Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dka Pathophysiology
Dka Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Clarissa GuifayaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- FUNDA0319Document11 pagesFUNDA0319Clarissa Guifaya50% (2)
- Maternity NursingDocument40 pagesMaternity NursingClarissa Guifaya100% (2)
- Pediatric Nursing Review NleDocument46 pagesPediatric Nursing Review NleClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Co AmoxiclavDocument1 pageCo AmoxiclavClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Asme Section II A Sa-31Document4 pagesAsme Section II A Sa-31Anonymous GhPzn1xNo ratings yet
- Schematic Pathophy DkaDocument2 pagesSchematic Pathophy DkaMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- AlgoDocument1 pageAlgoErrold Joseph LahaganNo ratings yet
- Assessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixDocument16 pagesAssessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixNalzaro Emyril89% (19)
- Pa Add Mga Ito Kapag May KulangDocument5 pagesPa Add Mga Ito Kapag May KulangJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyjohnbech07No ratings yet
- DM Type 2 Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument4 pagesDM Type 2 Pa Tho PhysiologyEllen Grace Cañarejo BaroyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.Document1 pagePathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.romeo riveraNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Fat in BodyDocument7 pagesGroup 2 - Fat in BodySisfa ShabelaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Importance Glycolysis Can Function Under Anaerobic ConditionsDocument5 pagesBiomedical Importance Glycolysis Can Function Under Anaerobic ConditionsCatalina Denise Blaquera FloresNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatDocument2 pagesAnatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatSkyerex100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus: Moderator: DR Ramesh Presented by AbishaDocument43 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Moderator: DR Ramesh Presented by AbishaSparrowNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument9 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisFeliipe CruzzNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology Client DMDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology Client DMMarty MartinezNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONSDocument1 pageBlood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONSfatimaNo ratings yet
- DM Type 1Document4 pagesDM Type 1Adiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Endo-Doc LapakDocument3 pagesEndo-Doc LapakHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- 041 LiverDocument3 pages041 Liveraistina100% (1)
- Hormone NotesDocument8 pagesHormone Noteslaeticia schmiesNo ratings yet
- Overview FastingDocument21 pagesOverview FastingBagusReka100% (1)
- Pathiophysiology Med Ward RevisionDocument6 pagesPathiophysiology Med Ward RevisionBrandt CajoconNo ratings yet
- Lecture-8-Fasting-Liver and AdiposeDocument21 pagesLecture-8-Fasting-Liver and AdiposeBagusRekaNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument5 pagesInsulinBobNo ratings yet
- PAthophysio (With Content)Document1 pagePAthophysio (With Content)liesel_12No ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesEndocrine DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: ChemistryDocument21 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: ChemistryAbdihakem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Glucose Physiology, Normal.Document8 pagesGlucose Physiology, Normal.hajrahsuhardiNo ratings yet
- Pathology of DiabetesDocument4 pagesPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Glucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsDocument31 pagesGlucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsnikenNo ratings yet
- OBAT ANTI-DIABETES - Hernita - 2019Document70 pagesOBAT ANTI-DIABETES - Hernita - 2019Hernita TaurustyaNo ratings yet
- 14-Gluconeogenesis TEAM436Document20 pages14-Gluconeogenesis TEAM436ashishmahawar1510No ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument34 pagesHomeostasisAwaid AsimNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis, Glycolysis, Regulation (DR - Javed)Document28 pagesGluconeogenesis, Glycolysis, Regulation (DR - Javed)saadzubair0307No ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument4 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisAbigael Patricia Gutierrez100% (1)
- 7 OAD DR - Elly 2015Document52 pages7 OAD DR - Elly 2015ainNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Glucagon FinalDocument27 pagesInsulin, Glucagon FinalDhruvil GadhiyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of DMDocument13 pagesNursing Care of DMItachi SanNo ratings yet
- Patho DM HTN FinalDocument1 pagePatho DM HTN FinalBryant Riego IIINo ratings yet
- Phys 10Document22 pagesPhys 10sakwork30No ratings yet
- Anesthesia and Co Existing Diseases Stoelting's 2018 468 496Document29 pagesAnesthesia and Co Existing Diseases Stoelting's 2018 468 496Desak PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Antihyperglycemics DrugsDocument3 pagesAntihyperglycemics DrugsUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Blood SugarDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Blood SugartagmanNo ratings yet
- Environmental FactorsDocument7 pagesEnvironmental FactorsjayrchinNo ratings yet
- Diseases of GlucocorticoidDocument3 pagesDiseases of GlucocorticoidKeneyziaNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Karbohidrat Dan Integrasinya DG Regulasi HormonalDocument21 pagesMetabolisme Karbohidrat Dan Integrasinya DG Regulasi HormonalMahendra Yudha NNo ratings yet
- Week 14 - Regulation of Metabolism and Diabetes Flashcards QuizletDocument11 pagesWeek 14 - Regulation of Metabolism and Diabetes Flashcards QuizletMorgan ChristNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsDocument3 pagesDrug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsSurria Suguna15No ratings yet
- Obat Antidiabetes: Hernita TaurustyaDocument70 pagesObat Antidiabetes: Hernita TaurustyaHernita TaurustyaNo ratings yet
- CC1Document6 pagesCC1Sandhya Narag SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Lecture Note-6thDocument46 pagesDiabetes Lecture Note-6tholawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Physiology DiabetesDocument48 pagesPhysiology Diabetesrajesh g100% (1)
- L11 Glucose RegulationDocument21 pagesL11 Glucose RegulationCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Patho 1Document1 pagePatho 1ricciNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose HomeostasisDocument84 pagesBlood Glucose Homeostasisabliltymark3No ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument10 pagesGluconeogenesismoneth gerarmanNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Written ReportDocument19 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Written ReportEros Victorino100% (2)
- Metabolic Pathways of GlucoseDocument31 pagesMetabolic Pathways of GlucoseLisandrea BrownNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)From EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliNo ratings yet
- I Wish I Were Not Born DeclamationDocument1 pageI Wish I Were Not Born DeclamationClarissa Guifaya0% (1)
- Med TagDocument23 pagesMed TagClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- E-Cart ChecklistDocument6 pagesE-Cart ChecklistClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- By: Clarissa E. Guifaya BSN301/GROUP 3Document17 pagesBy: Clarissa E. Guifaya BSN301/GROUP 3Clarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- NP2 Nursing Board Exam November 2008Document16 pagesNP2 Nursing Board Exam November 2008Clarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases ReviewerDocument12 pagesCommunicable Diseases ReviewerClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Immediate Newborn CareDocument1 pageImmediate Newborn CareClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Royal: The Pentagon Review Specialist, IncDocument31 pagesRoyal: The Pentagon Review Specialist, IncClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- September: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 pagesSeptember: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Gladys Bautista Jaime 2010Document10 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Gladys Bautista Jaime 2010Clarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Narrowing of BronchiDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Narrowing of BronchiClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- HS RRLDocument1 pageHS RRLClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Student Nurse: - DateDocument3 pagesStudent Nurse: - DateClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 5 QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuiz No. 5 QuestionsClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument2 pagesDefinitionClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Classic Techniques in Medicine: Methods of Obtaining Peripheral Venous Access in Di Ycult SituationsDocument4 pagesClassic Techniques in Medicine: Methods of Obtaining Peripheral Venous Access in Di Ycult SituationsClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Ampisul, Hydrocort, Salbu, Mupirocin DrugsDocument4 pagesAmpisul, Hydrocort, Salbu, Mupirocin DrugsClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Hiv LabsDocument4 pagesHiv LabsClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-15-10 - 11th (J-Batch)Document11 pagesCHEMISTRY-15-10 - 11th (J-Batch)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Wartsila OEM Engine Manufacturer ApprovalsDocument8 pagesWartsila OEM Engine Manufacturer ApprovalsSivakumar SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Solutions Mind Map PDFDocument4 pagesSolutions Mind Map PDFvashuy091No ratings yet
- Laboratory Chemical and Reagents-2Document2 pagesLaboratory Chemical and Reagents-2Faris BahauddinNo ratings yet
- 02 Clinker Formation PDFDocument74 pages02 Clinker Formation PDFSokreach Din100% (4)
- Chemistry SPM Kbat Form 4Document14 pagesChemistry SPM Kbat Form 4Gloria Yong100% (1)
- Water PHDocument21 pagesWater PHJay MeeNo ratings yet
- Lab - Water PotentialDocument9 pagesLab - Water PotentialAleka AlexisNo ratings yet
- Swimming Pool Uv System Material Sub. - r1Document40 pagesSwimming Pool Uv System Material Sub. - r1Renjith RaveendranNo ratings yet
- D 3023 - 98 Stain TestDocument3 pagesD 3023 - 98 Stain TestJohnNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed ReactorDocument12 pagesFluidized Bed Reactoradnantayyab100% (1)
- Synthesis Characterization ADMET in Vitro and in Vivo Studies of Mixed Ligand Metal Complexes From A Curcumin Schiff Base and LawsoneDocument23 pagesSynthesis Characterization ADMET in Vitro and in Vivo Studies of Mixed Ligand Metal Complexes From A Curcumin Schiff Base and LawsoneartprogressivaNo ratings yet
- Sika Floorjoint PB 30pdrsDocument4 pagesSika Floorjoint PB 30pdrsRukmana's FamilyNo ratings yet
- AMS6265 Gear Material PropertiesDocument2 pagesAMS6265 Gear Material PropertiesSinan YıldızNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Phenol From CumeneDocument8 pagesManufacture of Phenol From CumeneFabi OneNo ratings yet
- Specification Sheet - Vmax® P550® Turf Reinforcement Mat: Index Property Test Method TypicalDocument2 pagesSpecification Sheet - Vmax® P550® Turf Reinforcement Mat: Index Property Test Method TypicalLuis MogrovejoNo ratings yet
- Glass Transition TemperatureDocument16 pagesGlass Transition TemperatureAnuNo ratings yet
- Solubility Curve WorksheetDocument5 pagesSolubility Curve WorksheetRohanee Hafsa KapusanNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Vol 1 EM - WWW - Tntextbooks.inDocument304 pages11th Chemistry Vol 1 EM - WWW - Tntextbooks.indorathy raniNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument9 pagesJurnalRina Boenda QueenRayaNo ratings yet
- Ribbon Anode Soil Och ConcreteDocument1 pageRibbon Anode Soil Och ConcreteSoltani AliNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY EXAM 2nd QDocument20 pagesCHEMISTRY EXAM 2nd Qjelosaliva2No ratings yet
- Micropropagation of BANANADocument30 pagesMicropropagation of BANANAraghuldon36No ratings yet
- Questioned Document MahinayDocument159 pagesQuestioned Document MahinayStephanie De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Rockland Community College BIO 107 Honors Review For Lab Practical IDocument2 pagesRockland Community College BIO 107 Honors Review For Lab Practical IkuriiriNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Solved Lec-16 Enzymes-Properties, Classification and NomenclatureDocument4 pagesMcqs Solved Lec-16 Enzymes-Properties, Classification and NomenclatureELAKKIYA .U BA Eng LitNo ratings yet
- AtpquestionsDocument16 pagesAtpquestionsBinesh Udaya100% (2)
- Problemario 3Document6 pagesProblemario 3itzel veronicaNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions: Teacher VersionDocument8 pagesStoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions: Teacher VersionBT Keith CelebreNo ratings yet
Dka Pathophysiology
Dka Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Clarissa GuifayaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dka Pathophysiology
Dka Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Clarissa GuifayaCopyright:
Available Formats
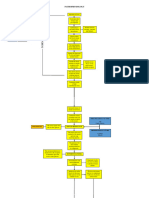
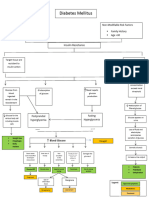
DM TYPE 1: Autoimmune destruction of beta cells the Islets of Langerhans within
the pancreas
Precipitating factors for DKA: Infection such as UTI, gastroenteritis, pneumonia, alcohol
or drug abuse, pancreatitis, stroke, trauma, Acute Myocardial Infarction
Decreased normal insulin secretion in the presence of glucose in the blood =
“FASTING STATE”
Decrease glucose transport from blood into Cortisol, growth hormone and Insulin normally regulates
muscles and other tissues catecholamine glucagon secretion
Glucagon secretion is uncontrolled in
the absence of insulin
Decreased glucose utilization as Lethargy
Brain does not require energy (glycolysis)
insulin for glucose transport
Increased Glycogenolysis
Switch to ketogenesis for ketone Polyphagia in response to increase Hyperglycemia
energy use in absence of glucose energy requirements
Weight loss Increase serum osmolarity
Lipolysis initiated in response
of fasting state
Free Fatty Acids (FFA) released from Polydipsia
adipocytes stored as triglycerides Osmotic diuresis secondary to
Osmotic fluid shift out of cells glucosuria
into intravenous space
Polyuria
FFA enters liver Dilutional
mitochondria hyponatremia
Dehydration
Increased glucagon promotes FFA
entry into liver mitochondria Beta oxidation of FFA
Decreased Renal Function
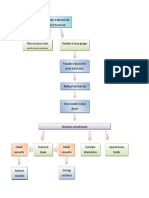
Acetyl-CoA produced in large numbers build
up in mitochondria
The Citric Acid Cycle is
normally used to produce Oxaloacetate is diverted away from the Citric Acetyl-CoA production exceeds
energy Acid Cycle in the fasting state in an attempt to oxidative capacity of the Citric
increase glucose production via glucogenesis Acid Cycle
Hyperglycemia
Citric Acid Cycle concurrently
slows down during fasting state
Acetyl-CoA diverted away from
the Citric Acid Cycle and
promotes ketogenesis
2x Acetyl-CoA bodies join to form
Acetoacetyl-CoA
Fasting state increases HMG-
CoA synthase production
HMG-CoA synthase helps form HMG-CoA from 1x
Acetoacetyl-CoA molecule
HMG-CoA lyase then forms
Acetoacetate (ketone body) which
breaks down
Acetone (ketone D-beta-hydroxybutyrate (ketone CO2
body) body released
Water soluble can cross Blood Brain
Characterized as a Barrier (BBB) in the CNS
The only ketone body that FRUITY ODOR in
cannot be used as energy DKA
Increased plasma ketone levels
of acetoacetate and D-beta-
hydroxybutyrate
Ketone bodies are Acetoacetate and D-beta- Circulating ketone bodies
acidic hydroxybutyrate are used as energy initiate systemic response
for organs, muscles and other tissues
Decreased serum pH
Nausea and vomiting
Confusion /decreased sensorium Abdominal pain and cramping
Metabolic Diabetic
Ketoacidosis
Extracellular H+ ions moves DKA estimated to occur at
Confusion and altered level of Compensatory release of CO2 into cells and exchange for K+ Blood Sugar Level (BSL) >15
consciousness to buffer acidosis ions mmol/L
Increased respiratory rate Hypokalemia may be in the
Diabetic Coma setting of normal serum K+
(tachypnea) = “Kussmaul
Respirations” levels (3.5-5.5)
You might also like
- FUNDA0319Document11 pagesFUNDA0319Clarissa Guifaya50% (2)
- Maternity NursingDocument40 pagesMaternity NursingClarissa Guifaya100% (2)
- Pediatric Nursing Review NleDocument46 pagesPediatric Nursing Review NleClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Co AmoxiclavDocument1 pageCo AmoxiclavClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Asme Section II A Sa-31Document4 pagesAsme Section II A Sa-31Anonymous GhPzn1xNo ratings yet
- Schematic Pathophy DkaDocument2 pagesSchematic Pathophy DkaMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- AlgoDocument1 pageAlgoErrold Joseph LahaganNo ratings yet
- Assessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixDocument16 pagesAssessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixNalzaro Emyril89% (19)
- Pa Add Mga Ito Kapag May KulangDocument5 pagesPa Add Mga Ito Kapag May KulangJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyjohnbech07No ratings yet
- DM Type 2 Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument4 pagesDM Type 2 Pa Tho PhysiologyEllen Grace Cañarejo BaroyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.Document1 pagePathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.romeo riveraNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Fat in BodyDocument7 pagesGroup 2 - Fat in BodySisfa ShabelaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Importance Glycolysis Can Function Under Anaerobic ConditionsDocument5 pagesBiomedical Importance Glycolysis Can Function Under Anaerobic ConditionsCatalina Denise Blaquera FloresNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatDocument2 pagesAnatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatSkyerex100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus: Moderator: DR Ramesh Presented by AbishaDocument43 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Moderator: DR Ramesh Presented by AbishaSparrowNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument9 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisFeliipe CruzzNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology Client DMDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology Client DMMarty MartinezNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONSDocument1 pageBlood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONSfatimaNo ratings yet
- DM Type 1Document4 pagesDM Type 1Adiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Endo-Doc LapakDocument3 pagesEndo-Doc LapakHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- 041 LiverDocument3 pages041 Liveraistina100% (1)
- Hormone NotesDocument8 pagesHormone Noteslaeticia schmiesNo ratings yet
- Overview FastingDocument21 pagesOverview FastingBagusReka100% (1)
- Pathiophysiology Med Ward RevisionDocument6 pagesPathiophysiology Med Ward RevisionBrandt CajoconNo ratings yet
- Lecture-8-Fasting-Liver and AdiposeDocument21 pagesLecture-8-Fasting-Liver and AdiposeBagusRekaNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument5 pagesInsulinBobNo ratings yet
- PAthophysio (With Content)Document1 pagePAthophysio (With Content)liesel_12No ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesEndocrine DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: ChemistryDocument21 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: ChemistryAbdihakem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Glucose Physiology, Normal.Document8 pagesGlucose Physiology, Normal.hajrahsuhardiNo ratings yet
- Pathology of DiabetesDocument4 pagesPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Glucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsDocument31 pagesGlucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsnikenNo ratings yet
- OBAT ANTI-DIABETES - Hernita - 2019Document70 pagesOBAT ANTI-DIABETES - Hernita - 2019Hernita TaurustyaNo ratings yet
- 14-Gluconeogenesis TEAM436Document20 pages14-Gluconeogenesis TEAM436ashishmahawar1510No ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument34 pagesHomeostasisAwaid AsimNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis, Glycolysis, Regulation (DR - Javed)Document28 pagesGluconeogenesis, Glycolysis, Regulation (DR - Javed)saadzubair0307No ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument4 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisAbigael Patricia Gutierrez100% (1)
- 7 OAD DR - Elly 2015Document52 pages7 OAD DR - Elly 2015ainNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Glucagon FinalDocument27 pagesInsulin, Glucagon FinalDhruvil GadhiyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of DMDocument13 pagesNursing Care of DMItachi SanNo ratings yet
- Patho DM HTN FinalDocument1 pagePatho DM HTN FinalBryant Riego IIINo ratings yet
- Phys 10Document22 pagesPhys 10sakwork30No ratings yet
- Anesthesia and Co Existing Diseases Stoelting's 2018 468 496Document29 pagesAnesthesia and Co Existing Diseases Stoelting's 2018 468 496Desak PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Antihyperglycemics DrugsDocument3 pagesAntihyperglycemics DrugsUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Blood SugarDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Blood SugartagmanNo ratings yet
- Environmental FactorsDocument7 pagesEnvironmental FactorsjayrchinNo ratings yet
- Diseases of GlucocorticoidDocument3 pagesDiseases of GlucocorticoidKeneyziaNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Karbohidrat Dan Integrasinya DG Regulasi HormonalDocument21 pagesMetabolisme Karbohidrat Dan Integrasinya DG Regulasi HormonalMahendra Yudha NNo ratings yet
- Week 14 - Regulation of Metabolism and Diabetes Flashcards QuizletDocument11 pagesWeek 14 - Regulation of Metabolism and Diabetes Flashcards QuizletMorgan ChristNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsDocument3 pagesDrug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsSurria Suguna15No ratings yet
- Obat Antidiabetes: Hernita TaurustyaDocument70 pagesObat Antidiabetes: Hernita TaurustyaHernita TaurustyaNo ratings yet
- CC1Document6 pagesCC1Sandhya Narag SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Lecture Note-6thDocument46 pagesDiabetes Lecture Note-6tholawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Physiology DiabetesDocument48 pagesPhysiology Diabetesrajesh g100% (1)
- L11 Glucose RegulationDocument21 pagesL11 Glucose RegulationCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Patho 1Document1 pagePatho 1ricciNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose HomeostasisDocument84 pagesBlood Glucose Homeostasisabliltymark3No ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument10 pagesGluconeogenesismoneth gerarmanNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Written ReportDocument19 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Written ReportEros Victorino100% (2)
- Metabolic Pathways of GlucoseDocument31 pagesMetabolic Pathways of GlucoseLisandrea BrownNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)From EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliNo ratings yet
- I Wish I Were Not Born DeclamationDocument1 pageI Wish I Were Not Born DeclamationClarissa Guifaya0% (1)
- Med TagDocument23 pagesMed TagClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- E-Cart ChecklistDocument6 pagesE-Cart ChecklistClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- By: Clarissa E. Guifaya BSN301/GROUP 3Document17 pagesBy: Clarissa E. Guifaya BSN301/GROUP 3Clarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- NP2 Nursing Board Exam November 2008Document16 pagesNP2 Nursing Board Exam November 2008Clarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases ReviewerDocument12 pagesCommunicable Diseases ReviewerClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Immediate Newborn CareDocument1 pageImmediate Newborn CareClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Royal: The Pentagon Review Specialist, IncDocument31 pagesRoyal: The Pentagon Review Specialist, IncClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- September: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 pagesSeptember: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Gladys Bautista Jaime 2010Document10 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Gladys Bautista Jaime 2010Clarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Narrowing of BronchiDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Narrowing of BronchiClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- HS RRLDocument1 pageHS RRLClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Student Nurse: - DateDocument3 pagesStudent Nurse: - DateClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 5 QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuiz No. 5 QuestionsClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument2 pagesDefinitionClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Classic Techniques in Medicine: Methods of Obtaining Peripheral Venous Access in Di Ycult SituationsDocument4 pagesClassic Techniques in Medicine: Methods of Obtaining Peripheral Venous Access in Di Ycult SituationsClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Ampisul, Hydrocort, Salbu, Mupirocin DrugsDocument4 pagesAmpisul, Hydrocort, Salbu, Mupirocin DrugsClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Hiv LabsDocument4 pagesHiv LabsClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-15-10 - 11th (J-Batch)Document11 pagesCHEMISTRY-15-10 - 11th (J-Batch)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Wartsila OEM Engine Manufacturer ApprovalsDocument8 pagesWartsila OEM Engine Manufacturer ApprovalsSivakumar SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Solutions Mind Map PDFDocument4 pagesSolutions Mind Map PDFvashuy091No ratings yet
- Laboratory Chemical and Reagents-2Document2 pagesLaboratory Chemical and Reagents-2Faris BahauddinNo ratings yet
- 02 Clinker Formation PDFDocument74 pages02 Clinker Formation PDFSokreach Din100% (4)
- Chemistry SPM Kbat Form 4Document14 pagesChemistry SPM Kbat Form 4Gloria Yong100% (1)
- Water PHDocument21 pagesWater PHJay MeeNo ratings yet
- Lab - Water PotentialDocument9 pagesLab - Water PotentialAleka AlexisNo ratings yet
- Swimming Pool Uv System Material Sub. - r1Document40 pagesSwimming Pool Uv System Material Sub. - r1Renjith RaveendranNo ratings yet
- D 3023 - 98 Stain TestDocument3 pagesD 3023 - 98 Stain TestJohnNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed ReactorDocument12 pagesFluidized Bed Reactoradnantayyab100% (1)
- Synthesis Characterization ADMET in Vitro and in Vivo Studies of Mixed Ligand Metal Complexes From A Curcumin Schiff Base and LawsoneDocument23 pagesSynthesis Characterization ADMET in Vitro and in Vivo Studies of Mixed Ligand Metal Complexes From A Curcumin Schiff Base and LawsoneartprogressivaNo ratings yet
- Sika Floorjoint PB 30pdrsDocument4 pagesSika Floorjoint PB 30pdrsRukmana's FamilyNo ratings yet
- AMS6265 Gear Material PropertiesDocument2 pagesAMS6265 Gear Material PropertiesSinan YıldızNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Phenol From CumeneDocument8 pagesManufacture of Phenol From CumeneFabi OneNo ratings yet
- Specification Sheet - Vmax® P550® Turf Reinforcement Mat: Index Property Test Method TypicalDocument2 pagesSpecification Sheet - Vmax® P550® Turf Reinforcement Mat: Index Property Test Method TypicalLuis MogrovejoNo ratings yet
- Glass Transition TemperatureDocument16 pagesGlass Transition TemperatureAnuNo ratings yet
- Solubility Curve WorksheetDocument5 pagesSolubility Curve WorksheetRohanee Hafsa KapusanNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Vol 1 EM - WWW - Tntextbooks.inDocument304 pages11th Chemistry Vol 1 EM - WWW - Tntextbooks.indorathy raniNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument9 pagesJurnalRina Boenda QueenRayaNo ratings yet
- Ribbon Anode Soil Och ConcreteDocument1 pageRibbon Anode Soil Och ConcreteSoltani AliNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY EXAM 2nd QDocument20 pagesCHEMISTRY EXAM 2nd Qjelosaliva2No ratings yet
- Micropropagation of BANANADocument30 pagesMicropropagation of BANANAraghuldon36No ratings yet
- Questioned Document MahinayDocument159 pagesQuestioned Document MahinayStephanie De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Rockland Community College BIO 107 Honors Review For Lab Practical IDocument2 pagesRockland Community College BIO 107 Honors Review For Lab Practical IkuriiriNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Solved Lec-16 Enzymes-Properties, Classification and NomenclatureDocument4 pagesMcqs Solved Lec-16 Enzymes-Properties, Classification and NomenclatureELAKKIYA .U BA Eng LitNo ratings yet
- AtpquestionsDocument16 pagesAtpquestionsBinesh Udaya100% (2)
- Problemario 3Document6 pagesProblemario 3itzel veronicaNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions: Teacher VersionDocument8 pagesStoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions: Teacher VersionBT Keith CelebreNo ratings yet