Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jim Fawcett CSE686 - Internet Programming Summer 2010
Jim Fawcett CSE686 - Internet Programming Summer 2010
Uploaded by
Elbert David0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views13 pagesMVC
Original Title
AspNetMVC(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMVC
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views13 pagesJim Fawcett CSE686 - Internet Programming Summer 2010
Jim Fawcett CSE686 - Internet Programming Summer 2010
Uploaded by
Elbert DavidMVC
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Jim Fawcett
CSE686 – Internet Programming
Summer 2010
What is Asp.Net MVC?
Framework for building web applications
Based on Model-View-Controller pattern
Model manages the applications data and
enforces constraints on that model.
Often accessed through persistent objects
Views are mostly passive presentations of
application state.
Views generate requests sent to a controller based
on client actions.
Controllers translate requests into actions on the
data model and generate subsequent views.
MVC Life Cycle
Clients request a named action on a specified
controller, e.g.:
http://localhost/aController/anAction
The request is routed to aController’s
anAction method.
That method decides how to handle the request,
perhaps by accessing a model’s state and
returning some information in a view.
What is a Model?
A model is a file of C# code and an associated
data store, e.g., an SQL database or XML file.
The file of C# code manages all access to the
application’s data through objects.
Linq to SQL and Linq to XML create queries into
these data stores
This can be direct
More often it is done through objects that wrap db
tables or XML files and have one public property for
each attribute column of the table.
FirstMVCDemoSu10 Model
namespace MvcApplication2.Models
{
public class FileHandler
{
public string path { get; set; }
public string[] files { get; set; }
public bool GetFiles(string pattern)
{
try
{
int pos = path.LastIndexOf("Home");
path = path.Substring(0, pos) + "Views\\Home";
files = System.IO.Directory.GetFiles(path);
return true;
}
catch { return false; }
}
}
}
What is a View?
Views are usually aspx files with only HTML
and inline code, e.g., <% … C# code here …
%>.
Code is used just to support presentation and does
no application processing.
The HTML is augmented by HTML Helpers,
provided by Asp.Net MVC that provide shortcuts
for commonly used HTML constructs.
Asp.Net MVC comes with jQuery (Javascript)
libraries to support reacting to client actions and
doing AJAX communication with the server.
FirstMVCDemoSu10 View
<%@ Page Language="C#" MasterPageFile="~/Views/Shared/Site.Master"
Inherits="System.Web.Mvc.ViewPage" %>
<asp:Content ID="aboutTitle" ContentPlaceHolderID="TitleContent" runat="server">
About Us
</asp:Content>
<asp:Content ID="aboutContent" ContentPlaceHolderID="MainContent" runat="server">
<h2>Demo Application</h2>
<%
try {
string[] files = ((MvcApplication2.Models.FileHandler)Model).files;
Response.Write("<br/>Find Files in Home Controller's Views Folder");
foreach (string file in files)
Response.Write("<br/>" + file);
string path = ((MvcApplication2.Models.FileHandler)Model).path;
System.IO.FileInfo fi = new System.IO.FileInfo(path + "\\Index.Aspx");
Response.Write("<p/>Index.Aspx Last Revised: " + fi.LastAccessTime.ToString());
}
catch { Response.Write("<p/>Error finding path or file"); }
%>
<p>
This application is intended to host a set of tutorial demos for Asp.Net MVC.
Each Tab will open a new demo example. Eventually I will segregate them into
demo categories with a controller for each category.
</p>
</asp:Content>
What is a Controller?
A controller is a C# file with controller classes
that derive from the class Controller.
A controller defines some category of processing
for the application.
Its methods define the processing details.
Routing to a controller is defined in the
Global.Asax.cs file. Its default processing is
usually what you need.
FirstMVCDemoSu10 Controller
namespace MvcApplication2.Controllers
{
[HandleError]
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewData["Message"] = "First Model-View-Controller Demos";
return View();
}
public ActionResult Form()
{
ViewData["Message"] = "Form not yet implemented";
return View();
}
// code removed here to fit on slide
public ActionResult About()
{
string path = Server.MapPath(".");
Models.FileHandler fh = new Models.FileHandler();
fh.path = path;
fh.GetFiles("*.*");
return View(fh);
}
}
}
Web Application Development
Create a new Asp.Net MVC project
Delete any part of that you don’t need
Add a controller for each category of processing
in your application:
A category is usually a few pages and db tables that
focus on some particular application area
Add methods to each controller for each request
you wish to handle.
Add views as needed for each controller action
Add Model classes to support the application
area:
Each model class has public properties that are
synchronized with data in the model db or XML file.
An Opinion
This Asp.Net MVC structure is very flexible:
You can have as many application categories as
you need, simply by adding controllers.
The controllers keep the application well
organized.
You can have as many views as you need. The
navigation is simple and provided mostly by the
MVC infrastructure, e.g., routing in Global.asax.cs.
You can have as many models as you need. Just
add classes and use Linq to access the data.
Things you need to know
LINQ – Language integrated query
Linq to XML and Linq to SQL are commonly used
by models to provide data needed by a controller
for one of its views.
Jquery – Javascript Query library
Jquery is frequently used by views to react to
client actions in the browser.
Jquery has facilities to use AJAX to retrieve small
amounts of information from the server without
loading a new view.
References
Class Text: “Pro Asp.Net MVC”
Asp.Net MVC Tutorials
http://weblogs.asp.net/scottgu/archive/2007/11/13/
asp-net-mvc-framework-part-1.aspx
http://nerddinnerbook.s3.amazonaws.com/Intro.htm
Linq:
http://dotnetslackers.com/articles/csharp/
introducinglinq1.aspx
Jquery
http://docs.jquery.com/
Tutorials:How_jQuery_Works#jQuery:_The_Basics
You might also like
- ActiveVFP DocumentationDocument18 pagesActiveVFP DocumentationthomasandriantoNo ratings yet
- Skipjack Server Application Development GuideDocument150 pagesSkipjack Server Application Development GuideMakoto MiharuNo ratings yet
- Oracle Risk Management Cloud Financial Reporting Compliance Fundamentals Sample PDFDocument30 pagesOracle Risk Management Cloud Financial Reporting Compliance Fundamentals Sample PDFsw21910No ratings yet
- MVC PresentationDocument20 pagesMVC PresentationjeffeliNo ratings yet
- ASPDocument11 pagesASPńazli AhmedNo ratings yet
- MVC 4Document79 pagesMVC 4paparos486No ratings yet
- Model Represents The Data .: MVC ArchitectureDocument49 pagesModel Represents The Data .: MVC ArchitectureHimanshu RawatNo ratings yet
- Concept and Basics: It19 - Advance ProgrammingDocument38 pagesConcept and Basics: It19 - Advance ProgrammingAidelbert SawitNo ratings yet
- MVC4 Applications Presented by QuontraSolutions QuontraSolutionsDocument11 pagesMVC4 Applications Presented by QuontraSolutions QuontraSolutionsQuontraSolutionsNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Lecture 3 TheoryDocument24 pagesWeek 2 Lecture 3 TheoryH.M. Jayed Chowdhury RabbyNo ratings yet
- Asp - Net MVCDocument20 pagesAsp - Net MVCJuan MedinaNo ratings yet
- Top 40 Most Asked ASP - Net MVC Interview Questions and Answers - Tutorial LinksDocument18 pagesTop 40 Most Asked ASP - Net MVC Interview Questions and Answers - Tutorial LinksVenkat MalepatiNo ratings yet
- Most Asked ASP - Net MVC Interview Questions and Answers C Sharp CornerDocument39 pagesMost Asked ASP - Net MVC Interview Questions and Answers C Sharp CornerLokesh RavindraNo ratings yet
- MVC ArchitectureDocument50 pagesMVC ArchitectureskakachNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ASP - NET MVC 4Document89 pagesIntroduction To ASP - NET MVC 4Ryan BaeNo ratings yet
- Florin Olariu: "Alexandru Ioan Cuza", University of Iași Department of Computer ScienceDocument45 pagesFlorin Olariu: "Alexandru Ioan Cuza", University of Iași Department of Computer ScienceGigi FloricaNo ratings yet
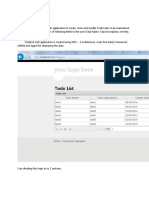
- Different Return Types of A Controller Action MethodDocument11 pagesDifferent Return Types of A Controller Action MethodBasil JacobNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ASP - NET MVC 4Document89 pagesIntroduction To ASP - NET MVC 4erraha5052100% (1)
- MVCDocument26 pagesMVCcaring clawsNo ratings yet
- JqgridDocument39 pagesJqgridmetro gNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Bean Factory and Application Context ?Document7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Bean Factory and Application Context ?RavikumarmaddiNo ratings yet
- Amit Kumar Singh ItbrainshapersDocument54 pagesAmit Kumar Singh ItbrainshapersJean-yves LapicqueNo ratings yet
- ASP - Net MVC IntroductionDocument45 pagesASP - Net MVC IntroductionJunaid ArshadNo ratings yet
- Using C#Document11 pagesUsing C#FUN FACTZNo ratings yet
- Controller) Architecture For Beginners: Kiran DangarDocument4 pagesController) Architecture For Beginners: Kiran DangarArun BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- MVC TutorialDocument21 pagesMVC TutorialStephen Folarin OladunniNo ratings yet
- Spring and SpringMVC SlidesDocument25 pagesSpring and SpringMVC Slidesggzxc12345678910No ratings yet
- Net Mvcmusicstore Models Customer Viewbag Title CustomernameDocument14 pagesNet Mvcmusicstore Models Customer Viewbag Title Customernamepaparos486No ratings yet
- What Is MVC (Model View Controller) ?Document105 pagesWhat Is MVC (Model View Controller) ?Ronesh KumarNo ratings yet
- MVC ShivprasadDocument44 pagesMVC ShivprasadANo ratings yet
- MVC Interview Questions and AnswersDocument19 pagesMVC Interview Questions and AnswersAfra Fathima100% (1)
- JWT Unit 5Document25 pagesJWT Unit 5bansariprajapati05No ratings yet
- ASP - NET-MVC-IntroductionDocument45 pagesASP - NET-MVC-IntroductionJunaid ArshadNo ratings yet
- Laravel Application Development 2021 - 1 - CSC - 006 - SubeczDocument8 pagesLaravel Application Development 2021 - 1 - CSC - 006 - Subeczblank anonimNo ratings yet
- MVC Interview Questions PDFDocument9 pagesMVC Interview Questions PDFRAJINo ratings yet
- Answers: AnswerDocument79 pagesAnswers: AnswerShaik Mohammad HaneefNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: The MVC Programming ModelDocument19 pagesTutorial: The MVC Programming ModelArun BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- The MVC Programming ModelDocument40 pagesThe MVC Programming ModelMarcelin LukuniNo ratings yet
- Explain MVC (Model-View-Controller) in General?Document195 pagesExplain MVC (Model-View-Controller) in General?nayab.mca2008No ratings yet
- Isolation Means: Onetariga: Develop Web Application That Enables A Clean Separation of CodeDocument20 pagesIsolation Means: Onetariga: Develop Web Application That Enables A Clean Separation of Codepravallika dasariNo ratings yet
- Instructor:: Humaira WaqasDocument22 pagesInstructor:: Humaira Waqasshehryar kiyaniNo ratings yet
- FSD Module 1 NOTESDocument20 pagesFSD Module 1 NOTESkyabhaitubhinaNo ratings yet
- Florin Olariu: "Alexandru Ioan Cuza", University of Iași Department of Computer ScienceDocument51 pagesFlorin Olariu: "Alexandru Ioan Cuza", University of Iași Department of Computer ScienceGigi FloricaNo ratings yet
- Spring MVC SLIDES - 1Document78 pagesSpring MVC SLIDES - 1Prashant SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Ruby On Rails With Ajax For Development of Web ApplicationsDocument12 pagesRuby On Rails With Ajax For Development of Web ApplicationsTeklit BerihuNo ratings yet
- Model View Controller (MVC) in PHP: PatternsDocument5 pagesModel View Controller (MVC) in PHP: PatternsjloemigNo ratings yet
- What Is MVC?: View Controller ModelDocument46 pagesWhat Is MVC?: View Controller ModelreshmaitagiNo ratings yet
- MVC Interview Questions - TutorialspointDocument12 pagesMVC Interview Questions - TutorialspointANo ratings yet
- Spring MVC TutorialDocument18 pagesSpring MVC TutorialKarthikhaKVNo ratings yet
- Spring - MVC Framework TutorialDocument4 pagesSpring - MVC Framework TutorialJogu InhosNo ratings yet
- Ventsislav Popov: Developer Evangelist at MicrosoftDocument36 pagesVentsislav Popov: Developer Evangelist at MicrosoftgoonsmanNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument29 pagesPPTSubrat Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Software Architecture Flow of Control Procedural Programming Flow Business Logic Subroutines Caller'sDocument8 pagesSoftware Architecture Flow of Control Procedural Programming Flow Business Logic Subroutines Caller'sreychNo ratings yet
- MCSD Web Applications Asp Net Courseware PDFDocument133 pagesMCSD Web Applications Asp Net Courseware PDFJavier Garcia RamosNo ratings yet
- Dot Net Interview Questions and Answers PDFDocument16 pagesDot Net Interview Questions and Answers PDFSavitaDarekarNo ratings yet
- MVC PDFDocument21 pagesMVC PDFSnehasish PatraNo ratings yet
- StrutsDocument43 pagesStrutsvedicsoft100% (4)
- StrutsDocument72 pagesStrutsdibsrucNo ratings yet
- Proforma 001-2020Document25 pagesProforma 001-2020Ababsa KomatsuNo ratings yet
- Titus VavDocument46 pagesTitus VavSantiago J. ramos jrNo ratings yet
- Brazil PIX Payments - Announcement On New Functionality PDFDocument5 pagesBrazil PIX Payments - Announcement On New Functionality PDFAlmirFuncionalFI100% (1)
- Northern Region S.No Mi Code Name of The InstituteDocument32 pagesNorthern Region S.No Mi Code Name of The Institutesjindal1989No ratings yet
- OFRS Report Django SynopsisDocument31 pagesOFRS Report Django SynopsisEnlightNo ratings yet
- Manual Book SICOMA MA02250 - 1500 SDocument61 pagesManual Book SICOMA MA02250 - 1500 SSitumorang David100% (1)
- NCM Chapter SixDocument20 pagesNCM Chapter Sixdimberu yirgaNo ratings yet
- Key IIS Final VIP David Hai 1Document443 pagesKey IIS Final VIP David Hai 1Hi LightNo ratings yet
- Lab 1and2Document4 pagesLab 1and2samrath grewalNo ratings yet
- Rec Erc 78 08Document22 pagesRec Erc 78 08Jerry PellerNo ratings yet
- Forensic PhotographyDocument10 pagesForensic PhotographyAbiñon Clark Kevin T.No ratings yet
- Java Lab Assignment-4Document27 pagesJava Lab Assignment-4manasi kumbharNo ratings yet
- NFS2 640 (E) ProgrammingDocument126 pagesNFS2 640 (E) ProgrammingfirealarmtechNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Scripting - Tutorial (Avidemux)Document4 pagesTutorial Scripting - Tutorial (Avidemux)Sasa MiljkovicNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24 JSON Web Token (JWT) - FinalDocument50 pagesLecture 24 JSON Web Token (JWT) - FinalNaveed100% (1)
- Logcat 1703850153356Document6 pagesLogcat 1703850153356rifaldimahmud70No ratings yet
- Safety and Relief Products: Kunkle Models 40R/40Rl Sentinel Relief ValvesDocument2 pagesSafety and Relief Products: Kunkle Models 40R/40Rl Sentinel Relief Valvesjithin.rjn4055No ratings yet
- Scan The QR Code or Search Twinkl Art Studio in The App Store On An Ios DeviceDocument19 pagesScan The QR Code or Search Twinkl Art Studio in The App Store On An Ios DevicertruNo ratings yet
- Integrated Circuits-Basic Electronics (Presentation)Document34 pagesIntegrated Circuits-Basic Electronics (Presentation)Iqra TabassumNo ratings yet
- Transport LayerDocument55 pagesTransport LayersrinusirisalaNo ratings yet
- 02-Motors & Motor DriversDocument25 pages02-Motors & Motor DriversJO MarthenNo ratings yet
- Which One of The Following Is The BEST Definition of An Incremental DevelopmentDocument10 pagesWhich One of The Following Is The BEST Definition of An Incremental DevelopmentReem HaithamNo ratings yet
- 09TP NetflixINC AdriagaAiraDocument19 pages09TP NetflixINC AdriagaAiraDaniel LamasonNo ratings yet
- Exploiting Additional Actuators and Sensors For Nano-Positioning Robust Motion ControlDocument7 pagesExploiting Additional Actuators and Sensors For Nano-Positioning Robust Motion ControlEdward KikkenNo ratings yet
- Fleetguard New MRPDocument104 pagesFleetguard New MRPAwaish Khan100% (2)
- REFCON Vessel and Terminal Monitoring: Yes NoDocument3 pagesREFCON Vessel and Terminal Monitoring: Yes NokEWQ 865kNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Org DevelopmentDocument13 pagesCase Study - Org DevelopmentShobhnaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Contract Work Travel USA 2024Document6 pagesContract Work Travel USA 2024dilafruztursunboyeva9901No ratings yet
- Nti P/N: E-Stsm-E7: RJ45-FF Coupler (Supplied)Document1 pageNti P/N: E-Stsm-E7: RJ45-FF Coupler (Supplied)Diana LopezNo ratings yet