Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phases of The Moon
Phases of The Moon
Uploaded by
Ernesto Adrian Aguilar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views24 pagesThe document discusses key facts about the moon's phases and orbit. It notes that the moon is Earth's only natural satellite, located about 240,000 miles away, and has a very thin atmosphere. It then describes the various phases of the moon in order - from new moon to waxing crescent to first quarter to full moon and back to new moon again - over the course of approximately 29.53 days, which is called a synodic month. Each phase represents a different portion of the moon's illuminated side facing the Earth as it orbits our planet.
Original Description:
Original Title
Phases of the Moon
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key facts about the moon's phases and orbit. It notes that the moon is Earth's only natural satellite, located about 240,000 miles away, and has a very thin atmosphere. It then describes the various phases of the moon in order - from new moon to waxing crescent to first quarter to full moon and back to new moon again - over the course of approximately 29.53 days, which is called a synodic month. Each phase represents a different portion of the moon's illuminated side facing the Earth as it orbits our planet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views24 pagesPhases of The Moon
Phases of The Moon
Uploaded by
Ernesto Adrian AguilarThe document discusses key facts about the moon's phases and orbit. It notes that the moon is Earth's only natural satellite, located about 240,000 miles away, and has a very thin atmosphere. It then describes the various phases of the moon in order - from new moon to waxing crescent to first quarter to full moon and back to new moon again - over the course of approximately 29.53 days, which is called a synodic month. Each phase represents a different portion of the moon's illuminated side facing the Earth as it orbits our planet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 24
Moon
It is the Earth’s only satellite and the fifth largest moon
in the solar system.
The Moon’s presence helps our planets wobble and
moderate our climate.
The Moon’s distance from Earth is about 240,000 miles
The Moon has a very thin atmosphere called an
exosphere.
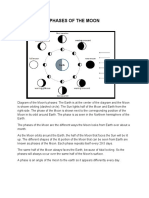
Phases of the moon
Sidereal Period
It is the time required for a celestial body within the
solar system to complete one revolution with respect to
the fixed stars
Phases of the moon
New Moon
It is the invisible phase of the Moon, with the
illuminated side of the Moon facing the sun and the
night side facing the Earth.
Syzygy
Is the nearly straight-line configuration of the three
celestial bodies (the Sun, the Moon and the Earth).
Waxing Crescent
This silver sliver of a Moon occurs when the
illuminated half of the Moon faces mostly away from
the Earth, with only a tiny portion visible to us from
our planet.
Waxing means its growing and crescent refers to the
curved sickle shape.
First Quarter
The Moon is 90 degrees away from the sun in the sky
and is half illuminated from our point of view. Also
called as a Half Moon.
It is called first quarter because the moon has travelled
about a quarter of the way around Earth since the New
Moon.
Waxing Gibbous
The area of illumination continues to increase. More
than half of the moon’s face appears to be getting
sunlight.
The word gibbous comes from a Latin for hump to
describe the rounded or convex shape
Full Moon
The Moon is 180 degrees away from the sun and is as
close as it can be to being fully being illuminated by the
sun from our perspective.
Waning Gibbous
More than half of the Moon’s face appears to be getting
sunlight, but the amount is decreasing.
Waning means that it is shrinking and getting smaller.
Third Quarter
This moon phase is also known as the Half Moon
because only the half of the Moon is visible. The reason
why is it called as the Third quarter is because the
Moon has completed ¾ of its orbit around the Earth.
Waning Crescent
The Moon is nearly back to the point in its orbit. Where
its day side directly faces the sun, and all that we see
from our perspective is a thin curve.
Synodic Month
A month of approximately 29.53 days, measured from
a Lunar phase until the return of that same phase.
You might also like
- Makalah MajuDocument14 pagesMakalah MajuIsnaNurhayatiNo ratings yet
- EN The Phases of The Moon by SlidesgoDocument14 pagesEN The Phases of The Moon by SlidesgohimynameishbubbunNo ratings yet
- Phases of Moon: Norasmidar Mohd Nasaruddin 5D 3 APRIL 2007Document21 pagesPhases of Moon: Norasmidar Mohd Nasaruddin 5D 3 APRIL 2007Mohamad DinNo ratings yet
- LlyDocument11 pagesLlyniloofar.anwary3No ratings yet
- Varied Phases of The Moon - Group 4Document5 pagesVaried Phases of The Moon - Group 4Kleo HenceforthNo ratings yet
- Moon Phases PowerPointDocument34 pagesMoon Phases PowerPointVilma RamonesNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv - Moon PhasesDocument13 pagesUnit Iv - Moon PhasesMoreen LamsenNo ratings yet
- Phases of The MoonDocument18 pagesPhases of The MoonSherwin D. Sungcalang100% (2)
- 8 Phases of The MoonDocument3 pages8 Phases of The MoonEclud100% (1)
- PhasesofthemoonDocument3 pagesPhasesofthemoonsquidblitzNo ratings yet
- The Movement of The Earth, Moon, & Sun: Measuring Time On EarthDocument6 pagesThe Movement of The Earth, Moon, & Sun: Measuring Time On EarthSofia VioletaNo ratings yet
- Phases of The MoonDocument9 pagesPhases of The MoonMarcus Skookumchuck VanniniNo ratings yet
- Earth MoonDocument11 pagesEarth MoonRoden Abel LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Group 24:: Alvaro, Glessy Lapid, JamaicaDocument42 pagesGroup 24:: Alvaro, Glessy Lapid, JamaicaGlessy AlvaroNo ratings yet
- LunarDocument8 pagesLunarБиљанаNo ratings yet
- Moon PhasesDocument7 pagesMoon PhasesResearchingPub100% (4)
- Phases DraftDocument6 pagesPhases DraftMarecar RabusaNo ratings yet
- Moon PhasesDocument1 pageMoon PhasesSonny Boy SajoniaNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument1 pageInglesAmador Ortiz Victor HugoNo ratings yet
- The Phases of The MoonDocument45 pagesThe Phases of The MoonLocal ClownNo ratings yet
- All About The Moon (Phases of the Moon) | 1st Grade Science WorkbookFrom EverandAll About The Moon (Phases of the Moon) | 1st Grade Science WorkbookNo ratings yet
- Phases of The MoonDocument2 pagesPhases of The MoonJoseph GratilNo ratings yet
- Fases de La LunaDocument5 pagesFases de La LunaLUIS DIEGO UREÑA SEGURANo ratings yet
- PhasesoftheMoon NotesDocument17 pagesPhasesoftheMoon NotesAntonietteSopinoCempronNo ratings yet
- Moon PhasesDocument3 pagesMoon PhasesnoemeNo ratings yet
- Moon PhasesDocument3 pagesMoon PhasesnoemeNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Week 6 Q4 1Document36 pagesScience 5 Week 6 Q4 1Smiley DeSmillingNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Astronomy 1 1Document52 pagesGroup 4 Astronomy 1 1Russelianne LindeNo ratings yet
- Reading Maths and Science - NadineDocument2 pagesReading Maths and Science - NadinemepetrescuNo ratings yet
- Earth's Place in SpaceDocument11 pagesEarth's Place in Spacerupalpatel0000No ratings yet
- Lesson 6.2-6.3Document13 pagesLesson 6.2-6.3fm5z2cbxkhNo ratings yet
- Final Assignment - Edu 214Document16 pagesFinal Assignment - Edu 214api-630088736No ratings yet
- Phases of The MoonDocument23 pagesPhases of The MoonMary Rose Bobis VicenteNo ratings yet
- Phases of The MoonDocument39 pagesPhases of The Moonpeachy042011No ratings yet
- Lunar PhasesDocument21 pagesLunar PhasesJun Karren CaparosoNo ratings yet
- Joan Pauline Guillermo Abpols-IiiDocument4 pagesJoan Pauline Guillermo Abpols-IiitjNo ratings yet
- Phases of The MoonDocument3 pagesPhases of The MooncyriaaNo ratings yet
- Gerhana BulanDocument5 pagesGerhana BulanFarida MauludiahNo ratings yet
- 1 The Phases of The MoonDocument5 pages1 The Phases of The Mooncharles blairNo ratings yet
- Different Faces of Moon and Its DefinitionDocument5 pagesDifferent Faces of Moon and Its DefinitionAron JohnMathewNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 3 - Chapter 12Document8 pagesExp SC 3 - Chapter 12megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Scientific Developments in Moon Sighting: Abuja Centre For Arabic Studies (ACAS) 3 Annual Ramadan SymposiumDocument81 pagesScientific Developments in Moon Sighting: Abuja Centre For Arabic Studies (ACAS) 3 Annual Ramadan SymposiumGREATIA BRITAINISNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument6 pagesSolar SystemwombadouglasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AstronomyDocument352 pagesIntroduction To AstronomyCaplan MarkleyNo ratings yet
- Seminar For ScienceDocument24 pagesSeminar For ScienceSankar PNo ratings yet
- Phases of The MoonDocument15 pagesPhases of The MoonCatherine WashingtonNo ratings yet
- What Is Known About The MoonDocument35 pagesWhat Is Known About The MoonAbi Manahan-DoriaNo ratings yet
- PHASES OF THE MOON and ACT. SHEETDocument6 pagesPHASES OF THE MOON and ACT. SHEETArenas JenNo ratings yet
- 55 The MoonDocument3 pages55 The MoonDaniel StandringNo ratings yet
- Earth and The Solar System (1) - 1Document44 pagesEarth and The Solar System (1) - 1Syed Mushiff Bahadur ShamsiNo ratings yet
- The Moon Part 1Document2 pagesThe Moon Part 1Cynthia CamposNo ratings yet
- Examples of Astronomical PhenominaDocument38 pagesExamples of Astronomical PhenominaMary Rhodelyn Fermin100% (1)
- Phases of The Moon:: StarsDocument1 pagePhases of The Moon:: StarsDebasisBarikNo ratings yet
- The Moon: It's Just A Phase It's Going Through..Document16 pagesThe Moon: It's Just A Phase It's Going Through..malaitamanNo ratings yet
- Gen SciDocument12 pagesGen SciVanessa DoofenshmirtzNo ratings yet
- Earth and SpaceDocument15 pagesEarth and SpaceAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- Phy 208 Lecture Note 2Document14 pagesPhy 208 Lecture Note 2Oluwaferanmi AwosanyaNo ratings yet
- Revolution/Rotation Day/Night Phases of The Moon SeasonsDocument41 pagesRevolution/Rotation Day/Night Phases of The Moon SeasonsNiña Socorro Macasil PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Sci5 - Q4 - Distance Learning April 29-30, 2024Document20 pagesSci5 - Q4 - Distance Learning April 29-30, 2024Lhei KismodNo ratings yet
- The Faces, or Phases, of the Moon - Astronomy Book for Kids | Children's Astronomy BooksFrom EverandThe Faces, or Phases, of the Moon - Astronomy Book for Kids | Children's Astronomy BooksNo ratings yet