Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seminar On Paper Battery: Submitted To: Submitted by
Seminar On Paper Battery: Submitted To: Submitted by
Uploaded by
Jyoti Jadon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views21 pagesA seminar was presented on paper batteries. Paper batteries combine carbon nanotubes with paper to create a flexible, ultra-thin energy storage device. They function similarly to lithium-ion batteries but incorporate all components into a lightweight paper structure. Paper batteries can be shaped as needed and have applications in electronics, medical devices, and other areas due to their flexibility and non-toxic properties. However, carbon nanotubes used in paper batteries are currently expensive to produce.
Original Description:
Paper Battery ppt
Original Title
Paper Battery
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA seminar was presented on paper batteries. Paper batteries combine carbon nanotubes with paper to create a flexible, ultra-thin energy storage device. They function similarly to lithium-ion batteries but incorporate all components into a lightweight paper structure. Paper batteries can be shaped as needed and have applications in electronics, medical devices, and other areas due to their flexibility and non-toxic properties. However, carbon nanotubes used in paper batteries are currently expensive to produce.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views21 pagesSeminar On Paper Battery: Submitted To: Submitted by
Seminar On Paper Battery: Submitted To: Submitted by
Uploaded by
Jyoti JadonA seminar was presented on paper batteries. Paper batteries combine carbon nanotubes with paper to create a flexible, ultra-thin energy storage device. They function similarly to lithium-ion batteries but incorporate all components into a lightweight paper structure. Paper batteries can be shaped as needed and have applications in electronics, medical devices, and other areas due to their flexibility and non-toxic properties. However, carbon nanotubes used in paper batteries are currently expensive to produce.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 21
Seminar
On
Paper Battery
Submitted To: Submitted By:
Dr. Ana Kumar Surendra Kumar
Himanshu
Ramveer Singh
Jyoti
Content
Introduction 1
Paper Battery
Principle 2
Applications 3
Uses 3
Construction 4
Working 5
Limitations 8
Needs(requirent) 6
Advantages 7
Disadvantages 8
Future Scope 9
Conclusion 9
Introduction
A paper battery acts as
both a high energy battery
and super capacitor,
combining two
components that are
separate in traditional
electronics.
This technology can be
greatly utilized by medical
devices.
Paper Battery
A paper battery is a flexible, ultra-thin energy storage and
production device formed by combining carbon nanotubes
with a conventional sheet of cellulose-based paper.
The nano materials are a one-dimensional structure with
very small diameters.
It can be bent and twisted, trimmed with scissors or molded
into any needed shape.
A paper battery acts as both a high-energy battery and super
capacitor. This combination allows the battery to provide
both long-term, steady power production and bursts of
energy.
It is non toxic, environment friendly and is everything that a
conventional battery is not.
Principal
The battery produces electricity in the same way as
the conventional lithium-ion batteries, but all the
components have been incorporated into a
lightweight, flexible sheet of paper.
The devices are formed by combining cellulose
with an infusion of aligned carbon nanotubes.
The electrolyte and the ions that carry the charge
can be varied depending the use of the battery.
A conventional Li-ion battery can be incorporated
in cellulose-nanotube composite as shown in the
next slide.
APPLICATIONS
Power papers can be laminated onto smart
cards and other micro devices and replace
ordinary tickets and tags.
Single use delivery and diagnostic devices
could have power paper incorporated in to
their construction to allow for sensors and
smart labels.
Used in electronic games and entertainment
devices.
APPLICATIONS
Uses
A paper battery is a battery engineered to use a
paper-thin sheet of cellulose infused with
aligned carbon nanotubes. nanotubes act as
electrodes; allowing the storage devices to
conduct electricity.
Integrates all of the battery components in a
single structure, making it more energy
efficient.
Uses….
Paper battery extreme flexibility; the sheets can
be rolled, twisted, folded, or cut into numerous
shapes with no loss of integrity or efficiency, or
stacked, like printer paper (or a Voltaic pile), to
boost total output.
Can be made in a variety of sizes, from postage
stamp to broadsheet.
Construction
Structure of Paper Battery
Working
The nano tubes acting as electrodes allow the
storage device to conduct electricity.
Chemical reaction in battery is occurs between
electrolyte and carbon nano tubes.
Battery produce electrons through a chemical
reaction between electrolyte and metal in the
traditional battery.
Working
Electrons must flow from the negative to the
positive terminal for the chemical reaction to
continue. Ionic liquid, essentially a liquid salt,
is used as the battery electrolyte.
The organic radical materials inside the battery
are in an “electrolyte-permeated gel state”,
which is about halfway between a solid and a
liquid. This helps ions to smooth move,
reducing resistance, allowing the batteries to
charge faster.
Working….
Limitations
Paper batteries have low strength they an be
‘torn’ easily.
The techniques and the set-ups used in the
production of Carbon Nano tubes are very
expensive and very less efficient.
Needs
Limited Life Time:
Primary batteries ‘irreversibly’ transform
chemical energy to electrical energy. Secondary
batteries can be recharged but they have very
short life time, paper batteries overcome both
problems.
Leakage:
In case of leakage the chemicals release may be
dangerous but no such toxic chemicals are used
in paper batteries.
Advantages
Used as both battery and capacitor.
It is flexible.
It is ultra thin energy storage device.
Long lasting.
Non toxic.
Steady power production.
Disadvantages
Prone to tearing.
Nanotubes made from carbon are expensive
due to use of procedures like electrolysis and
laser ablation.
Should not be inhaled, as they can damage
lungs.
Future Scope
It holds great potential to advance capabilities
in portable power design for applications
ranging from bioinstrumentation to consumer
electronics and even large power systems
served by conventional batteries.
The paper like qualities of the material make it
especially attractive for energy storage in
medically implanted devices (for example, a
pacemaker, insulin pump or the implantable
radio chip).
Conclusion
A paper battery is a paper like device formed
by the combination of carbon nanotubes and a
conventional sheet of cellulose-based paper
which act as a flexible ultra-thin energy storage
and energy production device.
As this technology is adapted it will prove to
be extremely useful and could even save not
only cost but lives also.
THANK
YOU
You might also like
- Example of Full Engine Overhaul ReportDocument90 pagesExample of Full Engine Overhaul ReportCwsNo ratings yet
- Synopsis On Paper BatteryDocument4 pagesSynopsis On Paper BatteryRahul Garg0% (1)
- Seminar ReportDocument25 pagesSeminar Reportpratt2012No ratings yet
- M.Tech Seminar Report GuidelinesDocument7 pagesM.Tech Seminar Report GuidelinesAnoop MathewNo ratings yet
- Multi Level Inverter DocumentationDocument25 pagesMulti Level Inverter Documentationn anushaNo ratings yet
- Paper BatteryDocument2 pagesPaper BatteryJeswanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Paper Battery: A Seminar Report OnDocument16 pagesPaper Battery: A Seminar Report OnSaawan HiwaleNo ratings yet
- Paper BatteryDocument5 pagesPaper BatteryBhavya SriNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report: Electrical Engineering Suraj Patel ROLL NO-1605420042Document23 pagesSeminar Report: Electrical Engineering Suraj Patel ROLL NO-1605420042Shafahad Ansari100% (1)
- Paper Battery ReportDocument17 pagesPaper Battery ReportIshuNo ratings yet
- Vishnu Institute of Technology: A Seminar Presentation ON Plastic Solar Cell TechnologyDocument12 pagesVishnu Institute of Technology: A Seminar Presentation ON Plastic Solar Cell Technologymyla ashwiniNo ratings yet
- Ieee Paper BatteryDocument1 pageIeee Paper Batteryanishkalra08100% (1)
- MajorProject (Batch1)Document65 pagesMajorProject (Batch1)tejNo ratings yet
- Anoop Seminar ReportDocument40 pagesAnoop Seminar ReportRijy Lorance100% (1)
- Seminar Report On Paper BatteryDocument40 pagesSeminar Report On Paper BatteryabhijeetNo ratings yet
- Easy To Swallow Wireless TelemetryDocument23 pagesEasy To Swallow Wireless TelemetryAshok GudivadaNo ratings yet
- Paper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inDocument12 pagesPaper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inPhebe PeterNo ratings yet
- Deep Space Optical Terminals: Bachelor of Engineering in Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument20 pagesDeep Space Optical Terminals: Bachelor of Engineering in Electronics and Communication EngineeringParu RJNo ratings yet
- Water Level Indicator Using Iot Blynk App With Sms NotificationDocument7 pagesWater Level Indicator Using Iot Blynk App With Sms NotificationHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Artificial Retina Using Thin-Film Transistors Driven by Wireless Power Supply - PDDocument31 pagesArtificial Retina Using Thin-Film Transistors Driven by Wireless Power Supply - PDGourav Panchal100% (2)
- Asynchronous ChipsDocument25 pagesAsynchronous ChipsAbin Varkey Varghese100% (1)
- Underwater Communication Using LI-FI Technology: Names of The Students 2. Aviraj Shejawal 3. Dharyashil WaghchaureDocument19 pagesUnderwater Communication Using LI-FI Technology: Names of The Students 2. Aviraj Shejawal 3. Dharyashil WaghchaureSudarshan RautNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Improvement in Distribution Network Using DSTATCOM With Battery Energy Storage SystemDocument22 pagesPower Quality Improvement in Distribution Network Using DSTATCOM With Battery Energy Storage Systemvipin chandNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks Seminar Report and TopicDocument32 pagesWireless Networks Seminar Report and TopicAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Mini Project of Paper BatteryDocument22 pagesMini Project of Paper BatteryvamsiNo ratings yet
- Triboelectric Nanogenerators As New Energy Technology For Self-Powered Systems and As Active Mechanical and Chemical SensorsDocument25 pagesTriboelectric Nanogenerators As New Energy Technology For Self-Powered Systems and As Active Mechanical and Chemical SensorsAnonymous AEicha08AF100% (1)
- Government Polytechnic College Nedumangadu: Snapdragon ProcessorsDocument17 pagesGovernment Polytechnic College Nedumangadu: Snapdragon ProcessorspremamohanNo ratings yet
- 2.technical Seminar Silent Sound Technolgy REPORTDocument35 pages2.technical Seminar Silent Sound Technolgy REPORTKirandhanu Kiran100% (1)
- Ece Seminar TopicsDocument17 pagesEce Seminar TopicsKrishna Chaitanya GorleNo ratings yet
- E Ink DocumentDocument29 pagesE Ink DocumentshajehanNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review On MEMS GyroscopeDocument6 pagesA Systematic Review On MEMS GyroscopeArjun KapoorNo ratings yet
- Women Safety Night Patrolling RobotDocument8 pagesWomen Safety Night Patrolling RobotIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Solar FenceDocument31 pagesSolar FenceSARIKANo ratings yet
- Vehical Starting System Using Finger PrintDocument18 pagesVehical Starting System Using Finger PrintVIKASH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting DiodesDocument17 pagesOrganic Light-Emitting DiodesSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Akshay Prakash - Technical Seminar-FINAL-1Document28 pagesAkshay Prakash - Technical Seminar-FINAL-1Yashpreet B Voladoddi Dept of AI & MLNo ratings yet
- Wireless Electric Vehicle Battery Charging System Using PV ArrayDocument9 pagesWireless Electric Vehicle Battery Charging System Using PV ArrayIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- E Paper PDFDocument19 pagesE Paper PDFLAVANYA VNo ratings yet
- Dipankar Seminar ReportDocument25 pagesDipankar Seminar Reportanoopk222100% (1)
- 4g Mobile Communication System A Seminar Report (1) Computer Science Seminar TopicsDocument7 pages4g Mobile Communication System A Seminar Report (1) Computer Science Seminar TopicsfinitehourabyssNo ratings yet
- Nyein Myo San R.ep-14Document73 pagesNyein Myo San R.ep-14Nyein Myo SanNo ratings yet
- Foot Step Piezo ElectricityDocument13 pagesFoot Step Piezo ElectricitysanjaysinghcoerNo ratings yet
- E Ink ReportDocument31 pagesE Ink ReportSʀɩŋʌtʜ SʀɩNo ratings yet
- Xmax SeminarDocument24 pagesXmax SeminarGirish ChouguleNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Power SystemDocument13 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Power SystemAayan SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Wireless Sensor NetworksJuan Sanchez Alarcon100% (1)
- B7 VarunDocument19 pagesB7 Varunridhima senNo ratings yet
- Protection of Transmission Lines Using Gps Full ReportDocument28 pagesProtection of Transmission Lines Using Gps Full ReportRamya GajjarapuNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesNuclear Power Plant Seminar Reportsushant kumarNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Hybrid Electric Aircraft MotorsDocument5 pagesAircraft Hybrid Electric Aircraft MotorsAdis Har-yo CahyonoNo ratings yet
- X MAXDocument20 pagesX MAXGirish Chougule100% (1)
- Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesSeminar Reportsuresh krishnanNo ratings yet
- Report - Smart Irrigation SystemDocument32 pagesReport - Smart Irrigation SystemKani mozhiNo ratings yet
- Soft SwitchDocument187 pagesSoft SwitchJong Hee LeeNo ratings yet
- AC Performance of NanoelectronicsDocument23 pagesAC Performance of Nanoelectronicspraveenpv7No ratings yet
- Smart Material Systems and MEMS: Design and Development MethodologiesFrom EverandSmart Material Systems and MEMS: Design and Development MethodologiesNo ratings yet
- Abhinav Final Seminar TopicDocument20 pagesAbhinav Final Seminar Topicabhinav GopirajNo ratings yet
- Paper Battery Technical Presentation by Sai SantoshDocument21 pagesPaper Battery Technical Presentation by Sai SantoshSwathi kNo ratings yet
- Sudhar SeminarDocument20 pagesSudhar SeminarSrilekha RajakumaranNo ratings yet
- Paper BatteryDocument20 pagesPaper Batterypiyujoshi157No ratings yet
- Smart Blind Eye - Glasses Using Arduino.Document19 pagesSmart Blind Eye - Glasses Using Arduino.Jyoti JadonNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Report On Embedded SystemDocument23 pagesIndustrial Training Report On Embedded SystemJyoti JadonNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Summer Training in NTPCDocument19 pagesDokumen - Tips - Summer Training in NTPCJyoti JadonNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training ReportDocument17 pagesIndustrial Training ReportJyoti JadonNo ratings yet
- Hygromatik Electrode Steam Humidifiers EU 2011Document6 pagesHygromatik Electrode Steam Humidifiers EU 2011portocala12No ratings yet
- Inaugral InviteDocument2 pagesInaugral InviteUtkarsh DaukiyaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument28 pagesReportDipanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report On Nuclear PDFDocument28 pagesA Seminar Report On Nuclear PDFIsmail Rohit RebalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29Document5 pagesChapter 29Rajkumar MaruthaiNo ratings yet
- Construction of 500w12vinverter ChargerDocument12 pagesConstruction of 500w12vinverter ChargerAbba SaadNo ratings yet
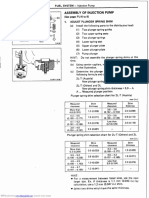
- Assembly of Injection Pump: FU-16 Fuel SystemDocument6 pagesAssembly of Injection Pump: FU-16 Fuel SystemDavid QuispeNo ratings yet
- BHCN 3500 123 EBV TS 20253D 0720 EnglishDocument38 pagesBHCN 3500 123 EBV TS 20253D 0720 EnglishGỗ MộcNo ratings yet
- UL Aires DAEWOO EMERSONDocument3 pagesUL Aires DAEWOO EMERSONeduin gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Newsletter Apr-June 23Document19 pagesNewsletter Apr-June 23avanishNo ratings yet
- Turbomachines 2: Sistem Kompresi FluidaDocument51 pagesTurbomachines 2: Sistem Kompresi FluidaMuhammadAkbarNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document83 pagesCH 10이잉No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Component Monitor (CCM)Document2 pagesComprehensive Component Monitor (CCM)rodrigo alexis aravena ponceNo ratings yet
- ARTES - Check Reactive Power Direction Undervoltage Protection Correctl... - MinDocument6 pagesARTES - Check Reactive Power Direction Undervoltage Protection Correctl... - MinharshitNo ratings yet
- SAUER - Maintenance Manual - CompressorDocument176 pagesSAUER - Maintenance Manual - CompressorFlo MarineNo ratings yet
- Sigma Coatings Is A Brand of The Sigmakalon GroupDocument8 pagesSigma Coatings Is A Brand of The Sigmakalon Groupmedkom2000No ratings yet
- Am048kn4dch AaDocument2 pagesAm048kn4dch AaOscar Barres MoreiraNo ratings yet
- ENGG 184.12 Lab Activity 4 - Manlapaz & DolalasDocument3 pagesENGG 184.12 Lab Activity 4 - Manlapaz & DolalasJuan Glicerio C. ManlapazNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Power Unit Series: Obel-PDocument2 pagesHydraulic Power Unit Series: Obel-Pxyz277807No ratings yet
- Važi Od: 20.03.2023 23 Rijeka - Matulji - PermaniDocument1 pageVaži Od: 20.03.2023 23 Rijeka - Matulji - PermaniTara JukicicNo ratings yet
- Unit1 EDCDocument24 pagesUnit1 EDCKarthick Sivakumar ChellamuthuNo ratings yet
- Fuel Consumption & THP Table 16-710G3C-ES - GT46ACDocument1 pageFuel Consumption & THP Table 16-710G3C-ES - GT46ACRafael Dutil LucianaNo ratings yet
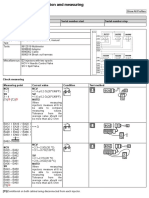
- MA2301-MA2306 Description and MeasuringDocument2 pagesMA2301-MA2306 Description and MeasuringwawanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change EQsDocument49 pagesClimate Change EQsValenciaNo ratings yet
- IAP Vacuum Hose ModDocument12 pagesIAP Vacuum Hose Modteepawat0No ratings yet
- LEED v4 For BD+C: Core and Shell: Project Checklist Project Name: DateDocument1 pageLEED v4 For BD+C: Core and Shell: Project Checklist Project Name: DateIan OsorioNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Engineering 22215 EEC MCQ (Elements of Electrical Engineering)Document34 pagesDepartment of Computer Engineering 22215 EEC MCQ (Elements of Electrical Engineering)Viraj TiwareNo ratings yet
- Development of Fuel Injection System On Single Cylinder Internal Combustion EngineDocument13 pagesDevelopment of Fuel Injection System On Single Cylinder Internal Combustion EngineJustin WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- General 6Document4 pagesGeneral 6Solomon AttaNo ratings yet