Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antitusif Dan Nasal Decongestant
Antitusif Dan Nasal Decongestant
Uploaded by
Putri Primandini0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views32 pagesThis document discusses drugs used for cough and nasal congestion. It describes the pathophysiology of cough and the mechanisms of action of different types of antitussive drugs like codeine, dextromethorphan, and benzonatate. It also discusses expectorants like glycerol guaiacolate and mucolytics like bromhexin. For nasal congestion, it covers systemic and topical decongestants such as pseudoephedrine and oxymetazolone. It provides details on the pharmacokinetics, dosing, side effects and interactions of these drugs.
Original Description:
Original Title
413096_Antitusif Dan Nasal Decongestant
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses drugs used for cough and nasal congestion. It describes the pathophysiology of cough and the mechanisms of action of different types of antitussive drugs like codeine, dextromethorphan, and benzonatate. It also discusses expectorants like glycerol guaiacolate and mucolytics like bromhexin. For nasal congestion, it covers systemic and topical decongestants such as pseudoephedrine and oxymetazolone. It provides details on the pharmacokinetics, dosing, side effects and interactions of these drugs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views32 pagesAntitusif Dan Nasal Decongestant
Antitusif Dan Nasal Decongestant
Uploaded by
Putri PrimandiniThis document discusses drugs used for cough and nasal congestion. It describes the pathophysiology of cough and the mechanisms of action of different types of antitussive drugs like codeine, dextromethorphan, and benzonatate. It also discusses expectorants like glycerol guaiacolate and mucolytics like bromhexin. For nasal congestion, it covers systemic and topical decongestants such as pseudoephedrine and oxymetazolone. It provides details on the pharmacokinetics, dosing, side effects and interactions of these drugs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 32
BAGIAN FARMAKOLOGI
FAKULTAS KEDOKTERAN
UNIVERSITAS TADULAKO
ANTITUSIF & NASAL
DECONGESTANT
Batuk
• proses eksipirasi eksplosif yg memberikan
mekanisme proteksi normal u/ membersihkan
saluran pernafasan dari sekresi a/ benda asing
bukan penyakit gejala atau tanda adanya
gangguan pada saluran pernafasan
Patofisiologi Batuk
• Melibatkan kompleks rangkaian refleks yang bermula dari stimulasi
terhadap reseptor iritan
OBAT BATUK
Antitusif
Ekspektoran
Mukolitik
ANTITUSIF
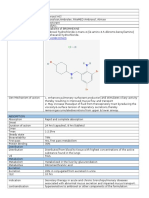
Codein, Dextromethorphan, Benzonatate, Difenhidramin Hcl
• Menekan frek batuk kering
• sentral (pusat batuk/medula)
meningkatkan ambang batas menurunkan
respon pusat batuk
• perifer (tr. respiratorius) frekuensi dan
blokade reseptor sensorik intensitas
menghambat peregangan paru batuk
Codein
Pharmacodynamics
• bekerja dgn cara menekan pusat batuk (medula)
menghambat impuls batuk
Pharmacokinetics
• Absorption
– gastrointestinal tract oral
• Distribution
– tersebar luas pd jaringan tubuh, melewati placenta &
jg tdpt di ASI. Ikatan dgn prot. plasma 7% - 25%.
Codein
• Metabolisme
– di hepar, 70% - 80% conjugation with glucuronic
acid codeine-6-glucuronide (C6G) ; 5% – 10%
by O-demethylation morphine ; 10% N-
demethylation to norcodeine
• Excretion
– ± 90% of the total dose of codeine is excreted
through the kidneys
– t½ codein dan metabolitnya ± 3jam.
Codein
• Side Effects
– Constipation, Drowsiness, Nausea/vomiting, Addictive
potential
– Cough suppression by opioids may allow accumulation
of secretions and lead to airway obstruction
• Dosis
– Adult: 15-30 mg 3-4 times daily.
– Child : 2-5 yr 3 mg; 6-12 yr 7.5-15 mg. Doses to be
taken 3-4 times daily
Codein
• Contraindication
– Acute or severe bronchial asthma
– Significant respiratory depression
– use of MAOIs within the last 14 days
– Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction,
including paralytic ileus
– Hypersensitivity to codeine
• Interaction
– Drugs interaction : MAO inhibitors
– Food interaction : Alcohol
Dextromethorphan
Pharmacodynamics
• bekerja dgn cara menekan pusat batuk (medula)
menghambat impuls batuk
Pharmacokinetics
• Absorption : GI tract.
• Distribution : Terdistribusi luas pd jaringan tubuh
• Metabolism : di hepar demetilasi mjd dextrorphan
(active)
• Excretion : >>> urine
Dextromethorphan
• Contraindications:
– penggunaan MAO inhibitor selama 2mgu dpt me↑kan
serotonergic effect of Dextromethorphan. This may cause
serotonin syndrome.
– ≠ u/ mengobati batuk yg disebabkan o/ merokok, asthma,
or emphysema
• Side Effects:
– severe dizziness, anxiety, restless feeling, or nervousness;
– confusion, hallucinations; or
– slow breathing
Benzonatate
• Pharmacodynamics
– menganestesi stretch receptors yg terdapat pada tr.
respiratorius,
• Pharmacokinetics:
– Taken orally as a softgel capsule.
– act 15 - 20 min’ and effect lasts for 3 - 8 hours.
EKSPEKTORAN
• Sebenarnya tidak lebih baik dari plasebo (IONI, 2017)
• Contoh :
– Glyseril Guaiacolate (Guaifenesin)
– Succus liquairitiae
– Ammonium klorida
Glyseril Guaiacolate
Pharmacodynamics
• increasing sputum volume and reducing the viscosity of
bronchial secretions, guaifenesin facilitates expectoration of
retained secretions
• helps loosen phlegm (mucus) and thin bronchial secretions,
make coughs more productive
Glyseril Guaiacolate
• Pharmacokinetics
– Absorption: Well absorbed from the GI tract.
– Distribution :
– Metabolism: di hepar (oksidasi & demetilasi)
– Excretion: Via urine. Elimination half-life: ±1 hr.
Glyseril Guaiacolate
• Contraindication
– Hypersensitivity
• Side effects
– Significant Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea.
– Rare Nervous: Dizziness, drowsiness, headache.
Genitourinary: Nephrolithiasis. Endocrine: Hypouricaemia.
Dermatologic: Rash.
• Dosis
– Adult: As conventional preparation 200-400 mg 4 hrly as needed. As
extended-release tab: 600-1,200 mg 12 hrly as needed. Max: 2,400
mg/daily.
– Child: 4-<6 yr 50-100 mg 4 hrly as needed. Max: 600 mg daily; 6-<12 yr 100-
200 mg 4 hrly as needed. Max: 1,200 mg daily; ≥12 yr Same as adult dose
MUKOLITIK
Bromhexin, Ambroxol, Erdosistein, Karbosistein, Mesistein
• untuk batuk berdahak, mempercepat ekspektorasi dgn cara
mengurangi viskositas sputum
• >>> pada batuk kronik
• Hati2 penggunaan pd px riw. peptic ulcer merusak sawar
mukosa lambung
BROMHEXIN
Pharmacodynamics
• acts on the mucus at the formative stages in the glands,
within the mucus-secreting cells disrupts the structure of
acid mucopolysaccharide fibres in mucoid sputum and
produces a less viscous mucus, which is easier to expectorate.
• enhances mucus transport by reducing mucus viscosity and by
activating the ciliated epithelium (mucociliary clearance)
Pharmacokinetics
• Absorption: Rapidly absorbed from the GI tract.
Bioavailability: Approx 20%. Time to peak plasma
concentration: Approx 1 hr.
• Distribution: Widely distributed to body tissues. Crosses
blood brain-barrier and placenta (small amounts). Plasma
protein binding: >90%.
• Metabolism: Extensive hepatic first-pass metabolism.
• Excretion: Via urine (approx 85-90%, mainly as metabolites).
t½: 13-40 hr
• Adverse Reactions
– GI side effects; headache, dizziness, sweating, skin rashes.
Inhalation: Cough or bronchospasm.
• Bromhexine and Pregnancy
– Category A: increase the frequency of malformations or
other direct or indirect harmful effects on the foetus
having been observed.
BROMHEXIN
• Kontraindikasi:
– Hipersensitivitas.
• Dosis:
– Adult: 8-16 mg
– Child: 2-5 yr 8 mg daily in 2-3 divided doses; 6-11 yr 4-8
mg; ≥12 yr Same as adult dose.
AMBROXOL
Pharmacodynamics:
• active metabolite of bromhexine
• causes an increase in secretion in the respiratory tract
• promotes surfactant production and stimulates ciliary
activity
assist the flow of mucus and its removal (mucociliary
clearance)
• significant reduction in cytokine release, both in the
blood and in mononuclear and polynuclear cells
Pharmacokinetics:
• Absorption: GI tract. Peak plasma levels are attained after 0.5-
3 hrs.
• Distribution: Plasma protein-binding is around 90%. After oral,
IV and IM administration, ambroxol is distributed rapidly and
extensively from the blood into the tissues. The highest active
ingredient concentrations are measured in the lung.
• Metabolism: in the liver mainly by conjugation.
• Elimination: Around 30% of an oral dose is eliminated via the
first-pass effect. t½ 10 hrs.
AMBROXOL
• Dosis
– Dewasa: kapsul lepas lambat 1 kali sehari 75 mg, sesudah makan. Dewasa dan
anak di atas 12 tahun:1 tablet (30 mg) 2-3 kali sehari; Anak 6-12 tahun: 1/2 tablet
2-3 kali sehari. Sirup tetes (drops): 15 mg/ml drops (1 mL= 20 tetes): Anak s/d 2
tahun: 0,5 mL (10 tetes) 2 kali sehari; Ambroksol drops dapat dicampur bersama
dengan sari buah, susu atau air.Sirup 15 mg/5 mL (1 sendok takar = 5 mL): Anak
usia 6-12 tahun: 2-3 kali sehari 1 sendok takar; 2-6 tahun: 3 kali sehari 1/2 sendok
takar; di bawah 2 tahun: 2 kali sehari 1/2 sendok takar.
• ADR
– Mild GI effects and allergic reactions.
• Precaution : 1st trimester of pregnancy
• Interaksi : Pemberian bersamaan dengan antibiotik (amoksisilin
sefuroksim, eritromisin, doksisiklin) menyebabkan peningkatan
penerimaan antibiotik kedalam jaringan paru-paru.
NASAL DECONGESTANT
• Sistemik
– Pseudoefedrin, phenilpropanolamin
• Topikal
– Oxymetazoline, naphazoline, efedrin, sodium chloride
NASAL DECONGESTANT
Pseudoephedrine
• Pharmacodynamics an α-and β-adrenergic receptor agonist. It
causes vasoconstriction via direct stimulation of α-adrenergic
receptors of the respiratory mucosa. It also directly stimulates
β-adrenergic receptors causing bronchial relaxation, increased
heart rate and contractility.
• Pharmacokinetics:
– Absorption: cepat diasorbsi dari GI tract.
– Distribusi : terdistribusi luas di jaringan tubuh, bisa ditemukan dlm
ASI.
– Metabolisme : di hepar
– Ekskresi : di urine, >>> dlm btk unchanged drug. Half-life: ±5-8 hr.
• Dosis (as hydrochloride or sulfate)
Dewasa : 60 mg every 4-6 hr. Max: 4 dosis /24jam.
Anak2 : 2-6 yr: 15 mg 3-4 times daily; 6-12 yr: 30 mg 3-4 times
daily.
• Kontraindikasi : Severe hypertension, phaeochromocytoma.
• ADR : Anginal pain; rebound congestion and rhinorrhoea;
fear, anxiety, restlessness, tremor, insomnia, confusion,
irritability and psychotic states; reduced appetite,
nausea, vomiting; gangrene; cerebral haemorrhage and
pulmonary oedema; reflex bradycardia, tachycardia and
cardiac arrhythmias, palpitations and cardiac arrest,
hypotension and dizziness, fainting and flushing. Tissue
necrosis and sloughing; myocardial and arterial necrosis.
• Drugs Interaction
– Increased risk of hypertension and arrhythmias if
given with cardiac glycosides, quinidine.
– Increased risk of vasoconstrictor effects if given with
ergot alkaloids or oxytocin.
– Co-admin with MAOIs may cause hypertensive crisis.
– Anaesthetics e.g. cyclopropane, halothane and other
halogenated anaesthestics
– antihypertensive agents
TERIMAKASIH
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaKath76% (21)
- 400m FactsheetDocument11 pages400m FactsheetR.P sprinter Runner100% (1)
- MIMS Drug StudyDocument6 pagesMIMS Drug StudyKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- DrugsDocument8 pagesDrugsShizuka Marycris AmaneNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The GitDocument29 pagesDrugs Acting On The GitIsheanesu MugwisiNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsDocument5 pagesTherapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsAbby MontealegreNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDocument9 pagesMetoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDominique RamosNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDocument9 pagesMetoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDominique RamosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyMadsNo ratings yet
- MucosolvanDocument2 pagesMucosolvanAyah Paasa100% (1)
- Drug CardsDocument3 pagesDrug CardsDave HillNo ratings yet
- 33-36 Medications PDFDocument15 pages33-36 Medications PDFJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- BNF ChilDocument12 pagesBNF ChilHeraNo ratings yet
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (Nsaids)Document46 pagesNonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (Nsaids)b3djo_76No ratings yet
- Betnesol InjectionDocument7 pagesBetnesol Injectionhiral mistryNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics in Pediatrics (Vancomycin, Quinolones, Aminoglycosides, Tetracyclines, Chloramphenicol, Clindamycin, Macrolides)Document90 pagesAntibiotics in Pediatrics (Vancomycin, Quinolones, Aminoglycosides, Tetracyclines, Chloramphenicol, Clindamycin, Macrolides)Jill PNo ratings yet
- Katzung LaxativesDocument6 pagesKatzung LaxativesLonnieAllenVirtudesNo ratings yet
- Anti Parasites Blok 3.2Document46 pagesAnti Parasites Blok 3.2Alda Herlen Kalkarina BangunNo ratings yet
- Antihelminths: DR Japhet Mangoyi Department of Clinical PharmacologyDocument15 pagesAntihelminths: DR Japhet Mangoyi Department of Clinical PharmacologyMitchelle SaurambaNo ratings yet
- Far MakoDocument15 pagesFar MakoFajar AnshoriNo ratings yet
- MucosolDocument2 pagesMucosolatiq999No ratings yet
- IT 32 - Obat-Obat Lepra - TEODocument20 pagesIT 32 - Obat-Obat Lepra - TEOHafim RasydinNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Obat Lepra Dan TBC Kutis: Dharma Permana, PHD, AptDocument33 pagesPharmacology Obat Lepra Dan TBC Kutis: Dharma Permana, PHD, AptanggiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 1Document32 pagesPharmacology 1jekeri bekeriNo ratings yet
- Amikacin SulfateDocument4 pagesAmikacin SulfateCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Gentamicin Sulfate and SalbutamolDocument7 pagesDrug Study Gentamicin Sulfate and SalbutamolEduardNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological SheetDocument21 pagesPharmacological SheetScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Adult Dosing & UsesDocument7 pagesAdult Dosing & UsesRegina Marhadi SoniNo ratings yet
- Learning Issue TrikuriasisDocument3 pagesLearning Issue TrikuriasisNyoman Arya Adi WangsaNo ratings yet
- Package Insert Template - AmbroxolDocument7 pagesPackage Insert Template - AmbroxolSuciOtsuNo ratings yet
- Cough 2020Document51 pagesCough 2020Noor SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used To Treat Digestive Problems: Classification: AntidiarrhealsDocument68 pagesDrugs Used To Treat Digestive Problems: Classification: AntidiarrhealsTom-tom LunaNo ratings yet
- Farmakokinetik & Farmakodinamik Ujian: Pemimbing Andri Tilaqza, S.Farm, M.Farm, AptvDocument35 pagesFarmakokinetik & Farmakodinamik Ujian: Pemimbing Andri Tilaqza, S.Farm, M.Farm, AptvMakmunNawilNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants 266: JSS College of Pharmacy, MysuruDocument68 pagesAntidepressants 266: JSS College of Pharmacy, MysurucrissNo ratings yet
- Day 17 AntihelminticsDocument28 pagesDay 17 AntihelminticskirundacalvinNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - Pharmacology: Agonist vs. AntagonistDocument4 pagesStudy Guide - Pharmacology: Agonist vs. Antagonistb2ktookie9455No ratings yet
- GentDocument2 pagesGentOxford666No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutic Phase: Drug Becomes A Solution So It Can Cross TheDocument8 pagesPharmaceutic Phase: Drug Becomes A Solution So It Can Cross TheSarah Jane NavascaNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyjennachristy03100% (3)
- Prodoxime 200 1. Composition: - 2. Indications:: Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument8 pagesProdoxime 200 1. Composition: - 2. Indications:: Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionNilisha PradhanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- Gentamycin: Classification of Antihypertensive DrugsDocument3 pagesGentamycin: Classification of Antihypertensive DrugsMargo Milad Fahim SaadNo ratings yet
- Chloramphenicol: Jagir R. Patel Asst Professor Dept.: PharmacologyDocument17 pagesChloramphenicol: Jagir R. Patel Asst Professor Dept.: PharmacologyJagirNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs Powerpoint (M)Document70 pagesAntifungal Drugs Powerpoint (M)nk999999No ratings yet
- Treatment of LeprosyDocument41 pagesTreatment of LeprosyRusty RyanNo ratings yet
- Medical DrugsDocument11 pagesMedical DrugshassanyarbareachNo ratings yet
- Organophosphate Poisoning 2Document12 pagesOrganophosphate Poisoning 2Diana MurguiaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics-1 Assignment: SelinexorDocument20 pagesPharmacotherapeutics-1 Assignment: SelinexorRobert Selvin MNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesDocument52 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesWidia Isa Aprillia SujanaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology of The Antihelminthic Drugs: Katzung, Bertram G. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. New York: LangeDocument16 pagesClinical Pharmacology of The Antihelminthic Drugs: Katzung, Bertram G. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. New York: LangeGrant Wynn ArnucoNo ratings yet
- Anti Leprosy DrugsDocument18 pagesAnti Leprosy DrugsRupali RautNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antiparasit DrugsDocument40 pagesPharmacology of Antiparasit Drugsakun scribNo ratings yet
- GUT Decontamination: Clinical Toxicology 4 Pharm DDocument39 pagesGUT Decontamination: Clinical Toxicology 4 Pharm DFeroze FathimaNo ratings yet
- First Generation: A. AntihistamineDocument32 pagesFirst Generation: A. AntihistamineAyumi StarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Presentation 1Document30 pagesPresentation 1Abas AhmedNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesAmoxicillinjedisay1No ratings yet
- Gut DecontaminationDocument17 pagesGut DecontaminationAkshay SatputeNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Document84 pagesFarmakologi Obat Kusta Dan Antiparasit 2015Alex FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)From EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliNo ratings yet
- Narrative On PSS SampleDocument2 pagesNarrative On PSS SampleCHERRIE R. DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Prelim Long Test StudentDocument10 pagesPrelim Long Test Studentmiracle kildoyleNo ratings yet
- Study in Europe-AdviceDocument12 pagesStudy in Europe-AdvicephillipobisesanNo ratings yet
- Oral Development PathologyDocument6 pagesOral Development PathologyKathyWNo ratings yet
- Concept Analysis Diagram - Leadership and Management: Nursing PracticeDocument2 pagesConcept Analysis Diagram - Leadership and Management: Nursing PracticeShroud GamingNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Maritime UniversityDocument26 pagesVietnam Maritime UniversityGinibo AghoghoNo ratings yet
- Urine-Sediment-Guide IDEXX PDFDocument2 pagesUrine-Sediment-Guide IDEXX PDFDani Marins0% (1)
- Final Research PaperDocument12 pagesFinal Research Paperapi-559013148No ratings yet
- Horse AnatomyDocument2 pagesHorse AnatomyJeremy AngeloNo ratings yet
- Urinary EliminationDocument7 pagesUrinary EliminationMarcus, RN100% (14)
- Business PPT Template High EndDocument32 pagesBusiness PPT Template High EndMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- PAL-letter 22janDocument2 pagesPAL-letter 22janyani_hamhampandaNo ratings yet
- Intensive & Critical Care NursingDocument7 pagesIntensive & Critical Care NursingFernando PintoNo ratings yet
- Professional Development PresentationDocument11 pagesProfessional Development Presentationapi-642424041No ratings yet
- Introduction To Burns: Bacteria VirusesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Burns: Bacteria Virusesanon-50728No ratings yet
- Reiteration On The Schedule For The Conduct of Cy 2021 Quarterly Nationwide Simultaneous Earthquake DrillDocument4 pagesReiteration On The Schedule For The Conduct of Cy 2021 Quarterly Nationwide Simultaneous Earthquake DrillElrick SanicoNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2 HRM 0292Document10 pagesMidterm 2 HRM 0292Novel LampitocNo ratings yet
- Docu Intro. Table Ppprobgroup1Document50 pagesDocu Intro. Table Ppprobgroup1Abegail PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Registration CertificateDocument1 pageRegistration Certificatepriya mishraNo ratings yet
- Clery Annual ReportDocument97 pagesClery Annual ReportPeopleNewspapersDallasNo ratings yet
- 2567-Article Text-15164-1-10-20230808Document14 pages2567-Article Text-15164-1-10-20230808reyhanfabian268No ratings yet
- Communication and Sexual Self Help: Erotica, Kink and The: Fifty Shades of Grey PhenomenonDocument23 pagesCommunication and Sexual Self Help: Erotica, Kink and The: Fifty Shades of Grey PhenomenoncherNo ratings yet
- Theories On AgingDocument5 pagesTheories On AgingZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Social 5-8 NotesDocument3,276 pagesSocial 5-8 NotesGershom Phiri100% (1)
- Sanitas International StudentsDocument3 pagesSanitas International StudentsIshita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Adult and Elder I. Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesAdult and Elder I. Nursing Care PlanteresapazNo ratings yet
- S.N. Sec/ SST/ DIG Name of The HospitalDocument21 pagesS.N. Sec/ SST/ DIG Name of The Hospitalmahwish khanNo ratings yet
- AZM-HSE-PSM-012 Project Safety Management PlanDocument75 pagesAZM-HSE-PSM-012 Project Safety Management PlansaftyantiayumNo ratings yet