Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 viewsKey Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties Properties
Key Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties Properties
Uploaded by
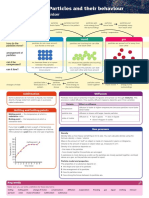
Shimaa Elsharnoby1) The particle model explains that all matter is made up of tiny particles and the properties of solids, liquids, and gases depend on how the particles behave.
2) In solids, particles are close together and vibrate in fixed positions. In liquids, particles are close but can move past each other allowing liquids to flow and take the shape of containers. Gases have particles that are far apart, spread out, and move quickly in all directions.
3) Changes in temperature and concentration affect the rate of diffusion, which is the spreading out of particles from an area of higher to lower concentration. Higher temperature and concentration increase the rate of diffusion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- TP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument2 pagesTP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterThabang Sbo PhokontsiNo ratings yet
- TP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1Document2 pagesTP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- States of Matter DiffusionDocument17 pagesStates of Matter Diffusion吕洁儿No ratings yet
- Lesson Note 3 - Investigating Diffusion-Unit 6.3Document6 pagesLesson Note 3 - Investigating Diffusion-Unit 6.3navidu dasisNo ratings yet
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- iGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4Document11 pagesiGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4SimonNo ratings yet
- Resource 1Document13 pagesResource 1eeren41789No ratings yet
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetDocument2 pagesStates of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument50 pagesUnderstanding Kinetic Particle TheoryozmanNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Group 2Document15 pagesDiffusion Group 2johndominicmmalubagoNo ratings yet
- C1 Chapter 1Document1 pageC1 Chapter 1Rehan ShahNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document58 pagesChem 1Heba HebaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesDocument3 pagesStates of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesMatipa DembureNo ratings yet
- Assumption College of NabunturanDocument4 pagesAssumption College of NabunturanAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- Grade 8 NotesDocument2 pagesGrade 8 NotesmunilalluNo ratings yet
- Phyw 2Document42 pagesPhyw 2Sajjad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings - NotesDocument18 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings - NotesRajveer KaushalNo ratings yet
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Document10 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Malith MadushanNo ratings yet
- 2 Diffusion Powerpoint 2Document17 pages2 Diffusion Powerpoint 2aisah isnaeniNo ratings yet
- Thermal Transfer IDocument6 pagesThermal Transfer Iashane dwightNo ratings yet
- CHEM-Chapter 2 - State of MatterDocument13 pagesCHEM-Chapter 2 - State of Mattersecag45630No ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10Document10 pagesCh. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10sarah awadNo ratings yet
- Chapter #1 - States of MatterDocument3 pagesChapter #1 - States of MattersurprisinglysarahytNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - IngallaDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - Ingallajet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- VIII Chemistry HO 01Document9 pagesVIII Chemistry HO 01AINo ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- 08 - Particles and PurificationDocument20 pages08 - Particles and PurificationDaniel IciousNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument8 pagesStates of Mattertanish.pujari17No ratings yet
- States of Matter Form 4 VersionDocument17 pagesStates of Matter Form 4 VersionNirvana SuggieNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument4 pagesMATTERRajiv BiswasNo ratings yet
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsDocument7 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument11 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsSandeep Kumar VRNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument26 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsULTRA BOSSNo ratings yet
- 1 States of MatterDocument7 pages1 States of MatterAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- Ngss Particle Model PDFDocument2 pagesNgss Particle Model PDFDarwinEspinoza100% (1)
- Topic 1Document3 pagesTopic 1rida ikramNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledNana MinNo ratings yet
- P.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamDocument2 pagesP.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamAnonymous IqtpuNEF0No ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - Matter and Its PropertiesDocument3 pagesExercise 1 - Matter and Its PropertiespututuPLNo ratings yet
- 1 States of Matter Particle Model PowerpointDocument23 pages1 States of Matter Particle Model Powerpointloupoo80No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics FlashcardsDocument18 pagesThermal Physics FlashcardsKhushi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesDocument10 pagesLesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesおっぱいNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Particle ModelDocument4 pages5.1 Particle ModelKris_14No ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument15 pagesCell PhysiologyTeacher AlexNo ratings yet
- Matters in Our SurroundingDocument48 pagesMatters in Our SurroundingXm PiratesNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)Document28 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)salma salNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Diffussion and OsmosisDocument9 pagesUnit 2 - Diffussion and OsmosisWaseem AhmedNo ratings yet
- States of MattesDocument3 pagesStates of Mattesyashmiganegoda13No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- 6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346Document5 pages6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346avantikajethani20No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings (N)Document5 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings (N)MGMT1 armNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument10 pagesStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocument17 pagesNotre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityGaylord M. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of ParticlesDocument14 pagesKinetic Theory of ParticlesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Design of Support BC BhattacharyaDocument24 pagesDesign of Support BC BhattacharyaRADHE GRAPHICSNo ratings yet
- AphiweDocument16 pagesAphiweaphiweshozi18No ratings yet
- Experiment 6 (Formal Report)Document9 pagesExperiment 6 (Formal Report)Thea IbarraNo ratings yet
- Section 18 24Document26 pagesSection 18 24hecirlene vieiraNo ratings yet
- X-Mas Tree 4-1/16'' X 3-1/8'', 5K, - 20 To 250°F, H S: Type Approval / Design Verification ReviewDocument1 pageX-Mas Tree 4-1/16'' X 3-1/8'', 5K, - 20 To 250°F, H S: Type Approval / Design Verification ReviewFernando OlaveoNo ratings yet
- 30% Glass Fiber (30 GF) PEEKDocument10 pages30% Glass Fiber (30 GF) PEEKReza ashtianiNo ratings yet
- Therminol & High Temperature FluidsDocument2 pagesTherminol & High Temperature FluidssanipoulouNo ratings yet
- Energy Recovery VentilationDocument16 pagesEnergy Recovery VentilationAlberto DiazNo ratings yet
- Contents of CAMPUSDocument78 pagesContents of CAMPUSVicky GautamNo ratings yet
- T650 - Engineering Science N4 April QP 2021Document10 pagesT650 - Engineering Science N4 April QP 2021Logan JesseNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document8 pagesHW 5Anonymous AjrDxGNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document35 pagesWeek 1EdinberSPNo ratings yet
- Amu DaDocument9 pagesAmu DaJerry LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Serway (641-648)Document8 pagesPhysics Serway (641-648)leandro veigaNo ratings yet
- X MPL PhyDocument111 pagesX MPL PhysugothaaaNo ratings yet
- TDP 796-060 PreviewDocument8 pagesTDP 796-060 PreviewSusan LamNo ratings yet
- Cooling Solidification Metal Parameters 2Document1 pageCooling Solidification Metal Parameters 2Erdi Sofyandra AdikriNo ratings yet
- Tedds Foundation DesignDocument7 pagesTedds Foundation DesignMasaba SolomonNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument185 pagesDistillationChai Hong Loh100% (1)
- Quiz Fluid LabDocument3 pagesQuiz Fluid LabMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Heat Lecture NotesDocument62 pagesHeat Lecture NotesAS HUMBLE PIANONo ratings yet
- Lecturenote 1288194012chapter 1-2Document61 pagesLecturenote 1288194012chapter 1-2Baysa CamadNo ratings yet
- Advance ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesAdvance Thermodynamicsrandy_yusufNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 - FiniteConVolAn - Spring 2020 ADocument39 pagesChapter5 - FiniteConVolAn - Spring 2020 AJohn SimonNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Ideal Gas LawDocument8 pagesLab 1 - Ideal Gas LawJammy TanNo ratings yet
- Faculty - Civil Engineering - 2022 - Session 1 - Degree - Ecs416Document4 pagesFaculty - Civil Engineering - 2022 - Session 1 - Degree - Ecs416Sarah ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Ghansali Pumping Water Supply SchemeDocument43 pagesGhansali Pumping Water Supply SchemeProject ManagerStructuresNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument12 pagesRankine CycleVishant GuliaNo ratings yet
- Splice Joint Design To EurocodeDocument3 pagesSplice Joint Design To Eurocodeikanyu79No ratings yet
Key Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties Properties
Key Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties Properties
Uploaded by
Shimaa Elsharnoby0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pages1) The particle model explains that all matter is made up of tiny particles and the properties of solids, liquids, and gases depend on how the particles behave.
2) In solids, particles are close together and vibrate in fixed positions. In liquids, particles are close but can move past each other allowing liquids to flow and take the shape of containers. Gases have particles that are far apart, spread out, and move quickly in all directions.
3) Changes in temperature and concentration affect the rate of diffusion, which is the spreading out of particles from an area of higher to lower concentration. Higher temperature and concentration increase the rate of diffusion.
Original Description:
Original Title
Particle Model
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The particle model explains that all matter is made up of tiny particles and the properties of solids, liquids, and gases depend on how the particles behave.
2) In solids, particles are close together and vibrate in fixed positions. In liquids, particles are close but can move past each other allowing liquids to flow and take the shape of containers. Gases have particles that are far apart, spread out, and move quickly in all directions.
3) Changes in temperature and concentration affect the rate of diffusion, which is the spreading out of particles from an area of higher to lower concentration. Higher temperature and concentration increase the rate of diffusion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesKey Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties Properties
Key Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties Properties
Uploaded by
Shimaa Elsharnoby1) The particle model explains that all matter is made up of tiny particles and the properties of solids, liquids, and gases depend on how the particles behave.
2) In solids, particles are close together and vibrate in fixed positions. In liquids, particles are close but can move past each other allowing liquids to flow and take the shape of containers. Gases have particles that are far apart, spread out, and move quickly in all directions.
3) Changes in temperature and concentration affect the rate of diffusion, which is the spreading out of particles from an area of higher to lower concentration. Higher temperature and concentration increase the rate of diffusion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
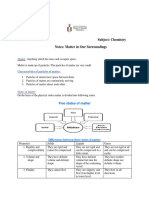
Knowledge Organiser – Particle model
Key Terms Definitions Particle Theory
State of matter Matter is divided into three states: solid, liquid, and gas. All matter is made up of particles. Particle theory is used to explain the properties of solids,
liquids and gases. Each of the states of matter is made up from particles, however the
Melting Change of state from solid to liquid. particles behave differently in each.
Freezing Change of state from liquid to solid Solids Liquids Gases
Evaporation Change of state from liquid to gas.
Condensation Change of state from gas to liquid.
Diffusion Particles spread from a region of higher concentration to a Properties Properties Properties
region of lower concentration. Fixed shape Take the shape of a Completely fill the space the
Cannot flow container occupy.
Rate How fast an event, e.g. diffusion, is happening. Can flow Can flow
Cannot be compressed (squashed)
Concentration The number of particles in a known volume. Particles are close together Cannot be compressed Can be compressed.
Particles vibrate next to each Particles are close together Particles move quickly in all
Particles All matter is made up of tiny particles. but able to move past each directions, are far apart and
other, but cannot move past each
Pressure Pressure is formed when particles collide with the walls of other. other. have space to move in and out.
containers.
Changes of state Factors affecting diffusion
Diffusion
The spreading out of particles is called There are 2 factors affecting the rate of diffusion:
diffusion. This diagram shows how 1.Temperature: When temperature increases,
particles move from an area of high particles gain more energy. They can then move and
concentration to an area of low spread out at a higher rate.
concentration. 2.Concentration: When concentration increases, the
rate of diffusion increases.
Knowledge Organiser – Particle model
Gas Pressure There are 3 factors affecting gas pressure:
Gas pressure is caused by gas particles colliding with the walls of the 1. Number of particles: The more gas particles inside the container, the more
container. A container also experiences pressure on the outside. often collisions will occur, creating a higher pressure.
Air particles on the outside collide with the outside wall. An imbalance 2. Temperature: If gas particles are heated up, they move with a higher speed
between the pressure on the inside and outside can cause the container to and collide more often with the walls of the container, causing a higher
change its shape. pressure.
3. Volume: If the same amount of gas particles are put into a container of a
smaller volume, pressure will increase because particles will collide more
frequently with the walls when they have less space.
You might also like
- TP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument2 pagesTP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterThabang Sbo PhokontsiNo ratings yet
- TP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1Document2 pagesTP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- States of Matter DiffusionDocument17 pagesStates of Matter Diffusion吕洁儿No ratings yet
- Lesson Note 3 - Investigating Diffusion-Unit 6.3Document6 pagesLesson Note 3 - Investigating Diffusion-Unit 6.3navidu dasisNo ratings yet
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- iGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4Document11 pagesiGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4SimonNo ratings yet
- Resource 1Document13 pagesResource 1eeren41789No ratings yet
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetDocument2 pagesStates of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument50 pagesUnderstanding Kinetic Particle TheoryozmanNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Group 2Document15 pagesDiffusion Group 2johndominicmmalubagoNo ratings yet
- C1 Chapter 1Document1 pageC1 Chapter 1Rehan ShahNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document58 pagesChem 1Heba HebaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesDocument3 pagesStates of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesMatipa DembureNo ratings yet
- Assumption College of NabunturanDocument4 pagesAssumption College of NabunturanAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- Grade 8 NotesDocument2 pagesGrade 8 NotesmunilalluNo ratings yet
- Phyw 2Document42 pagesPhyw 2Sajjad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings - NotesDocument18 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings - NotesRajveer KaushalNo ratings yet
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Document10 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Malith MadushanNo ratings yet
- 2 Diffusion Powerpoint 2Document17 pages2 Diffusion Powerpoint 2aisah isnaeniNo ratings yet
- Thermal Transfer IDocument6 pagesThermal Transfer Iashane dwightNo ratings yet
- CHEM-Chapter 2 - State of MatterDocument13 pagesCHEM-Chapter 2 - State of Mattersecag45630No ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10Document10 pagesCh. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10sarah awadNo ratings yet
- Chapter #1 - States of MatterDocument3 pagesChapter #1 - States of MattersurprisinglysarahytNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - IngallaDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - Ingallajet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- VIII Chemistry HO 01Document9 pagesVIII Chemistry HO 01AINo ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- 08 - Particles and PurificationDocument20 pages08 - Particles and PurificationDaniel IciousNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument8 pagesStates of Mattertanish.pujari17No ratings yet
- States of Matter Form 4 VersionDocument17 pagesStates of Matter Form 4 VersionNirvana SuggieNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument4 pagesMATTERRajiv BiswasNo ratings yet
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsDocument7 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument11 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsSandeep Kumar VRNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument26 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsULTRA BOSSNo ratings yet
- 1 States of MatterDocument7 pages1 States of MatterAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- Ngss Particle Model PDFDocument2 pagesNgss Particle Model PDFDarwinEspinoza100% (1)
- Topic 1Document3 pagesTopic 1rida ikramNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledNana MinNo ratings yet
- P.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamDocument2 pagesP.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamAnonymous IqtpuNEF0No ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - Matter and Its PropertiesDocument3 pagesExercise 1 - Matter and Its PropertiespututuPLNo ratings yet
- 1 States of Matter Particle Model PowerpointDocument23 pages1 States of Matter Particle Model Powerpointloupoo80No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics FlashcardsDocument18 pagesThermal Physics FlashcardsKhushi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesDocument10 pagesLesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesおっぱいNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Particle ModelDocument4 pages5.1 Particle ModelKris_14No ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument15 pagesCell PhysiologyTeacher AlexNo ratings yet
- Matters in Our SurroundingDocument48 pagesMatters in Our SurroundingXm PiratesNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)Document28 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)salma salNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Diffussion and OsmosisDocument9 pagesUnit 2 - Diffussion and OsmosisWaseem AhmedNo ratings yet
- States of MattesDocument3 pagesStates of Mattesyashmiganegoda13No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- 6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346Document5 pages6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346avantikajethani20No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings (N)Document5 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings (N)MGMT1 armNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument10 pagesStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocument17 pagesNotre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityGaylord M. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of ParticlesDocument14 pagesKinetic Theory of ParticlesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Design of Support BC BhattacharyaDocument24 pagesDesign of Support BC BhattacharyaRADHE GRAPHICSNo ratings yet
- AphiweDocument16 pagesAphiweaphiweshozi18No ratings yet
- Experiment 6 (Formal Report)Document9 pagesExperiment 6 (Formal Report)Thea IbarraNo ratings yet
- Section 18 24Document26 pagesSection 18 24hecirlene vieiraNo ratings yet
- X-Mas Tree 4-1/16'' X 3-1/8'', 5K, - 20 To 250°F, H S: Type Approval / Design Verification ReviewDocument1 pageX-Mas Tree 4-1/16'' X 3-1/8'', 5K, - 20 To 250°F, H S: Type Approval / Design Verification ReviewFernando OlaveoNo ratings yet
- 30% Glass Fiber (30 GF) PEEKDocument10 pages30% Glass Fiber (30 GF) PEEKReza ashtianiNo ratings yet
- Therminol & High Temperature FluidsDocument2 pagesTherminol & High Temperature FluidssanipoulouNo ratings yet
- Energy Recovery VentilationDocument16 pagesEnergy Recovery VentilationAlberto DiazNo ratings yet
- Contents of CAMPUSDocument78 pagesContents of CAMPUSVicky GautamNo ratings yet
- T650 - Engineering Science N4 April QP 2021Document10 pagesT650 - Engineering Science N4 April QP 2021Logan JesseNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document8 pagesHW 5Anonymous AjrDxGNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document35 pagesWeek 1EdinberSPNo ratings yet
- Amu DaDocument9 pagesAmu DaJerry LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Serway (641-648)Document8 pagesPhysics Serway (641-648)leandro veigaNo ratings yet
- X MPL PhyDocument111 pagesX MPL PhysugothaaaNo ratings yet
- TDP 796-060 PreviewDocument8 pagesTDP 796-060 PreviewSusan LamNo ratings yet
- Cooling Solidification Metal Parameters 2Document1 pageCooling Solidification Metal Parameters 2Erdi Sofyandra AdikriNo ratings yet
- Tedds Foundation DesignDocument7 pagesTedds Foundation DesignMasaba SolomonNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument185 pagesDistillationChai Hong Loh100% (1)
- Quiz Fluid LabDocument3 pagesQuiz Fluid LabMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Heat Lecture NotesDocument62 pagesHeat Lecture NotesAS HUMBLE PIANONo ratings yet
- Lecturenote 1288194012chapter 1-2Document61 pagesLecturenote 1288194012chapter 1-2Baysa CamadNo ratings yet
- Advance ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesAdvance Thermodynamicsrandy_yusufNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 - FiniteConVolAn - Spring 2020 ADocument39 pagesChapter5 - FiniteConVolAn - Spring 2020 AJohn SimonNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Ideal Gas LawDocument8 pagesLab 1 - Ideal Gas LawJammy TanNo ratings yet
- Faculty - Civil Engineering - 2022 - Session 1 - Degree - Ecs416Document4 pagesFaculty - Civil Engineering - 2022 - Session 1 - Degree - Ecs416Sarah ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Ghansali Pumping Water Supply SchemeDocument43 pagesGhansali Pumping Water Supply SchemeProject ManagerStructuresNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument12 pagesRankine CycleVishant GuliaNo ratings yet
- Splice Joint Design To EurocodeDocument3 pagesSplice Joint Design To Eurocodeikanyu79No ratings yet