Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BOT 404 Lecture Slide 1
BOT 404 Lecture Slide 1
Uploaded by
Evans Timothy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views8 pagesThis document discusses soil formation processes and factors. It explains that soil is formed from parent materials like rocks through weathering and takes millions of years to form. The key factors that influence soil formation are climate, topography, living organisms, parent material, and time, as represented in Jenny's state factor equation. The document also outlines the main components of soil and different processes involved in soil formation like additions, losses, transformations, and translocations.
Original Description:
Soil plant interaction
Original Title
BOT 404 Lecture slide 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses soil formation processes and factors. It explains that soil is formed from parent materials like rocks through weathering and takes millions of years to form. The key factors that influence soil formation are climate, topography, living organisms, parent material, and time, as represented in Jenny's state factor equation. The document also outlines the main components of soil and different processes involved in soil formation like additions, losses, transformations, and translocations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views8 pagesBOT 404 Lecture Slide 1
BOT 404 Lecture Slide 1
Uploaded by
Evans TimothyThis document discusses soil formation processes and factors. It explains that soil is formed from parent materials like rocks through weathering and takes millions of years to form. The key factors that influence soil formation are climate, topography, living organisms, parent material, and time, as represented in Jenny's state factor equation. The document also outlines the main components of soil and different processes involved in soil formation like additions, losses, transformations, and translocations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
BOT 404: Soil Plant Interaction
• Scope of the course
• Processes and Factors of Soil formation
• Weathering: Definition and its classification
• Soil profile and components of soil
BOT 404: Soil Plant Interaction
Processes and Factors of Soil formation
• Objectives:
• By the end of this class, the students should
be able to:
• Define soil
• Mention the processes of soil formation
• Explain the factors of soil formation
• Identify the Jenny’s state factor equation for
soil formation:
Processes and Factors of Soil formation
• Introduction
• Soils are the products of weathering from some parent rocks. All soils
initially come from some pre-existing rocks. They are called as ‘parent
materials’. The Parent Material may be directly below the soil, or at
great distances away from it. It is necessary to understand the factors
and processes that are responsible for the formation of soils.
• Soil formation is a long term process. It takes several million years to
form a thin layer of soil. As soil is a complex mixture of various
components, its formation is also more complex. The formation of a
particular type of soil depends upon the physico-chemical properties
of the parent rock, intensity and duration of weathering, climatic and
other parameters.
Four Types of Soil Forming Processes
• A. Additions: Materials added to the soil, such as decomposing
vegetation and organisms (organic matter--OM), or new mineral
materials deposited by wind or water.
• B. Losses: Through the movement of wind or water, or uptake by plants,
soil particles (sand, silt, clay, and OM) or chemical compounds can be
eroded, leached, or harvested from the soil, altering the chemical and
physical makeup of the soil.
• C. Translocations: The chemical weathering of sand and formation of
clay minerals, transformation of coarse OM into decay resistant organic
compounds (humus).
• D. Transformations: Movement of soil constituents (organic or mineral)
within the profile and/or between horizons. Over time, this process is
one of the more visibly noticeable as alterations in color, texture, and
structure become apparent.
Factors of Soil forming
• Soils are dynamic, forming continuously over a long
period of time. Soil types differ, depending on the parent
materials from which they came and from the
surrounding environment. The way in which soil forms
depends on:
• Parent material
• Climate
• Topography
• Biota (Living organisms)
• Time
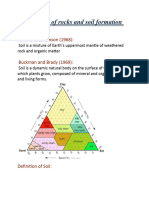
Soil is a natural medium made up of five
major components:
• Mineral particles: clay, silt, sand and gravel
• Organic matter: decaying plant and animal
material
• Water
• Air
• Living organisms (soil biota): ranging from
bacteria, fungi and earthworms A healthy soil
should have a balance of these components.
The Jenny’s equation
• Soil scientist, Hans Jenny has suggested that type of soil
found on any site is dependent upon the interaction of
five factors.
• Jenny’s state factor equation for soil genesis:
• S = f (C, O, R, P, T, . . .)
• C = Climate
• O = Organisms
• R = Relief (topography)
• P = Parent Material
• T = Time
State Factor Analysis
• Folger’s concept of sediment genesis
• Se = f (G, H, B) (G, H, B) „
• Se = sediment characteristics „
• G = source geology
• H = hydrology (flow regime)
• B = bathymetry
You might also like
- Fundamental of Soil Science For Agriculture Purpose Part 2-CHRISTIAN PDFDocument243 pagesFundamental of Soil Science For Agriculture Purpose Part 2-CHRISTIAN PDFuwiringiyimana etienne100% (1)
- Lec 3 4LDnotesDocument8 pagesLec 3 4LDnotesAsish BarailiNo ratings yet
- Ex5 Soil CharacterizationDocument27 pagesEx5 Soil CharacterizationPrincess RomoNo ratings yet
- Soil Survey For WatershedDocument40 pagesSoil Survey For Watersheddenaso desoNo ratings yet
- Soil Survey For WatershedDocument40 pagesSoil Survey For Watersheddenaso desoNo ratings yet
- Study Note Soil Science Lecture 2Document11 pagesStudy Note Soil Science Lecture 2MOHAMMAD IRFAN LAJINo ratings yet
- Geology Chapter 7Document24 pagesGeology Chapter 7Fatin SyakirahNo ratings yet
- Soil Science 1Document98 pagesSoil Science 1aise kaise100% (2)
- SoilDocument13 pagesSoilMadona Mathew IypeNo ratings yet
- Geo 101-Soils - SM - 2018Document45 pagesGeo 101-Soils - SM - 2018amosadjartey42No ratings yet
- Soils, An Introduction: EAS 21700 System Analysis of The Earth Angelo Lampousis, PH.DDocument33 pagesSoils, An Introduction: EAS 21700 System Analysis of The Earth Angelo Lampousis, PH.Dlam lamNo ratings yet
- L6 - Soil Forming FactorDocument8 pagesL6 - Soil Forming FactorShuvankarNo ratings yet
- Hag Soil Science NotesDocument42 pagesHag Soil Science NotesAshley Tanya GilbertNo ratings yet
- Geotechnic 4Document69 pagesGeotechnic 4Naimah Nursha Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 18 Geography of SoilsDocument7 pagesChapter - 18 Geography of Soilspintogeorge88No ratings yet
- Processes and Factors of Soil FormingDocument35 pagesProcesses and Factors of Soil FormingPeter MukunzaNo ratings yet
- How Does Soil Form?: GLOBE NY Metro, 2008Document8 pagesHow Does Soil Form?: GLOBE NY Metro, 2008Mabellee CabreraNo ratings yet
- Factors of Soil FormationDocument5 pagesFactors of Soil Formationpartha das100% (1)
- 1.1-Introduction To Soil and SoilFromRockDocument56 pages1.1-Introduction To Soil and SoilFromRockrieNo ratings yet
- EXTERNAL EARTH PROCESSES NOTES - Part 1Document23 pagesEXTERNAL EARTH PROCESSES NOTES - Part 1Kisaakye GraceNo ratings yet
- Week 04Document73 pagesWeek 04Mohamed EzzNo ratings yet
- EAT 131-Soil Chemistry Part 1Document73 pagesEAT 131-Soil Chemistry Part 1Man Yung HoNo ratings yet
- Soil ScienceDocument71 pagesSoil ScienceJoysatur Operario100% (2)
- Soil Genesis, Composition & Dev. - RJ GavilenoDocument37 pagesSoil Genesis, Composition & Dev. - RJ GavilenorjbgavilenoNo ratings yet
- Soil As An Important ElementDocument16 pagesSoil As An Important ElementGaurika GroverNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Soil FormationDocument16 pagesFactors Affecting Soil FormationAlma NazarioNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Soil Science: NRMH 1.1 (2 + 1) First Semester B.Sc. (Hons.) HorticultureDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Soil Science: NRMH 1.1 (2 + 1) First Semester B.Sc. (Hons.) HorticultureMakarim KhusnulNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics by Mark ManassahDocument15 pagesSoil Mechanics by Mark ManassahMark ManassahNo ratings yet
- 2 18kp1go1 2020120403085432Document156 pages2 18kp1go1 2020120403085432am869577No ratings yet
- Jump To: ,: Navigation SearchDocument16 pagesJump To: ,: Navigation SearchRashi AnandNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical EnggDocument259 pagesGeotechnical EnggNoah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Soil Forming ProcessesDocument11 pagesSoil Forming ProcessesArbab Sharif Arbab0% (1)
- Module 8 Soil ChemistryDocument12 pagesModule 8 Soil ChemistryMido IzukuNo ratings yet
- Weathering of Rocks and Soil FormationDocument6 pagesWeathering of Rocks and Soil Formationshrishaktawat9No ratings yet
- Soil and Its FormationDocument11 pagesSoil and Its FormationrppoudyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Week-1Document41 pagesChapter-1 Week-1TamraNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Soil and LandDocument27 pagesWeek 9 Soil and LandVincent CheungNo ratings yet
- KIMIA LINGKUNGAN MHDocument114 pagesKIMIA LINGKUNGAN MHDzaki Al furqonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ExerciseDocument15 pagesLaboratory Exercisecarlafaith06No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Soils, Soil Formation and TerminologyDocument29 pagesAn Introduction To Soils, Soil Formation and Terminologypieterjpeeters9924No ratings yet
- Prentice Hall: Earth ScienceDocument40 pagesPrentice Hall: Earth ScienceJulius Memeg PanayoNo ratings yet
- Why Investigate Soils?: Scientists Need GLOBE DataDocument15 pagesWhy Investigate Soils?: Scientists Need GLOBE DataPrasanth ManupatiNo ratings yet
- APES 2e TRM CH 08 PPT Presentation 8Document50 pagesAPES 2e TRM CH 08 PPT Presentation 8Arashi MurataNo ratings yet
- Theme 11 Soil Classification - UpdatedDocument65 pagesTheme 11 Soil Classification - UpdatedogntshabeleNo ratings yet
- Pelapukan Tanah DDITDocument60 pagesPelapukan Tanah DDITloraaviaaNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics: - The Geologist Defines Soil As An Altered Rock. The Geotechnical Engineer DefinesDocument14 pagesSoil Mechanics: - The Geologist Defines Soil As An Altered Rock. The Geotechnical Engineer DefinesMiguel A. NewmanNo ratings yet
- BKP L 1 Introductiontosoilscience 141214011854 Conversion Gate01Document23 pagesBKP L 1 Introductiontosoilscience 141214011854 Conversion Gate01qadriranaNo ratings yet
- Soil Chemistry EngineeringDocument59 pagesSoil Chemistry EngineeringNickNo ratings yet
- Soil Systems Outline: WeatheringDocument25 pagesSoil Systems Outline: Weatheringelfira rosantiNo ratings yet
- Soil Science-1Document53 pagesSoil Science-1Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 - 2 Ajam Jun 2011Document42 pagesBab 1 - 2 Ajam Jun 2011Ctnurtasnim Mat ZukiNo ratings yet
- What Is Soil? (4-6) : 1 Introduction To Soil Science 1Document17 pagesWhat Is Soil? (4-6) : 1 Introduction To Soil Science 1Ptb4docNo ratings yet
- Definition of Soil The Composition of The SoilDocument39 pagesDefinition of Soil The Composition of The SoilZainab QuddoosNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Chemistry of Soils & RocksDocument64 pagesGroup 1 Chemistry of Soils & Rocksimani12No ratings yet
- 3-Site Analysis - Natural Factors Part 1Document54 pages3-Site Analysis - Natural Factors Part 1Catherine Joy TagsipNo ratings yet
- EHN-Lecture 02 (16&20sept13)Document28 pagesEHN-Lecture 02 (16&20sept13)ia.fap.agri.tbkNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document4 pagesLab 2Matthew BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Soil Chemistry: Analysis and InstrumentationFrom EverandIntroduction to Soil Chemistry: Analysis and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- Soil Microbiology: Sana'a University Faculty of Science Biology DepartmentDocument38 pagesSoil Microbiology: Sana'a University Faculty of Science Biology DepartmentNesma NsrNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement - Prefabricated Vertical Drain (PVD)Document1 pageGround Improvement - Prefabricated Vertical Drain (PVD)Ahmad Nor AriffNo ratings yet
- Measuring EarthworkDocument25 pagesMeasuring EarthworkSHAHAN NAFEESNo ratings yet
- RI ConeDocument6 pagesRI Coneabhay2357No ratings yet
- Effects of Soil Properties and Slope Angle On DefoDocument10 pagesEffects of Soil Properties and Slope Angle On DefoHaya ZuaiterNo ratings yet
- Management of Saline and Sodic SoilsDocument4 pagesManagement of Saline and Sodic SoilsFlor De Jazmín CGNo ratings yet
- CBR Test.Document9 pagesCBR Test.Dilanka S GunasinghaNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Holiday Home WorkDocument4 pagesClass 10th Holiday Home WorkRithwik NambiarNo ratings yet
- Tatek WorkuDocument92 pagesTatek Workuesttif02No ratings yet
- Directory of PHD and M.SC - ThesesDocument76 pagesDirectory of PHD and M.SC - ThesesMustafa Khandgawi100% (2)
- Agriculture, Ecosystems and EnvironmentDocument13 pagesAgriculture, Ecosystems and EnvironmentEder ChaveiroNo ratings yet
- Review Paper On "Irrigation Water Pollution and Its Minimization Measures"Document10 pagesReview Paper On "Irrigation Water Pollution and Its Minimization Measures"Abayneh WubetuNo ratings yet
- 2appendices GGDocument556 pages2appendices GGSheril ChandraboseNo ratings yet
- Wavistrong Installation ManualDocument63 pagesWavistrong Installation ManualRenganathan Prabunath0% (1)
- LEA SA PP RevisedDocument178 pagesLEA SA PP RevisedRhene BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Academic Year 2017 - Part Time Programme Advanced Diploma Level Stage IIDocument6 pagesAcademic Year 2017 - Part Time Programme Advanced Diploma Level Stage IIIMJ JNo ratings yet
- LabEx1 - Scientific MethodDocument8 pagesLabEx1 - Scientific MethodLEAH VENICE CANSONNo ratings yet
- Way To MBBSDocument32 pagesWay To MBBSSagarNo ratings yet
- (David L. Hawksworth, Alan T. Bull) Forest DiversiDocument538 pages(David L. Hawksworth, Alan T. Bull) Forest DiversiAnindyaMustikaNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument69 pagesGeographyRahulNo ratings yet
- 2012 Questions: Answer ALL The Questions in This Section in The Spaces ProvidedDocument5 pages2012 Questions: Answer ALL The Questions in This Section in The Spaces Providedlixus mwangiNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument14 pages1 PBwww050No ratings yet
- NURSERY MANAGEMENT Handbook For Beginner PDFDocument92 pagesNURSERY MANAGEMENT Handbook For Beginner PDFAdrian FilipNo ratings yet
- Is.6313.3.2001 - ANTI TERMITEDocument14 pagesIs.6313.3.2001 - ANTI TERMITEsunitkghosh50% (2)
- NACHURS Start2Finish Growmark FS 4-13-20Document40 pagesNACHURS Start2Finish Growmark FS 4-13-20Nick SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Zelbrite: Advanced Filtration MediaDocument2 pagesZelbrite: Advanced Filtration MediaMohammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- قائمة بأسماء خريجين الدكتوراة من عام 1964-2005مDocument346 pagesقائمة بأسماء خريجين الدكتوراة من عام 1964-2005مSaaNo ratings yet
- AQIS Inspection ProtocolDocument49 pagesAQIS Inspection Protocolpilot760% (1)
- PK Gupta 2Document5 pagesPK Gupta 2mspark futuristicNo ratings yet
- Agrometeorology and Wheat ProductionDocument12 pagesAgrometeorology and Wheat ProductionRoci AVNo ratings yet