Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Social Construction of Gender
Social Construction of Gender
Uploaded by
Bhoomejaa SK0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views17 pagesGender refers to culturally constructed roles that are learned and performed by men and women. It is shaped through socialization processes like family, education systems, peer groups, and media, which teach and reinforce masculine and feminine behaviors. Gender socialization begins in childhood, where girls and boys are given different opportunities, toys, and verbal instructions to mold their behavior according to cultural expectations of femininity and masculinity. These gender roles and stereotypes are then perpetuated and strengthened by societal institutions.
Original Description:
Original Title
Social Construction of Gender (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGender refers to culturally constructed roles that are learned and performed by men and women. It is shaped through socialization processes like family, education systems, peer groups, and media, which teach and reinforce masculine and feminine behaviors. Gender socialization begins in childhood, where girls and boys are given different opportunities, toys, and verbal instructions to mold their behavior according to cultural expectations of femininity and masculinity. These gender roles and stereotypes are then perpetuated and strengthened by societal institutions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views17 pagesSocial Construction of Gender
Social Construction of Gender
Uploaded by
Bhoomejaa SKGender refers to culturally constructed roles that are learned and performed by men and women. It is shaped through socialization processes like family, education systems, peer groups, and media, which teach and reinforce masculine and feminine behaviors. Gender socialization begins in childhood, where girls and boys are given different opportunities, toys, and verbal instructions to mold their behavior according to cultural expectations of femininity and masculinity. These gender roles and stereotypes are then perpetuated and strengthened by societal institutions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 17
INTRODUCTION
GENDER refers to culturally constructed roles
that are played by men and women in society
Gender is used as a concept to analyse the
shaping of womens and mens behaviour.
It is conceptual tool to analyse the structural
relationships of inequality existing between
women and men.
Gender emphasizes that masculinity and
feminity are the products of social,cultural, and
psychological factors which are acquired by an
individual in the process of becoming a man or
woman.
Gender is learnt through socialization.
Gender is a device by which society controls
its members.
It opens and closes accessto power, prestige
and property.
Roles and responsibilities of men and women
that are created in our families, societies
and cultures.
DEFINITIONS
GERDE LERNER in her book ‘The creation of
patriarchy’ defines
gender is a costume, a mask, a straight
jacket in which men and women dance their
unequal dance”.
WEST ANDZIMMERMAN : gender is not
something we are born with and not
something we have, but something we do.
BUTLER: gender is something we perform.
SOCIAL CONSTRUCTION OF
GENDER
Due to the influence of role behaviour,girls
and boys come to know type of behavior
expected.
GIRLS- domestic roles/ feminine roles
BOYS- masculine roles.
Pattern of behavior continue to be accepted
norms
Important social consequence too.
Socialisation –gender roles begin
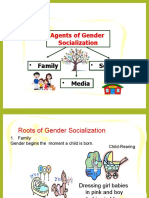
SOCIALISATION AND GENDER
ROLES
SEX ROLES ARE NOT INBORN, BUT LEARNT.
Socialization
Status is male-trained for masculine
behaviour
Status is female- trained feminine
Basic patterns are learnt from family
Strengthened – schools, peer groups, mass
media.
FAMILY AND FAMILY INFLUENCE
When the child grows , gender identity is
established through four process.
→ Moulding and Re-inforcement.
→Opportunities.
→Role modelling.
→Explicit verbal instruction.
MOULDING AND RE-
INFORCEMENT.
Boys are given more freedom, rigorous sex
role training.
Girls to be protected, mild, gentle,
pleasing.
Any girly character observed in boy is seen as
psychological disturbance.
OPPORTUNITIES
TOYS
DRESSES
MOTHERS JEWLLERY ONLY TO GIRLS
BOYS PLAY WITH FATHERS THINGS- PENS,
DAIRIES, CALCULATORS.
DAUGHTERS EXPECTED TO HELP IN KITCHEN.
ROLE MODELLING
By the age of three – children know whether
male and female.
Acceptance as categorization as boy or girl
Boys to be assertive and courageous
behaviour
Where as girls passive, submissive , mild and
gentle.
EXPLICIT VERBAL INSTRUCTION
Boys are stronger than girls
Ladies first, gents next.
Girls make the house beautiful
Boys do not cry like girls
Girls shouldn’t play rough.
Verbal instructions too have their importance
particularly when the individual has not
already begun to identify with the proper
role model.
SCHOOL
TEXT BOOKS: comment on gender roles
through characters in lesson.
Female and male characters in the lessons
provide models.
Encourage acceptance of sex roles.
Also suggests how children and adults
belonging to female and male should behave.
Example“: lenore –has found one third of
books had no female characters
Presented articles made sure boys to be
active and girls to be passive.
LEISURE READING
Typical social stories father is the bread
winner and mother confined to kitchen work.
Leisure time influences their gender role
assumptions.
Girls being depicted as carryng on household
of her mother.
Boys presented as taking part In adventurous
activities.
COURSE SEGREGATION
Academic courses and sports activities are
gender based.
Sewing, embroidery, home science for girls.
Carpentry, plumbing, garage work for boys
Sports like wrestling, football,cricket, volley
ball restricted to male sex.
MASS MEDIA
Mass media which includes films, books,
magazines, comics,television,radio, and
records are a powerful agency of socialization.
Most of the information are facts, but most of
them are exaggerated.
ADVERTISING: portray images of men and
women to impress the customers.
Ex: Sponsors portray genders in ways appealing
to the oppossite sex.
Images of women portrayed as sex objects to
market various products.
Seductively smiling female faces to reach the
male audience.
Images of women so vulgar in magazines ,
advertising, telivision.
Sexuality of women is thus exploited.
ROLE OF CULTURE
Language that we speak and the institutions
through which we work also influence
circulation of idea.
LANGUAGE: in every discussion of person,
gender is revealed,but not age, race,ethic
background, religion etc. which is contant
reminder who is male and female.
Ex: name calling provides strong social
control.
INTERACTION IN INSTITUTIONS
ON GENDER SOCIALIZATION
Women play a minor role in major social
institutions, govt,religion, economy, legal
institution, education.
Political participation is far from
satisfactory.
Leadership positions adies constitute
minority.
Propotion of female participation is
comparatively low
Ex: not a single women has assumed office as
president of America or india till date.
You might also like
- In Search of Respect: Selling Crack in El Barrio - Philippe BourgoisDocument22 pagesIn Search of Respect: Selling Crack in El Barrio - Philippe BourgoisTimothy EllisonNo ratings yet
- Gender Equality PresentationDocument13 pagesGender Equality PresentationEdward CalisingNo ratings yet
- Orientation On Gender SensitivityDocument67 pagesOrientation On Gender SensitivityCalapati, Jhon Rovic R.No ratings yet
- Gender SocializationDocument13 pagesGender Socializationreenachrn78% (9)
- Gender SocializationDocument13 pagesGender Socializationreenachrn78% (9)
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledParofil NestleNo ratings yet
- Gender SocializationDocument25 pagesGender SocializationAshley JoyceNo ratings yet
- Gender SensitivityDocument73 pagesGender Sensitivitylovelymaegallardo90No ratings yet
- Gender PresentationDocument35 pagesGender Presentation00062481No ratings yet
- Agents and Gender SocializationDocument16 pagesAgents and Gender SocializationWelanie TatelNo ratings yet
- Gendersensitivity 130417221952 Phpapp01Document27 pagesGendersensitivity 130417221952 Phpapp01Jesivel GempesawNo ratings yet
- Iii. Socialization Into Gender: Reporter: Aira Jane Villa Course Facilitator: Prof. DemaisipDocument2 pagesIii. Socialization Into Gender: Reporter: Aira Jane Villa Course Facilitator: Prof. Demaisiparia jen05No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (2-2-2020)Document6 pagesLecture 1 (2-2-2020)Zaisha RahmanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gender and SexualityDocument32 pagesModule 2 Gender and SexualityChloe MaciasNo ratings yet
- Martinez GenSocDocument6 pagesMartinez GenSocJenecile ParambitaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Social Construct With St. Scho.Document41 pagesModule 2 Social Construct With St. Scho.Janna Mae Villa-GenoveaNo ratings yet
- Week 10 UCSP Module 10 Edited by GlenDocument30 pagesWeek 10 UCSP Module 10 Edited by GlenJose Reymart BariasNo ratings yet
- Good Thesis For Gender RolesDocument4 pagesGood Thesis For Gender Rolesandreachristianreno100% (2)
- PRARE Gender RolesDocument8 pagesPRARE Gender RolesBelle HonaNo ratings yet
- MidsDocument11 pagesMidsAaleen KttkNo ratings yet
- Gender and SocietyDocument6 pagesGender and SocietybadiabhiNo ratings yet
- Socialisation of Gender RolesDocument21 pagesSocialisation of Gender RolesBrandon WeberNo ratings yet
- Basic Gad ConceptsDocument54 pagesBasic Gad ConceptsJohn Carlo Benitez MendejaNo ratings yet
- Socializing GenderDocument9 pagesSocializing GenderMohammed Hasnain MansooriNo ratings yet
- Gender and SocializationDocument18 pagesGender and SocializationmsotandoyNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gender SensitivityDocument63 pagesModule 2 Gender Sensitivitymgllacuna100% (4)
- CFLM-1 Chapter 5Document17 pagesCFLM-1 Chapter 5Rico T. MusongNo ratings yet
- Types of Gender Roles ExplanationDocument2 pagesTypes of Gender Roles ExplanationTanvirNo ratings yet
- GAD Basic PresentationDocument38 pagesGAD Basic PresentationArden LoNo ratings yet
- Gender Sensitivity Training For PNP WCPD Officers: PNP Police Regional Office III Camp Olivas July 24, 2019Document148 pagesGender Sensitivity Training For PNP WCPD Officers: PNP Police Regional Office III Camp Olivas July 24, 2019Yane Ltikas LinNo ratings yet
- 1 - Understanding The Basic Concepts of GenderDocument10 pages1 - Understanding The Basic Concepts of GenderHouse of GodNo ratings yet
- Gender Sensitivity 101Document130 pagesGender Sensitivity 101Maria Fiona Duran Merquita100% (4)
- Gender and Society-LectureDocument3 pagesGender and Society-LectureElmaNo ratings yet
- GenderDocument37 pagesGendersaudshaikh89No ratings yet
- GenSoc Notes 4Document5 pagesGenSoc Notes 4Jandel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Orientation On Basic GAD ConceptsDocument34 pagesOrientation On Basic GAD ConceptsMelymay Palaroan Remorin100% (3)
- Gender and SexualityDocument3 pagesGender and Sexualityboytheawesome883No ratings yet
- #Likeagirl Assingment1Document2 pages#Likeagirl Assingment1zozozNo ratings yet
- Gender Stereotypes - CultureDocument17 pagesGender Stereotypes - Cultureaswathy100% (2)
- Gender Convergence and Role EquityDocument24 pagesGender Convergence and Role EquityJhiean IruguinNo ratings yet
- PD GadDocument45 pagesPD GadB I N SNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Lesson 1-3Document26 pagesUNIT 2 Lesson 1-3rachelleann.convocarNo ratings yet
- 1Document5 pages1M KNo ratings yet
- Gender and FamiliesDocument24 pagesGender and FamiliesQuintowas Jr RazumanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.2 Gender SocializationDocument22 pagesChapter 3.2 Gender SocializationMA. NECOLE JEREMIAH GONZALESNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic GAD ConceptsDocument40 pages1 Basic GAD ConceptsDas GNo ratings yet
- 5 Gender SensitivityDocument19 pages5 Gender SensitivitySHEM B. PANGANIBANNo ratings yet
- Ans 2 JjjjnskjlefhDocument4 pagesAns 2 JjjjnskjlefhJayesh TanejaNo ratings yet
- BFP Orientation On Basic GAD Concepts DEC 2020Document58 pagesBFP Orientation On Basic GAD Concepts DEC 2020Rachel MiguelNo ratings yet
- P 1 FinalDocument5 pagesP 1 Finalapi-340387052No ratings yet
- Eache R Nduct ION Rogra MDocument58 pagesEache R Nduct ION Rogra MJBSUNo ratings yet
- Gender Role Attitudes: Presented by Sabahat Fida Atiya Rehman Zainab BibiDocument38 pagesGender Role Attitudes: Presented by Sabahat Fida Atiya Rehman Zainab Bibimaria100% (3)
- GE Elec 7 UNIT-2 NoDocument36 pagesGE Elec 7 UNIT-2 NoLyleNo ratings yet
- Gender SensitivityDocument32 pagesGender SensitivityLuis Masangkay100% (1)
- 6gad Basic ConceptsDocument48 pages6gad Basic ConceptsMj Ong Pierson GarboNo ratings yet
- Gender and DevelopmentDocument52 pagesGender and DevelopmentArlo SpotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 4 Gender and SocializationDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 4 Gender and SocializationTrisha SamasNo ratings yet
- Gender in EducationDocument7 pagesGender in EducationAnonymous v8AfMnT5No ratings yet
- Gender and Development (GAD) : By: Eloisa A. RiveraDocument52 pagesGender and Development (GAD) : By: Eloisa A. RiveraRomnick ArenasNo ratings yet
- GAD0007Document50 pagesGAD0007Jea Caderao AlapanNo ratings yet
- Gender Roles in Society New Topic and New ExplanationDocument6 pagesGender Roles in Society New Topic and New ExplanationTanvirNo ratings yet
- Women in Modern India FinalDocument10 pagesWomen in Modern India FinalBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Women in Ancient IndiaDocument13 pagesWomen in Ancient IndiaBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Sociology of Gender IntroductionDocument16 pagesSociology of Gender IntroductionBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Why Feminism Is Important For IndiaDocument8 pagesWhy Feminism Is Important For IndiaBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Crimes Against Women - An: Dr. Pratima Narayan Advocate & Mediator Founder Partner, Techlawlogi Consulting LLPDocument26 pagesCrimes Against Women - An: Dr. Pratima Narayan Advocate & Mediator Founder Partner, Techlawlogi Consulting LLPBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Impact of Abortion PublicationDocument15 pagesImpact of Abortion PublicationBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Traditional Bases of Sexual IdentityDocument11 pagesTraditional Bases of Sexual IdentityBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- National Policy For The Empowernment of Women-2001Document11 pagesNational Policy For The Empowernment of Women-2001Bhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Radical FeminismDocument9 pagesRadical FeminismBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Impact of AbortionDocument28 pagesImpact of AbortionBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Indecent and Obscene Behaviour: - Ayesha Khyser Harshitha S Radhika KulthiaDocument23 pagesIndecent and Obscene Behaviour: - Ayesha Khyser Harshitha S Radhika KulthiaBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Gender FinalDocument10 pagesGender FinalBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- 4 Health Enhancing BehavioursDocument11 pages4 Health Enhancing BehavioursBhoomejaa SK100% (1)
- Feminism in India: at DefiningDocument6 pagesFeminism in India: at DefiningBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Dowry SystemDocument10 pagesDowry SystemBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- 2 Psychological Issues in Advancing IllnessDocument11 pages2 Psychological Issues in Advancing IllnessBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Concept of FeminismDocument12 pagesConcept of FeminismBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Social PsychologyDocument101 pagesUnit 2 - Social PsychologyBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Abortion ProjectDocument44 pagesAbortion ProjectBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- (2013) Moore, Gino - Ethically Adrift, Moral Compass - ROBDocument25 pages(2013) Moore, Gino - Ethically Adrift, Moral Compass - ROBMoe EcchiNo ratings yet
- BA Prog Discipline Course EducationDocument17 pagesBA Prog Discipline Course EducationKunalPandeyNo ratings yet
- Sed2601 Assignment 02Document9 pagesSed2601 Assignment 02mamolokoben228No ratings yet
- Aula 8 - ZIVIC - Mapping Global Virtual Team Leadership Actions To Organizational RolesDocument9 pagesAula 8 - ZIVIC - Mapping Global Virtual Team Leadership Actions To Organizational RolescarlosadmgoNo ratings yet
- Bed Med CurriculumDocument62 pagesBed Med CurriculumSunny PK0% (2)
- Principles of Sport Management First Pages Chapter 42Document39 pagesPrinciples of Sport Management First Pages Chapter 42Meenu SofiaNo ratings yet
- Ebook The Sociology of Childhood William A Corsaro Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook The Sociology of Childhood William A Corsaro Online PDF All Chapterrick.gordo650100% (8)
- Time Management and Academic Achievement: Examining The Roles of Prioritization, Procrastination and SocializationDocument10 pagesTime Management and Academic Achievement: Examining The Roles of Prioritization, Procrastination and SocializationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Positive Cultural PracticesDocument5 pagesPositive Cultural Practicesjkkonadu550% (2)
- Social Studies Scheme of Work For Semester One1stDocument4 pagesSocial Studies Scheme of Work For Semester One1stDOMINIC ANTHONY DEKUNo ratings yet
- SocializatiionDocument26 pagesSocializatiionAnam DaymaNo ratings yet
- Test MKTDocument44 pagesTest MKTsarvar911No ratings yet
- CPJGender 0001Document4 pagesCPJGender 0001Gordon HutchisonNo ratings yet
- Cross Cutural Understanding ModuleDocument86 pagesCross Cutural Understanding Modulefajar nurwantiNo ratings yet
- Role of Parenting Practices To Construct Gender Roles Attitude Among Children A Cross Sectional StudyDocument15 pagesRole of Parenting Practices To Construct Gender Roles Attitude Among Children A Cross Sectional StudySair Abdulrehman ButtNo ratings yet
- Gender Sensitivity: Davao CityDocument46 pagesGender Sensitivity: Davao CityMedardo BombitaNo ratings yet
- Understanding CultureDocument5 pagesUnderstanding CultureShendy AcostaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Political SocializationDocument27 pagesUnderstanding Political SocializationPoojaNo ratings yet
- Educational SociologyDocument20 pagesEducational SociologyJason BautistaNo ratings yet
- SocializationDocument16 pagesSocializationtreyshey03100% (1)
- Sociology Education Dissertation IdeasDocument8 pagesSociology Education Dissertation IdeasProfessionalCollegePaperWritersFrisco100% (1)
- UCSP WEEK 2 Analyze The Concept Aspects and Changes in of Culture and SocietyDocument8 pagesUCSP WEEK 2 Analyze The Concept Aspects and Changes in of Culture and SocietyPaula DT PelitoNo ratings yet
- HSP3C Summative With RubricDocument2 pagesHSP3C Summative With RubricD'Andre Brookes - David Suzuki SS (2662)No ratings yet
- Vos Et Al-2005-International Journal of Selection and AssessmentDocument12 pagesVos Et Al-2005-International Journal of Selection and AssessmentLemon-No ratings yet
- "Child in The Street": Higher School For Social Work and Social Pedagogics "Attīstība" &Document70 pages"Child in The Street": Higher School For Social Work and Social Pedagogics "Attīstība" &Yoga Adhie PratamaNo ratings yet
- Character, Personality and Professional SM: SC T Onal 0970 1087Document21 pagesCharacter, Personality and Professional SM: SC T Onal 0970 1087Muh AliNo ratings yet
- Rites and Rituals of Iwa Akwa As The Gateway To Manhood in Igboland1Document12 pagesRites and Rituals of Iwa Akwa As The Gateway To Manhood in Igboland1amaraaugustine300No ratings yet
- Gen 002 Day 5 - Lesson 3Document5 pagesGen 002 Day 5 - Lesson 3Zschaila QuiñoNo ratings yet