Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 viewsAir-Conditioning Principle & Trouble Shooting
Air-Conditioning Principle & Trouble Shooting
Uploaded by
Eko PrasetiyoThe document describes the principles and components of air conditioning systems, as well as some common troubleshooting issues. It explains that air conditioning works by transferring heat from inside a space to outside using a refrigeration cycle. The main components are a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. Common issues addressed include reduced cooling, compressor malfunctions, unusual sounds, high or low pressures, and refrigerant issues. Troubleshooting tips are provided for each problem.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Oxford Six Class Science NotesDocument15 pagesOxford Six Class Science NotesLisha85% (13)
- How To Measure Superheat and SubcoolingDocument10 pagesHow To Measure Superheat and SubcoolingRay Ravel88% (8)
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning System Operation and Refrigerant Cycle of Motor Vehicles PDFDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning System Operation and Refrigerant Cycle of Motor Vehicles PDFmariA ANNANo ratings yet
- Ship Air Conditioning SystemDocument9 pagesShip Air Conditioning SystemMEET PATEL100% (2)
- Fridge SystemDocument8 pagesFridge SystemJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Fridge System: Vapour-Compression Theoretical GraphsDocument14 pagesFridge System: Vapour-Compression Theoretical GraphsBhargav Krsna GayanNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Proper Cooling of Power TransformersDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Proper Cooling of Power Transformersلندا أسحق حنوNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleramsiNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleGerardo DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleSATNA GSTNo ratings yet
- A C Cycle WWW - Innovationdiscoveries.spaceDocument49 pagesA C Cycle WWW - Innovationdiscoveries.spaceNaveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleZakir R. AliNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CyclemohdNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant Cycleravi prajapatNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleMubarek TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Refeer Air CompressorDocument12 pagesRefeer Air CompressorSantharam MarinerNo ratings yet
- Why Compressors FailDocument57 pagesWhy Compressors FailNowshad AlamNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Air Conditioning (VAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesVehicle Air Conditioning (VAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleVarun RaizadaNo ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1senaNo ratings yet
- 01 Hydraulic GroupDocument81 pages01 Hydraulic Groupgica100% (1)
- MP - 15 - Ref FaultsDocument33 pagesMP - 15 - Ref FaultsbalramtcsNo ratings yet
- Auto AC Flow DiagramDocument1 pageAuto AC Flow DiagramppolanskyNo ratings yet
- Table Z Troubleshooting Chart For Air ConditionersDocument7 pagesTable Z Troubleshooting Chart For Air Conditionersvalentinlupascu33No ratings yet
- Air Conditioner Pump System PressuresDocument11 pagesAir Conditioner Pump System PressuresingenierosunidosNo ratings yet
- Compressor Trouble ShootingDocument7 pagesCompressor Trouble ShootingAnkush Nayar100% (1)
- 03 Refrigeration&Air Conditioning-1Document50 pages03 Refrigeration&Air Conditioning-1AmiNo ratings yet
- Cooling SystemDocument26 pagesCooling Systemdoreen ann montanoNo ratings yet
- HVAC Basic TroubleshootingDocument11 pagesHVAC Basic TroubleshootingKrishnaNo ratings yet
- BSL Presentation On BasicsDocument41 pagesBSL Presentation On BasicsSathishNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems Onboard Ships-Vapour Compression SystemsDocument32 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems Onboard Ships-Vapour Compression SystemsSatyabrat GaanNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Troubleshooting AC SystemDocument13 pagesKnowledge Troubleshooting AC SystemRupak KumarNo ratings yet
- Compressor FinalDocument20 pagesCompressor FinalshihabNo ratings yet
- Compressors: Basic Classification and Design Overview andDocument20 pagesCompressors: Basic Classification and Design Overview andshihabNo ratings yet
- Engine Cooling System: 1988 Toyota CelicaDocument12 pagesEngine Cooling System: 1988 Toyota CelicaToua YajNo ratings yet
- Solving Hydraulic System Overheating ProblemsDocument9 pagesSolving Hydraulic System Overheating Problemsmahadev100% (1)
- Ac IntroductionDocument28 pagesAc Introductionthermopolis3012No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Vijay RajaindranNo ratings yet
- Air CondDocument50 pagesAir CondIzad Bin Idris100% (2)
- Aux Mach 222 Midterm Week 4Document14 pagesAux Mach 222 Midterm Week 4Janoel LucañasNo ratings yet
- System Pendingin Mesin Aerio Next G Dan Cara Kuras RadiatorDocument74 pagesSystem Pendingin Mesin Aerio Next G Dan Cara Kuras RadiatorGatotGtToroNo ratings yet
- A/C-Heater System - Manual: 1990 Nissan 240SXDocument11 pagesA/C-Heater System - Manual: 1990 Nissan 240SXRonald FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ac General Description and System OperationDocument2 pagesAc General Description and System OperationDavid Wise-MannNo ratings yet
- Land Robert EnfriamientoDocument8 pagesLand Robert EnfriamientoJose Luis LopezNo ratings yet
- Engine Cooling FanDocument9 pagesEngine Cooling FanJosé Torcato AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Coc Oral Exam PreparationDocument105 pagesCoc Oral Exam PreparationAshok Kumar0% (1)
- Compressor Troubleshooting GuideDocument40 pagesCompressor Troubleshooting GuideDejan KolarecNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument26 pagesRefrigeration SystemMdshajiNo ratings yet
- NEWS December 3, 2018Document6 pagesNEWS December 3, 2018Insoluperez FPNo ratings yet
- Design Consideration of Hot Oil SystemDocument24 pagesDesign Consideration of Hot Oil SystemOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- Knowing Your Cooling SystemDocument119 pagesKnowing Your Cooling SystemDaniel Amanor100% (1)
- Air PreheaterDocument31 pagesAir PreheaterAkashKishoreNo ratings yet
- Air Condition How Does It Works?Document10 pagesAir Condition How Does It Works?Gwapong CrisNo ratings yet
- The Importance of A Clean CondenserDocument5 pagesThe Importance of A Clean CondenserD HarNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Know About TX ValvesDocument6 pagesEverything You Need To Know About TX Valvescalishe1No ratings yet
- Test On Vapor Compression Refrigeration FINALDocument8 pagesTest On Vapor Compression Refrigeration FINALUdara ManawaduNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Hassan Alqarni Abdullah AlsubahiDocument50 pagesPrepared By: Hassan Alqarni Abdullah Alsubahiاشرينكيل مسونكيل100% (1)
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesFrom EverandTroubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Process Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesFrom EverandProcess Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Ship Barge Hatch Cover Parts General CatalogDocument1 pageShip Barge Hatch Cover Parts General CatalogEko PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Continuous Machinery SurveyDocument7 pagesContinuous Machinery SurveyEko Prasetiyo100% (2)
- Ballast Tank Vents InspectionDocument7 pagesBallast Tank Vents InspectionEko Prasetiyo100% (1)
- Engine Girder CalculationsDocument1 pageEngine Girder CalculationsEko PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- The Earth - A Living Planet: Warming UpDocument6 pagesThe Earth - A Living Planet: Warming UpCristiana PopaNo ratings yet
- SOL 6.2a-D & 6.3a, B, D Earth & Space Systems Common Assessment #1Document13 pagesSOL 6.2a-D & 6.3a, B, D Earth & Space Systems Common Assessment #1Kymoni MobleyNo ratings yet
- Basic AerodynamicsDocument43 pagesBasic AerodynamicsSagar LEMONIACNo ratings yet
- Absorption & StrippingDocument17 pagesAbsorption & StrippingGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Fluorocarbons: Are We Still Warming Towards Them?: Adam Bland, Director Specialty Chemicals, IHS MarkitDocument32 pagesFluorocarbons: Are We Still Warming Towards Them?: Adam Bland, Director Specialty Chemicals, IHS MarkitYang SunmanNo ratings yet
- Set ADocument6 pagesSet AJabeguero Marvelyn JessicaNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud Seeding and Did It Cause Dubai FloodingDocument5 pagesWhat Is Cloud Seeding and Did It Cause Dubai FloodingproducaocpmNo ratings yet
- Principles of Physical GeologyDocument644 pagesPrinciples of Physical GeologyAnubhab Dey100% (1)
- Changde Cigarette Factory - Parts EnquiryDocument4 pagesChangde Cigarette Factory - Parts Enquiry樊瞳No ratings yet
- Choose The Most Suitable AnswerDocument4 pagesChoose The Most Suitable AnswerSusithra BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Refrigeration TutorDocument11 pagesExperiment On Refrigeration TutorGgNo ratings yet
- Habitat DestructionDocument12 pagesHabitat DestructionGaurjan0% (1)
- Absorption Refrigeration UnitDocument20 pagesAbsorption Refrigeration UnitAlyan YousafNo ratings yet
- Api Spec 14LDocument2 pagesApi Spec 14L高守No ratings yet
- SHS Earth SystemDocument25 pagesSHS Earth SystemJames JaymeNo ratings yet
- Changes of State - Information SheetDocument2 pagesChanges of State - Information SheetBert RoseteNo ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13Document8 pagesInteractive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13api-240094705No ratings yet
- Grade: Prepared By: Mrs. Ronalyn B. Adrias Saint Paul School of Buug Science TeaherDocument26 pagesGrade: Prepared By: Mrs. Ronalyn B. Adrias Saint Paul School of Buug Science TeaherGlydyll Lhane OmongosNo ratings yet
- THOMSON 1965 Air PollutionDocument22 pagesTHOMSON 1965 Air PollutionbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Performance Specification Oxygen, Aviator'S Breathing, Liquid and GasDocument11 pagesPerformance Specification Oxygen, Aviator'S Breathing, Liquid and GasAviasafe AviationNo ratings yet
- Everyday Science General InformationDocument28 pagesEveryday Science General InformationShahzadNo ratings yet
- Stas ReviewDocument35 pagesStas Reviewchristine manaloNo ratings yet
- Pre - Test ELSDocument5 pagesPre - Test ELSLorena DizonNo ratings yet
- MET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityDocument21 pagesMET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityMalik ForbesNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer From A Gas Into A Liquid IIDocument7 pagesMass Transfer From A Gas Into A Liquid IIZeynep BudakoğluNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Liquid Vapor & Liquid - Liquid Equilibrium-Tran Thuy Tuyet MaiDocument40 pagesChapter 8 - Liquid Vapor & Liquid - Liquid Equilibrium-Tran Thuy Tuyet MaiPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Layers of NeptuneDocument4 pagesLayers of NeptuneMarilysse Monay NagrampaNo ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument22 pagesPRESSUREnomoszengNo ratings yet
- Separator and Slug Catcher DesignDocument46 pagesSeparator and Slug Catcher DesignAndrea Alicia Jimenez NuñezNo ratings yet
Air-Conditioning Principle & Trouble Shooting
Air-Conditioning Principle & Trouble Shooting
Uploaded by
Eko Prasetiyo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views35 pagesThe document describes the principles and components of air conditioning systems, as well as some common troubleshooting issues. It explains that air conditioning works by transferring heat from inside a space to outside using a refrigeration cycle. The main components are a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. Common issues addressed include reduced cooling, compressor malfunctions, unusual sounds, high or low pressures, and refrigerant issues. Troubleshooting tips are provided for each problem.
Original Description:
troubleshooting AC central
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the principles and components of air conditioning systems, as well as some common troubleshooting issues. It explains that air conditioning works by transferring heat from inside a space to outside using a refrigeration cycle. The main components are a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. Common issues addressed include reduced cooling, compressor malfunctions, unusual sounds, high or low pressures, and refrigerant issues. Troubleshooting tips are provided for each problem.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views35 pagesAir-Conditioning Principle & Trouble Shooting
Air-Conditioning Principle & Trouble Shooting
Uploaded by
Eko PrasetiyoThe document describes the principles and components of air conditioning systems, as well as some common troubleshooting issues. It explains that air conditioning works by transferring heat from inside a space to outside using a refrigeration cycle. The main components are a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. Common issues addressed include reduced cooling, compressor malfunctions, unusual sounds, high or low pressures, and refrigerant issues. Troubleshooting tips are provided for each problem.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 35
Air-Conditioning Principle &
Troubleshooting
Purpose
To maintain Temperature & Humidity of the Air
inside Accommodation for Human Comfort. (By
Cooling, Heating, Humidifying, depending on
outside temperature)
The desired & Most Comfortable range for
Humans is: Temperature: 22-24 Deg. C & Relative
Humidity: 40-60%.
Comfort Zone
Comfort Zone
How Its Done
Air-con System is like a Heat Pump: I.E. Transferring
Heat from inside accommodation to Outside.
(Same principle applies to Refrigeration System as
well)
How Air Conditioners Work
Principle of Refrigeration Cycle:
Saturation temperature (Boiling Point) of a liquid
varies with change in pressure) . At Sat. Point is like
Transition phase. An addition of heat will boil
(evaporate) the liquid into vapour and an removal of
heat will condense it to liquid. Temp. remains same
during phase change & the heat added/removed is
called latent heat(Panas Laten).
At Higher Pressure Boiling Point (Temp.) is higher &
at Lower Pressure Boiling Point is lower.
E.G. Water boils at 100 deg C at Atm. Pressure. If We
reduce pressure (as in FWG), water boils at abt 500 C.
Same way in Boiler water boils at 1200 & above (when
pressure is higher)
Boiling Point Variation with Pressure
Principle of Refrigeration Cycle:
When a liquid boils or evaporates it absorbs heat
(from hot surroundings) and when it condenses it is
releases heat (to a cooling medium).
So we want a Refrigerant material which:
Absorbs heat from accommodation while
evaporating (for example at 18 Deg C) [ At Low
Pressure] and
Releases heat to outside atmosphere (Air or Water
e.g. at 40 Deg C) while condensing, [at High
Pressure].
Boiling Point Variation with Pressure
Principle of Refrigeration Cycle:
Principle of Refrigeration Cycle:
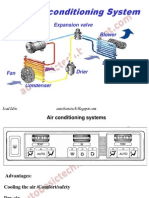
Main Components
Compressor: Reciprocating single or two stage
compressor is commonly used for compressing and
supplying the refrigerant to the system.
Condenser: Shell and tube type condenser is used to
cool down the refrigerant in the system.
Receiver: The cooled refrigerant is supplied to the
receiver, which is also used to drain out the
refrigerant from the system for maintenance purpose.
Drier: The drier connected in the system consists of
silica gel to remove any moisture from the refrigerant
Main Components
Solenoids: Solenoid valves are used to control the flow
of refrigerant into the hold or room.
Expansion valve: Reduces the pressure & regulates the
refrigerant to maintain the correct hold or room temp.
Evaporator unit: The evaporator unit act as a
heat exchanger to cool down the hold or room area by
transferring heat to the refrigerant.
Control unit: The control unit consist of different
safety and operating circuits for safe operation of the
refer plant.
Main Components
Capacity Controller: Controls the output of the
plant depending on the load demand. (e.g. Change in
Atmosphere Temperature, Frequent Opening of
Doors, More people or fresh food stored in the fridge
rooms). By unloading the Suction Valves.
Safety Devices:
a)Low Pressure or LP cut off.
b)High pressure or HP cut out
c)Oil differential cut out
d)Relief valves
e)Solenoid valves
f)Oil heater
Common Troubles
We shall discuss following common troubles in
next session. Please send me the specific
problems you are facing on your ships:
a)No or reduced cooling Effect
b)Compressor Not Working
c)Reducing oil level in compressor
d)Unusual Sound from Compressor
e)High Compressor Discharge Temperature
f)Compressor Starts But Stops immediately
g)Compressor Start and Stops Frequently
h)Compressor is Running Continuously (fridge)
i)Discharge Pressure Too Low
j)Discharge Pressure Too High
Common Troubles
k) High Pressure Switch Cuts-Off
l) Suction Pressure Too High
m) Suction Pressure Too Low
n) Low Pressure Switch Cuts-Off
o) Evaporator Coil Icing
p) Evaporator Not Cooling
q) Reduced Cooling Capacity
r) Icing on Suction Pipe
No or Reduced Cooling Effect
Less Refrigerant quantity (undercharged)
Too much leakage from the Accommodation (Doors &
portholes always kept open)
Air conditioner unit is under capacity
Compressor valve damage or ineffective compression due to
Piston/Liner/Piston ring issues.
Expansion valve not effective or incorrect size
Filter drier or strainer is clogged (Refrigerant)
Air filter is clogged
Evaporator is dirty/clogged
Fan motor belt loose or slip
Temp. setting of thermostat too high or sensor placed at wrong
place
Duct damper is closed, Duct trunking corroded (leaking),
Compressor Not Working
A) Check the Power supply, Motor, Belts or any
Trip/Alarm on panel.
B) Check if broken: Reasons:
a) No correct assembly.
b) Not genuine spare parts
c) Alarms & Trip malfunction.
d) Suction & Discharge valves problem
e) Oil pressure not enough
f) Under capacity compressor (Over load)
g) System malfunction (Liquid carry over, over
charge, air or moisture in the system)
Reducing oil level in compressor
Due to leakage or increase in consumption of lube oil due to
following reasons:
Nozzle or filter clogged (Ensure that the nozzle in oil return line
or filter in solenoid valve is cleaned and not choked)
Foaming of oil due to liquid in suction line (Foaming of oil may
arise due to liquid refrigerant entering the crankcase. Replenish
oil and troubleshoot cause of liquid in suction of compressor)
Drive side seal leaking (The compressor is provided with oil seal
at the drive side. Ensure it is not leaking and renew it if required)
Worn out piston rings/ liner leading to oil carryover in the
system (Renew the compressor piston rings or liner)
Oil separator not working properly
Unusual Sound from Compressor
This may be due to trouble with mechanical components
inside the compressor:
Incorrect alignment of compressor and motor (Check the
alignment and set motor and compressor in one line)
Loose foundation (Ensure that the compressor foundation is
secured and all foundation bolts are checked for tightness)
Loosening of driving belt (Ensure to check the elasticity of
the belt and renew if the belt is slack)
The capacity control setting is too high, leading to knocking
sound during starting (Reduce the capacity control setting)
The oil pressure is low (Ensure that the oil level is
maintained and no foaming of oil is developed. Replenish or
refill the lube oil if required)
High Compressor Discharge Temperature
Excessive suction temperature due to less refrigerant in the
circuit (Recharge the circuit to maintain refrigerant
quantity in the circuit. Ensure Expansion valve is of correct
type and is set properly and supplying enough to the
evaporator.
Leak in the discharge valve leads to generation of heat
(renew the leaky valve)
Leak in the safety valve (Renew safety valve)
Compressor Starts But Stops immediately
Low pressure cut out gets activated (Ensure that all the suction
line valves are in open condition, the refrigeration is properly
charged and the low pressure cut out is not defective)
Defective oil pressure cut out (Check for proper functioning of oil
pressure cut out and replace the defective cutout)
Defrosting timer is getting activated frequently (If the defrost
timer is getting activated frequently, leading to cutout of
compressor, check and repair defrost timer) (Fridge)
The lube oil level is below required level (This can be because of
leakage of lube oil from seal or carry over of oil. Rectify the
leakage and refill the oil level)
Foaming of oil leading to reduced oil pressure (Ensure no foaming
takes place, renew the oil if required)
Motor overload cut outs are activating (Ensure that electrical
motor trips are working properly.)
Compressor Start and Stops Frequently
Applicable mainly for Fridge:
Wrong Setting of Cutouts: It may be because the high pressure (HP)
cutout is set too low or LP cutout is set too high (Check and change
the setting to limit as per makers)
Differential Setting Gap is Small: The low pressure (LP) cut out is
provided with starting and stopping pressure setting. If the setting gap
is too small, it will lead to frequent cut-in and cut-out of the
compressor (Change the setting and increase the span between
starting and stopping compressor pressures.)
Defective Valves: If the compressor discharge valve is leaky or the
line solenoid valve is not closing properly, this will lead to variation in
sensor pressure and result in frequent cut-in and cut-out of
compressor (Replace all the defective valves)
Clogged Suction Filters: Compressor is provided with a filter in the
suction line. If that is clogged, it will lead to frequent LP cut out (clean
the filter)
Compressor is Running Continuously (fridge)
Not sufficient Refrigerant for cooling evaporator
(Ensure thermostatic expansion valve is working
properly and clean the filters inside TEV)
Thermostat low pressure cut-out not activated at
low temperature/ pressure (Correctly set the LP
cut-out to correct setting)
Refrigerant charge is low in the circuit (Check for
leakage of refrigerant and charge with required
refrigerant)
Discharge Pressure Too High (High
Pressure Switch Cuts-Off)
Overcharge of refrigerant
Air inside refrigerant circuit
Condenser is dirty, water flow too little, inlet
water temperature too high, flow direction wrong,
cooling water short circuit (broken division plate)
Refrigerant discharge valve blocked or closed
Air conditioner system is under capacity
Discharge Pressure Too Low
Refrigerant is undercharged
Excessive condenser water flow
Condenser outlet water temperature too low
Air conditioner unit is over capacity
Ineffective compression of compresor or valve is
damaged
Ambient temperature too low
Suction Pressure Too High
Refrigerant is overcharged
Expansion valve is oversized
Air conditioner unit is under capacity
Excessive opening of Thermo valve
Ineffective compression of compressor or valve is
damaged
Ineffective contact of sensor bulb of Thermo valve
Suction Pressure Too Low / Low Pressure
Switch Cuts-Off
Refrigerant is undercharged
Evaporator coil is dirty
Temperature setting of thermostat too low
Duct damper is closed
Duct resistance too high
Supply air short-circuit
Expansion valve undersized
Air conditioner unit is over capacity
Not enough opening of thermo valve
Expansion valve clogged
Ineffective expansion valve
Air filter is clogged
Room temperature is too low
Both Low Pressure and High Pressure Too High
Condenser dirty, not enough water flow, inlet
water temperature too high
Overcharge of refrigerant
Air inside refrigerant circuit
Excessive opening of thermo valve
Ineffective contact of sensor bulb of thermo valve
Condenser water is circulating in the reverse
direction
Air conditioner unit is under capacity
Both Low Pressure and High Pressure Too Low
Expansion valve undersized or clogged
Refrigerant is undercharged
Filter drier or strainer is clogged
Evaporator coil is dirty
Excessive condenser water flow, cooling water temperature
too low
Air conditioner unit is over capacity,
Not enough opening of thermo valve
Temperature setting of thermostat too low
Duct damper is closed, Duct resistance too high
Air filter is clogged, Supply air short-circuit
Room temperature is too low, Ambient temperature too low
High Pressure Too Low and Low Pressure Too High
Compressor valve damaged or ineffective
compression
Evaporator Coil Icing
Too low temperature setting ( Increase the coil
temperature by adjusting TEV or it’s sensor)
The coil capacity is less (Install large capacity
evaporator coils)
Defrost is not operational (Check if the defrost
system is functioning at regular intervals)
Icing on Suction Pipe
Air conditioner unit is over capacity
Air filter is clogged
Ambient/ accomodation temperature is too low
Evaporator is dirty,
Fan motor belt loose or slip
Fan motor in rotating in the reverse direction
Temperature setting of thermostat too low
Duct damper is closed, Duct resistance too high
Supply air short-circuit
Routine Maintenance
1) Leak test by flame or electronic meter.
2) Defrosting evaporator coil.
3) Compressor oil level check and top up as
required by Oil Charging pump.
4) Check refrigerant level in compressor
5) Clean condenser routinely.
6) Clean air filter from time to time.
7) Charging the Refrigerant (Gas or Liquid
charging)
8) After Compressor maintenance or opening the
system (Use Vacuum pump & N2 purging)
9) Replace oil separator cartridge or Silica Gel (as
par maker’s recommendation)
Symptoms of Good Working System
1) Good cooling with normal parameters
2) No Loss of Refrigerant. (Normal Refrigerant
level in condenser is seen)
3) No loss of compressor oil (Normal oil level
maintained)
4) No frosting on suction pipe (Should be slight
cold).
5) Suction pressure and discharge pressure in
normal range.
6) Oil pressure 2-3 bars more than suction
pressure.
7) Normal sound and vibrations.
To be continued
You might also like
- Oxford Six Class Science NotesDocument15 pagesOxford Six Class Science NotesLisha85% (13)
- How To Measure Superheat and SubcoolingDocument10 pagesHow To Measure Superheat and SubcoolingRay Ravel88% (8)
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning System Operation and Refrigerant Cycle of Motor Vehicles PDFDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning System Operation and Refrigerant Cycle of Motor Vehicles PDFmariA ANNANo ratings yet
- Ship Air Conditioning SystemDocument9 pagesShip Air Conditioning SystemMEET PATEL100% (2)
- Fridge SystemDocument8 pagesFridge SystemJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Fridge System: Vapour-Compression Theoretical GraphsDocument14 pagesFridge System: Vapour-Compression Theoretical GraphsBhargav Krsna GayanNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Proper Cooling of Power TransformersDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Proper Cooling of Power Transformersلندا أسحق حنوNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleramsiNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleGerardo DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleSATNA GSTNo ratings yet
- A C Cycle WWW - Innovationdiscoveries.spaceDocument49 pagesA C Cycle WWW - Innovationdiscoveries.spaceNaveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleZakir R. AliNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CyclemohdNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant Cycleravi prajapatNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesMotor Vehicle Air Conditioning (MVAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleMubarek TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Refeer Air CompressorDocument12 pagesRefeer Air CompressorSantharam MarinerNo ratings yet
- Why Compressors FailDocument57 pagesWhy Compressors FailNowshad AlamNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Air Conditioning (VAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleDocument49 pagesVehicle Air Conditioning (VAC) : System Operation and The Refrigerant CycleVarun RaizadaNo ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1senaNo ratings yet
- 01 Hydraulic GroupDocument81 pages01 Hydraulic Groupgica100% (1)
- MP - 15 - Ref FaultsDocument33 pagesMP - 15 - Ref FaultsbalramtcsNo ratings yet
- Auto AC Flow DiagramDocument1 pageAuto AC Flow DiagramppolanskyNo ratings yet
- Table Z Troubleshooting Chart For Air ConditionersDocument7 pagesTable Z Troubleshooting Chart For Air Conditionersvalentinlupascu33No ratings yet
- Air Conditioner Pump System PressuresDocument11 pagesAir Conditioner Pump System PressuresingenierosunidosNo ratings yet
- Compressor Trouble ShootingDocument7 pagesCompressor Trouble ShootingAnkush Nayar100% (1)
- 03 Refrigeration&Air Conditioning-1Document50 pages03 Refrigeration&Air Conditioning-1AmiNo ratings yet
- Cooling SystemDocument26 pagesCooling Systemdoreen ann montanoNo ratings yet
- HVAC Basic TroubleshootingDocument11 pagesHVAC Basic TroubleshootingKrishnaNo ratings yet
- BSL Presentation On BasicsDocument41 pagesBSL Presentation On BasicsSathishNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems Onboard Ships-Vapour Compression SystemsDocument32 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems Onboard Ships-Vapour Compression SystemsSatyabrat GaanNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Troubleshooting AC SystemDocument13 pagesKnowledge Troubleshooting AC SystemRupak KumarNo ratings yet
- Compressor FinalDocument20 pagesCompressor FinalshihabNo ratings yet
- Compressors: Basic Classification and Design Overview andDocument20 pagesCompressors: Basic Classification and Design Overview andshihabNo ratings yet
- Engine Cooling System: 1988 Toyota CelicaDocument12 pagesEngine Cooling System: 1988 Toyota CelicaToua YajNo ratings yet
- Solving Hydraulic System Overheating ProblemsDocument9 pagesSolving Hydraulic System Overheating Problemsmahadev100% (1)
- Ac IntroductionDocument28 pagesAc Introductionthermopolis3012No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Vijay RajaindranNo ratings yet
- Air CondDocument50 pagesAir CondIzad Bin Idris100% (2)
- Aux Mach 222 Midterm Week 4Document14 pagesAux Mach 222 Midterm Week 4Janoel LucañasNo ratings yet
- System Pendingin Mesin Aerio Next G Dan Cara Kuras RadiatorDocument74 pagesSystem Pendingin Mesin Aerio Next G Dan Cara Kuras RadiatorGatotGtToroNo ratings yet
- A/C-Heater System - Manual: 1990 Nissan 240SXDocument11 pagesA/C-Heater System - Manual: 1990 Nissan 240SXRonald FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ac General Description and System OperationDocument2 pagesAc General Description and System OperationDavid Wise-MannNo ratings yet
- Land Robert EnfriamientoDocument8 pagesLand Robert EnfriamientoJose Luis LopezNo ratings yet
- Engine Cooling FanDocument9 pagesEngine Cooling FanJosé Torcato AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Coc Oral Exam PreparationDocument105 pagesCoc Oral Exam PreparationAshok Kumar0% (1)
- Compressor Troubleshooting GuideDocument40 pagesCompressor Troubleshooting GuideDejan KolarecNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration SystemDocument26 pagesRefrigeration SystemMdshajiNo ratings yet
- NEWS December 3, 2018Document6 pagesNEWS December 3, 2018Insoluperez FPNo ratings yet
- Design Consideration of Hot Oil SystemDocument24 pagesDesign Consideration of Hot Oil SystemOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- Knowing Your Cooling SystemDocument119 pagesKnowing Your Cooling SystemDaniel Amanor100% (1)
- Air PreheaterDocument31 pagesAir PreheaterAkashKishoreNo ratings yet
- Air Condition How Does It Works?Document10 pagesAir Condition How Does It Works?Gwapong CrisNo ratings yet
- The Importance of A Clean CondenserDocument5 pagesThe Importance of A Clean CondenserD HarNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Know About TX ValvesDocument6 pagesEverything You Need To Know About TX Valvescalishe1No ratings yet
- Test On Vapor Compression Refrigeration FINALDocument8 pagesTest On Vapor Compression Refrigeration FINALUdara ManawaduNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Hassan Alqarni Abdullah AlsubahiDocument50 pagesPrepared By: Hassan Alqarni Abdullah Alsubahiاشرينكيل مسونكيل100% (1)
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesFrom EverandTroubleshooting Process Plant Control: A Practical Guide to Avoiding and Correcting MistakesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Process Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesFrom EverandProcess Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Ship Barge Hatch Cover Parts General CatalogDocument1 pageShip Barge Hatch Cover Parts General CatalogEko PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Continuous Machinery SurveyDocument7 pagesContinuous Machinery SurveyEko Prasetiyo100% (2)
- Ballast Tank Vents InspectionDocument7 pagesBallast Tank Vents InspectionEko Prasetiyo100% (1)
- Engine Girder CalculationsDocument1 pageEngine Girder CalculationsEko PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- The Earth - A Living Planet: Warming UpDocument6 pagesThe Earth - A Living Planet: Warming UpCristiana PopaNo ratings yet
- SOL 6.2a-D & 6.3a, B, D Earth & Space Systems Common Assessment #1Document13 pagesSOL 6.2a-D & 6.3a, B, D Earth & Space Systems Common Assessment #1Kymoni MobleyNo ratings yet
- Basic AerodynamicsDocument43 pagesBasic AerodynamicsSagar LEMONIACNo ratings yet
- Absorption & StrippingDocument17 pagesAbsorption & StrippingGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Fluorocarbons: Are We Still Warming Towards Them?: Adam Bland, Director Specialty Chemicals, IHS MarkitDocument32 pagesFluorocarbons: Are We Still Warming Towards Them?: Adam Bland, Director Specialty Chemicals, IHS MarkitYang SunmanNo ratings yet
- Set ADocument6 pagesSet AJabeguero Marvelyn JessicaNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud Seeding and Did It Cause Dubai FloodingDocument5 pagesWhat Is Cloud Seeding and Did It Cause Dubai FloodingproducaocpmNo ratings yet
- Principles of Physical GeologyDocument644 pagesPrinciples of Physical GeologyAnubhab Dey100% (1)
- Changde Cigarette Factory - Parts EnquiryDocument4 pagesChangde Cigarette Factory - Parts Enquiry樊瞳No ratings yet
- Choose The Most Suitable AnswerDocument4 pagesChoose The Most Suitable AnswerSusithra BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Refrigeration TutorDocument11 pagesExperiment On Refrigeration TutorGgNo ratings yet
- Habitat DestructionDocument12 pagesHabitat DestructionGaurjan0% (1)
- Absorption Refrigeration UnitDocument20 pagesAbsorption Refrigeration UnitAlyan YousafNo ratings yet
- Api Spec 14LDocument2 pagesApi Spec 14L高守No ratings yet
- SHS Earth SystemDocument25 pagesSHS Earth SystemJames JaymeNo ratings yet
- Changes of State - Information SheetDocument2 pagesChanges of State - Information SheetBert RoseteNo ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13Document8 pagesInteractive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13api-240094705No ratings yet
- Grade: Prepared By: Mrs. Ronalyn B. Adrias Saint Paul School of Buug Science TeaherDocument26 pagesGrade: Prepared By: Mrs. Ronalyn B. Adrias Saint Paul School of Buug Science TeaherGlydyll Lhane OmongosNo ratings yet
- THOMSON 1965 Air PollutionDocument22 pagesTHOMSON 1965 Air PollutionbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Performance Specification Oxygen, Aviator'S Breathing, Liquid and GasDocument11 pagesPerformance Specification Oxygen, Aviator'S Breathing, Liquid and GasAviasafe AviationNo ratings yet
- Everyday Science General InformationDocument28 pagesEveryday Science General InformationShahzadNo ratings yet
- Stas ReviewDocument35 pagesStas Reviewchristine manaloNo ratings yet
- Pre - Test ELSDocument5 pagesPre - Test ELSLorena DizonNo ratings yet
- MET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityDocument21 pagesMET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityMalik ForbesNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer From A Gas Into A Liquid IIDocument7 pagesMass Transfer From A Gas Into A Liquid IIZeynep BudakoğluNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Liquid Vapor & Liquid - Liquid Equilibrium-Tran Thuy Tuyet MaiDocument40 pagesChapter 8 - Liquid Vapor & Liquid - Liquid Equilibrium-Tran Thuy Tuyet MaiPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Layers of NeptuneDocument4 pagesLayers of NeptuneMarilysse Monay NagrampaNo ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument22 pagesPRESSUREnomoszengNo ratings yet
- Separator and Slug Catcher DesignDocument46 pagesSeparator and Slug Catcher DesignAndrea Alicia Jimenez NuñezNo ratings yet