 1912donNo ratings yet
- Indira Gandhi International Airport Business AnalyisDocument10 pagesIndira Gandhi International Airport Business AnalyisRenjitha rajuNo ratings yet
- Ad8 Research PrelimDocument11 pagesAd8 Research PrelimQuinn HarloweNo ratings yet
- Development of Air Transportation in India and CurrentDocument31 pagesDevelopment of Air Transportation in India and CurrentKishore100% (2)
- Airport Planning and DesignDocument203 pagesAirport Planning and DesignSushant SauravNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Aviation SectorDocument3 pagesLiterature Review Aviation SectorabhinavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4Ajay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- The Indian Aviation IndustryDocument24 pagesThe Indian Aviation IndustryNaresh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies,: "Airline Industry - Changing Times"Document36 pagesNarsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies,: "Airline Industry - Changing Times"Uma Shankar AravapalliNo ratings yet
- Rise and Fall of Air IndiaDocument39 pagesRise and Fall of Air IndianARAYANNo ratings yet
- Rise and Fall of Air IndiaDocument44 pagesRise and Fall of Air IndianARAYANNo ratings yet
- Principles of Airline and Airport ManagementDocument118 pagesPrinciples of Airline and Airport ManagementShreyas JsNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Aviation SectorDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Aviation SectorAlok Agarwal80% (5)
- Air India IPTDocument22 pagesAir India IPTRaj KiranNo ratings yet
- Aviation Management - Sae1403Document80 pagesAviation Management - Sae1403Pongsiri KamkankaewNo ratings yet
- Blackbook ProjectDocument37 pagesBlackbook ProjectShruti MhatreNo ratings yet
- Airports Veer Savarkar International AirportDocument73 pagesAirports Veer Savarkar International AirportsharlinsdgmailcomNo ratings yet
- Civil Aviation in IndiaDocument10 pagesCivil Aviation in IndiashyamNo ratings yet
- Indira Gandhi International AirportDocument28 pagesIndira Gandhi International AirportRenjitha raju0% (1)
- Chapter - I IntroductionDocument38 pagesChapter - I IntroductionKirti JindalNo ratings yet
- Trivandrum International Airport Since 1932Document64 pagesTrivandrum International Airport Since 1932Varun sam jacobNo ratings yet
- Apd PPT Ver1Document203 pagesApd PPT Ver1Rutvik100% (1)
- Kingfisher Airlines - Business StartegyDocument16 pagesKingfisher Airlines - Business Startegymakann1100% (1)
- CASE STUDY of Air IndiaDocument10 pagesCASE STUDY of Air IndiasonaljimsNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Introduction To Airline IndustryDocument55 pages1st Sem Introduction To Airline IndustryK ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Airports: by Mahesh RamtekeDocument55 pagesAirports: by Mahesh RamtekeMahesh RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Airport and Plane Runaway in INDIADocument9 pagesAirport and Plane Runaway in INDIATomi ZuhriNo ratings yet
- Aanchal Final MRPDocument101 pagesAanchal Final MRPGaurav GagwaniNo ratings yet
- FINAL Project Presentation Islamabad International Airport: Group # 1 Afzal Ahmed 21015Document10 pagesFINAL Project Presentation Islamabad International Airport: Group # 1 Afzal Ahmed 21015Aamir YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Aviation Sector in IndiaDocument66 pagesAviation Sector in Indiasrpvicky100% (1)
- Airport Planning and Design: by SrinivasDocument55 pagesAirport Planning and Design: by SrinivasSaketSinghNo ratings yet
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj International Airport - WikipediaDocument27 pagesChhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj International Airport - WikipediaSelvakumar ChinnaduraiNo ratings yet
- Mini Project On Airport Planning and Design: Ce - 1308 (Transportation Engineering-Ii)Document29 pagesMini Project On Airport Planning and Design: Ce - 1308 (Transportation Engineering-Ii)Pradeepta DeyNo ratings yet
- AAI Project ReportDocument45 pagesAAI Project Reportmanav rahejaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Industry Profile: History of Civil AviationDocument54 pagesChapter - 1 Industry Profile: History of Civil AviationsilkysilverNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Strategic ManagementDocument12 pagesAssignment On Strategic ManagementAshok Nigam0% (1)
- History: Size of TheindustryDocument38 pagesHistory: Size of TheindustryDikshit KothariNo ratings yet
- Air India: "Your Palace in The SkyDocument21 pagesAir India: "Your Palace in The SkyRashi ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Air Port - 6th SemDocument35 pagesAir Port - 6th SemSayantan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Air IndiaDocument12 pagesAir IndiaRahul GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Dubai International AirportDocument19 pagesDubai International AirportelcivilengNo ratings yet
- Trusses, Frames & MachinesDocument55 pagesTrusses, Frames & MachinesCivil RguktNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Civil Engineering: Unit - 1Document51 pagesIntroduction To Civil Engineering: Unit - 1Civil RguktNo ratings yet
- Durability of Concrete (Affecting Factors and Measures To Control)Document42 pagesDurability of Concrete (Affecting Factors and Measures To Control)Civil RguktNo ratings yet
- Railway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 1 & 2Document95 pagesRailway & Airport Engineering: UNIT - 1 & 2Civil RguktNo ratings yet
- Cockpit Voice Recorder Inspection CheckDocument2 pagesCockpit Voice Recorder Inspection CheckEleazarNo ratings yet
- La 5 InstructionsDocument10 pagesLa 5 InstructionsAbel MongelosNo ratings yet
- Htza PDFDocument2 pagesHtza PDFМистермарк МистерклимюкNo ratings yet
- Hurricane 25 - Team 3 TranscriptDocument2 pagesHurricane 25 - Team 3 Transcriptdoquocviet0505No ratings yet
- CS-26 Easy Access Rules For Additional Airworthiness Specifications (Jan 2018)Document28 pagesCS-26 Easy Access Rules For Additional Airworthiness Specifications (Jan 2018)Ferhan SadikogluNo ratings yet
- GTE B1 2019 All SessionDocument17 pagesGTE B1 2019 All SessionChalla Amarsrinu100% (1)
- HW 2 Isd 520Document3 pagesHW 2 Isd 520HemaNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Practice: P. Pounds, R. Mahony, P. CorkeDocument9 pagesControl Engineering Practice: P. Pounds, R. Mahony, P. CorkeKhalil HsaineNo ratings yet
- Course Introduction To Database: PROJECT: Airplane Ticket Buying Management SystemDocument21 pagesCourse Introduction To Database: PROJECT: Airplane Ticket Buying Management SystemHamim hasan HimuNo ratings yet
- AerodynamicsDocument42 pagesAerodynamicsFreda FungNo ratings yet
- 3504 S 63 Rev 0 ENDocument2 pages3504 S 63 Rev 0 ENIbrahim AsifNo ratings yet
- At-38B Phase ManualDocument189 pagesAt-38B Phase ManualTate100% (2)
- Homework Unit 8, NovDocument5 pagesHomework Unit 8, NovAlbert Miguelangel HernandezNo ratings yet
- OPLADocument47 pagesOPLAsohaib arifNo ratings yet
- Beechcraft King Air 350 SME ConfigurationDocument1 pageBeechcraft King Air 350 SME ConfigurationNudin SeninNo ratings yet
- Air Frame & Aircraft System 2 1Document16 pagesAir Frame & Aircraft System 2 1Alpha DeltaNo ratings yet
- 17 - Propellers Cat ADocument335 pages17 - Propellers Cat AFitrianisutantiNo ratings yet
- EASA-TCDS A 439 DV20 Issue 03Document10 pagesEASA-TCDS A 439 DV20 Issue 03Dennis HNo ratings yet
- Nothing by ChanceDocument3 pagesNothing by ChanceDarjan SušaNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Better PilotDocument48 pagesHow To Be A Better PilotAntonio Pereira95% (19)
- Future of Air Traffic ManagementDocument12 pagesFuture of Air Traffic ManagementHamza MughalNo ratings yet
- Robert M Pimpsner - Orbital Debris Mitigation - ENS 100Document18 pagesRobert M Pimpsner - Orbital Debris Mitigation - ENS 100RobertMPimpsnerNo ratings yet
- Test Plan Votv-FimpDocument4 pagesTest Plan Votv-FimpNagarjuna Reddy TNo ratings yet
- GMX 200 InstalDocument100 pagesGMX 200 InstalLaboratorio01 AvionicsNo ratings yet
- 10, Zara Rutherford - WikipediaDocument6 pages10, Zara Rutherford - WikipediaGost hunterNo ratings yet
- Ho 49Document68 pagesHo 49Lavern P. SipinNo ratings yet