Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infections of The Liver Revised - Nick Griffin
Infections of The Liver Revised - Nick Griffin
Uploaded by
Microposter0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views1 pageKlebsiella pneumoniae is a bacterium that can cause liver abscesses. Symptoms include fever, jaundice, nausea and dark urine. Treatment involves antibiotics and sometimes draining the abscess surgically. K. pneumoniae is becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics, making treatment more complex. Proper diagnosis and use of the appropriate antibiotic based on the infectious agent is crucial for successfully fighting the infection.
Original Description:
Original Title
Infections of the Liver Revised - Nick Griffin
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentKlebsiella pneumoniae is a bacterium that can cause liver abscesses. Symptoms include fever, jaundice, nausea and dark urine. Treatment involves antibiotics and sometimes draining the abscess surgically. K. pneumoniae is becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics, making treatment more complex. Proper diagnosis and use of the appropriate antibiotic based on the infectious agent is crucial for successfully fighting the infection.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views1 pageInfections of The Liver Revised - Nick Griffin
Infections of The Liver Revised - Nick Griffin
Uploaded by
MicroposterKlebsiella pneumoniae is a bacterium that can cause liver abscesses. Symptoms include fever, jaundice, nausea and dark urine. Treatment involves antibiotics and sometimes draining the abscess surgically. K. pneumoniae is becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics, making treatment more complex. Proper diagnosis and use of the appropriate antibiotic based on the infectious agent is crucial for successfully fighting the infection.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
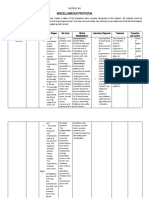
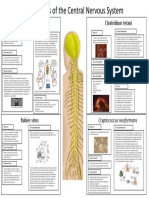
Many different types of bacteria can cause a liver
abscess, including Klebsiella pneumoniea. While E. coli
and other bacteria are also frequently identified as a
cause of pyogenic liver abscesses, Klebsiella pnuemoniea Hepatitis B, also known as serum hepatitis, is an incredibly common infection. Hepatitis B also infects
has been increasingly identified as a cause of liver other mammals and birds. Hepatitis is also very tough virus—it is heat resistant, pH resistant and stable
abscesses. However, diagnosis of a liver abscess is only
the first part, as administration of appropriate antibiotics in organic solvents. There are three forms of Hepatitis B infection: chronic, acute and perinatal. Chronic
according to the infectious agent remains the crucial in
http://medicalopaedia.com/medical-news/ndm-1-gene-bacteria-says-humans-its-a-war/ infections are the most common, accounting for an estimated 800,000-1.4 million people in the US and
fighting infection. Many different infectious bacteria may
cause pyogenic liver abscesses and many of these an astounding 350 million cases worldwide. Acute hepatitis causes jaundice, vomiting and
bacteria have developed anti-biotic resistance including inflammation. Chronic carriers of hepatitis B may develop serious complications including cirrhosis or
bacteroides, enterococcus, streptococcus and
staphylococcus making antibiotic selection more complex
liver cancer. However, infection is preventable by vaccination. It is a very nasty virus that is also very
for physicians. prevalent and preventable.
A liver abscesses are pus filled masses inside or attached to the liver. The word pyogenic refers to a Hepatitis B is a protein coated, incompletely double stranded DNA virus. This is known as the Hepatitis
bacterial infection that creates pus. Individuals with Klebsiella pneumoniae infections experience
fever, chills, jaundice, nausea or vomiting, dark urine and other symptoms. Treatment includes
B virus (HBV). HBV replication is interesting as it occurs through a RNA proviral intermediate. Via
antibiotics, and surgery with a needle or tube to drain the abscess. reverse transcriptase, HBV integrates its RNA genome and DNA intermediate into the host cell’s
Klebsiella pnuemoniae is also a diverse chromosomes helping the establishment of chronic infection.
bacterium that can cause infections including
urinary tract infections, nosocomial HBV interferes with liver function by
pneumonia, and intra-abdominal infections. K. replicating in the cytosol of
pnuemononiae is a facultative anaerobe, gram
negative, lactose fermenting, rod shaped,
hepatocytes. The innate immune
non-motile, and encapsulated. K. system plays little role in clearing HBV
pnuemononiae is found in the normal flora of while virus-specific cytoxic T
humans (intestines, skin), but can be
lymphocytes contribute most of the
pathogenic. Certain antibiotic resistant strains
of K. pnuemoniae that can be particularly liver damage associated with HBV
difficult to handle in a clinical setting. infection. CTLs kill the infected
hepatocytes, causing tissue damage
while also clearing the virus.
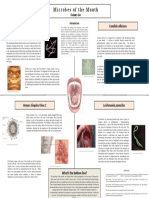
Candida albicans is a diploid fungus that is an opportunistic
Also known as the Liver Fluke, Fasciola hepatica is a parasitic
flatworm commonly found in rural areas that eats your liver and pathogen. Candida can infect many different areas of the
blood. This parasite is viscous. Infection, also known as
fascioliasis, typically occurs through ingestion of raw watercress
body, including the skin, nails, vagina and liver. Candida
or other water plants infected with larvae. An average liver fluke is
30mm long (a little over an inch) and 13mm wide. Prevalence of
albicans, the most common of the Candida strains, can
infection is highest in areas that raise cattle and sheep. An
estimated 2.4 million people are infected around the world. Frank
cause many different diseases including thrush, an infection
disease may take only a few days to manifest or as long as a few
years after ingestion of the parasite. Immature flukes migrate
of mouth tissue, and yeast infections of the vagina.
through the intestinal wall, the abdominal cavity and the liver Nosocomial candidiasis is the main fungal infection in liver
tissue into the bile duct. In the bile duct the parasite matures and
may produce eggs. The parasite sustains itself on blood of it’s transplant recipients. Surgical and medical nosocomial
host. The full life cycle of Fasciola hepatica can be seen in the
graphic to the left. candida infections are a growing problem in hospitals.
Candida grows as true hyphae in the human body creating
filamentous structures that can disrupt liver function.
Candida albicans is a dimorphic fungus. It has two forms: ovoid (unicellular
Liver fluke infections is diagnosed by the presence of yellow-brown eggs in feces. Fascioliasis is both
preventable and treatable. There are two phases of disease: acute and chronic. Acute symtoms and round) and hyphae (invasive and multicellular). Grown at STP, Candida
include fever, tenderness of the liver and abdominal pain. Chronic symptoms include bilary cholic,
liver tenderness, abdominal pain and jaundice. The liver will be inflamed and bile ducts may be
favors the ovoid form while in environments that mimic human tissue, it
obstructed. Management of Fasciola hepatica infection includes administration of parasite fighting prefers to form hyphae. The genome of the fungus is modified by
drugs (Triclabendazole or bithionol are commonly used), or surgical removal of the parasite.
environmental conditions to express the two different morphologies. The
Sources two forms are expressed due to two different genomes that have external
"CDC - Fasciola." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Web. 24 May 2011. <http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/fasciola/index.html>.
pressures
Han, Steven. "Review of Hepatic Abscess From Klebsiella Pneumoniae An Association With Diabetes Mellitus and Septic Endophthalmitis." Departmentthat
of regulate gene expression. You can think of it as hiding in the
Medicine, Santa Clara Valley Medical Center. <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1022703/pdf/westjmed00055-0026.pdf>.
"Fasciola Hepatica." Health Information and Advice | Medicines Guide | Patient.co.uk. Doctor | Patient UK. Web. 26 May 2011. as a normal part of the flora like its just hanging out until it has the
<http://www.patient.co.uk/doctor/Fasciola-Hepatica.htm>.
resources and conditions it like to grow and multiply, and new genes get
"HBV FAQs for Health Professionals." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Web. 26 May 2011. <http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/HBV/HBVfaq.htm>.
Hildalgo, Jose. "Candidiasis." Medscape Refrence. Web. 26 May 2011. <http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/213853-overview>. turned on that make filamentous structures. The ovoid form is typically
Leher, Martin, and Robert Chase. "Leukocyte Myeloperoxidase Deficiency and Disseminated Candidiasis: the Role of Myeloperoxidase in Resistance to Candida
nonpathogenic, while the hyphae form is more often pathogenic.
Infection." Journal of Clinical Investigation. Web. <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC322375/pdf/jcinvest00214-0142.pdf>.
You might also like
- NRNP 6635 Final ExamDocument17 pagesNRNP 6635 Final Examerick kanyiNo ratings yet
- AGA DDSEP 10 Chapter 11 1653072830031Document26 pagesAGA DDSEP 10 Chapter 11 1653072830031Sara VelezNo ratings yet
- Manual of Standards and Guidelines On The Management of The Hospital Emergency Department 2nd Ed 2022Document169 pagesManual of Standards and Guidelines On The Management of The Hospital Emergency Department 2nd Ed 2022shane natividad100% (1)
- Edexcel As Biology Revision Guide PDF FreeDocument108 pagesEdexcel As Biology Revision Guide PDF Freebody fayez100% (1)
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureapi-282047984No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology DengueDocument1 pagePathophysiology DengueKevin67% (3)
- Pathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowDocument1 pagePathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowMicroposterNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Hepa Mid. CHN SDocument6 pages9.2 Hepa Mid. CHN SEllaine FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Challenge of Urinary Tract Infections in Renal Transplant RecipientsDocument14 pagesThe Challenge of Urinary Tract Infections in Renal Transplant RecipientsdevinaNo ratings yet
- Immune Response in Hepatitis B Virus InfectionDocument18 pagesImmune Response in Hepatitis B Virus InfectionaaryaachokshiNo ratings yet
- Immunology: MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesImmunology: MicrobiologyRemus MarasiganNo ratings yet
- (SURG) GU Infections - Part 2Document4 pages(SURG) GU Infections - Part 2vmdcabanillaNo ratings yet
- Project Report FinalDocument22 pagesProject Report FinalVinu NishiNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Microorganisms That Drive DiseaseDocument4 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease: Microorganisms That Drive DiseaseIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Guoying Wang, Guo ZhaoDocument17 pagesGuoying Wang, Guo ZhaoHQ HQNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan HepatitisDocument12 pagesLesson Plan HepatitisRubina MasihNo ratings yet
- Liver PathogensDocument1 pageLiver PathogensMicroposterNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument18 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptAnonymous 7dsX2F8nNo ratings yet
- INCOMPLETE Miscellaneous - ProtozoaDocument11 pagesINCOMPLETE Miscellaneous - ProtozoaNOR-FATIMAH BARATNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B VirusDocument31 pagesHepatitis B VirusFriyoga SyahrilNo ratings yet
- MicrobioDocument34 pagesMicrobiodead yrroehNo ratings yet
- Quizlet BacteDocument18 pagesQuizlet BacteMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- The EntericsDocument8 pagesThe EntericsDexcel concepcionNo ratings yet
- Uti-0005-2012Document17 pagesUti-0005-2012Rakhmatul Binti SulistyaNo ratings yet
- Diseased Cause by BacteriaDocument2 pagesDiseased Cause by BacteriaGraciaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B: Raymond D'Souza Graham R FosterDocument4 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B: Raymond D'Souza Graham R FosterrayNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke-3 GASTRODocument36 pagesPertemuan Ke-3 GASTROwidya melianitaNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms: Microfluidic-Based Approaches For Foodborne Pathogen DetectionDocument19 pagesMicroorganisms: Microfluidic-Based Approaches For Foodborne Pathogen DetectionbismillahNo ratings yet
- 4 Infección Neonatal C. DifficileDocument5 pages4 Infección Neonatal C. DifficileLuis Astudillo MedinaNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument17 pagesNIH Public Access: Author Manuscriptcalixto hernandezNo ratings yet
- Herpes and Cytomegalovirus Esophagitis: Endoscopy June 2012Document3 pagesHerpes and Cytomegalovirus Esophagitis: Endoscopy June 2012Shahid HussainNo ratings yet
- Bacteri Pathology&pathogenesisDocument22 pagesBacteri Pathology&pathogenesisAsem AlhazmiNo ratings yet
- Daren G. Linatoc, RN, RM, LPT, Man, MaedDocument36 pagesDaren G. Linatoc, RN, RM, LPT, Man, MaedMike Faustino SolangonNo ratings yet
- Colonization, Infection, and The Accessory Genome of KlebsiellaDocument15 pagesColonization, Infection, and The Accessory Genome of KlebsiellaStephanie ZengNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract Infections: Practical Interpretations of Commonly Used TermsDocument6 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract Infections: Practical Interpretations of Commonly Used TermsPaullette SanjuanNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative RodsDocument8 pagesGram Negative RodsRuel Maddawin100% (1)
- Infecciones Del Hígado y Vía Biliar (Mandell 9th)Document12 pagesInfecciones Del Hígado y Vía Biliar (Mandell 9th)claudio vargasNo ratings yet
- Gut MicroDocument2 pagesGut MicroRamesh SarmaNo ratings yet
- Enterovirus Infections: Theoklis Zaoutis, MD and Joel D. Klein, MDDocument11 pagesEnterovirus Infections: Theoklis Zaoutis, MD and Joel D. Klein, MDBmNo ratings yet
- Pato HEP BDocument6 pagesPato HEP BErena HairunisaNo ratings yet
- Host-Microorganism Integration and PathogenicityDocument31 pagesHost-Microorganism Integration and PathogenicityRanda AlmasriNo ratings yet
- Hospitalized Adult Female Who Develops Diarrhea Case 16Document4 pagesHospitalized Adult Female Who Develops Diarrhea Case 16Fernamdo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ch20, GI Tract, SummaryDocument55 pagesCh20, GI Tract, Summaryn75nnp4bz6No ratings yet
- Non-Enteric Git Pathogens by PoloDocument8 pagesNon-Enteric Git Pathogens by Poloantonette.jstnnnNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Infeksi Saluran PencernaanDocument22 pagesJurnal Infeksi Saluran PencernaanDini Okta PutriNo ratings yet
- Chronic and Acute Infection of TheDocument6 pagesChronic and Acute Infection of Thecarlos.alberto.palacios.serratNo ratings yet
- Chapter 47 - Infective Syndromes of Hepatobiliary SystemDocument37 pagesChapter 47 - Infective Syndromes of Hepatobiliary SystemKevil LoriyaNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis in Children Acute Gastroenteritis in ChildrenDocument28 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis in Children Acute Gastroenteritis in ChildrenFernando AnibanNo ratings yet
- Longo 2015Document10 pagesLongo 2015Juan Jose SantivañezNo ratings yet
- longo2015Document10 pageslongo2015guillito85No ratings yet
- Activity IiDocument5 pagesActivity IiYVONNE PEARL BALIQUIDNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Introduction To Virology: Dr. Esra HassanDocument9 pagesMicrobiology Introduction To Virology: Dr. Esra HassanjasnaldNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Virus Biology: Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19111Document18 pagesHepatitis B Virus Biology: Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19111ZmajNo ratings yet
- Kinney1994 PDFDocument17 pagesKinney1994 PDFEmilio Emmanué Escobar CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EHSDocument123 pagesModule 1 EHSMUBEENANo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis To Viruses DDocument16 pagesPathogenesis To Viruses DJaydee PlataNo ratings yet
- Act 13Document13 pagesAct 13Bel Cabading AgbunagNo ratings yet
- Infections in Patients Affected by Liver Cirrhosis: An UpdateDocument8 pagesInfections in Patients Affected by Liver Cirrhosis: An UpdateandreeaNo ratings yet
- Viruses Against BacteriaDocument1 pageViruses Against Bacteriasergio.siracusaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument6 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsSemut BarbarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Medically Most Important BacteriaDocument5 pagesChapter 5 Medically Most Important BacteriaclarisseNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases'Document27 pagesInfectious Diseases'p1awh1786No ratings yet
- Biology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseFrom EverandBiology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeFrom EverandFemale Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeBob YangNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Vagina-CitationsDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-CitationsMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Liver PathogensDocument1 pageLiver PathogensMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Jesse Wackerbarth - CNS Pathogens RevisedDocument1 pageJesse Wackerbarth - CNS Pathogens RevisedMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Savannah Whitington: Your Brain On DrugsDocument1 pageSavannah Whitington: Your Brain On DrugsMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductive Site, Erika HuertaDocument1 pagePathogens of The Female Reproductive Site, Erika HuertaMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Meghan Cule-Pathogens of The CNSDocument1 pageMeghan Cule-Pathogens of The CNSMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Eye Infections by Allison BakerDocument1 pageEye Infections by Allison BakerMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Pathogens in The Lungs-Jeffrey DelgadilloDocument1 pagePathogens in The Lungs-Jeffrey DelgadilloMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Lungs - Michelle CumbaaDocument1 pagePathogens of The Lungs - Michelle CumbaaMicroposterNo ratings yet
- The Urogenital Tract-Maija SwansonDocument1 pageThe Urogenital Tract-Maija Swansonmswanson5975No ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowDocument1 pagePathogens of The Gut - Christine ProchnowMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Emily Scroggs Microorganisms Affecting The KidneyDocument1 pageEmily Scroggs Microorganisms Affecting The KidneyMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Liver PathogensDocument1 pageLiver PathogensMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Wylie, ClareDocument1 pageWylie, ClareMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Gaby Saenz - The MeningesDocument1 pageGaby Saenz - The MeningesMicroposterNo ratings yet
- CNS Pathogens-Jesse WackerbarthDocument1 pageCNS Pathogens-Jesse WackerbarthMicroposterNo ratings yet
- EarInfections FatimaKhalidDocument1 pageEarInfections FatimaKhalidMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Lung Infections - Jessica de AndaDocument1 pageLung Infections - Jessica de AndaMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinDocument1 pagePathogens of The Female Reproductive System - Leah NechamkinMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie EspinosaDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosaannie_espinosa_2No ratings yet
- Pathogen (Poster Med Micro)Document1 pagePathogen (Poster Med Micro)joejackson6No ratings yet
- BlaC Genes and The Battle Against B-Lactamse in MDA TuberculosisDocument1 pageBlaC Genes and The Battle Against B-Lactamse in MDA TuberculosisMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Courtney Chinn - Skin InfectionsDocument1 pageCourtney Chinn - Skin InfectionsMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Zach Lee - Mouth MicrobesDocument1 pageZach Lee - Mouth MicrobesMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Maladies of The Heart - Milan KantariaDocument1 pageMaladies of The Heart - Milan KantariaMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Radiology ChantingDocument37 pagesRadiology ChantingKapilNo ratings yet
- Student'S Name: Kim Christian P. Pagobo Subject: Science 120: Anatomy and Physciology Instructor: Mrs. Roma Grace DizonDocument9 pagesStudent'S Name: Kim Christian P. Pagobo Subject: Science 120: Anatomy and Physciology Instructor: Mrs. Roma Grace Dizonkim christianNo ratings yet
- Ghai Essential PediatricsDocument768 pagesGhai Essential Pediatricsdivine venturo100% (1)
- Brain SpectDocument10 pagesBrain SpectKevinNo ratings yet
- Arabic To Communicate With PatientsDocument19 pagesArabic To Communicate With PatientsDK Aquino GomezNo ratings yet
- PJIsDocument29 pagesPJIsMohammed Alfahal100% (1)
- All in Adults ProtocolsDocument60 pagesAll in Adults ProtocolsH.B.ANo ratings yet
- QCTT - PPT - ScriptDocument4 pagesQCTT - PPT - ScriptCông TânNo ratings yet
- Research A2 Diabetes PDFDocument6 pagesResearch A2 Diabetes PDFbing bongNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Iqos 2.4 PlusDocument12 pagesUser Guide: Iqos 2.4 PlusMirko StakićNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease COVID-19Document953 pagesCoronavirus Disease COVID-19Claudio GodoyNo ratings yet
- Health Sector in Ghana ReviewDocument17 pagesHealth Sector in Ghana ReviewBriant BlantonNo ratings yet
- 2 - Patient Safety CultureDocument21 pages2 - Patient Safety CultureMohammed HammedNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam Kit For The Mblex: Your Test StatisticsDocument24 pagesPractice Exam Kit For The Mblex: Your Test StatisticslevarjaoNo ratings yet
- What Would You Do? Would You Kill One Person To Save Five People?Document1 pageWhat Would You Do? Would You Kill One Person To Save Five People?Christine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- UHSAA Preparticipation FormDocument4 pagesUHSAA Preparticipation FormThe Salt Lake TribuneNo ratings yet
- Cure & Prevent Type 2 Diabetes With DietDocument36 pagesCure & Prevent Type 2 Diabetes With DietCyndee777No ratings yet
- MSDS Fluphenazine DecanoateDocument14 pagesMSDS Fluphenazine Decanoatetatih_meilani100% (1)
- A Study About The Relocation of Badjao Community in Totolan 4Document17 pagesA Study About The Relocation of Badjao Community in Totolan 4welpNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Foot Drop Management - Review of The CuDocument10 pagesConcepts in Foot Drop Management - Review of The CuIntanicNo ratings yet
- INDIN-DDocument1 pageINDIN-DIndine DagsonNo ratings yet
- Klayman Lawsuit Against ChinaDocument24 pagesKlayman Lawsuit Against ChinaLaw&Crime100% (5)
- 9D-NLS Features and Warranty (2021)Document10 pages9D-NLS Features and Warranty (2021)Danutz ChirilaNo ratings yet
- Computed Tomography Examination: Patient Information LeafletDocument2 pagesComputed Tomography Examination: Patient Information Leafletmary joyNo ratings yet
- Pe SbaDocument30 pagesPe Sbaselina fraser100% (1)
- VNSG 1409 - Exam 3Document24 pagesVNSG 1409 - Exam 3luna nguyenNo ratings yet