Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 2020 7.3 Microscope Calculations
4 2020 7.3 Microscope Calculations
Uploaded by
Dumbass Life Okay, let's break this down step-by-step:
* Sarah's field of view under high power is 0.4 mm (given)
* 5 bacteria fit across her field of view
* So each bacterium must be 0.4 mm / 5 = 0.08 mm across
* Sarah measured her drawing of the bacterium to be 5.6 mm
* To calculate the scale:
Scale = Drawing size / Actual size
= 5.6 mm / 0.08 mm
= 70
So the actual size of each bacterium is 0.08 mm, and the scale of Sarah's drawing is 70.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Spectrophotometric Analysis of A Two Component MixtureDocument3 pagesSpectrophotometric Analysis of A Two Component MixtureDozdi100% (11)
- Using Compound and Dissecting Microscopes ObjectivesDocument4 pagesUsing Compound and Dissecting Microscopes ObjectivesAdam LopezNo ratings yet
- Microscope Types and UseDocument23 pagesMicroscope Types and UseSabesan TNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportElisa NovakNo ratings yet
- Microscope Lab - Estimating Field DiameterDocument9 pagesMicroscope Lab - Estimating Field DiametervedreagNo ratings yet
- Microscope 2015 NOTES 2Document20 pagesMicroscope 2015 NOTES 2Rdh MnbNo ratings yet
- Microscope Skills ReviewDocument5 pagesMicroscope Skills Reviewapi-329085879No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology MicroscopeDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Microscopeapi-27463865100% (1)
- 2 Parts Function of The MicroscopeDocument40 pages2 Parts Function of The MicroscopeEmerson GongoraNo ratings yet
- Pratical 1 - MicrosDocument7 pagesPratical 1 - MicrosanthorNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Bio Elab ManualDocument5 pagesExp 1 Bio Elab ManualFATIN FARHANAH BINTI HALIDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- TemporaryDocument351 pagesTemporaryPak RisNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Measurements Laboratory Activity: Background InformationDocument4 pagesMicroscopic Measurements Laboratory Activity: Background InformationPaige EvansNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The MicroscopeDocument33 pagesIntroduction To The MicroscopecrixiamaebNo ratings yet
- Lec.2 MicroscopeDocument16 pagesLec.2 MicroscopeSahar HassanNajadNo ratings yet
- How To Correctly Use A Microscope UpdatedDocument18 pagesHow To Correctly Use A Microscope UpdatedShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- How To Correctly Use A Microscope UpdatedDocument16 pagesHow To Correctly Use A Microscope Updatedtyler.alt345No ratings yet
- Lab 2 MicrosDocument15 pagesLab 2 Microsjohn NisNo ratings yet
- How To Use A Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesHow To Use A Light MicroscopebasondesaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Calculations Related To The MicroscopeDocument7 pages3 - Calculations Related To The MicroscoperaysklineNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 For BiologyDocument5 pagesPractical 1 For BiologyWinndell DupresNo ratings yet
- 3.1 MicroscopeBasicsDocument22 pages3.1 MicroscopeBasicsJamaica Salas SuacilloNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument24 pagesMicroscopeMark Nelson OfrasioNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up: - K-W-L: MicroscopesDocument34 pagesWarm-Up: - K-W-L: MicroscopesNyajah AllaharNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Microscope: Care Parts FocusingDocument16 pagesIntroduction To The Microscope: Care Parts FocusingVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- General Biology Laboratory ModuleDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Laboratory ModuleEunice Moureen MaravillaNo ratings yet
- General Biology I Lab Manual 1 2Document12 pagesGeneral Biology I Lab Manual 1 2Jean HapinNo ratings yet
- A.M.D.G. Investigation Into Size and Scale of Microscopic TissuesDocument9 pagesA.M.D.G. Investigation Into Size and Scale of Microscopic TissueszeeNo ratings yet
- Microscope Section 2Document23 pagesMicroscope Section 2karim adelNo ratings yet
- Bio-Pr0cess Training HandoutDocument11 pagesBio-Pr0cess Training HandoutKaname KuranNo ratings yet
- How To Correctly Use A MicroscopeDocument15 pagesHow To Correctly Use A MicroscopeDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Care Parts FocusingDocument12 pagesCare Parts FocusingOmamaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 What Is A Cell?Document15 pages2.1 What Is A Cell?SITI ZAIDAH AHMADNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument2 pagesMicrosAishahNo ratings yet
- 1) Microscopy HandoutDocument4 pages1) Microscopy HandoutsadyaNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument18 pagesMicroscopeClyde AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- B1.1 MicroscopesDocument25 pagesB1.1 MicroscopesReef SalterNo ratings yet
- Microscope CalculationsDocument17 pagesMicroscope Calculationsapi-1764024810% (1)
- Lab 2 Microscopy and Biological MolecDocument18 pagesLab 2 Microscopy and Biological MolecAndrew MartiniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 2Document3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 2Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity1Document17 pagesLab Activity1Paulus VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Microscopy ReviewDocument30 pagesMicroscopy ReviewMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- CArter Mostrom - Microscope Notes NarrowDocument15 pagesCArter Mostrom - Microscope Notes NarrowCarter MostromNo ratings yet
- 2A MicrosDocument38 pages2A MicrosbrucehungNo ratings yet
- 2014S BIO153H5S Lab1 MicrosDocument9 pages2014S BIO153H5S Lab1 MicrosMichael CarnovaleNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 MicroscopeDocument21 pagesLESSON 1 MicroscopelarepancolNo ratings yet
- CP5Document17 pagesCP5Adrian Safa khouryNo ratings yet
- PH Bio Sci Activity 2Document6 pagesPH Bio Sci Activity 2Jaira ArboladoNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument22 pagesMicroscopeershjncNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Lab 3Document8 pagesMicroscopy Lab 3AhmadNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument43 pagesMicrosAlice PavesiNo ratings yet
- Observing Microorganisms Through MicroscopeDocument19 pagesObserving Microorganisms Through Microscopewmaximoff426No ratings yet
- Nosepiece, Which Allow The Selection of Objectives of Different Magnifications. TheseDocument8 pagesNosepiece, Which Allow The Selection of Objectives of Different Magnifications. Theserashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Length Measurements - Microscope Work - Cape BiologyDocument2 pagesLength Measurements - Microscope Work - Cape BiologyJade-Ann BennettNo ratings yet
- How To Use Micrometer On Microscopes: Biology 1Document7 pagesHow To Use Micrometer On Microscopes: Biology 1Rakeesh VeeraNo ratings yet
- FOV WorksheetDocument2 pagesFOV WorksheetJoshua BirmanNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1210 Lab 1 Cell BiologyDocument23 pagesBIOL 1210 Lab 1 Cell BiologymannymathNo ratings yet
- Lab 2, Microscope Calculations - Lab Manual, 22 Final VersionDocument6 pagesLab 2, Microscope Calculations - Lab Manual, 22 Final VersionIsella ShoNo ratings yet
- Microscope HandoutDocument3 pagesMicroscope HandoutvalerieNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Lab AgendaDocument2 pagesMicroscopy Lab AgendaSteve SullivanNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument4 pagesThe MicroscopeRyz DoctoraNo ratings yet
- 02 Basic-XrdDocument48 pages02 Basic-XrdsayyadmannanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PrismDocument3 pagesLesson Plan PrismPuia ChinzahNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit 1 SEM II 2021-2022Document2 pagesQuestion Bank Unit 1 SEM II 2021-2022Sanat NarangNo ratings yet
- Hollow Prism Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 CBSEDocument11 pagesHollow Prism Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 CBSERishab Mishra100% (2)
- Chapter - 7 Overall Fiber Dispersion: Multimode FibersDocument8 pagesChapter - 7 Overall Fiber Dispersion: Multimode FibersRajesh RishiNo ratings yet
- Visual Optics 1,2.......Document468 pagesVisual Optics 1,2.......henok birukNo ratings yet
- Catálogo Olympus - Microscope Comprehensive Catalog - M05E-072016 PDFDocument24 pagesCatálogo Olympus - Microscope Comprehensive Catalog - M05E-072016 PDFyudisamaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Trends WorksheetDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Trends WorksheetSHEILA MAE VILLANTESNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document208 pagesUnit 3suresh kumarNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Practice SheetDocument14 pagesRay Optics Practice SheetyashietasethiNo ratings yet
- Phy - Dpp-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument10 pagesPhy - Dpp-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsSrusti Srujanika100% (1)
- ENGG1310, 2020-2021 Second Term Assignment 4 (Due Date: 10 Apr 2021) Answer All Questions. Show All Steps of Your Derivations and ReasoningDocument4 pagesENGG1310, 2020-2021 Second Term Assignment 4 (Due Date: 10 Apr 2021) Answer All Questions. Show All Steps of Your Derivations and Reasoningkant734No ratings yet
- Science 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 2nd Quarter ReviewerjazttamNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics: Chapter #6 Optical Sources 1: The LaserDocument14 pagesOptoelectronics: Chapter #6 Optical Sources 1: The LaserMehroz FatimaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets: ScienceDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheets: ScienceBen Josiah BayotNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACT Uv 2 PrintDocument8 pagesABSTRACT Uv 2 PrintNur AsyikinNo ratings yet
- Make A Rainbow: Strand Topic Primary SOL 5.3Document6 pagesMake A Rainbow: Strand Topic Primary SOL 5.3lauraNo ratings yet
- Optical Coherence Tomography - Signal Processing and AlgorithmDocument36 pagesOptical Coherence Tomography - Signal Processing and AlgorithmRajendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Excitons - Types, Energy TransferDocument24 pagesExcitons - Types, Energy Transferroysoumyadeep2013No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Science - Light, Shadows and ReflectionsDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 6 Science - Light, Shadows and ReflectionsUshma PunatarNo ratings yet
- HCNA-Transmission Training MaterialDocument625 pagesHCNA-Transmission Training MaterialDung Phan Van100% (7)
- Chapter 2 ZyBooksDocument73 pagesChapter 2 ZyBooksDAKSH CHETAN HATHINo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 1 MicrosDocument4 pagesLab Experiment 1 Microsseyoung sonNo ratings yet
- Flow Cytometry Basic TrainingDocument56 pagesFlow Cytometry Basic TrainingLinguumNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument21 pagesAssignment IChocolaMeilleurNo ratings yet
- TECNIS Synergy Spec SheetDocument2 pagesTECNIS Synergy Spec SheetGuilherme Bender LimaNo ratings yet
- HW ch12Document15 pagesHW ch12fatima mahfoudiNo ratings yet
- Optical Mineralogy Tutorial 1Document23 pagesOptical Mineralogy Tutorial 1Istrate IsabelaNo ratings yet
4 2020 7.3 Microscope Calculations
4 2020 7.3 Microscope Calculations
Uploaded by
Dumbass Life0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views14 pages Okay, let's break this down step-by-step:
* Sarah's field of view under high power is 0.4 mm (given)
* 5 bacteria fit across her field of view
* So each bacterium must be 0.4 mm / 5 = 0.08 mm across
* Sarah measured her drawing of the bacterium to be 5.6 mm
* To calculate the scale:
Scale = Drawing size / Actual size
= 5.6 mm / 0.08 mm
= 70
So the actual size of each bacterium is 0.08 mm, and the scale of Sarah's drawing is 70.
Original Description:
Original Title
4 2020 7.3 Microscope Calculations (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Okay, let's break this down step-by-step:
* Sarah's field of view under high power is 0.4 mm (given)
* 5 bacteria fit across her field of view
* So each bacterium must be 0.4 mm / 5 = 0.08 mm across
* Sarah measured her drawing of the bacterium to be 5.6 mm
* To calculate the scale:
Scale = Drawing size / Actual size
= 5.6 mm / 0.08 mm
= 70
So the actual size of each bacterium is 0.08 mm, and the scale of Sarah's drawing is 70.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views14 pages4 2020 7.3 Microscope Calculations
4 2020 7.3 Microscope Calculations
Uploaded by
Dumbass Life Okay, let's break this down step-by-step:
* Sarah's field of view under high power is 0.4 mm (given)
* 5 bacteria fit across her field of view
* So each bacterium must be 0.4 mm / 5 = 0.08 mm across
* Sarah measured her drawing of the bacterium to be 5.6 mm
* To calculate the scale:
Scale = Drawing size / Actual size
= 5.6 mm / 0.08 mm
= 70
So the actual size of each bacterium is 0.08 mm, and the scale of Sarah's drawing is 70.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
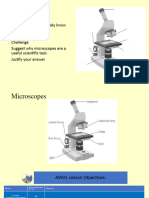
Microscopy
-How to handle a microscope
-How to focus on a specimen
-How to calculate scale and drawing size
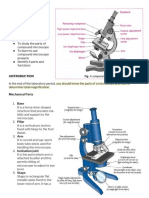
Rules of the microscope
1. ALWAYS carry with two hands
2. Store the microscope on the LOWEST power objective
lens
3. Clean with lens paper
4. NEVER use the coarse adjust knob on anything but
lowest magnification
Microscopes
•Allow us to see TINY structures only a few
micrometers long (small scale objects)
•A micro-meter is one millionth of a meter… or one
thousandth of a millimeter
If you have a specimen that is 2.4 mm long, how
many micrometers long is it?
Microscope Calculations
Magnification = power of ocular x power of
objective
Low power = 4x
Medium power = 10x
High power = 40x
(Ocular is typically 10x magnification)
Calculating Magnification
If the ocular lens magnifies 10 x, what is the total
magnification under the microscope if you use the
a) 4x objective? _________
b) 10x objective? _________
c) 40x objective? _________
How do you calculate total microscope magnification?
Estimating the Size of an Object
Field of View is a measurement of the actual diameter
of the circular area visible through a lens
Low power = 4.0 mm
Medium power = 1.6 mm
High power = 0.40 mm
What is the relationship between magnification and
field of view?
If you know the size of the field of view and how many
objects fit across that field of view, you can calculate
the size of one of the objects:
Size of object = field of view
fit number
Focusing a Specimen
1. Make sure the stage is lowered all the way, place
slide on the stage
2. Focus the specimen on the LOWEST objective
power with the coarse and then fine focus
3. NEVER TOUCH THE COARSE FOCUS AGAIN
4. Raise the magnification power, adjust ONLY with
the fine focus
40X magnified
Estimating size
•Know your field of view
•Look at ONE specimen on your slide
•How much of your field of view does it take up?
1/5? (fit # = 5)
•If you specimen is 1/5 the field of view, and your
field of view is 1.6 mm wide (medium power)
•How big is your specimen?
Scale of diagram/drawing
Scale = drawing size
actual size
Note: Measure consistently, comparing the same
features under the microscope as in your drawing.
Also, same units!!
Estimating the Size of A Drawing
You will draw/diagram specimens you see under the
microscope
There are rules for making a formal biological drawing
Once you have drawn your specimen, you must record
on your drawing the scale (magnification) of the
drawing
Observing a specimen - diagram
1. Select ONE specimen to draw
2. Draw nice & Big
3. NO shading & NO field of view circle
4. Line labels up on the right
5. Write the title at the bottom
6. In the bottom left corner, write the magnification of
the microscope, and the total magnification of the
drawing
Example:
Sarah makes a drawing of her bacterium and
measures it to be 5.6 mm across. Five bacteria
will fit across her field of view when she is
viewing it under high power. Calculate the actual
size and scale of her drawing.
You might also like
- Spectrophotometric Analysis of A Two Component MixtureDocument3 pagesSpectrophotometric Analysis of A Two Component MixtureDozdi100% (11)
- Using Compound and Dissecting Microscopes ObjectivesDocument4 pagesUsing Compound and Dissecting Microscopes ObjectivesAdam LopezNo ratings yet
- Microscope Types and UseDocument23 pagesMicroscope Types and UseSabesan TNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportElisa NovakNo ratings yet
- Microscope Lab - Estimating Field DiameterDocument9 pagesMicroscope Lab - Estimating Field DiametervedreagNo ratings yet
- Microscope 2015 NOTES 2Document20 pagesMicroscope 2015 NOTES 2Rdh MnbNo ratings yet
- Microscope Skills ReviewDocument5 pagesMicroscope Skills Reviewapi-329085879No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology MicroscopeDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Microscopeapi-27463865100% (1)
- 2 Parts Function of The MicroscopeDocument40 pages2 Parts Function of The MicroscopeEmerson GongoraNo ratings yet
- Pratical 1 - MicrosDocument7 pagesPratical 1 - MicrosanthorNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Bio Elab ManualDocument5 pagesExp 1 Bio Elab ManualFATIN FARHANAH BINTI HALIDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- TemporaryDocument351 pagesTemporaryPak RisNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Measurements Laboratory Activity: Background InformationDocument4 pagesMicroscopic Measurements Laboratory Activity: Background InformationPaige EvansNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The MicroscopeDocument33 pagesIntroduction To The MicroscopecrixiamaebNo ratings yet
- Lec.2 MicroscopeDocument16 pagesLec.2 MicroscopeSahar HassanNajadNo ratings yet
- How To Correctly Use A Microscope UpdatedDocument18 pagesHow To Correctly Use A Microscope UpdatedShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- How To Correctly Use A Microscope UpdatedDocument16 pagesHow To Correctly Use A Microscope Updatedtyler.alt345No ratings yet
- Lab 2 MicrosDocument15 pagesLab 2 Microsjohn NisNo ratings yet
- How To Use A Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesHow To Use A Light MicroscopebasondesaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Calculations Related To The MicroscopeDocument7 pages3 - Calculations Related To The MicroscoperaysklineNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 For BiologyDocument5 pagesPractical 1 For BiologyWinndell DupresNo ratings yet
- 3.1 MicroscopeBasicsDocument22 pages3.1 MicroscopeBasicsJamaica Salas SuacilloNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument24 pagesMicroscopeMark Nelson OfrasioNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up: - K-W-L: MicroscopesDocument34 pagesWarm-Up: - K-W-L: MicroscopesNyajah AllaharNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Microscope: Care Parts FocusingDocument16 pagesIntroduction To The Microscope: Care Parts FocusingVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- General Biology Laboratory ModuleDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Laboratory ModuleEunice Moureen MaravillaNo ratings yet
- General Biology I Lab Manual 1 2Document12 pagesGeneral Biology I Lab Manual 1 2Jean HapinNo ratings yet
- A.M.D.G. Investigation Into Size and Scale of Microscopic TissuesDocument9 pagesA.M.D.G. Investigation Into Size and Scale of Microscopic TissueszeeNo ratings yet
- Microscope Section 2Document23 pagesMicroscope Section 2karim adelNo ratings yet
- Bio-Pr0cess Training HandoutDocument11 pagesBio-Pr0cess Training HandoutKaname KuranNo ratings yet
- How To Correctly Use A MicroscopeDocument15 pagesHow To Correctly Use A MicroscopeDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Care Parts FocusingDocument12 pagesCare Parts FocusingOmamaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 What Is A Cell?Document15 pages2.1 What Is A Cell?SITI ZAIDAH AHMADNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument2 pagesMicrosAishahNo ratings yet
- 1) Microscopy HandoutDocument4 pages1) Microscopy HandoutsadyaNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument18 pagesMicroscopeClyde AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- B1.1 MicroscopesDocument25 pagesB1.1 MicroscopesReef SalterNo ratings yet
- Microscope CalculationsDocument17 pagesMicroscope Calculationsapi-1764024810% (1)
- Lab 2 Microscopy and Biological MolecDocument18 pagesLab 2 Microscopy and Biological MolecAndrew MartiniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 2Document3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 2Shela Lebasnon CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity1Document17 pagesLab Activity1Paulus VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Microscopy ReviewDocument30 pagesMicroscopy ReviewMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- CArter Mostrom - Microscope Notes NarrowDocument15 pagesCArter Mostrom - Microscope Notes NarrowCarter MostromNo ratings yet
- 2A MicrosDocument38 pages2A MicrosbrucehungNo ratings yet
- 2014S BIO153H5S Lab1 MicrosDocument9 pages2014S BIO153H5S Lab1 MicrosMichael CarnovaleNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 MicroscopeDocument21 pagesLESSON 1 MicroscopelarepancolNo ratings yet
- CP5Document17 pagesCP5Adrian Safa khouryNo ratings yet
- PH Bio Sci Activity 2Document6 pagesPH Bio Sci Activity 2Jaira ArboladoNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument22 pagesMicroscopeershjncNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Lab 3Document8 pagesMicroscopy Lab 3AhmadNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument43 pagesMicrosAlice PavesiNo ratings yet
- Observing Microorganisms Through MicroscopeDocument19 pagesObserving Microorganisms Through Microscopewmaximoff426No ratings yet
- Nosepiece, Which Allow The Selection of Objectives of Different Magnifications. TheseDocument8 pagesNosepiece, Which Allow The Selection of Objectives of Different Magnifications. Theserashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Length Measurements - Microscope Work - Cape BiologyDocument2 pagesLength Measurements - Microscope Work - Cape BiologyJade-Ann BennettNo ratings yet
- How To Use Micrometer On Microscopes: Biology 1Document7 pagesHow To Use Micrometer On Microscopes: Biology 1Rakeesh VeeraNo ratings yet
- FOV WorksheetDocument2 pagesFOV WorksheetJoshua BirmanNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1210 Lab 1 Cell BiologyDocument23 pagesBIOL 1210 Lab 1 Cell BiologymannymathNo ratings yet
- Lab 2, Microscope Calculations - Lab Manual, 22 Final VersionDocument6 pagesLab 2, Microscope Calculations - Lab Manual, 22 Final VersionIsella ShoNo ratings yet
- Microscope HandoutDocument3 pagesMicroscope HandoutvalerieNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Lab AgendaDocument2 pagesMicroscopy Lab AgendaSteve SullivanNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument4 pagesThe MicroscopeRyz DoctoraNo ratings yet
- 02 Basic-XrdDocument48 pages02 Basic-XrdsayyadmannanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PrismDocument3 pagesLesson Plan PrismPuia ChinzahNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit 1 SEM II 2021-2022Document2 pagesQuestion Bank Unit 1 SEM II 2021-2022Sanat NarangNo ratings yet
- Hollow Prism Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 CBSEDocument11 pagesHollow Prism Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 CBSERishab Mishra100% (2)
- Chapter - 7 Overall Fiber Dispersion: Multimode FibersDocument8 pagesChapter - 7 Overall Fiber Dispersion: Multimode FibersRajesh RishiNo ratings yet
- Visual Optics 1,2.......Document468 pagesVisual Optics 1,2.......henok birukNo ratings yet
- Catálogo Olympus - Microscope Comprehensive Catalog - M05E-072016 PDFDocument24 pagesCatálogo Olympus - Microscope Comprehensive Catalog - M05E-072016 PDFyudisamaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Trends WorksheetDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Trends WorksheetSHEILA MAE VILLANTESNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document208 pagesUnit 3suresh kumarNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Practice SheetDocument14 pagesRay Optics Practice SheetyashietasethiNo ratings yet
- Phy - Dpp-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument10 pagesPhy - Dpp-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsSrusti Srujanika100% (1)
- ENGG1310, 2020-2021 Second Term Assignment 4 (Due Date: 10 Apr 2021) Answer All Questions. Show All Steps of Your Derivations and ReasoningDocument4 pagesENGG1310, 2020-2021 Second Term Assignment 4 (Due Date: 10 Apr 2021) Answer All Questions. Show All Steps of Your Derivations and Reasoningkant734No ratings yet
- Science 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 2nd Quarter ReviewerjazttamNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics: Chapter #6 Optical Sources 1: The LaserDocument14 pagesOptoelectronics: Chapter #6 Optical Sources 1: The LaserMehroz FatimaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets: ScienceDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheets: ScienceBen Josiah BayotNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACT Uv 2 PrintDocument8 pagesABSTRACT Uv 2 PrintNur AsyikinNo ratings yet
- Make A Rainbow: Strand Topic Primary SOL 5.3Document6 pagesMake A Rainbow: Strand Topic Primary SOL 5.3lauraNo ratings yet
- Optical Coherence Tomography - Signal Processing and AlgorithmDocument36 pagesOptical Coherence Tomography - Signal Processing and AlgorithmRajendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Excitons - Types, Energy TransferDocument24 pagesExcitons - Types, Energy Transferroysoumyadeep2013No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Science - Light, Shadows and ReflectionsDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 6 Science - Light, Shadows and ReflectionsUshma PunatarNo ratings yet
- HCNA-Transmission Training MaterialDocument625 pagesHCNA-Transmission Training MaterialDung Phan Van100% (7)
- Chapter 2 ZyBooksDocument73 pagesChapter 2 ZyBooksDAKSH CHETAN HATHINo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 1 MicrosDocument4 pagesLab Experiment 1 Microsseyoung sonNo ratings yet
- Flow Cytometry Basic TrainingDocument56 pagesFlow Cytometry Basic TrainingLinguumNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument21 pagesAssignment IChocolaMeilleurNo ratings yet
- TECNIS Synergy Spec SheetDocument2 pagesTECNIS Synergy Spec SheetGuilherme Bender LimaNo ratings yet
- HW ch12Document15 pagesHW ch12fatima mahfoudiNo ratings yet
- Optical Mineralogy Tutorial 1Document23 pagesOptical Mineralogy Tutorial 1Istrate IsabelaNo ratings yet