Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Journal: All Transactions Recorded in Books of Business Is From Business Point of View
Journal: All Transactions Recorded in Books of Business Is From Business Point of View
Uploaded by
incredible me0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views23 pagesOriginal Title
JOURNAL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views23 pagesJournal: All Transactions Recorded in Books of Business Is From Business Point of View
Journal: All Transactions Recorded in Books of Business Is From Business Point of View
Uploaded by
incredible meCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 23
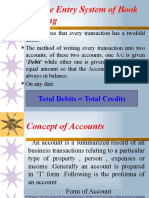
JOURNAL
All transactions recorded in books of
business is from business point of
view
Journal
• JOUR (French word) daily records
• It is a book of accounts
• Journalising – the process of recording
transactions in journal
Features & Functions & Advantages (ledger)
1. Book of original entry :- All the business transactions r recorded /copied for the first time from a source
document /memorandum / waste book (maintenance not necessary & useful to organise a journal) /
when they take place . This minimise omission of transaction in ledger
2. Book of primary/original entry [ Professor Carter] All the business transactions recorded in journal r
subsequently transferred to ‘ledger’ [principle book of accounts] . Hence journal provides basis for
posting into ledger conveniently
3. Daily Accounting Record :- All the business transactions of each day r recorded in the journal on the same
day .
4. Chronological order :- All the business transactions r recorded in date wise order which helps to locate a
particular transaction when required
5. Double entry system :- All the business transactions r classified into credit & debit according to
principles of double entry system of book keeping which helps in their correct posting in ledger
6. Journal Entry :- Business transactions when recorded in journal r called JOURNAL ENTRY .
1 – simple journal entry - a single journal entry
2 – compound journal entry – a single journal entry capable of recording
more than 1 business transactions involving more than 2 accounts .
Eg- opening entry
7. Individual Identity :- journal maintains the identity of each transaction on permanent basis & provides
a complete picture of the same in 1 entry along with amount of each transaction
8. Narration :- it should be short , complete , clear . Each entry in journal is followed by a brief explanation
of the transactions. It helps to know the reason of entry or why particular A/C was Dr. or Cr. In future&
helps in posting into ledger without any explanation
9. Journal facilitates cross checking of ledger accounts in case a trial balance does not agree (with help of
L.F column )
Limitations
1. Sub –journal :- When size of business increases, the no. Of transaction
is large , it become bulky & voluminous to record all the transactions in
Journal . Hence Journal is sub divided into no. of Sub – journals -
special purpose subsidiary books / books of original entry . Each type
of transaction is recorded in separate subsidiary book according to the
need of business. Eg – cash book , journal proper etc
2. Repetitive posting labour :- many transactions r repetitive in nature
which involve debiting & crediting same accounts time & again when
recorded in journal leading to Repetitive posting labour .
3. Cash book :- cash transactions need not to be recorded in journal as
they r recorded in separate book – cash book to ascertain cash balance
everyday
4. Journal does not provide required information on prompt basis
Format of journal
DATE PARTICULARS L.F - Ledger folio Amount
Dr. (Rs)
Amount
Cr. (Rs)
[2022]
The year ----- A/C _____________Dr. All entries from journal r later Addebi
& month To ----A/C posted into ledger a/c . tare &
is written (Being -----(narration)) The page / folio number of ledger debere
only once _____(end line)________ A/C where the posting has been the
made from the journal is recorded verb
forms
in L.F column of journal . of
Advantages :- debit
1. This column shows whether an (Dr.) in
entry has been posted or not , Italian
no page no. means it has not & latin
been posted to ledger so far langua
2. Understanding & checking ge
ledger posting at a glance in
future
3. Journal facilitates cross
checking of ledger accounts in
case a trial balance does not
agree with help of L.F column
Steps of Journalising
• Analyse A/C involved in journal entry
• Apply rules ( modern & traditional approach )
• Do totalling & Total Dr. = Total Cr. . Dr. & Cr.
Terms represent both favourable (increase) &
unfavourable (decrease) depending upon nature
of A/C
• C/F (carried forward) – written at end of page
• B/F (brought forward) – written at start of page
Rules of Credit & Debit (Journalising )
• MODERN /AMERICAN APPROACH :-
1. Assets A/C (A)
increase (i) – Debit (Dr.)
decrease (d) – Credit (Cr.)
2. Liabilities A/C (L)
increase –Cr.
decrease – Dr.
3. Losses /Expense / Taxes A/C (E)
increase –Dr.
decrease – Cr.
4. Revenue / Income A/C (I)
increase –Cr.
decrease – Dr.
5. Capital / Owner’s Equity A/C
increase –Cr.
decrease – Dr.
Personal Natural Real Tangible
ENGLISH / TRADITIONAL
APPROACH :- Artificial Intangible
( double entry system ) Representative
Nominal
Impersonal
• ENGLISH / TRADITIONAL APPROACH :-
1. Personal A/C – Dr. the receiver It is not necessary to mention A/C
Cr. the giver after personal accounts
(i) Natural – individual A/C . Eg- mohan , capital , drawings , debtor , creditor A/C
(ii) Artificial – firm/company/institution/bank A/C .
(iii) Representative – p/p (prepaid) expenses , o/s (outstanding) expenses , Accrued (earned
but not received) income , pre received income , unearned (not by employment ) income
2. Impersonal A/C –
With the addition of prefix / suffix ,
I- Real A/C (properties) - Dr. What comes in
Nominal A/C Representative A/C
Cr. What goes out
(i) Tangible – it has monetary value & can be touched , felt , measured , purchased , sold .
Eg- cash , stock , furniture ,machinery, land , building A/C
(ii) Intangible – it has monetary value & can’t be touched, felt, measured, purchased ,sold .
Eg- goodwill , patents , copyrights , trademarks A/C
II – Nominal A/C (expenses& incomes ) - Dr. All expenses/losses – Eg : salaries , rent ,
discount allowed, bad debts , advertisement , audit fees , repair , bank charges , purchase ,
purchase return
Cr. All income / gain - Eg: commission , interest ,
discount received , sales , sales return
Opening entry
1. Ravi started a business with Rs 2,00,000 .
A – Cash A/C – i – Dr
L – Capital A/C –i – Cr
2. Furniture / Machinery purchased for 10,000
A – Cash A/C – d– Cr
A– Furniture Machinery A/C –i – Dr
3. Paid salary /wages/advertisement/rent
expenses to Gopal 500
A – Cash A/C – d– Cr
E – salary /wages/advertisement /rent A/C –i
Dr
4. Received commission / interest 500
A – cash A/C – i– Dr
I – commission / / interest A/C –i – Cr
Journal of Ravi
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
[2022] F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
1 June Cash A/C ___________________________Dr. 2,00,000
To Capital A/C 2,00,000
(Being Ravi started a business with Rs 2,00,000 )
______________________________________________
2 June Furniture A/C ___________________________Dr. 10,000
Machinery A/C ___________________________Dr. 10,000
To Cash A/C 20,000
(Being Furniture /Machinery purchased for 10,000)
______________________________________________
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
[2022] F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
6 June wages A/C ___________________________Dr 500
salary A/C ___________________________Dr 500
advertisement A/C ____________________Dr 500
rent A/C __________________________Dr 500
To Cash A/C 2000
(Being Paid salary /wages/advertisement/rent expenses
to Gopal 500)
______________________________________________
7 June Cash A/C ___________________________Dr 1000
To commission A/C 500
To interest A/C 500
(Being Received commission / interest 500)
______________________________________________
1. Paid into bank for opening a current A/C 20000
A – Cash A/C – d – Cr
A – Bank A/C – i – Dr
2. Placed a fixed deposit A/C by bank by transferring from current A/C 20000
A – fixed asset A/C – i – Dr
A – bank A/C – d– Cr
3. Withdraw from bank for personal/private use 1,000
A – bank A/C – d– Cr
E – Drawings A/C –i – Dr
4. Withdraw from bank 1,000
A – Cash A/C – i – Dr
A – Bank A/C – d – Cr
5. Withdraw cash for personal/private use 1,000
A – Cash A/C – d– Cr
E – Drawings A/C –i – Dr /
L – Capital A/C – d –Dr
6. Paid life insurance premium by cheque 1000
A – Bank A/C – d– Cr
E– Drawings A/C –i – Dr
7. Paid insurance premium by cheque 1000
A – Bank A/C – d– Cr
E– insurance A/C –i – Dr
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
[2022] F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
6 June bank A/C ___________________________Dr 20000
To Cash A/C 20000
(Being Paid into bank for opening a current A/C 20000 )
______________________________________________
6 June fixed deposit A/C ___________________________Dr 20000
To bank A/C 20000
(Being Placed a fixed deposit A/C by bank by transferring
from current A/C 20000 )
______________________________________________
3 June Drawings A/C ____________________Dr. 1,000
To bank A/C 1,000
(Being Withdraw from bank for personal/private use
1,000 )
______________________________________________
3 June Cash A/C ____________________Dr. 1,000
To bank A/C 1,000
(Being Withdraw from bank 1,000)
______________________________________________
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
[2022] F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
3 June Drawings A/C / Capital A/C ____________________Dr. 1,000
To Cash A/C 1,000
(Being Withdraw cash for personal use 1,000 )
______________________________________________
4 June Drawings A/C / ____________________________Dr. 1,000
To bank A/C 1,000
(Being Paid life insurance premium by cheque 1000)
______________________________________________
5 June insurance A/C / __________________________Dr. 1,000
To bank A/C 1,000
(Being Paid insurance premium by cheque 1000 )
______________________________________________
Purchase = expense
1. Goods purchased for 40,000 / cash purchase E – Purchase A/C –i – Dr
A – Cash A/C – d– Cr 7. Returned goods to chavi of the list price of
E – Purchase A/C –i – Dr 2000 [ 1700] / returned goods to creditor
2. Goods purchased for 40,000 from Shankar / along with td
credit purchase L – Chavi A/C – d – Dr
L – Shankar A/C – i – Cr E – Purchase return A/C –d– Cr
E – Purchase A/C –i – Dr 8. Purchased goods from mohit of the list price
3. Paid cash to Shankar 8,000 / paid cash to of 20000 at 15% trade discount [ 20000 –
creditor 3000 = 17000 ] & 10% CD credit purchase
A – Cash A/C – d– Cr along with td & cd
L – Shankar A/C – d – Dr E – Purchase A/C –i – Dr
4. Goods returned to Shankar 10,000 / L – mohit A/C – i – Cr
returned goods to creditor I – Discount Received A/C –i – Cr
L – Shankar A/C – d – Dr 9. Purchase goods from harsh of the list price of
E – Purchase Return A/C –d– Cr 20000 at 15% trade discount [ 20000 – 3000
5. Paid cash to Shankar 20,000 in full settlement = 17000 ] & 10% CD. Done half payment
of 22,000 (CD) / paid cash to creditor in full immediately , half by cheque & half by cash
settlement with cd (6800) credit / cash / cheque purchase
A – Cash A/C – d– Cr along with td & cd on x paisa (percent)
I – Discount Received A/C –i – Cr L– harsh A/C – i– Cr
L – Shankar A/C – d – Dr E – purchase A/C–i – Dr
6. Purchased goods from chavi of the list price A – Cash A/C –d– Cr
of 20000 at 15% trade discount [ 20000 – A – Bank A/C - d– Cr
3000 = 17000 ] / credit purchase along with I – Discount received A/C –i – Cr
td
L – Chavi A/C – i – Cr
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
1 July Purchase A/C ________________________Dr 40,000
To cash A/C 40,000
(Being Goods purchased for 40,000)
_______________________________________________
2 July Purchase A/C ________________________Dr 40,000
To Shankar A/C 40,000
(Being Goods purchased for 40,000 from Shankar )
_______________________________________________
3 July Shankar A/C ________________________Dr 8,000
To cash A/C 8,000
(Being Paid cash to Shankar 8,000 )
_______________________________________________
4 July Shankar A/C ________________________Dr 10,000
To Purchase Return A/C 10,000
(Being Goods returned to Shankar 10,000)
_______________________________________________
5 July Shankar A/C ________________________Dr 22,000
To cash A/C 2,000
To Discount Received A/C 20,000
(Being Paid cash to Shankar 20,000 & Discount Received
of 2,000)
_______________________________________________
C/F 1,20,000 1,20,000
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
B/F 1,20,000 1,20,000
6 July Purchase A/C ___________________________Dr 17000
To Chavi A/C 17000
(Being Purchased goods from chavi of the list price of
20000 at 15% trade discount )
_______________________________________________
7 July Chavi A/C ___________________________Dr 1700
To Purchase return A/C 1700
(Being Returned goods to chavi of the list price of 2000 )
_______________________________________________
8 July Purchase A/C ___________________________Dr 17000
To mohit A/C 15300
To Discount Received A/C 1700
(Being Purchased goods from mohit of the list price of
20000 at 15% trade discount [ 20000 – 3000 = 17000 ] &
10% CD)
_______________________________________________
9 July Purchase A/C ___________________________Dr 17000
To harsh A/C 8500
To Discount Received A/C 850
To cash A/C 3825
To bank A/C 3825
(Being Purchase goods from harsh of the list price of
20000 at 15% trade discount & 10% CD. Done half
payment immediately , half by cheque & half by cash
Sales = income
1. Goods sold for 30,000 / cash sales 8. Sold goods to sohan of the list price of 20000 at
A – Cash A/C – i– Dr 15% trade discount [ 20000 – 3000 = 17000 ] & 10%
I – Sales A/C –i – Cr CD / credit sales along with td & cd
2. Goods sold for 30,000 to meena / credit sales A – sohan A/C – i– Dr
A – meena A/C – i– Dr E – Discount Allowed A/C –i – Dr
I – Sales A/C –i – Cr I – Sales A/C –i – Cr
3. Received cash from meena 15,000 / received cash 9. Sold goods to harsh of the list price of 20000 at 15%
from debtor trade discount [ 20000 – 3000 = 17000 ] & 10% CD.
A – meena A/C – d– Cr Harsh did 40% payment immediately half by cheque
A – Cash A/C – i – Dr & half by cash (6800) credit / cash / cheque sales
4. Meena returned goods 1,000 / goods returned by along with td & cd on x paisa (percent)
debtor A – harsh A/C – i– Dr
A – meena A/C –d– Cr E – Discount Allowed A/C –i – Dr
I – Sales Return A/C –d– Dr A – Cash A/C – i– Dr
A – Bank A/C – i– Dr
5. Received cash from meena 12000 in settlement of I – Sales A/C –i – Cr
14000 (CD) / received cash from debtor in full
settlement with cd 10.Goods sold for 40,000 out of this 30000 deposited
A – meena A/C – d– Cr in bank
A – Cash A/C – i – Dr A – Cash A/C – i– Dr
E – Discount Allowed A/C –i – Dr A – Bank A/C - i– Dr
E – Purchase A/C –d– Cr
6. Sold goods to mohan of the list price of 20000 at
15% trade discount [ 20000 – 3000 = 17000 ] / 11.Sold goods to harsh of the list price of 20000 at 15%
credit sales along with td trade discount [ 20000 – 3000 = 17000 ] & 10% CD
A – mohan A/C – i– Dr if payment is received within 10 days . She paid half
I – Sales A/C –i – Cr the amount within 6 days & 30% of remainder
within 12 days [ 3 entry]
7. Mohan returned goods of the list price of 2000
[ 1700] / goods returned by debtor along with td 12.Sold goods to kanika 10000at 20% profit , 10%
A – mohan A/C – d– Cr td,5% cd . She paid 40% payment immediately by
I – Sales return A/C –d – Dr cheque
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
1 Aug Cash A/C ___________________________Dr 30,000
To Sales A/C 30,000
(Being Goods sold for 30,000 )
______________________________________________
2 Aug meena A/C ___________________________Dr 30,000
To Sales A/C 30,000
(Being Goods sold for 30,000 to meena)
______________________________________________
3 Aug Cash A/C ___________________________Dr 15,000
To meena A/C 15,000
(Being Received cash from meena 15,000)
______________________________________________
4 Aug Sales Return A/C ___________________________Dr 1,000
To meena A/C 1,000
(Being Meena returned goods 1,000)
______________________________________________
5 Aug Discount Allowed A/C ________________________Dr 2,000
Cash A/C _________________________________Dr 12,000
To Meena A/C 14,000
(Being Received cash from meena 12000 & Discount
Allowed 14000)
______________________________________________
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
6 Aug Mohan A/C ___________________________Dr 17000
To sales A/C 17000
(Being Sold goods to mohan of the list price of 20000 at
15% trade discount)
_______________________________________________
7 Aug Sales return A/C ___________________________Dr 17000
To Mohan A/C 17000
(Being Mohan returned goods of the list price of 2000 )
_______________________________________________
8 Aug Sohan A/C ___________________________Dr 17000
Discount Allowed A/C ______________________Dr. 1700
To Sales A/C 15300
(Being Sold goods to sohan of the list price of 20000 at
15% trade discount [ 20000 – 3000 = 17000 ] & 10% CD)
_______________________________________________
9 Aug Cash A/C ___________________________Dr 3060
bank A/C ___________________________Dr 3060
Harsh A/C ___________________________Dr 10200
Discount Allowed A/C ______________________Dr. 680
To Sales A/C 17000
(Being Sold goods to harsh of the list price of 20000 at
15% trade discount & 10% CD. Harsh did 40% payment
immediately half by cheque & half by cash
_______________________________________________
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
10 Aug Cash A/C ___________________________Dr 10000
bank A/C ___________________________Dr 30000
To Sales A/C 40000
(Being Goods sold for 40,000 , 30000 deposited in bank )
______________________________________________
11 Aug Sudha A/C ________________________Dr 17000
To sales A/C
(Being Sold goods to harsh of the list price of 20000 at 17000
15% trade discount (17000))
______________________________________________
17 Aug Discount Allowed A/C ________________________Dr 850
Cash A/C _________________________________Dr 7650
To Harsh A/C 8500
(10% CD if payment is received within 10 days . She paid
half the amount within 6 days & 30% of remainder within
12 days )
______________________________________________
23 Aug Cash A/C _________________________________Dr 2550
To Harsh A/C 2550
(30% of remainder within 12 days )
______________________________________________
DATE PARTICULARS L. Amount Amount
F Dr. (Rs) Cr. (Rs)
10 Aug Discount Allowed A/C ___________________________Dr 216
bank A/C ___________________________Dr 4104
kanika A/C ____________________________Dr. 6480
To Sales A/C 10800
(Being Sold goods to kanika 10000at 20% profit , 10%
td,5% cd . She paid 40% payment immediately by cheque )
______________________________________________
11 Aug Sudha A/C ________________________Dr 17000
To sales A/C
(Being Sold goods to harsh of the list price of 20000 at 17000
15% trade discount (17000))
______________________________________________
17 Aug Discount Allowed A/C ________________________Dr 850
Cash A/C _________________________________Dr 7650
To Harsh A/C 8500
(10% CD if payment is received within 10 days . She paid
half the amount within 6 days & 30% of remainder within
12 days )
______________________________________________
23 Aug Cash A/C _________________________________Dr 2550
To Harsh A/C 2550
(30% of remainder within 12 days )
______________________________________________
You might also like
- 8 Lakh All India Online Seller Database Price: Rs. 2030/-OnlyDocument50 pages8 Lakh All India Online Seller Database Price: Rs. 2030/-OnlySudhanshu Goyal0% (1)
- Wells Fargo Convertible Bonds Case AnalysisDocument8 pagesWells Fargo Convertible Bonds Case AnalysisMikhail Parmar0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Problems and SolutionDocument19 pagesChapter 2 Problems and SolutionSaidurRahaman100% (1)
- Acct 4Document5 pagesAcct 4Annie RapanutNo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting in Simlified MannerDocument15 pagesBasics of Accounting in Simlified Mannerricky gargNo ratings yet
- Financial-Accounting-Analysis. Dec22Document11 pagesFinancial-Accounting-Analysis. Dec22Harish KumarNo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting Till Balance SheetDocument39 pagesBasics of Accounting Till Balance Sheetjayti desaiNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument20 pagesUnit IinamianNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Finance Assignment Sem 1Document12 pagesFinancial Accounting and Finance Assignment Sem 1missmanju4uNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Analysis 4cm 238Document12 pagesFinancial Accounting Analysis 4cm 238Yatharth NarangNo ratings yet
- Befa Unit 345 Mid CompletedDocument18 pagesBefa Unit 345 Mid Completedsvkr00001No ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE 4thDocument3 pagesSUMMATIVE 4thCattleya78% (9)
- BY Mr. M. Ijaya AgunathanDocument67 pagesBY Mr. M. Ijaya Agunathandeepakarora201188100% (1)
- 2 Book Keeping - AFB Module-BDocument30 pages2 Book Keeping - AFB Module-Bwaste mailNo ratings yet
- Financial Management & Cost Accounting: Lesson 6 Introduction To JournalDocument4 pagesFinancial Management & Cost Accounting: Lesson 6 Introduction To JournalAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument3 pagesFinancial Accountingjayprakash singhNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting & Analysis-1Document10 pagesFinancial Accounting & Analysis-1Abhishek JhaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and AnalysisDocument9 pagesFinancial Accounting and AnalysisYT MotivationNo ratings yet
- 1 The Accounting Equation Accounting Cycle Steps 1 4Document6 pages1 The Accounting Equation Accounting Cycle Steps 1 4Jerric CristobalNo ratings yet
- Far Chapter 5Document39 pagesFar Chapter 5Danica TorresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Analyzing Recording TransactionsDocument6 pagesLesson 1 Analyzing Recording TransactionsklipordNo ratings yet
- Handouts Chapter 4 56 7 CombinedDocument21 pagesHandouts Chapter 4 56 7 CombinedShane Khezia Abriol BaclayonNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Ledger Trial Balance and Bank Reconciliation Statement 02 PDFDocument30 pagesPreparation of Ledger Trial Balance and Bank Reconciliation Statement 02 PDFzaya sarwarNo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument14 pagesFinancial AccountingUmesh SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Tai Lieu Ke Toan - Docx Khanh.Document20 pagesTai Lieu Ke Toan - Docx Khanh.copmuopNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and AnalysisDocument8 pagesFinancial Accounting and Analysisdisha.pcm22103No ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument10 pagesFinancial AccountingTeesha jainNo ratings yet
- Journal EntriesDocument25 pagesJournal EntriesViren DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Abm 005 2Q Week 12 PDFDocument10 pagesAbm 005 2Q Week 12 PDFJoel Vasquez MalunesNo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting: Chanakya Introduced The Accounting Concepts in His Book Arthashastra. in His Book, HeDocument15 pagesBasics of Accounting: Chanakya Introduced The Accounting Concepts in His Book Arthashastra. in His Book, HeShams100% (1)
- Fabm1 & 2 - ReviewDocument77 pagesFabm1 & 2 - ReviewBernice Jayne MondingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document38 pagesChapter 4Haidee Sumampil67% (3)
- Books of Accounts & Accounting RecordsDocument34 pagesBooks of Accounts & Accounting RecordsCA Deepak Ehn67% (3)
- The Accounting Equation & The Accounting Cycle: Steps 1 - 4: Acct 1A&BDocument5 pagesThe Accounting Equation & The Accounting Cycle: Steps 1 - 4: Acct 1A&BKenneth Christian WilburNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Analysis PDFDocument18 pagesFinancial Accounting and Analysis PDFDirghayu MaliNo ratings yet
- Test Review Answer Key - InternetDocument8 pagesTest Review Answer Key - InternetSR - 12MD 762521 The Woodlands SSNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesLecture NotesLyaman TagizadeNo ratings yet
- Tally Accounting Book by Ca MD ImranDocument6 pagesTally Accounting Book by Ca MD ImranMd ImranNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Part 5Document19 pagesFinancial Accounting Part 5dannydoly100% (1)
- Assignment Answers AccountingDocument8 pagesAssignment Answers AccountingAnkitNo ratings yet
- Lecture FiveDocument32 pagesLecture Fivebeysam240No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Analysis Dec 2022 RfaxjtDocument13 pagesFinancial Accounting Analysis Dec 2022 RfaxjtRajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Primary Books (Journal) : 1.1 Meaning and Definition: Journal Is Derived From The French Word " Jour" Which MeansDocument6 pagesUnit - 2 Primary Books (Journal) : 1.1 Meaning and Definition: Journal Is Derived From The French Word " Jour" Which MeansdeepshrmNo ratings yet
- Journal & LedgerDocument14 pagesJournal & Ledgerzaya sarwar100% (1)
- ACC 102 - Week 5 - Worksheet and Adjustments - LectureDocument2 pagesACC 102 - Week 5 - Worksheet and Adjustments - LectureJorecan Enad DacupNo ratings yet
- Service Bus - Acctg CycleDocument11 pagesService Bus - Acctg Cyclews. cloverNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Analysis WelabyDocument9 pagesFinancial Accounting Analysis WelabyPubg loverNo ratings yet
- Journal Ledger Journal EntryDocument48 pagesJournal Ledger Journal EntryFaith CasasolaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and AnalysisDocument13 pagesFinancial Accounting and AnalysisAditya Raj DuttaNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Financial Management PDFDocument66 pagesAccounting and Financial Management PDFbitturai9900No ratings yet
- SAMK-05-Week 4-Recording Process - Journal and LedgerDocument26 pagesSAMK-05-Week 4-Recording Process - Journal and LedgerBabang KhaeruddinNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Tally BookDocument10 pagesAccounting and Tally BookCA PASSNo ratings yet
- AF1401 2020 Autumn Lecture 3Document30 pagesAF1401 2020 Autumn Lecture 3Dhan AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions With SolutionsDocument8 pagesPractice Questions With SolutionsrsaldreesNo ratings yet
- Stages in Preparing The Final AccountsDocument24 pagesStages in Preparing The Final AccountsvineettibrewalNo ratings yet
- 04.recording Process Journal - TB FinalDocument49 pages04.recording Process Journal - TB FinalChowdhury Mobarrat Haider Adnan100% (1)
- Reviewer For First Periodical - ABM G12Document4 pagesReviewer For First Periodical - ABM G12ErleNo ratings yet
- Recording of Accounting Transaction (Theory and Practical Problem)Document13 pagesRecording of Accounting Transaction (Theory and Practical Problem)Mubin Shaikh NooruNo ratings yet
- 2.recording ProcessDocument30 pages2.recording Processwpar815No ratings yet
- Technopreneurship: - Module 5Document33 pagesTechnopreneurship: - Module 5Joseph AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Sushil MundadaDocument20 pagesSushil Mundada1986anuNo ratings yet
- The Entrepreneur’S Dictionary of Business and Financial TermsFrom EverandThe Entrepreneur’S Dictionary of Business and Financial TermsNo ratings yet
- Business Trade & CommerceDocument6 pagesBusiness Trade & Commerceincredible meNo ratings yet
- Economics & EconomyDocument11 pagesEconomics & Economyincredible meNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concepts and ConventionsDocument9 pagesAccounting Concepts and Conventionsincredible meNo ratings yet
- Theory of Accounting CH - 2Document8 pagesTheory of Accounting CH - 2incredible meNo ratings yet
- 237.esponcilla v. Bagong Tanyag 529 SCRA 654Document8 pages237.esponcilla v. Bagong Tanyag 529 SCRA 654Trebx Sanchez de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Test Bank AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 12 Test Bank AnswersYumna WafaNo ratings yet
- 12th Computer Applications Chapter 15 To 18 Study Material Tamil Medium PDF DownloadDocument25 pages12th Computer Applications Chapter 15 To 18 Study Material Tamil Medium PDF Downloadsaoja3No ratings yet
- Understanding Devops Critical Success Factors and Organizational PracticesDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Devops Critical Success Factors and Organizational PracticesLuis Gustavo NetoNo ratings yet
- BSBLDR601 - Assessment Task 3 EnviarDocument37 pagesBSBLDR601 - Assessment Task 3 Enviardsharlie94No ratings yet
- Magic Quadrant For Talent Management SuitesDocument24 pagesMagic Quadrant For Talent Management SuitesaseemNo ratings yet
- Corporate Strategy and LogisticsDocument5 pagesCorporate Strategy and LogisticsPugalendhi Selva100% (1)
- Afc Futsal Club Championship 2018 Rights Protection ProgrammeDocument20 pagesAfc Futsal Club Championship 2018 Rights Protection Programme4zjb9cxqjzNo ratings yet
- HRDocument2 pagesHRkiranaNo ratings yet
- Role of Circular Economy in Resource SustainabilityDocument160 pagesRole of Circular Economy in Resource SustainabilityMohammad Hyder AliNo ratings yet
- Marketing Proj Moov FinalDocument26 pagesMarketing Proj Moov FinalAbhi Modak33% (9)
- Grade 5 L-8Document22 pagesGrade 5 L-8Michael Angelo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bangalore Metallurgy in AIM BrochureDocument7 pagesBangalore Metallurgy in AIM Brochurebhavesh solankiNo ratings yet
- Social Responsibility and Ethics in Marketing: A Project ReportDocument51 pagesSocial Responsibility and Ethics in Marketing: A Project ReportAayush GuptaNo ratings yet
- SIP Mantra - HDFC Flexi Cap Fund (Aprt 2023)Document2 pagesSIP Mantra - HDFC Flexi Cap Fund (Aprt 2023)DeepakNo ratings yet
- Judge, A Robot Stole My Job' - Spain's Courts Take On Automation in The Workplace - Reader ViewDocument2 pagesJudge, A Robot Stole My Job' - Spain's Courts Take On Automation in The Workplace - Reader ViewrienNo ratings yet
- 2022 Omnibus Sworn Statement (Revised) - DILGDocument2 pages2022 Omnibus Sworn Statement (Revised) - DILGmaxor4242No ratings yet
- Insurance Law: Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority CODE 1743Document28 pagesInsurance Law: Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority CODE 1743Anjuman Jangra 406No ratings yet
- Project Outline: Oman Car Wash Mobile ApplicationDocument1 pageProject Outline: Oman Car Wash Mobile ApplicationUsama MunirNo ratings yet
- International Business WikiDocument4 pagesInternational Business WikiPranay PrannuNo ratings yet
- Streamhub: Versatile Transceiver PlatformDocument2 pagesStreamhub: Versatile Transceiver PlatformBanidula WijesiriNo ratings yet
- Cracking The CaseDocument17 pagesCracking The CaseK60 Đào Phạm Lan AnhNo ratings yet
- KSB Mechanical Seals For: Water and Waste Water ApplicationsDocument8 pagesKSB Mechanical Seals For: Water and Waste Water ApplicationsAghan100% (1)
- Network Engineer Resume TemplateDocument2 pagesNetwork Engineer Resume TemplateTauseef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Agile E1 Questions and Answers CompressDocument1 pageAgile E1 Questions and Answers CompressLawrence VaIenciaNo ratings yet
- Ict and Business Transformation Business Plan 2019 - 2022: G R E A TDocument16 pagesIct and Business Transformation Business Plan 2019 - 2022: G R E A TAmalih BahanzaNo ratings yet
- LogStar Billing BrochureDocument1 pageLogStar Billing BrochureGayatri AtishNo ratings yet
- Pre-Construction Meeting Manual PDFDocument21 pagesPre-Construction Meeting Manual PDFBambangShrNo ratings yet