Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsTongue Anatomy
Tongue Anatomy
Uploaded by
Arnab KalitaThe tongue has three parts - oral, pharyngeal, and root. It has two surfaces - dorsal and ventral. The dorsal surface is divided into anterior two thirds and posterior one third by a sulcus terminalis. The anterior two thirds contains three types of papillae while the posterior one third contains lingual tonsils. The ventral surface is smooth. The tongue contains intrinsic muscles that alter its shape and extrinsic muscles that connect it to surrounding structures. The tongue receives sensory innervation from different nerves in its anterior, posterior and root regions. It is supplied by arteries including the lingual artery and drains lymphatically to various cervical nodes depending on location.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Oral Cavity585689409Document37 pagesOral Cavity585689409mittal.shubham0007No ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument37 pages14-Oral CavitySajid AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The TongueDocument36 pagesAnatomy of The TongueDrMohmd ZidaanNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument59 pagesOral CavityshaisidroNo ratings yet
- 14 Oral CavityDocument41 pages14 Oral Cavityhamokimo65No ratings yet
- 4TONGUEDocument15 pages4TONGUEZakaria Abdul HafizNo ratings yet
- Fuad Ridha MahabotDocument36 pagesFuad Ridha MahabotLore DanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 64: Anatomy of Tongue: Dr. Mohammad Rehan AsadDocument20 pagesLecture 64: Anatomy of Tongue: Dr. Mohammad Rehan AsadRehan Asad0% (1)
- 14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalDocument50 pages14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalSudeep DhakalNo ratings yet
- TONGUEDocument63 pagesTONGUEAthulya Lakshmanan100% (1)
- Tongue IDocument25 pagesTongue Igajendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument10 pagesTongueBhuwanesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tongue IDocument25 pagesTongue IJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Tongue IDocument25 pagesTongue Iilagernischit321No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Oral CavityDocument44 pagesAnatomy of Oral CavityRamesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tongue and PalateDocument103 pagesTongue and PalateHeba S RadaidehNo ratings yet
- Tongue - AnatomyDocument46 pagesTongue - AnatomyAswitha GanapathyNo ratings yet
- TONGUE Seminar by MeDocument84 pagesTONGUE Seminar by MeArpita SankhwarNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument20 pagesOral CavityadileidalaaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY ORAL CAVITY and TONGUE JelDocument54 pagesANATOMY ORAL CAVITY and TONGUE JelCoy EnNo ratings yet
- Tongue IIDocument15 pagesTongue IIilagernischit321No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Oral Cavity, Pharynx and EsophagusDocument52 pagesAnatomy of Oral Cavity, Pharynx and EsophagusYashoda Amarasekera100% (1)
- Amirhossein Vaezi MS121 Oral CavityDocument27 pagesAmirhossein Vaezi MS121 Oral Cavityamirhossein vaeziNo ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument36 pages14-Oral CavitykavindukarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of AirwaysDocument6 pagesAnatomy of Airwaysgdubs215No ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Document47 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Aditya FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- W2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFDocument69 pagesW2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFSAHIL AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Tongue IiDocument15 pagesTongue Iigajendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Cavum OrisDocument40 pagesCavum OrisharisNo ratings yet
- Drain The Central Portion of The Anterior Two-Third of The Tongue Bilaterally Into The Deep Cervical Lymph NodesDocument3 pagesDrain The Central Portion of The Anterior Two-Third of The Tongue Bilaterally Into The Deep Cervical Lymph NodesÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Tongue and Its MusculatureDocument89 pagesTongue and Its MusculaturedrsanketcNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Histology of The Oral Cavity2 3Document31 pagesAnatomy Histology of The Oral Cavity2 3drsondosNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity NursingDocument38 pagesOral Cavity NursingRiya AktarNo ratings yet
- Oral RegionDocument40 pagesOral RegionDayen LimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Oral Cavity: DR Farhan FaderDocument25 pagesAnatomy of Oral Cavity: DR Farhan FaderFarhan Fader100% (1)
- 1.gastrointestinal SystemDocument69 pages1.gastrointestinal SystemNELSONJD20195No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgiDocument77 pagesAnatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgideepNo ratings yet
- Tongue & It's Applied AspectsDocument64 pagesTongue & It's Applied AspectsPrachi MulayNo ratings yet
- Anatomi MenelanDocument74 pagesAnatomi MenelanAnonymous KrEomRrNo ratings yet
- Tongue, Deglutation and SpeechDocument65 pagesTongue, Deglutation and SpeechtamannaNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument52 pagesTongueNANDANA BOSENo ratings yet
- Accessory Organs of The Git - Gross AnatomyDocument172 pagesAccessory Organs of The Git - Gross AnatomyManisha RaoNo ratings yet
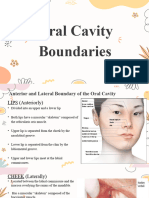
- Oral Cavity BoundariesDocument8 pagesOral Cavity BoundariesLean Edrielle BillonesNo ratings yet
- TONGUE SeminarDocument82 pagesTONGUE SeminarArun MamachanNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument7 pagesTongueIzhaan AkmalNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument98 pagesOral CavitynicewanNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument79 pagesOral CavityueumanaNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Head and NeckDocument43 pagesBlood Supply of Head and NeckSaman FirdousNo ratings yet
- The Larynx: Portion of The Respiratory Tract 2-Inch-Long Laryngeal Part of The Pharynx TracheaDocument22 pagesThe Larynx: Portion of The Respiratory Tract 2-Inch-Long Laryngeal Part of The Pharynx TracheaNAND KUMARNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHDocument21 pagesAnatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHAdam NoheNo ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument30 pages14-Oral CavityNeeta ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Salivary Glands, The Oral Fissure and LipsDocument53 pagesSalivary Glands, The Oral Fissure and LipsGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Role of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTDocument18 pagesRole of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTashoorocksNo ratings yet
- GIT Anatomy Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesGIT Anatomy Learning ObjectivesangrypandasaredangerousNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity and TongueDocument46 pagesOral Cavity and TongueAayush BhattaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Study GuideDocument19 pagesRespiratory System Study GuideOaya Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nose and TongueDocument40 pagesAnatomy of Nose and TongueDanial SharizulNo ratings yet
- Descriptions of New Hylid Frogs From Mexico and Central AmericaFrom EverandDescriptions of New Hylid Frogs From Mexico and Central AmericaNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- A New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasFrom EverandA New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasNo ratings yet
Tongue Anatomy
Tongue Anatomy
Uploaded by
Arnab Kalita0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views15 pagesThe tongue has three parts - oral, pharyngeal, and root. It has two surfaces - dorsal and ventral. The dorsal surface is divided into anterior two thirds and posterior one third by a sulcus terminalis. The anterior two thirds contains three types of papillae while the posterior one third contains lingual tonsils. The ventral surface is smooth. The tongue contains intrinsic muscles that alter its shape and extrinsic muscles that connect it to surrounding structures. The tongue receives sensory innervation from different nerves in its anterior, posterior and root regions. It is supplied by arteries including the lingual artery and drains lymphatically to various cervical nodes depending on location.
Original Description:
Original Title
TONGUE ANATOMY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe tongue has three parts - oral, pharyngeal, and root. It has two surfaces - dorsal and ventral. The dorsal surface is divided into anterior two thirds and posterior one third by a sulcus terminalis. The anterior two thirds contains three types of papillae while the posterior one third contains lingual tonsils. The ventral surface is smooth. The tongue contains intrinsic muscles that alter its shape and extrinsic muscles that connect it to surrounding structures. The tongue receives sensory innervation from different nerves in its anterior, posterior and root regions. It is supplied by arteries including the lingual artery and drains lymphatically to various cervical nodes depending on location.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views15 pagesTongue Anatomy
Tongue Anatomy
Uploaded by
Arnab KalitaThe tongue has three parts - oral, pharyngeal, and root. It has two surfaces - dorsal and ventral. The dorsal surface is divided into anterior two thirds and posterior one third by a sulcus terminalis. The anterior two thirds contains three types of papillae while the posterior one third contains lingual tonsils. The ventral surface is smooth. The tongue contains intrinsic muscles that alter its shape and extrinsic muscles that connect it to surrounding structures. The tongue receives sensory innervation from different nerves in its anterior, posterior and root regions. It is supplied by arteries including the lingual artery and drains lymphatically to various cervical nodes depending on location.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
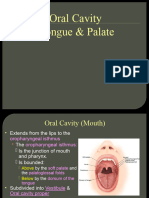
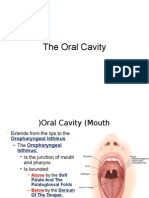
TONGUE ANATOMY
• Divided into right and left halves by a median
septum
• Three parts:
• Oral (anterior ⅔)
• Pharyngeal (posterior ⅓)
• Root (base)
• Two surfaces:DorsalVentra
• Dorsal Surface
• Divided into anterior two third and posterior one third by a V-shaped
sulcus terminalis.
• The apex of the sulcus faces backward and is marked by a pit called the
foramen cecum.
• Foramen cecum, an embryological remnant, marks the site of the upper
end of the thyroglossal duct
• Anterior two third: mucosa is rough, shows three
types of papillae:
Filliform
Fungiform
Circumvallate
Posterior one third: No papillae but shows
nodular surface because of underlying lymphatic
nodules, the lingual tonsils
• Ventral Surface Smooth (no papillae)
In the midline anteriorly, a mucosal fold, frenulum connects the tongue with the
floor of the mouth
• Lateral to frenulum, deep lingual vein can be seen through the mucosa
• Lateral to lingual vein, a fold of mucosa forms the plica fimbriata
• Muscles The tongue is composed of two
types of muscles:
• Intrinsic
Extrinsic
• Intrinsic Muscles
• Confined to tongue
• No bony attachment Consist of:
Longitudinal fibers
• Transverse fibers
• Vertical fibers
• Function: Alter the shape of the tongue
• Extrinsic Muscles
• Connect the tongue to the surrounding structures: the soft palate and the bones
(mandible, hyoid bone, styloid process)
• Include:
• Palatoglossus
• Genioglossus
• Hyoglossus
• Styloglossus
• Function: Help in movements of the tongue
• Sensory Nerve Supply Anterior ⅔: Posterior
⅓: Base:
• General sensations: Lingual nerve
• Special sensations : chorda tympani
• Posterior ⅓:General
• & special sensations: glossopharyngeal nerve
• Base:General & special sensations: internal
laryngeal nerve
• Motor Nerve Supply
• Intrinsic muscles: Hypoglossal nerve
• Extrinsic muscles:All supplied by the
hypoglossal nerve, except the palatoglossus
• The palatoglossus supplied by the pharyngeal
plexus
• Blood Supply Arteries:
• Lingual artery
• Tonsillar branch of facial artery
• Ascending pharyngeal artery
• Veins:Lingual vein, ultimately drains into the
internal jugular vein
• Lymphatic Drainage
• Tip: Submental nodes bilaterally & then deep
cervical nodes
• Anterior two third:Submandibular unilaterally
& then deep cervical nodes
• Posterior third:Deep cervical nodes
(jugulodigastric mainly)
Thank you
You might also like
- Oral Cavity585689409Document37 pagesOral Cavity585689409mittal.shubham0007No ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument37 pages14-Oral CavitySajid AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The TongueDocument36 pagesAnatomy of The TongueDrMohmd ZidaanNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument59 pagesOral CavityshaisidroNo ratings yet
- 14 Oral CavityDocument41 pages14 Oral Cavityhamokimo65No ratings yet
- 4TONGUEDocument15 pages4TONGUEZakaria Abdul HafizNo ratings yet
- Fuad Ridha MahabotDocument36 pagesFuad Ridha MahabotLore DanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 64: Anatomy of Tongue: Dr. Mohammad Rehan AsadDocument20 pagesLecture 64: Anatomy of Tongue: Dr. Mohammad Rehan AsadRehan Asad0% (1)
- 14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalDocument50 pages14-ORAL CAVITY and Pharynx FinalSudeep DhakalNo ratings yet
- TONGUEDocument63 pagesTONGUEAthulya Lakshmanan100% (1)
- Tongue IDocument25 pagesTongue Igajendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument10 pagesTongueBhuwanesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tongue IDocument25 pagesTongue IJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Tongue IDocument25 pagesTongue Iilagernischit321No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Oral CavityDocument44 pagesAnatomy of Oral CavityRamesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tongue and PalateDocument103 pagesTongue and PalateHeba S RadaidehNo ratings yet
- Tongue - AnatomyDocument46 pagesTongue - AnatomyAswitha GanapathyNo ratings yet
- TONGUE Seminar by MeDocument84 pagesTONGUE Seminar by MeArpita SankhwarNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument20 pagesOral CavityadileidalaaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY ORAL CAVITY and TONGUE JelDocument54 pagesANATOMY ORAL CAVITY and TONGUE JelCoy EnNo ratings yet
- Tongue IIDocument15 pagesTongue IIilagernischit321No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Oral Cavity, Pharynx and EsophagusDocument52 pagesAnatomy of Oral Cavity, Pharynx and EsophagusYashoda Amarasekera100% (1)
- Amirhossein Vaezi MS121 Oral CavityDocument27 pagesAmirhossein Vaezi MS121 Oral Cavityamirhossein vaeziNo ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument36 pages14-Oral CavitykavindukarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of AirwaysDocument6 pagesAnatomy of Airwaysgdubs215No ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Document47 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Aditya FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- W2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFDocument69 pagesW2-8 Oral Region Lecture PDFSAHIL AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Tongue IiDocument15 pagesTongue Iigajendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Cavum OrisDocument40 pagesCavum OrisharisNo ratings yet
- Drain The Central Portion of The Anterior Two-Third of The Tongue Bilaterally Into The Deep Cervical Lymph NodesDocument3 pagesDrain The Central Portion of The Anterior Two-Third of The Tongue Bilaterally Into The Deep Cervical Lymph NodesÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Tongue and Its MusculatureDocument89 pagesTongue and Its MusculaturedrsanketcNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Histology of The Oral Cavity2 3Document31 pagesAnatomy Histology of The Oral Cavity2 3drsondosNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity NursingDocument38 pagesOral Cavity NursingRiya AktarNo ratings yet
- Oral RegionDocument40 pagesOral RegionDayen LimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Oral Cavity: DR Farhan FaderDocument25 pagesAnatomy of Oral Cavity: DR Farhan FaderFarhan Fader100% (1)
- 1.gastrointestinal SystemDocument69 pages1.gastrointestinal SystemNELSONJD20195No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgiDocument77 pagesAnatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgideepNo ratings yet
- Tongue & It's Applied AspectsDocument64 pagesTongue & It's Applied AspectsPrachi MulayNo ratings yet
- Anatomi MenelanDocument74 pagesAnatomi MenelanAnonymous KrEomRrNo ratings yet
- Tongue, Deglutation and SpeechDocument65 pagesTongue, Deglutation and SpeechtamannaNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument52 pagesTongueNANDANA BOSENo ratings yet
- Accessory Organs of The Git - Gross AnatomyDocument172 pagesAccessory Organs of The Git - Gross AnatomyManisha RaoNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity BoundariesDocument8 pagesOral Cavity BoundariesLean Edrielle BillonesNo ratings yet
- TONGUE SeminarDocument82 pagesTONGUE SeminarArun MamachanNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument7 pagesTongueIzhaan AkmalNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument98 pagesOral CavitynicewanNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument79 pagesOral CavityueumanaNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Head and NeckDocument43 pagesBlood Supply of Head and NeckSaman FirdousNo ratings yet
- The Larynx: Portion of The Respiratory Tract 2-Inch-Long Laryngeal Part of The Pharynx TracheaDocument22 pagesThe Larynx: Portion of The Respiratory Tract 2-Inch-Long Laryngeal Part of The Pharynx TracheaNAND KUMARNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHDocument21 pagesAnatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHAdam NoheNo ratings yet
- 14-Oral CavityDocument30 pages14-Oral CavityNeeta ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Salivary Glands, The Oral Fissure and LipsDocument53 pagesSalivary Glands, The Oral Fissure and LipsGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Role of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTDocument18 pagesRole of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTashoorocksNo ratings yet
- GIT Anatomy Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesGIT Anatomy Learning ObjectivesangrypandasaredangerousNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity and TongueDocument46 pagesOral Cavity and TongueAayush BhattaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Study GuideDocument19 pagesRespiratory System Study GuideOaya Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nose and TongueDocument40 pagesAnatomy of Nose and TongueDanial SharizulNo ratings yet
- Descriptions of New Hylid Frogs From Mexico and Central AmericaFrom EverandDescriptions of New Hylid Frogs From Mexico and Central AmericaNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- A New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasFrom EverandA New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasNo ratings yet