Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 viewsAcute Uterine Inversion
Acute Uterine Inversion
Uploaded by
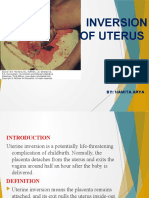
victor onapaAcute uterine inversion is a life-threatening complication that can occur during the third stage of labor, with an incidence ranging from 1 in 2,000 to 1 in 50,000 deliveries. It is classified as acute (within 24 hours of delivery), sub-acute (between 24 hours to 4 weeks postpartum), or chronic (more than 4 weeks postpartum). Causes include mismanagement of the third stage of labor, fundal pressure, short umbilical cord, abdominal pressure increases, and placenta issues. Clinically, it presents with severe pain, shock, hemorrhage, and an inability to palpate the uterus. Management involves antibiotics, manual repositioning, anesthesia, to
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Simple Nursing NotesDocument35 pagesSimple Nursing NotesJoyy96% (24)
- Retdem ReviewerDocument2 pagesRetdem Reviewerjustinejeon6No ratings yet
- Complications With The Power of LaborDocument8 pagesComplications With The Power of LaborEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal Complications: Problems With The PowerDocument10 pagesIntrapartal Complications: Problems With The PowerkeinwayNo ratings yet
- Management of Uterine InversionDocument36 pagesManagement of Uterine Inversionogundapo100% (2)
- Normal Labour& Abnormal LabourDocument23 pagesNormal Labour& Abnormal LabourThetnaungsoe100% (1)
- Notes On The Complications During The Labor and Delivery ProcessDocument7 pagesNotes On The Complications During The Labor and Delivery ProcessjyzzadNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal Complications 2023 PDFDocument8 pagesIntrapartal Complications 2023 PDFBrianna ValerioNo ratings yet
- Labour Presentation ObsDocument48 pagesLabour Presentation ObsVera BannorNo ratings yet
- 1066 Complications of 3rd Stage of Labour Injuries To Birth CanalDocument110 pages1066 Complications of 3rd Stage of Labour Injuries To Birth CanalSweety YadavNo ratings yet
- Stages of LabourDocument14 pagesStages of LabourSuriya KalaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument10 pagesAbruptio PlacentaDoc DudayNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Hemorrhage PPHDocument70 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage PPHLoungayvan BatuyogNo ratings yet
- Rle FinalsDocument9 pagesRle FinalsMary Florence VelardeNo ratings yet
- Uterine RuptureDocument19 pagesUterine RuptureAna Denise Quinajon0% (1)
- Third Stage of LaborDocument32 pagesThird Stage of LaborWhirmey ChinyamaNo ratings yet
- Joshi Abhishek F.Y.P.B.B.SC - Nursing Govt College of Nursing JamnagarDocument49 pagesJoshi Abhishek F.Y.P.B.B.SC - Nursing Govt College of Nursing JamnagarPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- Print OutDocument8 pagesPrint OutMadhu BalaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Dev, AbortionDocument128 pagesFetal Dev, AbortionAr JayNo ratings yet
- Inversion, Retained Placenta, AfeDocument95 pagesInversion, Retained Placenta, Afesushma sharmaNo ratings yet
- Management of Intrapartal ComplicationsDocument3 pagesManagement of Intrapartal Complicationsadrian nakilaNo ratings yet
- MCN ObDocument7 pagesMCN ObJoshua SaelNo ratings yet
- Means Ebesate Montebon Patigayon Ulile TitoDocument38 pagesMeans Ebesate Montebon Patigayon Ulile TitoJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- DaaanDocument19 pagesDaaanduca.danrainer02No ratings yet
- 8 Uterine Prolapse by HINADocument34 pages8 Uterine Prolapse by HINAmasalakhan555No ratings yet
- Dysfunctional LaborDocument29 pagesDysfunctional LaborKolimlim, Marienne SD.No ratings yet
- Third Stage Complications and Post-Partum CollapseDocument44 pagesThird Stage Complications and Post-Partum CollapseRamlah Ibrahim100% (1)
- Displacement of The Uterus: DR Sahar Anwar RizkDocument32 pagesDisplacement of The Uterus: DR Sahar Anwar RizkWida Ratna SariNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour July 2013Document13 pagesNormal Labour July 2013Logan MakolaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labor ASHEDocument124 pagesAbnormal Labor ASHENatif BoteNo ratings yet
- Introduction EctopicDocument5 pagesIntroduction EctopicRenalyn AgdaNo ratings yet
- Active Management of Third Stage of LaborDocument29 pagesActive Management of Third Stage of LaborChristoffer SamaristaNo ratings yet
- Complications During Labor and BirthDocument4 pagesComplications During Labor and BirthAudree Bustamante100% (2)
- "Types of Abortion": A Reading ONDocument3 pages"Types of Abortion": A Reading ONJannine BensiNo ratings yet
- Problemofthe PowerDocument8 pagesProblemofthe Powerjadeyorong2002No ratings yet
- Inversion of Uterus: By: Namita AryaDocument29 pagesInversion of Uterus: By: Namita Aryanamita0% (1)
- Dysfunctional LaborDocument25 pagesDysfunctional Laborelleas24thNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor NSG MGTDocument3 pagesStages of Labor NSG MGTMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDocument69 pagesAbnormal Uterine ActionBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDocument27 pagesAbnormal Uterine Actiontanmai noolu100% (1)
- Normal Labour: PRESENTED BY DR Tsitsi Vimbayi ChatoraDocument13 pagesNormal Labour: PRESENTED BY DR Tsitsi Vimbayi ChatoraChatora Tsitsi VimbayiNo ratings yet
- Uterine InversionDocument5 pagesUterine InversionJemin KimNo ratings yet
- Before Starting The Presentation, I Am Requesting You All To Get A HandkerchiefDocument35 pagesBefore Starting The Presentation, I Am Requesting You All To Get A HandkerchiefOng KarlNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother and Child at Risk or With Problems (Acute and Chronic)Document14 pagesCare of Mother and Child at Risk or With Problems (Acute and Chronic)Nicole Mendonis LunarNo ratings yet
- Inversion of Uterus 170225210149Document54 pagesInversion of Uterus 170225210149anju kumawatNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labour and It ManagementDocument27 pagesAbnormal Labour and It ManagementOsama AhmadNo ratings yet
- Complications of Labor & DeliveryDocument7 pagesComplications of Labor & DeliveryPatricia Anne Nicole CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Displacement of The UterusDocument32 pagesDisplacement of The UterusRaja100% (1)
- Week 5 NotesDocument12 pagesWeek 5 NotesgherlethrNo ratings yet
- Government College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)Document6 pagesGovernment College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)priyankaNo ratings yet
- M102 Remedial ModuleDocument14 pagesM102 Remedial ModuleMA. JYRELL BONITONo ratings yet
- Uterine Inversion1Document26 pagesUterine Inversion1Meylinda OctavianaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Client With High Risk Labor and Her FamilyDocument37 pagesNursing Care of The Client With High Risk Labor and Her Familyanne_088No ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NotesDocument9 pagesMaternal and Child NotesAngela Marjorie JimenezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document73 pagesUnit 2Bharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDocument8 pagesAbnormal Uterine ActionZechariah NicholasNo ratings yet
- Post Partum HemorhageDocument7 pagesPost Partum HemorhageLithiya JoseNo ratings yet
- Done Uterine RuptureDocument3 pagesDone Uterine RupturejnapalaNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour in Obstetric2Document17 pagesNormal Labour in Obstetric2Tejasvi ChavdaNo ratings yet
- Getting Pregnant Faster: Step-By-Step Guide To Achieving PregnancyFrom EverandGetting Pregnant Faster: Step-By-Step Guide To Achieving PregnancyNo ratings yet
- Hysterectomy, (Removal of Uterus) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHysterectomy, (Removal of Uterus) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Operative Obstetrics: Madira Emmanuel Lira UniversityDocument27 pagesOperative Obstetrics: Madira Emmanuel Lira Universityvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid DisordersDocument22 pagesAmniotic Fluid Disordersvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument36 pagesBleeding in Early Pregnancyvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Disorders During Pregnancy and BirthDocument39 pagesPsychiatric Disorders During Pregnancy and Birthvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- Anemia in Pregnancy: Dr. Inzama WilfredDocument17 pagesAnemia in Pregnancy: Dr. Inzama Wilfredvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- MCHN Popphi Amtsl Ref Man 2of3Document24 pagesMCHN Popphi Amtsl Ref Man 2of3Andhika Madang WijayaNo ratings yet
- Example QuizDocument17 pagesExample QuizDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- Obg Gyne PranavDocument5 pagesObg Gyne PranavPranav ThakoreNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing RevisedDocument345 pagesObstetric Nursing Revisedkarendelarosa06100% (1)
- DrillsDocument18 pagesDrillsJean CuentaNo ratings yet
- PPH 2024Document25 pagesPPH 2024Anthony Mwangi100% (1)
- Internal Podalic Version For Neglected Shoulder Presentation With Fetal DemiseDocument4 pagesInternal Podalic Version For Neglected Shoulder Presentation With Fetal DemiseErlangga DayudNo ratings yet
- What Is A Normal DeliveryDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Normal DeliveryVincentus BinNo ratings yet
- Mca (107) RleDocument13 pagesMca (107) RleGulayan, Renz Bryelle T.No ratings yet
- Maternal and Child: Skills LabDocument14 pagesMaternal and Child: Skills Labzenab32003No ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document63 pagesChapter 25Jœnríčk AzueloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Labor and BirthDocument7 pagesNursing Care During Labor and BirthRegine VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Midwifery 101Document7 pagesMidwifery 101Anne PalmaNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery ConceptsDocument8 pagesLabor and Delivery ConceptsNisah CabugatanNo ratings yet
- MCN PartographDocument2 pagesMCN PartographAlec AnonNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Case Scenario Activity Sheet: Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesDelivery Room Case Scenario Activity Sheet: Guide QuestionsMark VincentNo ratings yet
- Operative Vaginal DeliveryDocument8 pagesOperative Vaginal DeliveryGerben VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- MCN PartographDocument2 pagesMCN PartographAlec Anon100% (1)
- Community Health NursingDocument8 pagesCommunity Health NursingKurt RoseteNo ratings yet
- The Third StageDocument7 pagesThe Third Stagebalaramani6890No ratings yet
- Marileth B. JeffersonDocument32 pagesMarileth B. JeffersonMarileth JeffersonNo ratings yet
- 3 Handling and Assiting Deliveries TransesDocument7 pages3 Handling and Assiting Deliveries TransesKeana DacayanaNo ratings yet
- NSDDocument44 pagesNSDabyssodeep100% (1)
- NSDDocument10 pagesNSDAeia de los SantosNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum PeriodDocument19 pagesIntrapartum Periodanon_915924422No ratings yet
- Evidenced Based Practice and Research PrioritiesDocument20 pagesEvidenced Based Practice and Research Prioritiesjyoti dhangalNo ratings yet
- Government College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)Document6 pagesGovernment College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)priyankaNo ratings yet
- Section A: MCQ (80 Questions)Document16 pagesSection A: MCQ (80 Questions)Muhammed MostafaNo ratings yet
Acute Uterine Inversion
Acute Uterine Inversion
Uploaded by
victor onapa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views9 pagesAcute uterine inversion is a life-threatening complication that can occur during the third stage of labor, with an incidence ranging from 1 in 2,000 to 1 in 50,000 deliveries. It is classified as acute (within 24 hours of delivery), sub-acute (between 24 hours to 4 weeks postpartum), or chronic (more than 4 weeks postpartum). Causes include mismanagement of the third stage of labor, fundal pressure, short umbilical cord, abdominal pressure increases, and placenta issues. Clinically, it presents with severe pain, shock, hemorrhage, and an inability to palpate the uterus. Management involves antibiotics, manual repositioning, anesthesia, to
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAcute uterine inversion is a life-threatening complication that can occur during the third stage of labor, with an incidence ranging from 1 in 2,000 to 1 in 50,000 deliveries. It is classified as acute (within 24 hours of delivery), sub-acute (between 24 hours to 4 weeks postpartum), or chronic (more than 4 weeks postpartum). Causes include mismanagement of the third stage of labor, fundal pressure, short umbilical cord, abdominal pressure increases, and placenta issues. Clinically, it presents with severe pain, shock, hemorrhage, and an inability to palpate the uterus. Management involves antibiotics, manual repositioning, anesthesia, to
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views9 pagesAcute Uterine Inversion
Acute Uterine Inversion
Uploaded by
victor onapaAcute uterine inversion is a life-threatening complication that can occur during the third stage of labor, with an incidence ranging from 1 in 2,000 to 1 in 50,000 deliveries. It is classified as acute (within 24 hours of delivery), sub-acute (between 24 hours to 4 weeks postpartum), or chronic (more than 4 weeks postpartum). Causes include mismanagement of the third stage of labor, fundal pressure, short umbilical cord, abdominal pressure increases, and placenta issues. Clinically, it presents with severe pain, shock, hemorrhage, and an inability to palpate the uterus. Management involves antibiotics, manual repositioning, anesthesia, to
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Acute Uterine Inversion
Lecturer; Dr. Inzama Wilfred
Dept; Obstetrics & Gynecology
30th/08/2019
Introduction
• Life threatening complication in third of labour
• Incidence varies widely between 1in 2000 to 1
in 50000
• Largely deeps on standard of management of
third stage of labor
Classification
Acute uterine inversion; within 24 hrs of
delivery
Sub-acute uterine inversion; between 24 hrs
to 4 weeks of delivery
Chronic uterine inversion; after 4weeks after
delivery
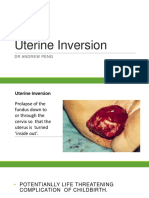
Types of uterine inversion
Incomplete; fundus of the uterus has turned
inside out, but the inverted fundus has not
descended though the cervix, also know type I
Complete; inverted fundus has passed
completely through the cervix to lie within the
vagina or, less often outside the introitus, also
known type I & II respectivefully
Causes
Mismanagement of third stage of labour
Fundal pressure to aid delivery
Abnormally short cord
Sudden rise of intra abdominal pressure e.g. cough,
vomiting
Morbid adherence of a fundally implanted placenta
Mannual removal of the placenta
Connective tissue disorders like Marfan’s syndrome.
Clinical presentation
Severe and sustained hypogastric pain in the third stage
of labor
Shock that is out of proportion with apparent blood loss
Associated haemorrhage and hypovolaemic shock
With complete inversion the uterus is not palpable per
abdomen and the inverted is either obvious at the
introitus
In case of incomplete inversion, fundus may feel normal
except in very thin women where you may feel a dimple
Management
Consent from the patient
Preoperative antibiotics
Try immediate manual replacement
Call for help
Intravenous crystalloids (large bore cannula 2)
Blood for grouping and cross match
Catheterize
Analgesia
Anesthesia (preferably general anesthesia)
Tocolysis (terbutalene & salbutamol)
Manual replacement of the uterus
Surgical method after failed manual replacement
Oxcytocic for 8-12 hours to keep the uterus contracted
Manual replacement of the uterus
• The uterine fundus is cupped in the palm of the hand.
• The fingers and thumb are extended to feel the utero-
cervical junction, to systematically & sequentially push
and squeeze the uterine wall back through the cervix
• This pressure is sustained for 3-5 minutes to achieve
complete replacement
• Keep the finger in the uterus and start oxytocin infusion
to keep the uterus contracted
• When the uterus is felt contracted, then remove the
hand slowly
Other method
O’sullivan’s hydrostatic replacement
technique
Surgical methods
Huntington’s operation
Haultain’s operation
You might also like
- Simple Nursing NotesDocument35 pagesSimple Nursing NotesJoyy96% (24)
- Retdem ReviewerDocument2 pagesRetdem Reviewerjustinejeon6No ratings yet
- Complications With The Power of LaborDocument8 pagesComplications With The Power of LaborEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal Complications: Problems With The PowerDocument10 pagesIntrapartal Complications: Problems With The PowerkeinwayNo ratings yet
- Management of Uterine InversionDocument36 pagesManagement of Uterine Inversionogundapo100% (2)
- Normal Labour& Abnormal LabourDocument23 pagesNormal Labour& Abnormal LabourThetnaungsoe100% (1)
- Notes On The Complications During The Labor and Delivery ProcessDocument7 pagesNotes On The Complications During The Labor and Delivery ProcessjyzzadNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal Complications 2023 PDFDocument8 pagesIntrapartal Complications 2023 PDFBrianna ValerioNo ratings yet
- Labour Presentation ObsDocument48 pagesLabour Presentation ObsVera BannorNo ratings yet
- 1066 Complications of 3rd Stage of Labour Injuries To Birth CanalDocument110 pages1066 Complications of 3rd Stage of Labour Injuries To Birth CanalSweety YadavNo ratings yet
- Stages of LabourDocument14 pagesStages of LabourSuriya KalaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument10 pagesAbruptio PlacentaDoc DudayNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Hemorrhage PPHDocument70 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage PPHLoungayvan BatuyogNo ratings yet
- Rle FinalsDocument9 pagesRle FinalsMary Florence VelardeNo ratings yet
- Uterine RuptureDocument19 pagesUterine RuptureAna Denise Quinajon0% (1)
- Third Stage of LaborDocument32 pagesThird Stage of LaborWhirmey ChinyamaNo ratings yet
- Joshi Abhishek F.Y.P.B.B.SC - Nursing Govt College of Nursing JamnagarDocument49 pagesJoshi Abhishek F.Y.P.B.B.SC - Nursing Govt College of Nursing JamnagarPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- Print OutDocument8 pagesPrint OutMadhu BalaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Dev, AbortionDocument128 pagesFetal Dev, AbortionAr JayNo ratings yet
- Inversion, Retained Placenta, AfeDocument95 pagesInversion, Retained Placenta, Afesushma sharmaNo ratings yet
- Management of Intrapartal ComplicationsDocument3 pagesManagement of Intrapartal Complicationsadrian nakilaNo ratings yet
- MCN ObDocument7 pagesMCN ObJoshua SaelNo ratings yet
- Means Ebesate Montebon Patigayon Ulile TitoDocument38 pagesMeans Ebesate Montebon Patigayon Ulile TitoJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- DaaanDocument19 pagesDaaanduca.danrainer02No ratings yet
- 8 Uterine Prolapse by HINADocument34 pages8 Uterine Prolapse by HINAmasalakhan555No ratings yet
- Dysfunctional LaborDocument29 pagesDysfunctional LaborKolimlim, Marienne SD.No ratings yet
- Third Stage Complications and Post-Partum CollapseDocument44 pagesThird Stage Complications and Post-Partum CollapseRamlah Ibrahim100% (1)
- Displacement of The Uterus: DR Sahar Anwar RizkDocument32 pagesDisplacement of The Uterus: DR Sahar Anwar RizkWida Ratna SariNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour July 2013Document13 pagesNormal Labour July 2013Logan MakolaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labor ASHEDocument124 pagesAbnormal Labor ASHENatif BoteNo ratings yet
- Introduction EctopicDocument5 pagesIntroduction EctopicRenalyn AgdaNo ratings yet
- Active Management of Third Stage of LaborDocument29 pagesActive Management of Third Stage of LaborChristoffer SamaristaNo ratings yet
- Complications During Labor and BirthDocument4 pagesComplications During Labor and BirthAudree Bustamante100% (2)
- "Types of Abortion": A Reading ONDocument3 pages"Types of Abortion": A Reading ONJannine BensiNo ratings yet
- Problemofthe PowerDocument8 pagesProblemofthe Powerjadeyorong2002No ratings yet
- Inversion of Uterus: By: Namita AryaDocument29 pagesInversion of Uterus: By: Namita Aryanamita0% (1)
- Dysfunctional LaborDocument25 pagesDysfunctional Laborelleas24thNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor NSG MGTDocument3 pagesStages of Labor NSG MGTMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDocument69 pagesAbnormal Uterine ActionBharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDocument27 pagesAbnormal Uterine Actiontanmai noolu100% (1)
- Normal Labour: PRESENTED BY DR Tsitsi Vimbayi ChatoraDocument13 pagesNormal Labour: PRESENTED BY DR Tsitsi Vimbayi ChatoraChatora Tsitsi VimbayiNo ratings yet
- Uterine InversionDocument5 pagesUterine InversionJemin KimNo ratings yet
- Before Starting The Presentation, I Am Requesting You All To Get A HandkerchiefDocument35 pagesBefore Starting The Presentation, I Am Requesting You All To Get A HandkerchiefOng KarlNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother and Child at Risk or With Problems (Acute and Chronic)Document14 pagesCare of Mother and Child at Risk or With Problems (Acute and Chronic)Nicole Mendonis LunarNo ratings yet
- Inversion of Uterus 170225210149Document54 pagesInversion of Uterus 170225210149anju kumawatNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labour and It ManagementDocument27 pagesAbnormal Labour and It ManagementOsama AhmadNo ratings yet
- Complications of Labor & DeliveryDocument7 pagesComplications of Labor & DeliveryPatricia Anne Nicole CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Displacement of The UterusDocument32 pagesDisplacement of The UterusRaja100% (1)
- Week 5 NotesDocument12 pagesWeek 5 NotesgherlethrNo ratings yet
- Government College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)Document6 pagesGovernment College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)priyankaNo ratings yet
- M102 Remedial ModuleDocument14 pagesM102 Remedial ModuleMA. JYRELL BONITONo ratings yet
- Uterine Inversion1Document26 pagesUterine Inversion1Meylinda OctavianaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Client With High Risk Labor and Her FamilyDocument37 pagesNursing Care of The Client With High Risk Labor and Her Familyanne_088No ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NotesDocument9 pagesMaternal and Child NotesAngela Marjorie JimenezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document73 pagesUnit 2Bharat ThapaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDocument8 pagesAbnormal Uterine ActionZechariah NicholasNo ratings yet
- Post Partum HemorhageDocument7 pagesPost Partum HemorhageLithiya JoseNo ratings yet
- Done Uterine RuptureDocument3 pagesDone Uterine RupturejnapalaNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour in Obstetric2Document17 pagesNormal Labour in Obstetric2Tejasvi ChavdaNo ratings yet
- Getting Pregnant Faster: Step-By-Step Guide To Achieving PregnancyFrom EverandGetting Pregnant Faster: Step-By-Step Guide To Achieving PregnancyNo ratings yet
- Hysterectomy, (Removal of Uterus) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHysterectomy, (Removal of Uterus) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Operative Obstetrics: Madira Emmanuel Lira UniversityDocument27 pagesOperative Obstetrics: Madira Emmanuel Lira Universityvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid DisordersDocument22 pagesAmniotic Fluid Disordersvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument36 pagesBleeding in Early Pregnancyvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Disorders During Pregnancy and BirthDocument39 pagesPsychiatric Disorders During Pregnancy and Birthvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- Anemia in Pregnancy: Dr. Inzama WilfredDocument17 pagesAnemia in Pregnancy: Dr. Inzama Wilfredvictor onapaNo ratings yet
- MCHN Popphi Amtsl Ref Man 2of3Document24 pagesMCHN Popphi Amtsl Ref Man 2of3Andhika Madang WijayaNo ratings yet
- Example QuizDocument17 pagesExample QuizDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- Obg Gyne PranavDocument5 pagesObg Gyne PranavPranav ThakoreNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing RevisedDocument345 pagesObstetric Nursing Revisedkarendelarosa06100% (1)
- DrillsDocument18 pagesDrillsJean CuentaNo ratings yet
- PPH 2024Document25 pagesPPH 2024Anthony Mwangi100% (1)
- Internal Podalic Version For Neglected Shoulder Presentation With Fetal DemiseDocument4 pagesInternal Podalic Version For Neglected Shoulder Presentation With Fetal DemiseErlangga DayudNo ratings yet
- What Is A Normal DeliveryDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Normal DeliveryVincentus BinNo ratings yet
- Mca (107) RleDocument13 pagesMca (107) RleGulayan, Renz Bryelle T.No ratings yet
- Maternal and Child: Skills LabDocument14 pagesMaternal and Child: Skills Labzenab32003No ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document63 pagesChapter 25Jœnríčk AzueloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Labor and BirthDocument7 pagesNursing Care During Labor and BirthRegine VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Midwifery 101Document7 pagesMidwifery 101Anne PalmaNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery ConceptsDocument8 pagesLabor and Delivery ConceptsNisah CabugatanNo ratings yet
- MCN PartographDocument2 pagesMCN PartographAlec AnonNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Case Scenario Activity Sheet: Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesDelivery Room Case Scenario Activity Sheet: Guide QuestionsMark VincentNo ratings yet
- Operative Vaginal DeliveryDocument8 pagesOperative Vaginal DeliveryGerben VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- MCN PartographDocument2 pagesMCN PartographAlec Anon100% (1)
- Community Health NursingDocument8 pagesCommunity Health NursingKurt RoseteNo ratings yet
- The Third StageDocument7 pagesThe Third Stagebalaramani6890No ratings yet
- Marileth B. JeffersonDocument32 pagesMarileth B. JeffersonMarileth JeffersonNo ratings yet
- 3 Handling and Assiting Deliveries TransesDocument7 pages3 Handling and Assiting Deliveries TransesKeana DacayanaNo ratings yet
- NSDDocument44 pagesNSDabyssodeep100% (1)
- NSDDocument10 pagesNSDAeia de los SantosNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum PeriodDocument19 pagesIntrapartum Periodanon_915924422No ratings yet
- Evidenced Based Practice and Research PrioritiesDocument20 pagesEvidenced Based Practice and Research Prioritiesjyoti dhangalNo ratings yet
- Government College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)Document6 pagesGovernment College of Nursing:, Jodhpur (Raj.)priyankaNo ratings yet
- Section A: MCQ (80 Questions)Document16 pagesSection A: MCQ (80 Questions)Muhammed MostafaNo ratings yet