Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsAnatomy and Physiology: An Introduction To The Human Body
Anatomy and Physiology: An Introduction To The Human Body
Uploaded by
Theophilus BaidooAnatomy is the study of body structures and their relationships, while physiology is the study of how body structures function and work together to sustain life. The human body has six levels of organization from chemicals to tissues to organs and systems. The four basic tissue types are epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue. The major organ systems include the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, digestive, urinary, lymphatic, respiratory and reproductive systems. Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to maintain internal equilibrium through regulatory processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Answers To QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnswers To QuestionsL-yeah Traifalgar52% (21)
- Prefixes and Suffixes ListDocument4 pagesPrefixes and Suffixes Listapi-262294171No ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Medical PrefixesDocument5 pagesMedical Terminology Medical PrefixesRicky Rhenzs Gultia Villafuerte100% (6)
- Health Care Terminology: Socorro Milagros C. Alcancia, RND, PHDDocument25 pagesHealth Care Terminology: Socorro Milagros C. Alcancia, RND, PHDShaina Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation 1Document14 pagesOxygenation 1Riño Roland RexNo ratings yet
- 01 Introductory PgyDocument76 pages01 Introductory Pgygbsreg gbsregNo ratings yet
- Histopath ReviewDocument389 pagesHistopath ReviewLucille MarieNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument10 pagesMedical TerminologyjoewelbyNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Red Blood Cells DisordersDocument47 pagesHaematology: Red Blood Cells Disordersbv2328002No ratings yet
- Trigger Topics For FMG Exams by MistDocument3 pagesTrigger Topics For FMG Exams by Mistvijay resuNo ratings yet
- Greek and Latin PrefixesDocument9 pagesGreek and Latin Prefixesmikesmith881No ratings yet
- Salivary Gland TumoursDocument131 pagesSalivary Gland TumoursSushmithaNo ratings yet
- State Council of Educational Research and Training TNCF 2017 - Draft SyllabusDocument12 pagesState Council of Educational Research and Training TNCF 2017 - Draft SyllabuspullaiNo ratings yet
- Patho1 Lab 2nd ExamDocument43 pagesPatho1 Lab 2nd ExambluebeeeNo ratings yet
- ImmunohistochemistryDocument29 pagesImmunohistochemistryAvi VermaNo ratings yet
- Pitu TaryDocument13 pagesPitu Taryمحمد عليNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Pathology: Lecture On Pathomorphology For 3-rd Year StudentsDocument44 pagesEndocrine Pathology: Lecture On Pathomorphology For 3-rd Year StudentsRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- SpleenDocument42 pagesSpleenRashed LabNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Assistant Surgeon Exam PDFDocument9 pagesSyllabus Assistant Surgeon Exam PDFMaguNo ratings yet
- The Spleen: by DR (MRS) BaulchDocument42 pagesThe Spleen: by DR (MRS) BaulchPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Baguio General Hospital and Medical Center Department of General SurgeryDocument27 pagesCase Presentation: Baguio General Hospital and Medical Center Department of General SurgeryJorge De VeraNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Endocrine System: Dr. Nesreen Bataineh MD, FrcpathDocument20 pagesPathology of Endocrine System: Dr. Nesreen Bataineh MD, FrcpathQutaybah JahmanyNo ratings yet
- Pathology Aspect Pituitary Gland: By. Meike Rachmawati, DR Pathology Anatomy Department Medical Faculty-UnisbaDocument35 pagesPathology Aspect Pituitary Gland: By. Meike Rachmawati, DR Pathology Anatomy Department Medical Faculty-UnisbadeasyahNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology FixedDocument3 pagesMedical Terminology FixedBaeman KyottNo ratings yet
- Main DivisionDocument61 pagesMain DivisionChadCowgillNo ratings yet
- Understand The Difference Between A Prefix and A SuffixDocument40 pagesUnderstand The Difference Between A Prefix and A Suffixlopezlozano.analilianNo ratings yet
- Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia: Mini-Symposium: Endometrial PathologyDocument8 pagesDemystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia: Mini-Symposium: Endometrial PathologyNi Wayan Ana PsNo ratings yet
- Anemia JournalDocument8 pagesAnemia JournalAmreen KausarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus FOR Undergraduate (BDS) : (Screening Test For Indian Nationals With Foreign Dental Qualifications)Document54 pagesSyllabus FOR Undergraduate (BDS) : (Screening Test For Indian Nationals With Foreign Dental Qualifications)Pulakit BhartiNo ratings yet
- All About Pleural EffusionDocument6 pagesAll About Pleural EffusionTantin KristantoNo ratings yet
- Nada's GI Path ReviewDocument44 pagesNada's GI Path ReviewNada Much100% (2)
- Bonemarrow 4 180106181202Document94 pagesBonemarrow 4 180106181202Caroline K.No ratings yet
- Bone MarrowDocument6 pagesBone MarrowKIPRUTO DENNISNo ratings yet
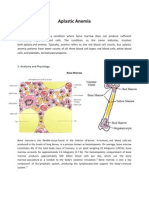
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument16 pagesAplastic Anemiahazelposis100% (1)
- KULIAH II Lymphoreticular Pathology Kuliah IIDocument75 pagesKULIAH II Lymphoreticular Pathology Kuliah IIWidya AnggrainyNo ratings yet
- 8-Trematodes Ibrahim2016Document35 pages8-Trematodes Ibrahim2016Buntukazi MapamelaNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasDocument39 pagesDysphagia: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviNo ratings yet
- (Surg 3A) Spleen and Friends-Dr. Segismundo, Dr. Broqueza (Aisle Paler, Joseph Tolentino)Document15 pages(Surg 3A) Spleen and Friends-Dr. Segismundo, Dr. Broqueza (Aisle Paler, Joseph Tolentino)Aria Jean MostajoNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Hematopoietic System: Myeloid Tissues Lymphoid TissuesDocument24 pagesPathology of The Hematopoietic System: Myeloid Tissues Lymphoid TissuesashaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument81 pagesThyroid Glanddr_shamimrNo ratings yet
- Spleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementDocument53 pagesSpleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOESISDocument71 pagesHEMATOPOESISHussenNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument17 pagesCell StructurekimberlynNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukaemia: Dr. Nuryanti, M.Ked (Clin - Path), SPPK Laboratory Patologi Clinic Rs GranmedDocument29 pagesAcute Leukaemia: Dr. Nuryanti, M.Ked (Clin - Path), SPPK Laboratory Patologi Clinic Rs GranmedArnita Elisabet ManurungNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 and 2 Introduction To Pathology Cellular Injury Death Adaptation Inflammation and RepairDocument96 pagesLecture1 and 2 Introduction To Pathology Cellular Injury Death Adaptation Inflammation and RepairMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The Lymphatic System: Russell C Hendershot DO, MS, FAAFPDocument50 pagesPhysical Examination of The Lymphatic System: Russell C Hendershot DO, MS, FAAFPNajwa100% (1)
- Understand The Difference Between A Prefix and A SuffixDocument38 pagesUnderstand The Difference Between A Prefix and A Suffixlopezlozano.analilianNo ratings yet
- Sa Gland - Pleomorphic Adenoma 6Document46 pagesSa Gland - Pleomorphic Adenoma 6akshayajeevaajaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara Discipline of ParasitologyDocument72 pagesParasitology: Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara Discipline of ParasitologyanaNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument29 pagesAplastic AnemiaAshish SoniNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Cell InjuryDocument42 pagesPraktikum Cell InjurySharmadave SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- HY PathologyDocument24 pagesHY Pathologyyahomed519No ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument5 pagesAplastic AnemiaVenice Marie GargantaNo ratings yet
- Dermatology A Manual of Differential DiagnosisDocument83 pagesDermatology A Manual of Differential Diagnosisع كيف كيفك Dhaif-saeedNo ratings yet
- Current and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 1: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryFrom EverandCurrent and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 1: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryNo ratings yet
- Health Law and Ethics Lecture 01Document49 pagesHealth Law and Ethics Lecture 01Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Mentoring For 37 Military Nurses Slide Share To GoDocument56 pagesPresentation On Mentoring For 37 Military Nurses Slide Share To GoTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Grnma NMCG Webinar Zoom 28th July 2023-1Document1 pageGrnma NMCG Webinar Zoom 28th July 2023-1Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Traffitech Brochure Update - 230818 - 123024Document1 pageTraffitech Brochure Update - 230818 - 123024Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Press Release - Dubai AmbulanceDocument1 pagePress Release - Dubai AmbulanceTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Practising As A Midwife in The UkDocument27 pagesPractising As A Midwife in The UkTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Courses For Second Semester 2023 - 1Document6 pagesCourses For Second Semester 2023 - 1Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Nurse-Client RelationshipDocument31 pagesTherapeutic Nurse-Client RelationshipTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Laryea's Care StudyDocument101 pagesLaryea's Care StudyTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Depressions in Various Age-Groups and Sub-PopulationsDocument75 pagesDepressions in Various Age-Groups and Sub-PopulationsTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Weather Warning 15052023Document1 pageWeather Warning 15052023Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport System: ATP Adp + ATP Synthase P Nadh + H EnergyDocument12 pagesElectron Transport System: ATP Adp + ATP Synthase P Nadh + H EnergyTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- African St. Political Systems LectureDocument23 pagesAfrican St. Political Systems LectureTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology 1Document60 pagesEpidemiology 1Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- University of Health and Allied Sciences (UHAS) Ho Department of General and Liberal Studies UHAS 114: Introduction To Ghanaian and African StudiesDocument18 pagesUniversity of Health and Allied Sciences (UHAS) Ho Department of General and Liberal Studies UHAS 114: Introduction To Ghanaian and African StudiesTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- BIO130 Chapter 17 SlidesDocument42 pagesBIO130 Chapter 17 SlidesTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- The Hogbetsotso FestivalDocument3 pagesThe Hogbetsotso FestivalTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Slave Trade and ColonialismDocument21 pagesSlave Trade and ColonialismTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- BIO130 Chapter 15&16 SlidesDocument26 pagesBIO130 Chapter 15&16 SlidesTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Specialised Traditions of Knowledge and Health Delivery-1Document40 pagesSpecialised Traditions of Knowledge and Health Delivery-1Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Animation: Mitosis and CytokinesisDocument10 pagesAnimation: Mitosis and CytokinesisTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- African Belief Systems, Religion in Trad. Soc.Document42 pagesAfrican Belief Systems, Religion in Trad. Soc.Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- African Marriage Forms and Health Implica-TionsDocument43 pagesAfrican Marriage Forms and Health Implica-TionsTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Metabolic Pathways: Limited Number of Regulatory Enzymes Negative FeedbackDocument12 pagesRegulation of Metabolic Pathways: Limited Number of Regulatory Enzymes Negative FeedbackTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- African Family and Health DeliveryDocument25 pagesAfrican Family and Health DeliveryTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Animation: Diffusion Through Cell MembranesDocument6 pagesAnimation: Diffusion Through Cell MembranesTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: By-Victor BawiahDocument42 pagesLymphatic System: By-Victor BawiahTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Animation: Primary Active TransportDocument12 pagesAnimation: Primary Active TransportTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: BY Victor BawiahDocument171 pagesSkeletal System: BY Victor BawiahTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Chapt01 Holes Lecture Animation JWTDocument34 pagesChapt01 Holes Lecture Animation JWTCut TirayaNo ratings yet
- 9.anesthesia For Obstetrics. Pediatric Anesthesia. Geriatric Anesthesia.Document52 pages9.anesthesia For Obstetrics. Pediatric Anesthesia. Geriatric Anesthesia.karim hassanNo ratings yet
- Mycology 2021Document211 pagesMycology 2021Shania DawnNo ratings yet
- Prurigo-Nodular Ro 383Document10 pagesPrurigo-Nodular Ro 383Alexandru Ionut SavuNo ratings yet
- SAMY MSK ArthritisDocument125 pagesSAMY MSK ArthritisZintan HospitalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: Seasons in The Philippines: Let Us StartDocument5 pagesLesson Title: Seasons in The Philippines: Let Us StartGlyd Peñarubia Gallego-Diaz100% (1)
- Bone and Joint InfectionDocument43 pagesBone and Joint Infectionraheeg siddigNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Vulnerable Orphans Children Project Enrollement FormDocument8 pages7.4 Vulnerable Orphans Children Project Enrollement Formمتعلم لغة أنجليزيةNo ratings yet
- EMTDocument5 pagesEMTJohn NaughtonNo ratings yet
- CPHM TransesDocument5 pagesCPHM TransesElizer Robles Jr.No ratings yet
- Preventive, Promotive, Curative, RehabilitativeDocument54 pagesPreventive, Promotive, Curative, Rehabilitativetintu100% (1)
- Espohagectomy: Done by DR - Abdallah HasandarrasDocument17 pagesEspohagectomy: Done by DR - Abdallah HasandarrasAbdallah DarrasNo ratings yet
- Ansh Manchanda Healthians ReportDocument2 pagesAnsh Manchanda Healthians Reportanon_291694160No ratings yet
- Physiogenesis and Psychogenesis in The 'Post-Concussional Syndrome'Document11 pagesPhysiogenesis and Psychogenesis in The 'Post-Concussional Syndrome'IgorNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathies: Cardiomyopathy Is A Heart Muscle Disease Associated With CardiacDocument10 pagesCardiomyopathies: Cardiomyopathy Is A Heart Muscle Disease Associated With Cardiacmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel Blockers - AMBOSS PDFDocument5 pagesCalcium Channel Blockers - AMBOSS PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Ferris Clinical Advisor 2019 Fred F Ferri Full ChapterDocument67 pagesFerris Clinical Advisor 2019 Fred F Ferri Full Chaptermichael.walker630100% (16)
- UTS - Final4 - Taking Charge of Ones Health - OriginalDocument28 pagesUTS - Final4 - Taking Charge of Ones Health - OriginalBernard PadillaNo ratings yet
- Cirrosis HepaticaDocument10 pagesCirrosis Hepaticaadriel710No ratings yet
- Hepatitis B VaccineDocument3 pagesHepatitis B VaccineChoox PriiNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY NardilDocument2 pagesDRUGSTUDY Nardiljanelle tapiruNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Format 1Document4 pagesCase Presentation Format 1Ayessa Camelle DumileNo ratings yet
- Consenso de Ultrasonografía para Masas de Tejidos Blandos - PDFDocument13 pagesConsenso de Ultrasonografía para Masas de Tejidos Blandos - PDFalejandro montesNo ratings yet
- Retinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentDocument3 pagesRetinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentJordz Placi100% (1)
- 9 Assessment of Gastrointestinal Function and Management of Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument61 pages9 Assessment of Gastrointestinal Function and Management of Gastrointestinal DisordersNoor MajaliNo ratings yet
- np1 5Document25 pagesnp1 5Sittie Haya LazimNo ratings yet
- Henoch-Schonlein PurpuraDocument10 pagesHenoch-Schonlein PurpurasagameteiroNo ratings yet
- Depression in Older Adults: A Treatable Medical ConditionDocument12 pagesDepression in Older Adults: A Treatable Medical ConditionJose Alonso Aguilar Valera100% (1)
- Crop 311 Crop Protection - Lecture 5Document18 pagesCrop 311 Crop Protection - Lecture 5CindyNo ratings yet
- Igg4 Related Kidney Disease An OverviewDocument7 pagesIgg4 Related Kidney Disease An OverviewHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
Anatomy and Physiology: An Introduction To The Human Body
Anatomy and Physiology: An Introduction To The Human Body
Uploaded by
Theophilus Baidoo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views64 pagesAnatomy is the study of body structures and their relationships, while physiology is the study of how body structures function and work together to sustain life. The human body has six levels of organization from chemicals to tissues to organs and systems. The four basic tissue types are epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue. The major organ systems include the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, digestive, urinary, lymphatic, respiratory and reproductive systems. Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to maintain internal equilibrium through regulatory processes.
Original Description:
Original Title
ch01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnatomy is the study of body structures and their relationships, while physiology is the study of how body structures function and work together to sustain life. The human body has six levels of organization from chemicals to tissues to organs and systems. The four basic tissue types are epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue. The major organ systems include the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, digestive, urinary, lymphatic, respiratory and reproductive systems. Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to maintain internal equilibrium through regulatory processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: An Introduction To The Human Body
Anatomy and Physiology: An Introduction To The Human Body
Uploaded by
Theophilus BaidooAnatomy is the study of body structures and their relationships, while physiology is the study of how body structures function and work together to sustain life. The human body has six levels of organization from chemicals to tissues to organs and systems. The four basic tissue types are epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue. The major organ systems include the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, digestive, urinary, lymphatic, respiratory and reproductive systems. Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to maintain internal equilibrium through regulatory processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 64
ANATOMY AND
PHYSIOLOGY
An Introduction to the Human Body
Tutor: Theophilus Baidoo
EXPLANATION OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
• Anatomy is the study of body structures and
the relationships among them.
• Physiology is the study of how the parts of the
body work, and the ways in which they
cooperate together to maintain life and health of
the individual.
• Whereas anatomy deals with structures of the
body, physiology is the study of body function.
COMMON PREFIXES, SUFFIXES AND ROOTS
Prefix/ To do with Examples in the text
suffix/root
a-/an- lack of anuria, agranulocyte, asystole, anaemia
-aemia of the anaemia, hypoxaemia, uraemia, hypovolaemia
blood
angio- vessel angiotensin, haemangioma
anti- against antidiuretic, anticoagulant, antigen, antimicrobial
-blast germ, bud reticuloblast, osteoblast
brady- slow bradycardia
COMMON PREFIXES, SUFFIXES AND ROOTS
bronch bronc bronchiole, bronchitis, bronchus
o- hus
card- heart cardiac, myocardium, tachycardia
chole- bile cholecystokinin, cholecystitis, cholangitis
cyto-/- cell erythrocyte, cytosol, cytoplasm, cytotoxic
cyte
derm- skin dermatitis, dermatome, dermis
COMMON PREFIXES, SUFFIXES AND ROOTS
dys- difficult dysuria, dyspnoea, dysmenorrhoea, dysplasia
-ema swelling oedema, emphysema, lymphoedema
endo- inner endocrine, endocytosis, endothelium
erythro- red erythrocyte, erythropoietin, erythropoiesis
exo- outside exocytosis, exophthalmos
extra- outside extracellular, extrapyramidal
-fferent carry afferent, efferent
COMMON PREFIXES, SUFFIXES AND ROOTS
gast- stomach gastric, gastrin, gastritis, gastrointestinal
-gen- origin/ production gene, genome, genetic, antigen, pathogen, allergen
-globin protein myoglobin, haemoglobin
haem- blood haemostasis, haemorrhage, haemolytic
-hydr- water dehydration, hydrostatic, hydrocephalus
hepat- liver hepatic, hepatitis, hepatomegaly, hepatocyte
hyper- excess/above hypertension, hypertrophy, hypercapnia
hypo- below/under hypoglycaemia, hypotension, hypovolaemia
intra- within intracellular, intracranial, intraocular
-ism condition hyperthyroidism, dwarfism, rheumatism
-itis inflammation appendicitis, hepatitis, cystitis, gastritis
lact milk lactation, lactic, lacteal
lymph- lymph tissue lymphocyte, lymphatic, lymphoedema
COMMON PREFIXES, SUFFIXES AND ROOTS
micro- small microbe, microtubules, microvilli
myo- muscle myocardium, myoglobin, myopathy, myosin
neo- new neoplasm, gluconeogenesis, neonate
nephro- kidney nephron, nephrotic, nephroblastoma, nephrosis
neuro- nerve neurone, neuralgia, neuropathy
-oid resembling myeloid, sesamoid, sigmoid
-oma tumour carcinoma, melanoma, fibroma
-ophth- eye xerophthalmia, ophthalmic, exophthalmos
-ory referring to secretory, sensory, auditory, gustatory
osteo- bone osteocyte, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis
-path- disease pathogenesis, neuropathy, nephropathy
COMMON PREFIXES, SUFFIXES AND ROOTS
-plasm substance cytoplasm, neoplasm
pneumo- lung/air pneumothorax, pneumonia, pneumotoxic
poly- many polypeptide, polyuria. polycythaemia
-rrhagia excessive flow menorrhagia
-rrhoea discharge dysmenorrhoea, diarrhoea, rhinorrhoea
sub- under subphrenic, subarachnoid, sublingual
Tachy- excessively fast tachycardia
thrombo- clot thrombocyte, thrombosis, thrombin, thrombus
-tox- poison toxin, cytotoxic, hepatotoxic
-uria urine anuria, polyuria, haematuria, nocturia
vas, vaso- vessel vasoconstriction, vas deferens, vascular
LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION
Six levels of organization:
• Chemical
• Cellular
• Tissue
• Organ
• System
• organismal
TYPES OF TISSUE
There are four basic types of tissue in your
body:
– epithelial tissue
– connective tissue
– muscular tissue
– nervous tissue.
The systems of the human body are the:
• Integumentary • Digestive system
system • Urinary system
• Skeletal system • Lymphatic system
• Muscular system • Immunity system
• Nervous system • Respiratory system
• Endocrine system • Reproductive
• Cardiovascular systems
system
BASIC LIFE PROCESSES
• METABOLISM
– Catabolism
– Anabolism
• RESPONSIVENESS
• MOVEMENT
• GROWTH
• DIFFERENTIATION
• REPRODUCTION
HOMEOSTASIS
• Homeostasis is the condition of equilibrium
(balance) in the body’s internal
environment due to the constant interaction
of the body’s many regulatory processes.
You might also like
- Answers To QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnswers To QuestionsL-yeah Traifalgar52% (21)
- Prefixes and Suffixes ListDocument4 pagesPrefixes and Suffixes Listapi-262294171No ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Medical PrefixesDocument5 pagesMedical Terminology Medical PrefixesRicky Rhenzs Gultia Villafuerte100% (6)
- Health Care Terminology: Socorro Milagros C. Alcancia, RND, PHDDocument25 pagesHealth Care Terminology: Socorro Milagros C. Alcancia, RND, PHDShaina Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation 1Document14 pagesOxygenation 1Riño Roland RexNo ratings yet
- 01 Introductory PgyDocument76 pages01 Introductory Pgygbsreg gbsregNo ratings yet
- Histopath ReviewDocument389 pagesHistopath ReviewLucille MarieNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument10 pagesMedical TerminologyjoewelbyNo ratings yet
- Haematology: Red Blood Cells DisordersDocument47 pagesHaematology: Red Blood Cells Disordersbv2328002No ratings yet
- Trigger Topics For FMG Exams by MistDocument3 pagesTrigger Topics For FMG Exams by Mistvijay resuNo ratings yet
- Greek and Latin PrefixesDocument9 pagesGreek and Latin Prefixesmikesmith881No ratings yet
- Salivary Gland TumoursDocument131 pagesSalivary Gland TumoursSushmithaNo ratings yet
- State Council of Educational Research and Training TNCF 2017 - Draft SyllabusDocument12 pagesState Council of Educational Research and Training TNCF 2017 - Draft SyllabuspullaiNo ratings yet
- Patho1 Lab 2nd ExamDocument43 pagesPatho1 Lab 2nd ExambluebeeeNo ratings yet
- ImmunohistochemistryDocument29 pagesImmunohistochemistryAvi VermaNo ratings yet
- Pitu TaryDocument13 pagesPitu Taryمحمد عليNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Pathology: Lecture On Pathomorphology For 3-rd Year StudentsDocument44 pagesEndocrine Pathology: Lecture On Pathomorphology For 3-rd Year StudentsRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- SpleenDocument42 pagesSpleenRashed LabNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Assistant Surgeon Exam PDFDocument9 pagesSyllabus Assistant Surgeon Exam PDFMaguNo ratings yet
- The Spleen: by DR (MRS) BaulchDocument42 pagesThe Spleen: by DR (MRS) BaulchPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Baguio General Hospital and Medical Center Department of General SurgeryDocument27 pagesCase Presentation: Baguio General Hospital and Medical Center Department of General SurgeryJorge De VeraNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Endocrine System: Dr. Nesreen Bataineh MD, FrcpathDocument20 pagesPathology of Endocrine System: Dr. Nesreen Bataineh MD, FrcpathQutaybah JahmanyNo ratings yet
- Pathology Aspect Pituitary Gland: By. Meike Rachmawati, DR Pathology Anatomy Department Medical Faculty-UnisbaDocument35 pagesPathology Aspect Pituitary Gland: By. Meike Rachmawati, DR Pathology Anatomy Department Medical Faculty-UnisbadeasyahNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology FixedDocument3 pagesMedical Terminology FixedBaeman KyottNo ratings yet
- Main DivisionDocument61 pagesMain DivisionChadCowgillNo ratings yet
- Understand The Difference Between A Prefix and A SuffixDocument40 pagesUnderstand The Difference Between A Prefix and A Suffixlopezlozano.analilianNo ratings yet
- Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia: Mini-Symposium: Endometrial PathologyDocument8 pagesDemystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia: Mini-Symposium: Endometrial PathologyNi Wayan Ana PsNo ratings yet
- Anemia JournalDocument8 pagesAnemia JournalAmreen KausarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus FOR Undergraduate (BDS) : (Screening Test For Indian Nationals With Foreign Dental Qualifications)Document54 pagesSyllabus FOR Undergraduate (BDS) : (Screening Test For Indian Nationals With Foreign Dental Qualifications)Pulakit BhartiNo ratings yet
- All About Pleural EffusionDocument6 pagesAll About Pleural EffusionTantin KristantoNo ratings yet
- Nada's GI Path ReviewDocument44 pagesNada's GI Path ReviewNada Much100% (2)
- Bonemarrow 4 180106181202Document94 pagesBonemarrow 4 180106181202Caroline K.No ratings yet
- Bone MarrowDocument6 pagesBone MarrowKIPRUTO DENNISNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument16 pagesAplastic Anemiahazelposis100% (1)
- KULIAH II Lymphoreticular Pathology Kuliah IIDocument75 pagesKULIAH II Lymphoreticular Pathology Kuliah IIWidya AnggrainyNo ratings yet
- 8-Trematodes Ibrahim2016Document35 pages8-Trematodes Ibrahim2016Buntukazi MapamelaNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasDocument39 pagesDysphagia: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviNo ratings yet
- (Surg 3A) Spleen and Friends-Dr. Segismundo, Dr. Broqueza (Aisle Paler, Joseph Tolentino)Document15 pages(Surg 3A) Spleen and Friends-Dr. Segismundo, Dr. Broqueza (Aisle Paler, Joseph Tolentino)Aria Jean MostajoNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Hematopoietic System: Myeloid Tissues Lymphoid TissuesDocument24 pagesPathology of The Hematopoietic System: Myeloid Tissues Lymphoid TissuesashaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument81 pagesThyroid Glanddr_shamimrNo ratings yet
- Spleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementDocument53 pagesSpleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOESISDocument71 pagesHEMATOPOESISHussenNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument17 pagesCell StructurekimberlynNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukaemia: Dr. Nuryanti, M.Ked (Clin - Path), SPPK Laboratory Patologi Clinic Rs GranmedDocument29 pagesAcute Leukaemia: Dr. Nuryanti, M.Ked (Clin - Path), SPPK Laboratory Patologi Clinic Rs GranmedArnita Elisabet ManurungNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 and 2 Introduction To Pathology Cellular Injury Death Adaptation Inflammation and RepairDocument96 pagesLecture1 and 2 Introduction To Pathology Cellular Injury Death Adaptation Inflammation and RepairMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The Lymphatic System: Russell C Hendershot DO, MS, FAAFPDocument50 pagesPhysical Examination of The Lymphatic System: Russell C Hendershot DO, MS, FAAFPNajwa100% (1)
- Understand The Difference Between A Prefix and A SuffixDocument38 pagesUnderstand The Difference Between A Prefix and A Suffixlopezlozano.analilianNo ratings yet
- Sa Gland - Pleomorphic Adenoma 6Document46 pagesSa Gland - Pleomorphic Adenoma 6akshayajeevaajaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara Discipline of ParasitologyDocument72 pagesParasitology: Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara Discipline of ParasitologyanaNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument29 pagesAplastic AnemiaAshish SoniNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Cell InjuryDocument42 pagesPraktikum Cell InjurySharmadave SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- HY PathologyDocument24 pagesHY Pathologyyahomed519No ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument5 pagesAplastic AnemiaVenice Marie GargantaNo ratings yet
- Dermatology A Manual of Differential DiagnosisDocument83 pagesDermatology A Manual of Differential Diagnosisع كيف كيفك Dhaif-saeedNo ratings yet
- Current and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 1: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryFrom EverandCurrent and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 1: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryNo ratings yet
- Health Law and Ethics Lecture 01Document49 pagesHealth Law and Ethics Lecture 01Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Mentoring For 37 Military Nurses Slide Share To GoDocument56 pagesPresentation On Mentoring For 37 Military Nurses Slide Share To GoTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Grnma NMCG Webinar Zoom 28th July 2023-1Document1 pageGrnma NMCG Webinar Zoom 28th July 2023-1Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Traffitech Brochure Update - 230818 - 123024Document1 pageTraffitech Brochure Update - 230818 - 123024Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Press Release - Dubai AmbulanceDocument1 pagePress Release - Dubai AmbulanceTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Practising As A Midwife in The UkDocument27 pagesPractising As A Midwife in The UkTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Courses For Second Semester 2023 - 1Document6 pagesCourses For Second Semester 2023 - 1Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Nurse-Client RelationshipDocument31 pagesTherapeutic Nurse-Client RelationshipTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Laryea's Care StudyDocument101 pagesLaryea's Care StudyTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Depressions in Various Age-Groups and Sub-PopulationsDocument75 pagesDepressions in Various Age-Groups and Sub-PopulationsTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Weather Warning 15052023Document1 pageWeather Warning 15052023Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport System: ATP Adp + ATP Synthase P Nadh + H EnergyDocument12 pagesElectron Transport System: ATP Adp + ATP Synthase P Nadh + H EnergyTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- African St. Political Systems LectureDocument23 pagesAfrican St. Political Systems LectureTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology 1Document60 pagesEpidemiology 1Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- University of Health and Allied Sciences (UHAS) Ho Department of General and Liberal Studies UHAS 114: Introduction To Ghanaian and African StudiesDocument18 pagesUniversity of Health and Allied Sciences (UHAS) Ho Department of General and Liberal Studies UHAS 114: Introduction To Ghanaian and African StudiesTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- BIO130 Chapter 17 SlidesDocument42 pagesBIO130 Chapter 17 SlidesTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- The Hogbetsotso FestivalDocument3 pagesThe Hogbetsotso FestivalTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Slave Trade and ColonialismDocument21 pagesSlave Trade and ColonialismTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- BIO130 Chapter 15&16 SlidesDocument26 pagesBIO130 Chapter 15&16 SlidesTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Specialised Traditions of Knowledge and Health Delivery-1Document40 pagesSpecialised Traditions of Knowledge and Health Delivery-1Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Animation: Mitosis and CytokinesisDocument10 pagesAnimation: Mitosis and CytokinesisTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- African Belief Systems, Religion in Trad. Soc.Document42 pagesAfrican Belief Systems, Religion in Trad. Soc.Theophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- African Marriage Forms and Health Implica-TionsDocument43 pagesAfrican Marriage Forms and Health Implica-TionsTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Metabolic Pathways: Limited Number of Regulatory Enzymes Negative FeedbackDocument12 pagesRegulation of Metabolic Pathways: Limited Number of Regulatory Enzymes Negative FeedbackTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- African Family and Health DeliveryDocument25 pagesAfrican Family and Health DeliveryTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Animation: Diffusion Through Cell MembranesDocument6 pagesAnimation: Diffusion Through Cell MembranesTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: By-Victor BawiahDocument42 pagesLymphatic System: By-Victor BawiahTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Animation: Primary Active TransportDocument12 pagesAnimation: Primary Active TransportTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: BY Victor BawiahDocument171 pagesSkeletal System: BY Victor BawiahTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Chapt01 Holes Lecture Animation JWTDocument34 pagesChapt01 Holes Lecture Animation JWTCut TirayaNo ratings yet
- 9.anesthesia For Obstetrics. Pediatric Anesthesia. Geriatric Anesthesia.Document52 pages9.anesthesia For Obstetrics. Pediatric Anesthesia. Geriatric Anesthesia.karim hassanNo ratings yet
- Mycology 2021Document211 pagesMycology 2021Shania DawnNo ratings yet
- Prurigo-Nodular Ro 383Document10 pagesPrurigo-Nodular Ro 383Alexandru Ionut SavuNo ratings yet
- SAMY MSK ArthritisDocument125 pagesSAMY MSK ArthritisZintan HospitalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: Seasons in The Philippines: Let Us StartDocument5 pagesLesson Title: Seasons in The Philippines: Let Us StartGlyd Peñarubia Gallego-Diaz100% (1)
- Bone and Joint InfectionDocument43 pagesBone and Joint Infectionraheeg siddigNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Vulnerable Orphans Children Project Enrollement FormDocument8 pages7.4 Vulnerable Orphans Children Project Enrollement Formمتعلم لغة أنجليزيةNo ratings yet
- EMTDocument5 pagesEMTJohn NaughtonNo ratings yet
- CPHM TransesDocument5 pagesCPHM TransesElizer Robles Jr.No ratings yet
- Preventive, Promotive, Curative, RehabilitativeDocument54 pagesPreventive, Promotive, Curative, Rehabilitativetintu100% (1)
- Espohagectomy: Done by DR - Abdallah HasandarrasDocument17 pagesEspohagectomy: Done by DR - Abdallah HasandarrasAbdallah DarrasNo ratings yet
- Ansh Manchanda Healthians ReportDocument2 pagesAnsh Manchanda Healthians Reportanon_291694160No ratings yet
- Physiogenesis and Psychogenesis in The 'Post-Concussional Syndrome'Document11 pagesPhysiogenesis and Psychogenesis in The 'Post-Concussional Syndrome'IgorNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathies: Cardiomyopathy Is A Heart Muscle Disease Associated With CardiacDocument10 pagesCardiomyopathies: Cardiomyopathy Is A Heart Muscle Disease Associated With Cardiacmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel Blockers - AMBOSS PDFDocument5 pagesCalcium Channel Blockers - AMBOSS PDFOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- Ferris Clinical Advisor 2019 Fred F Ferri Full ChapterDocument67 pagesFerris Clinical Advisor 2019 Fred F Ferri Full Chaptermichael.walker630100% (16)
- UTS - Final4 - Taking Charge of Ones Health - OriginalDocument28 pagesUTS - Final4 - Taking Charge of Ones Health - OriginalBernard PadillaNo ratings yet
- Cirrosis HepaticaDocument10 pagesCirrosis Hepaticaadriel710No ratings yet
- Hepatitis B VaccineDocument3 pagesHepatitis B VaccineChoox PriiNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY NardilDocument2 pagesDRUGSTUDY Nardiljanelle tapiruNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Format 1Document4 pagesCase Presentation Format 1Ayessa Camelle DumileNo ratings yet
- Consenso de Ultrasonografía para Masas de Tejidos Blandos - PDFDocument13 pagesConsenso de Ultrasonografía para Masas de Tejidos Blandos - PDFalejandro montesNo ratings yet
- Retinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentDocument3 pagesRetinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentJordz Placi100% (1)
- 9 Assessment of Gastrointestinal Function and Management of Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument61 pages9 Assessment of Gastrointestinal Function and Management of Gastrointestinal DisordersNoor MajaliNo ratings yet
- np1 5Document25 pagesnp1 5Sittie Haya LazimNo ratings yet
- Henoch-Schonlein PurpuraDocument10 pagesHenoch-Schonlein PurpurasagameteiroNo ratings yet
- Depression in Older Adults: A Treatable Medical ConditionDocument12 pagesDepression in Older Adults: A Treatable Medical ConditionJose Alonso Aguilar Valera100% (1)
- Crop 311 Crop Protection - Lecture 5Document18 pagesCrop 311 Crop Protection - Lecture 5CindyNo ratings yet
- Igg4 Related Kidney Disease An OverviewDocument7 pagesIgg4 Related Kidney Disease An OverviewHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet