Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12c .Standard Costs & Variance-Analysis
12c .Standard Costs & Variance-Analysis
Uploaded by
Abhinav AshishOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12c .Standard Costs & Variance-Analysis
12c .Standard Costs & Variance-Analysis
Uploaded by
Abhinav AshishCopyright:
Available Formats
Variance Analysis
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Standard Costs
Standards are benchmarks or “norms”
for measuring performance. Two types
of standards are commonly used.
Quantity standards Cost (price)
specify how much of an standards specify
input should be used to how much should be
make a product or paid for each unit
provide a service. of the input.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Exh.
Variance Analysis Cycle
10-1
Take
Identify Receive corrective
questions explanations actions
Conduct next
Analyze period’s
variances operations
Prepare standard
Begin
cost performance
report
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Setting Standard Costs
Accountants, engineers, purchasing
agents, and production managers
combine efforts to set standards that encourage
efficient future production.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Setting Direct Material Standards
Price Quantity
Standards Standards
Final, delivered Summarized in
cost of materials, a Bill of Materials.
net of discounts.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Setting Direct Labor Standards
Rate Time
Standards Standards
Often a single Use time and
rate is used that reflects motion studies for
the mix of wages earned. each labor operation.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Setting Variable Overhead Standards
Rate Activity
Standards Standards
The rate is the The activity is the
variable portion of the base used to calculate
predetermined overhead the predetermined
rate. overhead.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Standards vs. Budgets
Are standards the A standard is a per
same as budgets? unit cost.
A budget is set for Standards are often
used when
total costs. preparing budgets.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Price and Quantity Standards
Price and quantity standards are
determined separately for two reasons:
The purchasing manager is responsible for raw
material purchase prices and the production manager
is responsible for the quantity of raw material used.
The buying and using activities occur at different times.
Raw material purchases may be held in inventory for a
period of time before being used in production.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
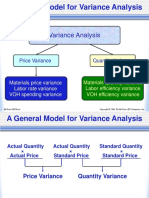
A General Model for Variance Analysis
Variance Analysis
Price Variance Quantity Variance
Difference between Difference between
actual price and actual quantity and
standard price standard quantity
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
A General Model for Variance Analysis
Variance Analysis
Price Variance Quantity Variance
Materials price variance Materials quantity variance
Labor rate variance Labor efficiency variance
VOH spending variance VOH efficiency variance
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
A General Model for Variance Analysis
Actual Quantity Actual Quantity Standard Quantity
× × ×
Actual Price Standard Price Standard Price
Price Variance Quantity Variance
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
A General Model for Variance Analysis
Actual Quantity Actual Quantity Standard Quantity
× × ×
Actual Price Standard Price Standard Price
Price Variance Quantity Variance
Actual quantity is the amount of direct
materials, direct labor, and variable
manufacturing overhead actually used.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
A General Model for Variance Analysis
Actual Quantity Actual Quantity Standard Quantity
× × ×
Actual Price Standard Price Standard Price
Price Variance Quantity Variance
Standard quantity is the standard quantity
allowed for the actual output for the period.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
A General Model for Variance Analysis
Actual Quantity Actual Quantity Standard Quantity
× × ×
Actual Price Standard Price Standard Price
Price Variance Quantity Variance
Actual price is the amount actually
paid for the for the input used.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
A General Model for Variance Analysis
Actual Quantity Actual Quantity Standard Quantity
× × ×
Actual Price Standard Price Standard Price
Price Variance Quantity Variance
Standard price is the amount that should
have been paid for the input used.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
A General Model for Variance Analysis
Actual Quantity Actual Quantity Standard Quantity
× × ×
Actual Price Standard Price Standard Price
Price Variance Quantity Variance
(AQ × AP) – (AQ × SP) (AQ × SP) – (SQ × SP)
AQ = Actual Quantity SP = Standard Price
AP = Actual Price SQ = Standard Quantity
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Material Variances Example
Glacier Peak Outfitters has the following direct
material standard for the fiberfill in its mountain
parka.
0.1 kg. of fiberfill per parka at $5.00 per kg.
Last month 210 kgs of fiberfill were purchased
and used to make 2,000 parkas. The material
cost a total of $1,029.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Material Variances Summary
Actual Quantity Actual Quantity Standard Quantity
× × ×
Actual Price Standard Price Standard Price
210 kgs. 210 kgs. 200 kgs.
× × ×
$4.90 per kg. $5.00 per kg. $5.00 per kg.
= $1,029 = $1,050 = $1,000
Price variance Quantity variance
$21 favorable $50 unfavorable
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Material Variances:
Using the Factored Equations
Materials price variance
MPV = AQ (AP - SP)
= 210 kgs ($4.90/kg - $5.00/kg)
= 210 kgs (-$0.10/kg)
= $21 F
Materials quantity variance
MQV = SP (AQ - SQ)
= $5.00/kg (210 kgs-(0.1 kg/parka 2,000 parkas))
= $5.00/kg (210 kgs - 200 kgs)
= $5.00/kg (10 kgs)
= $50 U
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Material Variances
The price variance is
computed on the entire
quantity purchased.
The quantity variance
is computed only on
the quantity used.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Responsibility for Material Variances
Materials Quantity Variance Materials Price Variance
Production Manager Purchasing Manager
The standard price is used to compute the quantity variance
so that the production manager is not held responsible for
the purchasing manager’s performance.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Labor Variances Example
Glacier Peak Outfitters has the following direct
labor standard for its mountain parka.
1.2 standard hours per parka at $10.00 per hour
Last month employees actually worked 2,500
hours at a total labor cost of $26,250 to make
2,000 parkas.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Labor Variances Summary
Actual Hours Actual Hours Standard Hours
× × ×
Actual Rate Standard Rate Standard Rate
2,500 hours 2,500 hours 2,400 hours
× × ×
$10.50 per hour $10.00 per hour. $10.00 per hour
= $26,250 = $25,000 = $24,000
Rate variance Efficiency variance
$1,250 unfavorable $1,000 unfavorable
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Labor Variances:
Using the Factored Equations
Labor rate variance
LRV = AH (AR - SR)
= 2,500 hours ($10.50 per hour – $10.00 per hour)
= 2,500 hours ($0.50 per hour)
= $1,250 unfavorable
Labor efficiency variance
LEV = SR (AH - SH)
= $10.00 per hour (2,500 hours – 2,400 hours)
= $10.00 per hour (100 hours)
= $1,000 unfavorable
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Responsibility for Labor Variances
Production managers are Mix of skill levels
usually held accountable assigned to work tasks.
for labor variances
because they can
Level of employee
influence the:
motivation.
Quality of production
supervision.
Quality of training
provided to employees.
Production Manager
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Variable Manufacturing Overhead
Variances Example
Glacier Peak Outfitters has the following direct
variable manufacturing overhead labor standard
for its mountain parka.
1.2 standard hours per parka at $4.00 per hour
Last month employees actually worked 2,500
hours to make 2,000 parkas. Actual variable
manufacturing overhead for the month was
$10,500.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Variable Manufacturing Overhead
Variances Summary
Actual Hours Actual Hours Standard Hours
× × ×
Actual Rate Standard Rate Standard Rate
2,500 hours 2,500 hours 2,400 hours
× × ×
$4.20 per hour $4.00 per hour $4.00 per hour
= $10,500 = $10,000 = $9,600
Spending variance Efficiency variance
$500 unfavorable $400 unfavorable
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Variable Manufacturing Overhead
Variances: Using Factored Equations
Variable manufacturing overhead spending variance
VMSV = AH (AR - SR)
= 2,500 hours ($4.20 per hour – $4.00 per hour)
= 2,500 hours ($0.20 per hour)
= $500 unfavorable
Variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance
VMEV = SR (AH - SH)
= $4.00 per hour (2,500 hours – 2,400 hours)
= $4.00 per hour (100 hours)
= $400 unfavorable
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Variance Analysis and
Management by Exception
Larger variances, in
How do I know dollar amount or as
which variances to a percentage of the
investigate? standard, are
investigated first.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Exh.
A Statistical Control Chart
10-9
Warning signals for investigation
Favorable Limit
• •
• • •
Desired Value
• •
Unfavorable Limit •
•
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Variance Measurements
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Advantages of Standard Costs
Management by Promotes economy
exception and efficiency
Advantages
Enhances
Simplified responsibility
bookkeeping accounting
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Potential Problems with Standard Costs
Emphasizing standards Favorable
may exclude other variances may
important objectives. be misinterpreted.
Potential
Problems
Standard cost Emphasis on
reports may negative may
not be timely. impact morale.
Continuous
Invalid assumptions improvement may
about the relationship be more important
between labor than meeting standards.
cost and output.
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
You might also like
- History of Economic Thought IDocument143 pagesHistory of Economic Thought IHailegeorgis MaruNo ratings yet
- L&T Mindtree Project PresentationDocument8 pagesL&T Mindtree Project PresentationPuneet Agarwal100% (2)
- Home Depot - Business Plan April 2015Document17 pagesHome Depot - Business Plan April 2015usergarciaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Brand in The Nonprofit Sector - Stanford Social Innovation ReviewDocument12 pagesThe Role of Brand in The Nonprofit Sector - Stanford Social Innovation ReviewGeorgianaYoungNo ratings yet
- Smoked FishDocument28 pagesSmoked FishA.R.M.Y foreverNo ratings yet
- Standard CostDocument16 pagesStandard CostRozibul BasarNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument11 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisMd AzimNo ratings yet
- 11 Edition: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument93 pages11 Edition: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinrisaNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost & VarianceDocument26 pagesStandard Cost & VarianceWaqar AhmadNo ratings yet
- StandardDocument77 pagesStandardshamsirarefin275285No ratings yet
- 8.31 - Standard CostingDocument109 pages8.31 - Standard CostingBhosx Kim100% (1)
- Standard Costs and Operating Performance MeasuresDocument70 pagesStandard Costs and Operating Performance MeasuresdianaNo ratings yet
- Spring 2022 - 09 - GN10 - Standard CostsDocument46 pagesSpring 2022 - 09 - GN10 - Standard Costsnicholas bryanNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument29 pagesStandard CostingEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Variance Analysis-Reading MaterialsDocument66 pagesVariance Analysis-Reading MaterialsSM RaselNo ratings yet
- Variance AnalysisDocument66 pagesVariance AnalysisSyed Adnan HossainNo ratings yet
- Week 11: Standard Costs and Operating Performance Measures: Chapter 11 (Page 451-465) FB2101 (2010/11 Sem B)Document91 pagesWeek 11: Standard Costs and Operating Performance Measures: Chapter 11 (Page 451-465) FB2101 (2010/11 Sem B)Javier TsangNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument62 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysishanaNo ratings yet
- 11 Standard CostingDocument109 pages11 Standard CostingrakibNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting, 13 Edition,: Standard Costs and Operating Performance MeasuresDocument17 pagesManagerial Accounting, 13 Edition,: Standard Costs and Operating Performance MeasuresAhsan Sayeed Nabeel DeproNo ratings yet
- Varince AnalysisDocument79 pagesVarince Analysisarshad mNo ratings yet
- Standard Costs and Variances II With IllustrationsDocument76 pagesStandard Costs and Variances II With IllustrationspaulalbarandoNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 NotesDocument93 pagesChap 10 NotesmarhamNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing PDFDocument143 pagesStandard Costing PDFYsabelle VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- 11 Edition: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument70 pages11 Edition: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinAdistra RifaldiNo ratings yet
- © 2015 Mcgraw-Hill Education Garrison, Noreen, Brewer, Cheng & YuenDocument110 pages© 2015 Mcgraw-Hill Education Garrison, Noreen, Brewer, Cheng & YuenVahrul DavidNo ratings yet
- GNBCY Chap12 Standard Costs and Variances With Cover PageDocument110 pagesGNBCY Chap12 Standard Costs and Variances With Cover PageNang Kit SzeNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing, Operational Performance Measures, and The Balanced ScorecardDocument69 pagesStandard Costing, Operational Performance Measures, and The Balanced ScorecardAcmad RedhoNo ratings yet
- Chap8 (E)Document101 pagesChap8 (E)Kiên Lê TrungNo ratings yet
- Variable Costing: A Tool For Management: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument40 pagesVariable Costing: A Tool For Management: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinAbed Al-Rahman SalehNo ratings yet
- 5130 - Chapter 10 Lecture - Student VersionDocument41 pages5130 - Chapter 10 Lecture - Student VersionIsaac SpoonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Standard Costs and The Balance ScorecardDocument101 pagesChapter 10 - Standard Costs and The Balance ScorecardAmy SIlverbergNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts and BehaviorsDocument41 pagesCost Concepts and BehaviorslongphungspNo ratings yet
- Standard Costs and The Balanced Scorecard: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument101 pagesStandard Costs and The Balanced Scorecard: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinSyed Ijlal HaiderNo ratings yet
- Standard Costs and The Balanced Scorecard: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument41 pagesStandard Costs and The Balanced Scorecard: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinShamittaaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Costing: Chapter NineDocument39 pagesInventory Costing: Chapter NineDio VinosaNo ratings yet
- Chap 007Document37 pagesChap 007AhsanNo ratings yet
- @PO Taken ATP Standard Costing N Variance Analysis - Pgs.40Document40 pages@PO Taken ATP Standard Costing N Variance Analysis - Pgs.40professional.ca728No ratings yet
- Variable Costing - PPT - 20231130 - 092302 - 0000Document43 pagesVariable Costing - PPT - 20231130 - 092302 - 00002230356No ratings yet
- Cost Behavior: Analysis and Use: Chapter FiveDocument60 pagesCost Behavior: Analysis and Use: Chapter Fiveayesha125865No ratings yet
- Standard Costing, Operational Performance Measures, and The Balanced ScorecardDocument60 pagesStandard Costing, Operational Performance Measures, and The Balanced ScorecardqueenfaustineeNo ratings yet
- Ch10 - SessionDocument122 pagesCh10 - SessionKow RyderNo ratings yet
- Sva - Student Copy P1Document101 pagesSva - Student Copy P1Joyce MamokoNo ratings yet
- Week 10: Standard Costs & Variance AnalysisDocument33 pagesWeek 10: Standard Costs & Variance AnalysisNizam JewelNo ratings yet
- 09 Standard CostingDocument5 pages09 Standard CostingabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Standard Costs and Variances THTDocument55 pagesStandard Costs and Variances THTHÀ LƯU HOÀNG THÚYNo ratings yet
- Cost Behavior: Analysis and Use: Chapter FiveDocument44 pagesCost Behavior: Analysis and Use: Chapter FiveBS StudioNo ratings yet
- Variable Costing: A Tool For ManagementDocument37 pagesVariable Costing: A Tool For ManagementumakantanayakNo ratings yet
- Cost Behavior: Analysis and Use: Chapter FiveDocument62 pagesCost Behavior: Analysis and Use: Chapter FiveJenny ManaladNo ratings yet
- 2 Standard Costing - DM - DLDocument60 pages2 Standard Costing - DM - DLJenika AtanacioNo ratings yet
- Variable Costing: A Tool For Management: Chapter SevenDocument37 pagesVariable Costing: A Tool For Management: Chapter SevenJavier TsangNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument10 pagesStandard Costingdharmendraparwar24No ratings yet
- Chap16-Standard Costing FOHDocument93 pagesChap16-Standard Costing FOHGeo Rublico ManilaNo ratings yet
- STRATCOSTDocument57 pagesSTRATCOSTVrix Ace MangilitNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost & Balanced Scorecard: Din Islam (Din)Document40 pagesStandard Cost & Balanced Scorecard: Din Islam (Din)ykamal7No ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument7 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisGian Carlo RamonesNo ratings yet
- Standard Costs and Operating Performance MeasuresDocument108 pagesStandard Costs and Operating Performance MeasuresCharlaign MalacasNo ratings yet
- Chap 011 Standard CostingDocument109 pagesChap 011 Standard CostingSpheros Indonesia100% (1)
- A-Variance AnalysisDocument33 pagesA-Variance AnalysisPallabNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing BCom VI SemDocument34 pagesStandard Costing BCom VI SemJay MahajanNo ratings yet
- DMMR Standard CostingDocument80 pagesDMMR Standard CostingArmanul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Dasar Akmen 4 - Variable Costing and Full CostingDocument42 pagesDasar Akmen 4 - Variable Costing and Full CostingDiandra OlivianiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Standard Costs and Variance Analysis (2017)Document37 pagesChapter 10 - Standard Costs and Variance Analysis (2017)romelover79152No ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- 12b.standard Costing XDocument18 pages12b.standard Costing XAbhinav AshishNo ratings yet
- 12a.costing MethodsDocument14 pages12a.costing MethodsAbhinav AshishNo ratings yet
- 10c.retail PricingDocument10 pages10c.retail PricingAbhinav AshishNo ratings yet
- Types of Costing: Export MerchandisingDocument11 pagesTypes of Costing: Export MerchandisingAbhinav AshishNo ratings yet
- 1.intruduction To Cost AccountingDocument13 pages1.intruduction To Cost AccountingAbhinav AshishNo ratings yet
- Unorganised Labour - Labour Law IIDocument23 pagesUnorganised Labour - Labour Law IIAman BeriwalNo ratings yet
- m2h HandbookDocument33 pagesm2h HandbookJohann DreierNo ratings yet
- Maturity Organization Level ISO 9004Document2 pagesMaturity Organization Level ISO 9004abimanyubawono100% (2)
- CSS Essay Poverty Alleviation - Complete Solved Essay (CSS Exams 2005)Document5 pagesCSS Essay Poverty Alleviation - Complete Solved Essay (CSS Exams 2005)Muhammad Gulraiz Muhammad GulraizNo ratings yet
- The Cemex WayDocument9 pagesThe Cemex Wayhassan ijazNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business & Management 1Document4 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business & Management 1Rodj Eli Mikael Viernes-IncognitoNo ratings yet
- Apparel and Footwear in South Korea (Full Market Report)Document80 pagesApparel and Footwear in South Korea (Full Market Report)vivianaliNo ratings yet
- Platts Nonferrous MetodologyDocument30 pagesPlatts Nonferrous Metodologynerolf73No ratings yet
- Financial EnvironmentDocument20 pagesFinancial EnvironmentZahidul Islam SoykotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document4 pagesChapter 9Hamayl ShaikhNo ratings yet
- What Is Industrial ConflictDocument4 pagesWhat Is Industrial Conflictcoolguys235100% (2)
- AUDCIS Problems PrelimDocument16 pagesAUDCIS Problems PrelimLian GarlNo ratings yet
- Esha Srivastava Bba M5aDocument31 pagesEsha Srivastava Bba M5adhruvpool01No ratings yet
- Master Circular - Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana - National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM)Document29 pagesMaster Circular - Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana - National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM)Vasu Ram JayanthNo ratings yet
- Petty Cash SummaryDocument1 pagePetty Cash SummaryBHCU PMNo ratings yet
- Cash Receipts Cash DisbursementDocument5 pagesCash Receipts Cash DisbursementLala BubNo ratings yet
- DEF (Luxury Lifestyle Leather) - Information Memorandum - Confidential Data HiddenDocument45 pagesDEF (Luxury Lifestyle Leather) - Information Memorandum - Confidential Data Hiddenarijit nayakNo ratings yet
- Startup GuideDocument32 pagesStartup Guidemikejablonski100% (1)
- Maximising Effectiveness: Learning From Effectiveness Case StudiesDocument70 pagesMaximising Effectiveness: Learning From Effectiveness Case StudiesPaulo CoelhoMendesNo ratings yet
- Slutsky CompensationDocument24 pagesSlutsky CompensationKhundkar Mohammad Arefin KamalNo ratings yet
- Noncurrent Asset Held For Sale Multiple Choice: A. B. C. DDocument5 pagesNoncurrent Asset Held For Sale Multiple Choice: A. B. C. Dlinkin soyNo ratings yet
- 02 - Tutorial 2 - Week 4 SolutionsDocument8 pages02 - Tutorial 2 - Week 4 SolutionsJason ChowNo ratings yet
- E Freight Handbook PDFDocument110 pagesE Freight Handbook PDFharikrishnanNo ratings yet
- REVA Electronics DT 22-Spet-22 (2239.4)Document2 pagesREVA Electronics DT 22-Spet-22 (2239.4)Swamy ChNo ratings yet
- FGFHFGHDocument2 pagesFGFHFGHMace MunchNo ratings yet