Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Smell and Taste
Smell and Taste
Uploaded by
Amanuel Dina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views17 pagesThe tongue contains thousands of taste buds that detect the four basic tastes: sweet, sour, bitter, and salty. The front third of the tongue detects sweet tastes while the sides detect sour and the back detects bitter tastes. Taste buds contain nerve cells that send signals to the brain. The sense of smell detects thousands of odors through smell receptors in the nose. Odor molecules bind to receptors and send signals to areas of the brain involved in memory and emotion. Together, taste and smell provide the sense of flavor.
Original Description:
Original Title
Smell and Taste Ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe tongue contains thousands of taste buds that detect the four basic tastes: sweet, sour, bitter, and salty. The front third of the tongue detects sweet tastes while the sides detect sour and the back detects bitter tastes. Taste buds contain nerve cells that send signals to the brain. The sense of smell detects thousands of odors through smell receptors in the nose. Odor molecules bind to receptors and send signals to areas of the brain involved in memory and emotion. Together, taste and smell provide the sense of flavor.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views17 pagesSmell and Taste
Smell and Taste
Uploaded by
Amanuel DinaThe tongue contains thousands of taste buds that detect the four basic tastes: sweet, sour, bitter, and salty. The front third of the tongue detects sweet tastes while the sides detect sour and the back detects bitter tastes. Taste buds contain nerve cells that send signals to the brain. The sense of smell detects thousands of odors through smell receptors in the nose. Odor molecules bind to receptors and send signals to areas of the brain involved in memory and emotion. Together, taste and smell provide the sense of flavor.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 17
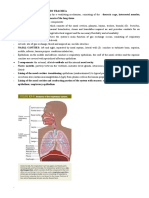
The sense of taste
• Tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth.it is
covered with moist, pink tissue called
mucosa.
• Tiny bumps called papillae give the tongue its
rough texture.
• Thousands of taste buds covers papillae.
• Taste buds are collections of nerve like cells
that connect to nerves running in to the brain
• Human tongue has three distinct divisions.
• Namely ;
the apex: accounts for 1/3rd of ant.surface
- sweet taste buds are present
the body:Ant. 2/3rd.
- Salt ,bitter and sour tastes are
present
the root : Attaches the tongue to the bottom
or floor of mouth cavity
• Smell and taste are Chemical sensations
• Taste is the gustatory sensation
• Smell is olfactory sensation
• Taste drives appetite and protects us from
poisons.
Sensory afferent nerves and pathways
• Taste buds on the posterior third of tongue
have a sensory pathway through
glossopharngeal nerve(9),whereas the
anterior 2/3rd of the tongues innervated by the
chorda tympani branch of the fascial nerves,
which then gets interpreted in parietal lobe.
Taste receptors;taste buds
• Taste buds are specialized sensory organs that
are most numerous on the surface of the tongue;
but also present on the soft palate and on the
walls of oropharynx.
• Their number declines with age.
• Taste receptors do not have an axon.
• Information is relayed to terminals of sensory
fibers by neurotransmitters. These fibers arise
from ganglion of cranial nerves.
Primary taste modalities
• There are only four basic tastes , which are sensed most
accurately on particular parts of the tongue.
• These are ;
• Sweet:Tip of tongue
• Sour:Side of tongue
• Bitter : Back of tongue and
• Salty: over most of tongue, but concentrated on the
sides.
• Combinations of these taste modalities allows for
impressive taste discrimanation.
• Sour tastes are produced by hydrogen ions(H+),
therefore all acids tastes sour.
• Salt tastes are produced by amiloride sensetive
Na+ channel.
• Sweet tastes are produced by glucose binding to
receptors activating adenylyl cyclase,thereby
elevating CAMP.
• Bitter tastes are produced by second
messenger(IP3) mediated release of Ca2+
New tastes(Umami taste)
• Is the taste of certain aminoacids(E.g.
Glutamate, Aspartate and related compounds.
• Metabotropic glutamate receptor mediates
this taste.
• Monosodium glutamate added to many foods
enhance their tastes.(The main ingridient of
soy sauce).
Flavour
• Is a combination of;
• taste, smell, texture, and other physical
feature(e.g temprature)
Abnormalities(taste blindness)
• Is a genetically programmed insensitivity to
bitterness and strong tastes.
• Nontasters or people who experience taste
blindness have fewer tastebuds on their
tongue than other people do.
Sense of smell
• Odour molecules must be small enough(<300-
400 relative molecular mass) so that they can
vapourise,reach the nose and then dissolve in
the mucos)
• We can distinguish around 10,000 different
smell.
• Anosmic(Someone who has lost some or all of
their sense of smell)
Sensory pathways in olfaction
• Olfactory ephithilium; contains sensory cells,
bowman’s glands (secreting bathing fluid and
proteins).
• Odorant binding proteins facilitates the transfer of
lipophilic ligands(odorants) across mucos layer to the
receptors.
• Odorant receptor neurons are bipolar neurons in the
nasal epithilium. And they are capable of
regenerating. They also contain cilia which project in
to the mucus(containing receptor proteins).
Odor qualities
• On the basis of the apparent similarities perceived
odour quality or confusions in naming, it was
concluded that there were six main odor qualities;
• FRUITY
• FLOWERY
• RESINOUS
• SPICY
• FOUL and
• BURNED.
Olfactory treshhold
• Is the lowest concentration of certain odor
compound that is perceivable by human sense
of smell.
• The treshhold of a chemical compound is in
part determined by its shape,polarity,partial
charges and molecular mass.
Central processing
• Neurons from the lateral olfactory tract
project to – areas of limbic system.
• Projections are also sent to the thalamus and
hence to frontal cortex for recognition.
You might also like
- Ebook Ebook PDF Sensation and Perception 2nd Edition by Bennett L Schwartz PDFDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Sensation and Perception 2nd Edition by Bennett L Schwartz PDFcharles.hurt81598% (40)
- Taste and Smell (Neurophysio)Document49 pagesTaste and Smell (Neurophysio)Rechie RechNo ratings yet
- GustationDocument21 pagesGustationAhaisibwe GordonNo ratings yet
- GustationDocument23 pagesGustationyazan.fadi123No ratings yet
- Chemical SensationsDocument38 pagesChemical SensationsMr mk RollinsNo ratings yet
- SENSE OF TASTE-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesSENSE OF TASTE-WPS OfficeHafsat BakuraNo ratings yet
- Taste SensationDocument56 pagesTaste SensationSyedaNaveenBatoolNo ratings yet
- TasteDocument14 pagesTasteburagohainaviNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Penghidu Dan PengecapanDocument48 pagesGangguan Penghidu Dan PengecapanUgaugaaNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Part 1 (Taste & Smell)Document18 pagesSpecial Senses Part 1 (Taste & Smell)rizwanbas100% (1)
- Sensory Physiology 2 Last 2023Document66 pagesSensory Physiology 2 Last 2023odiodi57No ratings yet
- 11-Taste and SmellDocument30 pages11-Taste and SmellOlaniyi EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Senses - Taste and SmellDocument28 pagesThe Chemical Senses - Taste and SmellZuri XimenaNo ratings yet
- L5 - Special SensesDocument39 pagesL5 - Special SensesNana Boakye Anthony AmpongNo ratings yet
- Taste and SmellDocument36 pagesTaste and SmellKarthikeyan Balakrishnan100% (2)
- Chemical Senses: Taste and Smell: Emmanuel A. Gutierrez, MDDocument57 pagesChemical Senses: Taste and Smell: Emmanuel A. Gutierrez, MDJimell ObradorNo ratings yet
- Taste and OlfactionDocument43 pagesTaste and OlfactionTanishq Hitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Iv: Gustation (Taste)Document14 pagesSpecial Senses Iv: Gustation (Taste)Francis ChegeNo ratings yet
- Sensory - Unit 1Document45 pagesSensory - Unit 1AKASH SNo ratings yet
- Physiology o F GustationDocument26 pagesPhysiology o F GustationPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- t3 Supplemental NotesDocument34 pagest3 Supplemental NotesAllyza MuñozNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Special Senses NotesDocument58 pagesAnatomy of Special Senses Notesglenian560No ratings yet
- Taste and SmellDocument39 pagesTaste and SmellAyi Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentapi-614390592No ratings yet
- Physiology of Smell and Taste-MyDocument46 pagesPhysiology of Smell and Taste-MyHamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Sense - TasteDocument21 pagesChemical Sense - TasteJoe WeahNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Senses-TasteDocument16 pagesThe Chemical Senses-TastejolilarmatarNo ratings yet
- Smell and TasteDocument16 pagesSmell and TasteHANIN KALEEM PASHA HKBK 47No ratings yet
- Olfaction: Chapter 15 Special SensesDocument3 pagesOlfaction: Chapter 15 Special SensesLynel Joy JamotilloNo ratings yet
- Taste and SmellDocument11 pagesTaste and SmellBoazNo ratings yet
- Olfaction and Gustation: What Does A Snake Smell/taste Like?Document23 pagesOlfaction and Gustation: What Does A Snake Smell/taste Like?Abiy Tewelde TekleNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: - Mohammad Waqas Lari - Karachi Med & DentalDocument18 pagesPrepared By:: - Mohammad Waqas Lari - Karachi Med & DentalalirazanaqwiNo ratings yet
- Sense of Taste: 13 Chemical Receptors in The Taste Cells Threshold For TasteDocument5 pagesSense of Taste: 13 Chemical Receptors in The Taste Cells Threshold For TasteAileen CastilloNo ratings yet
- Sense of TasteDocument10 pagesSense of TasteGatita LindaNo ratings yet
- 11 Paper Title Food Analysis and Quality Control Module-08 SensoryDocument11 pages11 Paper Title Food Analysis and Quality Control Module-08 Sensorymonera carinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: The Chemical Senses 11/24/2009Document6 pagesChapter 8: The Chemical Senses 11/24/2009kamalleryNo ratings yet
- Chemical Senses: TasteDocument26 pagesChemical Senses: TasteanisaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26Document9 pagesLecture 26Shakeel ButtNo ratings yet
- Special Senses NotesDocument17 pagesSpecial Senses NotesizabelaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Tutorial Task 6 & 7Document19 pages2.1 Tutorial Task 6 & 7ENOCH NAPARI ABRAMANNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Skin Receptors, Taste and Smell Nov 4th 2016Document23 pagesAnatomy Skin Receptors, Taste and Smell Nov 4th 2016HollyNo ratings yet
- Pragyan College of Nursing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Sense of Taste/TongueDocument3 pagesPragyan College of Nursing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Sense of Taste/TongueNeelofur Ibran AliNo ratings yet
- Taste (Gustation)Document29 pagesTaste (Gustation)kityamuwesi100% (1)
- BMC L11Document5 pagesBMC L11Sweta KannanNo ratings yet
- The Chemical SensesDocument1 pageThe Chemical Senseskristine maeNo ratings yet
- Taste and SmellDocument22 pagesTaste and SmellabdirizakNo ratings yet
- Dila MateriDocument4 pagesDila MateriAnisa Farah DillaNo ratings yet
- Special Assignment Lab PortfolioDocument13 pagesSpecial Assignment Lab Portfolioveer the robo boyNo ratings yet
- Audition: Hearing, The Ear, and Sound LocalizationDocument5 pagesAudition: Hearing, The Ear, and Sound LocalizationTanishqa RawlaniNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of ToungeDocument1 pageStructure and Function of ToungeDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- Taste and Taste Work in LanguageDocument26 pagesTaste and Taste Work in LanguageSallarNo ratings yet
- Sense of TasteDocument13 pagesSense of TastefihaNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Tongue and TasteDocument21 pagesStructure of The Tongue and Tastessiwe145No ratings yet
- The Sense of Smell - MMO 2023Document34 pagesThe Sense of Smell - MMO 2023dr MohammedNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument6 pagesSpecial SensesGunal KuttyNo ratings yet
- Tongue & It's Applied AspectsDocument64 pagesTongue & It's Applied AspectsPrachi MulayNo ratings yet
- Taste and Smell: - by Group 3BDocument11 pagesTaste and Smell: - by Group 3BDeepak DelphyNo ratings yet
- MIT9 35s09 Lec04 TasteDocument40 pagesMIT9 35s09 Lec04 TasteJuan David BrandNo ratings yet
- Sense of Touch (Skin) ..: (B) Number of Receptor PresentDocument8 pagesSense of Touch (Skin) ..: (B) Number of Receptor Presentkaiozone4530No ratings yet
- Olfactory recep-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesOlfactory recep-WPS OfficecimdesadesuNo ratings yet
- 3 CommunicationDocument58 pages3 CommunicationAmanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- Eye PhysiologyDocument11 pagesEye PhysiologyAmanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiol-OGY: DR I.GDocument55 pagesRenal Physiol-OGY: DR I.GAmanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- Functional Pattern Approach CaseDocument20 pagesFunctional Pattern Approach CaseAmanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- Ethics-Legal Aspects To Nursing: By: Lami. G (MSC in M&RHN)Document37 pagesEthics-Legal Aspects To Nursing: By: Lami. G (MSC in M&RHN)Amanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Professional Nursing and Ethics: By:Lami Gurmessa (Bsc. MSCDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Professional Nursing and Ethics: By:Lami Gurmessa (Bsc. MSCAmanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- ZhongHuangDong Bodilysensationandembodiment JCLPREPRINTDocument36 pagesZhongHuangDong Bodilysensationandembodiment JCLPREPRINTEnjoy GoNo ratings yet
- SMART CHEMICAL SENSING Electronic NoseDocument278 pagesSMART CHEMICAL SENSING Electronic NoseSadeq NeiroukhNo ratings yet
- Quality Assessment and Acceptability of Hog Plum FruitDocument85 pagesQuality Assessment and Acceptability of Hog Plum FruitJenniebeth ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- LS2SC-BC-PSD-LE/AE-18 LS2SC-BC-PSD-LE/AE/JHS-19: SchoolDocument4 pagesLS2SC-BC-PSD-LE/AE-18 LS2SC-BC-PSD-LE/AE/JHS-19: SchoolZaibell Jane TareNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub Xenolinguistics Towards A Science of Extraterrestrial Language 1nbsped 9781003352174 9781032399607 9781032399591Document248 pagesDokumen - Pub Xenolinguistics Towards A Science of Extraterrestrial Language 1nbsped 9781003352174 9781032399607 9781032399591daftarkhokhaNo ratings yet
- Nasal BreathingDocument3 pagesNasal BreathingDenis Alibor MajhenNo ratings yet
- PURPLE CORN FLOUR STA MARIA THESIS OUTLINE Final Revised2Document43 pagesPURPLE CORN FLOUR STA MARIA THESIS OUTLINE Final Revised2Jain EpifanioNo ratings yet
- Zingerman's Sept-Oct 2022 - NewsletterDocument7 pagesZingerman's Sept-Oct 2022 - NewsletterZingerman's Community of BusinessesNo ratings yet
- 6 ImageryDocument41 pages6 ImageryGodwayne0% (1)
- LUISIER Et Al., 2015Document10 pagesLUISIER Et Al., 2015pedroNo ratings yet
- 075 - Neurology Physiology) Cerebrum - Temporal Lobe Anatomy & FunctionDocument2 pages075 - Neurology Physiology) Cerebrum - Temporal Lobe Anatomy & Functionzayat13No ratings yet
- Stars Without Number Alien GeneratorDocument40 pagesStars Without Number Alien GeneratorKacper Andrzejak100% (3)
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory SystemZeianne BosabicaNo ratings yet
- Sensory Testing Process DetailsDocument40 pagesSensory Testing Process DetailsMario JiménezNo ratings yet
- General Symptomatology of Psychiatric DisorderDocument58 pagesGeneral Symptomatology of Psychiatric DisorderAhmed HegazyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Test - Reading - 230124Document8 pagesAssessment Test - Reading - 230124qthongngoc179No ratings yet
- Final Chapter Research Abm 1Document10 pagesFinal Chapter Research Abm 1Lemuel Umpad VillacortaNo ratings yet
- Pido Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesPido Lesson PlanMariter PidoNo ratings yet
- Ncert - Exemplar - Control and CoordinationDocument18 pagesNcert - Exemplar - Control and CoordinationRagini BaghelNo ratings yet
- Biopsychology AssignmentDocument35 pagesBiopsychology Assignmentbishakha stylesNo ratings yet
- HES 101 - Lesson 11-SensesDocument4 pagesHES 101 - Lesson 11-SensesLAGUERTA, JOHN MICHAEL A.No ratings yet
- Pub - Swim Like A Pro How To Swim Faster Amp Smarter With A Holistic Training Guide 9798704873587Document206 pagesPub - Swim Like A Pro How To Swim Faster Amp Smarter With A Holistic Training Guide 9798704873587Rafael100% (1)
- HAP Practical PDFDocument44 pagesHAP Practical PDFVaishnavi SinghNo ratings yet
- AromaTouch Technique® CertificationDocument56 pagesAromaTouch Technique® CertificationJUDY BERGRENNo ratings yet
- (NEU) 3.4 Examination of The Cranial Nerves - Dr. Nico Paulo M. Dimal MD FPNADocument11 pages(NEU) 3.4 Examination of The Cranial Nerves - Dr. Nico Paulo M. Dimal MD FPNAGeraldine TeopyNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Topics For Biology StudentsDocument4 pagesResearch Paper Topics For Biology Studentsfvgbhswf100% (1)
- To Cause To Make Divine Through Smoke AnDocument14 pagesTo Cause To Make Divine Through Smoke AnTom ReményiNo ratings yet
- Early Medieval Europe - 2020 - Burridge - Incense in Medicine An Early Medieval PerspectiveDocument37 pagesEarly Medieval Europe - 2020 - Burridge - Incense in Medicine An Early Medieval PerspectiveVratislav ZervanNo ratings yet
- Special - Senses (Chapter 8)Document14 pagesSpecial - Senses (Chapter 8)Joanna Marie TulioNo ratings yet