Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Animal and Plant Cells
Animal and Plant Cells
Uploaded by
nika zana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views40 pagesThe document discusses the history and development of cell theory, noting that Robert Hooke first observed cells in 1665 and that Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann established that plants and animals are made of cells in 1838-1839, with Rudolf Virchow further establishing that cells only come from pre-existing cells. It also outlines the key similarities and differences between animal and plant cells, describing some of their major organelles and how they work together harmoniously to keep the cell alive.
Original Description:
biology
Original Title
Animal and Plant Cells Ppt (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the history and development of cell theory, noting that Robert Hooke first observed cells in 1665 and that Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann established that plants and animals are made of cells in 1838-1839, with Rudolf Virchow further establishing that cells only come from pre-existing cells. It also outlines the key similarities and differences between animal and plant cells, describing some of their major organelles and how they work together harmoniously to keep the cell alive.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views40 pagesAnimal and Plant Cells
Animal and Plant Cells
Uploaded by
nika zanaThe document discusses the history and development of cell theory, noting that Robert Hooke first observed cells in 1665 and that Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann established that plants and animals are made of cells in 1838-1839, with Rudolf Virchow further establishing that cells only come from pre-existing cells. It also outlines the key similarities and differences between animal and plant cells, describing some of their major organelles and how they work together harmoniously to keep the cell alive.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 40
ANIMAL AND PLANT
CELLS
SIMILARITIES AND DIFFERENCES
LEARNING COMPETENCIES:
1) Differentiate plant and animal cells according
to presence or absence of certain organelles
2) Explain why the cell is considered the basic
structural and functional unit of all organisms.
WHAT
CHARACTERISTICS DO
ALL LIVING THINGS
SHARE?
WHAT IS A
CELL?
HOW WAS THE
CELL
DISCOVERED?
THE CELL AND ITS BEGINNING
• ROBERT HOOKE
- English scientist who discovered cell
- devised one of the earliest microscope
- first observed cell using thin slice of cork from a
bark of an oak tree
Hooke discovered many tiny pores that he named
“cellulae”, latin word for a “small room”. He
described the cells as tiny boxes or a honeycomb and
thought that cells only existed in plants and fungi.
THE CELL AND ITS BEGINNING
• ANTONIE VAN LEEUWENHOEK
- a Dutch naturalist, was credited to be the first
to study magnified cells
- first invention was a simple microscope with
one lens
-observed pond water and discovered moving
single celled organisms which he called
“animalcules”, meaning “little animals”
WHAT IS THE
CELL THEORY
ABOUT?
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CELL THEORY
• 1838 – German Botanist, Matthias Schleiden,
concluded that all plant parts are made of cells
• 1839 – German Physiologist, Theodore Schwann,
stated that all animal tissues are composed of cells
• 1858 – German Physician, Rudolf Virchow, after
extensive study of cellular pathology, concluded
that cells must arise from pre-existing cells
THE CELL THEORY
All organisms are composed of one or
more cells.
Cells are the smallest and basic units of
structure and function in living organisms.
Cells arise only from pre-existing cells.
WHAT ARE THE
TWO BASIC
TYPES OF A
CELL?
OVERVIEW
Video will be sent separately
ANIMAL CELL VS. PLANT CELL
HOW DO CELL PARTS
HARMONIOUSLY
FUNCTION TO KEEP
THE CELL ALIVE?
ACTIVITY
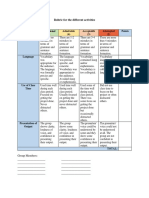
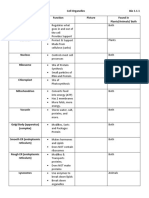
GROUP ACTIVITY:
Divide the members of the class into 14 groups with the following assigned
cell parts:
Group 1: Cell membrane Group 8: Endoplasmic reticulum
Group 2: Cell wall Group 9: Golgi apparatus
Group 3: Cytoskeleton Group 10: Vacuoles
Group 4: Nucleus Group 11: Cytoplasm
Group 5: Mitochondria Group 12: Lysosomes
Group 6: Plastids Group 13: Perixosomes
Group 7: Centrioles and centrosomes Group 14: Cilia and Flagella
GROUP ACTIVITY:
Directions:
Do an internet research about the structure or
appearance and function of cell part assigned to
you. After the research, prepare a short
infographic poster to highlight the assigned cell
part. On the next meeting, one representative
from each group will present their work.
You might also like
- Cell TheoryDocument32 pagesCell TheorySumana BasuNo ratings yet
- Bio CellsDocument4 pagesBio CellsONIPOP OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Cell Structure and Function: MATH Excellence Academy of Binalonan, IncDocument1 pageChapter 1: Cell Structure and Function: MATH Excellence Academy of Binalonan, IncMark Jesson DatarioNo ratings yet
- Cell DiscoveryDocument3 pagesCell DiscoverycgoldcafeNo ratings yet
- Bio Lesson 1Document47 pagesBio Lesson 1ricoanonuevo400No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Cell Theory Gen. Bio 1Document27 pagesLesson 1 Cell Theory Gen. Bio 1Trisha Anthony CortazNo ratings yet
- Unit 1:: Learning OutcomesDocument15 pagesUnit 1:: Learning OutcomesJhenny Lyn CamanoNo ratings yet
- 01 Cell TheoryDocument9 pages01 Cell TheoryRay NavarroNo ratings yet
- Life Is CellularDocument15 pagesLife Is Cellularapi-240096234No ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument70 pagesCell TheoryBeejay.No ratings yet
- Cell Discovery and TheoryDocument14 pagesCell Discovery and TheoryDiana Lynn FaderogaoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Module1Document12 pagesBiochem Module1ShannNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument8 pagesCell Theorysuraya9No ratings yet
- Senior High School - STEMDocument85 pagesSenior High School - STEMMary Grace MacadiniNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument31 pagesCell TheoryMarc Ian Young100% (1)
- 10 Cell Structure and Function PDFDocument42 pages10 Cell Structure and Function PDFJay Anne RulesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Cell TheoryDocument12 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Cell TheoryPercival RiegoNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Cell TheoryDocument31 pagesHistorical Development of Cell TheoryRamona BaculinaoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Topic 1Document37 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Topic 1Johnry HullezaNo ratings yet
- 02 BH - Stage 1 (Week 1)Document31 pages02 BH - Stage 1 (Week 1)AndreaArizpeNo ratings yet
- What Is A CellDocument12 pagesWhat Is A CellMaries San PedroNo ratings yet
- GenBio Q1 - LP1Document4 pagesGenBio Q1 - LP1CATHERINE MAE ARIENDANo ratings yet
- Bgy 101 Lecture NotesDocument48 pagesBgy 101 Lecture Notesidrisaminuabdullahi26No ratings yet
- Science7 - q2 - slk4.2 - The Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell - v1Document21 pagesScience7 - q2 - slk4.2 - The Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell - v1alain presillasNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module 2Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 2Ennyliejor YusayNo ratings yet
- Concept123Document23 pagesConcept123Diztrict GarageNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Lesson 1 - CELL THEORYDocument26 pagesGeneral Biology - Lesson 1 - CELL THEORYHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Bio Lesson 1Document63 pagesBio Lesson 1gabionzalawrencejayNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument15 pagesCell TheoryAmitanshu PandaNo ratings yet
- (E-Module) BNA - Science - Class 9 - Part 1Document73 pages(E-Module) BNA - Science - Class 9 - Part 1Neetu SinhaNo ratings yet
- GB1 - S4 Cell Theory and Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument51 pagesGB1 - S4 Cell Theory and Cell Structures and FunctionsAndreau GranadaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3: CellsDocument15 pagesActivity 3: CellsJerneth Nyka FloresNo ratings yet
- Tatva CellDocument66 pagesTatva CellGuriya Kumari100% (1)
- The Basics of BiologyDocument127 pagesThe Basics of BiologyMonica SevillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Cell Theory: Plant Cell Animal CellDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - Cell Theory: Plant Cell Animal CellS3 Oxibillo, Gabriel Dominic C.No ratings yet
- Cell The Cell StructuresDocument38 pagesCell The Cell StructuresrmgeradaNo ratings yet
- The Smallest Unit of Life: Submitted By: Submitted To: Biology TeacherDocument30 pagesThe Smallest Unit of Life: Submitted By: Submitted To: Biology TeacherJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Cells: The Basis of Life: Mevan Siriwardane Mrs. Rolle's Biology - Barringer High School October 25, 2007Document14 pagesCells: The Basis of Life: Mevan Siriwardane Mrs. Rolle's Biology - Barringer High School October 25, 2007SAmi BalochNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3-4Document6 pagesGen Bio 3-4Honey Joy Leopando SabadoNo ratings yet
- Genereal BiologyDocument6 pagesGenereal BiologyEd JayNo ratings yet
- Jilbert B. Gumaru, LPTDocument85 pagesJilbert B. Gumaru, LPTJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- History of CELL: Hooke in 1665. He Examined (UnderDocument2 pagesHistory of CELL: Hooke in 1665. He Examined (UnderPark Chan Yeol100% (1)
- 1 Cell TheoryDocument44 pages1 Cell TheoryJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life EditedDocument22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life EditedQuerubin SalesNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 Cell TheoryDocument1 pageNotes 1 Cell TheoryjoyNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument21 pagesCell TheoryAnjali KashyapNo ratings yet
- Postulate of Cell TheoryDocument31 pagesPostulate of Cell TheoryChrystal Tala CustodioNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument9 pagesCellsagrim dosajNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument20 pagesCell TheoryrizzmuizzNo ratings yet
- Senior High School - STEMDocument93 pagesSenior High School - STEMMaam Elle CruzNo ratings yet
- EED 5 Unit 3Document23 pagesEED 5 Unit 3Lara Mariz FragataNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument13 pagesCell TheoryDaryll BorjaNo ratings yet
- Cell ThoeryDocument1 pageCell Thoeryjyothi sai sriNo ratings yet
- Biotech Cell TheoryDocument4 pagesBiotech Cell TheoryDietrich Jamiro DizonNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document2 pagesBiology 1Karriel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Science7 q2 Week5 Refined FinalDocument13 pagesScience7 q2 Week5 Refined FinalRonalynAlonsabeBernadasNo ratings yet
- CH 7 1 Cell Discovery and Theory PDFDocument22 pagesCH 7 1 Cell Discovery and Theory PDFghalia.amkNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document66 pagesWeek 1Erica CelesteNo ratings yet
- Gen. BioDocument6 pagesGen. BioMarxinne PajarinNo ratings yet
- Rubric For The Differentiated TasksDocument1 pageRubric For The Differentiated Tasksnika zanaNo ratings yet
- PieceDocument2 pagesPieceFresher Madrid Jr.No ratings yet
- Module 1 BiotechnologyDocument18 pagesModule 1 Biotechnologynika zanaNo ratings yet
- Q4 - Module 1Document23 pagesQ4 - Module 1nika zanaNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Katangiang Pisikal NG DaigdigDocument9 pagesMod 1 Katangiang Pisikal NG Daigdignika zanaNo ratings yet
- PE Module 1Document24 pagesPE Module 1nika zanaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Module2Document21 pagesQ4 Module2nika zanaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 1 (Geometry)Document20 pagesQ3 Module 1 (Geometry)nika zanaNo ratings yet
- Bio - CH 2 TissuesDocument92 pagesBio - CH 2 TissuesPagli MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure QuizDocument2 pagesCell Structure QuizshavindriNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Botany and Taxonomy M1-M5Document10 pagesPharmaceutical Botany and Taxonomy M1-M5MARQUEZ, Yancy KateNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesrhdoiuaNo ratings yet
- Dent I No GenesisDocument14 pagesDent I No Genesisandre gidion laseNo ratings yet
- Cells: The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of LifeDocument34 pagesCells: The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of LifeAngel Trisha De LeonNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 1 TO 4 RECALLS CombinedDocument13 pagesQUIZ 1 TO 4 RECALLS CombinedLancer BlazeNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupsDocument5 pagesBlood Groupsamir elhadiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Shs Stem - Biology 1Document17 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Shs Stem - Biology 1Dette Dominic BallanoNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument16 pagesBLOODMuhammad ArdhanNo ratings yet
- DR Mohamed Serar Yusuf MSC, BSC, Ascpi, UMST/SudanDocument32 pagesDR Mohamed Serar Yusuf MSC, BSC, Ascpi, UMST/SudanAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer. Absolutely No ErasuresDocument2 pagesEncircle The Letter of The Correct Answer. Absolutely No ErasuresARISNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument13 pagesCell AnalogySideTrip SideKickNo ratings yet
- Bacterial StainingDocument43 pagesBacterial StainingRatih wahyuniNo ratings yet
- Blood PhysiologyDocument82 pagesBlood PhysiologyVioleta Voinovan100% (2)
- Pap Stain Introduction, Principle, Staining ProcDocument1 pagePap Stain Introduction, Principle, Staining ProcSuchana AcNo ratings yet
- I) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueDocument44 pagesI) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueSaralitaNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: Sudhanshu Shekhar, M.Tech BiotechDocument22 pagesNucleus: Sudhanshu Shekhar, M.Tech BiotechSudhanshu ShekharNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells - RuahDocument16 pagesEukaryotic Cells - RuahruahNo ratings yet
- Bones PPTDocument18 pagesBones PPTPrasannaNo ratings yet
- pr7IfQFJTnaR deKnLv7lhrDocument7 pagespr7IfQFJTnaR deKnLv7lhrSamarthsinh VaghelaNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument9 pagesBloodrraaNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Q2 Mod4 EggsAreWhiteLemonsAreYellowLikeMeandYouTheyreMadeofCellsToo EditedAug3Document35 pagesSci7 Q2 Mod4 EggsAreWhiteLemonsAreYellowLikeMeandYouTheyreMadeofCellsToo EditedAug3Shenzhen Henry-PachecoNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells Types of TissuesDocument1 pageTypes of Cells Types of TissuesNicole Audrey Ignacio DuqueNo ratings yet
- MCQs For Essentials of Oral Histology and Embryology (2015) PDFDocument199 pagesMCQs For Essentials of Oral Histology and Embryology (2015) PDFLokesh Bakshi100% (1)
- Perio PrelimsDocument12 pagesPerio PrelimsathenaNo ratings yet
- Long Test g7Document2 pagesLong Test g7Earn cruzNo ratings yet
- Autoanalyzer Dan Manual Menggunakan Amonium Oksalat 1%: Validasi Hasil Pemeriksaan Jumlah Trombosit SecaraDocument4 pagesAutoanalyzer Dan Manual Menggunakan Amonium Oksalat 1%: Validasi Hasil Pemeriksaan Jumlah Trombosit SecaraAnonymous NEsneMqNo ratings yet
- Tissue Processing and StainingDocument29 pagesTissue Processing and StainingMuhammad kamran ameerNo ratings yet
- Meat and Meat Products Technology Including Poultry Products Technology PDFDocument76 pagesMeat and Meat Products Technology Including Poultry Products Technology PDFDhanya M AlexNo ratings yet