Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AI Lecure 7
AI Lecure 7
Uploaded by
h_shat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views30 pagesThe document discusses knowledge representation using production rules and the components of expert systems. It provides information on the following:
1. Production rules are a common methodology for representing knowledge using an "IF-THEN" structure. They are modular, define independent knowledge spaces, and allow adding or deleting rules.
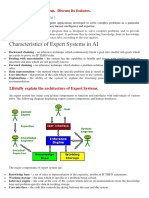
2. The main components of expert systems are the knowledge base, inference engine, and user interface. The knowledge base contains facts and rules represented by domain experts. The inference engine uses the rules to provide inferences to answer user questions.
3. Expert systems aim to emulate human expert knowledge and problem-solving skills in a particular domain. They allow transferring expert knowledge to non-experts through an interactive process of
Original Description:
Original Title
AI_Lecure_7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses knowledge representation using production rules and the components of expert systems. It provides information on the following:
1. Production rules are a common methodology for representing knowledge using an "IF-THEN" structure. They are modular, define independent knowledge spaces, and allow adding or deleting rules.
2. The main components of expert systems are the knowledge base, inference engine, and user interface. The knowledge base contains facts and rules represented by domain experts. The inference engine uses the rules to provide inferences to answer user questions.
3. Expert systems aim to emulate human expert knowledge and problem-solving skills in a particular domain. They allow transferring expert knowledge to non-experts through an interactive process of
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views30 pagesAI Lecure 7
AI Lecure 7
Uploaded by
h_shatThe document discusses knowledge representation using production rules and the components of expert systems. It provides information on the following:
1. Production rules are a common methodology for representing knowledge using an "IF-THEN" structure. They are modular, define independent knowledge spaces, and allow adding or deleting rules.
2. The main components of expert systems are the knowledge base, inference engine, and user interface. The knowledge base contains facts and rules represented by domain experts. The inference engine uses the rules to provide inferences to answer user questions.
3. Expert systems aim to emulate human expert knowledge and problem-solving skills in a particular domain. They allow transferring expert knowledge to non-experts through an interactive process of
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 30
Lecture : 7
Knowledge Representation Using Rules
There are common methodologies for the representation of
knowledge such as: production rules , semantic networks, and
frames .The production rules are sometimes called (IF THEN),
rules. (IF condition THEN action) ,and it is one of the most
common ways of representation knowledge .
Advantages of production rules:
1-It's modular (standard)
2-Every rule defines a small and independent space of
knowledge .((ك لق انونی ع رفحیز ص غیر ومستقلمنا لمع رفة
3- Enable adding new rules or deleting old ones.
4-The rules produced are usually independent of any other
rules.ا لقواعد ا لمنتجة عادة ما ت كونمستقلة عنأيق واعد أخرى.
Types of Rules:
There are three types of rules that are widely used in
production rules systems :
1- Knowledge Declarative Rules ق وانینا لمع رفة ا لتصریحية:
These rules set out all the facts and relationships of the
problem .
Example : IF inflation rate declines THEN the price of gold
goes down .
. فإن سعر الذهب سیقل،إذا انخفضت نسبة التضخم
2- Inference Procedural Rules : ق وانینا الستدال ال إِل جرائیة
Used to solve problems that we know some facts about
them .
For example: IF the data needed is not in the system,
THEN request it from the user .
3- Meta Rules ق وانینا لقوانين:
These rules give explanations as to which rules should be
taken into account in order to begging the inference .
Expert systems: ( Definition and concept)
Is a software that imitates the behavior of the human expert in
a particular field by extraction, compiling, analyzing and
reusing the information and experience of that expert in the
field and include them into a system called the expert system.
So that these systems can processing problems in this area
rather than people with experience and help transfer these
experiences to other people.
ه ي برمجيات تقوم بتقليد س لوك اإلنس ان الخ بير ف ي مجال معين وذل ك ع ن طريق
اس تخالص وتجميع وتحليل وإعادة اس تخدام معلومات وخ برة ذل ك الخ بير ف ي المجال
بحيث يصبح بإمكان هذه النظم معالجة المشاكل في.وضمها في نظام يُدعى النظام الخبير
هذا المجال بدالً م ن األشخاص أص حاب الخ برة والمس اعدة ف ي نق ل هذه الخ برات ألناس
.آخرين
It is also: an intensive knowledge program that works to
treating the difficult problems that are treated only by
human experts (such as medical diagnosis).
وهي ايضا برامج للمعرفة المكثفة تعمل على عالج المشاكل الصعبة التي ال تعالج إال
.)من قبل الخبراء من البشر ( مثل التشخيص الطبي
Expert systems are characterized as the domain in which
knowledge is represented and search is controlled within
knowledge bases.
وتتميز النظم الخبيرة بأنها المجال الذي يتم فيه تمثيل المعرفة ويتم التحكم في البحث
. ضمن قواعد المعرفة
Expert system concept :
Is a computer program designed to modeling human
experience in problems solving .
. هو برنامج كمبيوتر مصمم لنمذجة خبرات اإلنسان في حل المشكالت
Expert Systems Classifications
:Knowledge can generally be classified into two categories
Public knowledge)1(
Private knowledge)2(
(1) Public knowledge
Means the knowledge that available in books, and the
media ...etc, and can be obtained through reading,
presentation, conclusion and others.
ويمك ن الحص ول، الخ... يقص د به ا المعرف ة المتاح ة ف ي الكت ب ووس ائل اإلعالم
. واالستنتاج وغيرها، والعرض،عليها من خالل القراءة
(2) Private knowledge
It is the accumulated knowledge of the expert through his
long experience in his field, which is often exclusive and does
not find its way to publication.
Private knowledge is the basis upon which the expert relies on
any decision or advice.
،هي المعرفة المتراكمة لدى الخبير من خالل خبرته الطويلة في مجال عمله
المعرفة الخاصة هي األساس الذي.والتي غالبا ما تكون حصرية وال تجد طريقها للنشر
يعتمد عليه الخبير عند اتخاذ أي قرار أو تقديم المشورة.
Expert systems components:
.:Consists of two parts
:First Tranche
In which the knowledge base is constructed in the following
:sequence
.: يتكون من شقين
: الشق األول
.والذي يتم فيه بناء قاعدة المعرفة وذلك بالتسلسل التالي
The Expert -1
Or a group of experts in the specific field whose expertise
system is required, giving all the experiences they have collect
it to the knowledge engineer
حيث، أو مجموعة الخبراء في المجال المعين المطلوب الحصول على نظام الخبرة فيه
يقوم بإعطاء كل ما جمعوه من خبرة بأدق التفاصيل إلى مهندس المعرفة
2-Knowledge Engineer
Which sets the experience in the form of rules for
conditional inclusion including the conditions and results
of these conditions as well as the application of different
techniques.
والذي يتول ى وض ع الخ برة ف ي شك ل قواع د للتضمي ن الشرط ي متضمن ة للشروط
. والنتائج لهذه الشروط وكذلك تطبيق التقنيات المختلفة
Second Tranche :
In which questions are asked by the user and obtained results
or advice from the expert system which is in the following
sequence :
:الشق الثاني
والذي يت م فيه طرح األس ئلة م ن قب ل المس تخدم والحص ول عل ى النتائ ج أ و النص يحة م ن
: النظام الخبير والذي يتم بالتسلسل التالي
(1)The User
Inexperienced or limited experience who wants to get the real
knowledge and experience gained for a problem in this area.
العديم الخبرة أو ذو الخبرة المحدودة والذي يريد أن يحصل على المعرفة الحقيقية والخبرة
.المكتسبة لمشكلة ما في هذا المجال
(2)User interface : واجهة ا لمستخدم )) مدخلا لمواءمة ل لمستخدم
Which allows the exchange of knowledge between the user
and the knowledge base, it makes the user's questions
understandable by the knowledge base.
والذي يسمح بتبادل المعرفة بين المستخدم وقاعدة المعرفة و يجعل اسئلة المستخدم
. مفهومة من قبل قاعدة المعرفة
(3)Control Mechanism
It is the internal control of the inference engine and
knowledge base to answer the questions asked by the user.
وهي التي تقوم بالتحكم الداخلي في محرك االستدالل وقاعدة المعرفة لإلجابة على
. االسئلة المطلوبة من قبل المستخدم
(4)Knowledge base:
Is a database that includes the knowledge and expertise of
experts in a field of human knowledge stored in a logical
sequence to implement the condition (if then), knowledge
base includes: facts, rules that show the relationships between
the facts, Knowledge base is flexible and can be updated
without affecting the work of other components
: قاعدة المعرفة-
ه ي قاعدة بيانات تشتم ل عل ى معارف وخ برات الخ براء ف ي مجال م ن مجاالت المعرف ة
وتض م، ) عندئ ذ---- البشرية مختزن ة ف ي شك ل تس لسل منطق ي لتنفيذ الشرط (اذا كان
وتتميز قاعدة المعرف ة، وقواع د ت بين العالقات بين الحقائ ق، حقائ ق: قاعدة المعرف ة
. بالمرونة حيث يمكن تحديثها دون المساس بعمل باقي المكونات
Inference Engine )5( : آلة االستدالل
Which directs research into different trends in the
knowledge base until the user's questions is answered .
والتي تقوم بتوجيه البحث في االتجاهات المختلفة بقاعدة المعرفة إلى أن تتم اإلجابة
على اسئلة المستخدم
:The Inference is done in two ways
Forward Chaining-1
Backward Chaining-2
Forward Chaining )1(: التسلسل االمامي
Where the system analyzes the data entered in it and when
the matching of conditions is achieved, the goal is
implemented .
حيث يقوم النظام بتحليل البيانات المدخلة اليه وعندما يصل الى تطابق الشروط يقوم
)بالتنفيذ (الوصول الى الهدف
Backward Chaining)2( : التسلسل الخلفي
Here, the inference engine starts with the search from the
general goal to the lowest level of sub-goals .
هنا تبدأ آلة االستدالل بالبحث بداية من الهدف العام حتى ادنى مستوى من االهداف
الفرعية
Expert Systems Features: مميزاتا لنظم ا لخبيرة:
1. It is easy to use for any user, whether a regular user or a
developer.
2. Able to learn from experts directly and indirectly.
3. Able to teach non-specialists.
4 - Able to interpret any solutions you reach and clarify how to
access them.
5. A useful means of providing high levels of expertise in the
absence of an expert.
6. Able to develop the performance of specialists with simple
experience.
7. Preservation of human knowledge from loss, loss or
distortion Since the majority of knowledge is limited to a few
experts, their loss often results in a significant loss, and expert
systems are therefore a repository of this expertise.
-1أنها سهلة االستخدام ألي مستخدم سواء مستخدم عادي أو مط ّور .
-2قادرة على التعلم من الخبراء بطريقة مباشرة وغير مباشرة .
-3قادرة على تعليم غير المتخصصين .
-4قادرة على تفسير أي حلول تتوصل إليها مع توضيح طريقة الوصول إليها .
-5وسيلة مفيدة في توفير مستويات عالية من الخبرة في حال عدم توفر خبير.
-6قادرة على تطوير أداء المتخصصين ذوي الخبرة البسيطة.
-7حفظ المعارف البشرية من الفقد أو الضياع أو التشوه آذ أن غالبية المعارف تكون
محصورة في قلة من الخبراء غالبا ما يؤدي فقدانهم إلى خسارة كبيرة ،وعلى ذلك فان
النظم الخبيرة تعد مستودعا أمينا لهذه الخبرة.
: Disadvantages of Expert System
.Limited areas compared to human activity .1
High costs of design, operation and maintenance of the .2
.system
3. Desired knowledge may not always be available or
difficult to use.
4 - Method of solving the problem may be different from
one expert to another
1-ت لمحدودة مقارنة ب ا لنشاط ا لبشري
ا لمجا ال ا.
2- ف صميم وتشغيلوصيانة ا لنظام
ارتفاع ت كا لي ت.
3- ف لمنشودة ق د ال ت كونمتوافرة دائما أو يصعباستخدامها
ا لمع ار ا.
4- منهج حلا لمشكلة ق د يختلفمنخبير إ لىأخر
Stages of building expert systems:
Stages of building expert systems
1.Definition of problem: The problem required by the
expert system is described in a precise description of the
cooperation between the knowledge engineer and the
expert domain .
يتم وصف المشكلة المطلوب من النظام الخبير حلها وصفا دقيقا:التعريف بالمشكلة
.بالتعاون بين مهندس المعرفة وخبير المجال
2 - The formation of concepts.
.تكوين المفاهيم
3. Drafting: Knowledge engineers choose the appropriate
techniques to develop the system.
يقوم مهندسي المعرفة باختيار التقنيات المناسبة لتطوير النظام:الصياغة
4. Application: Concepts that are formulated using the
computer are programmed.
. يتم برمجة المفاهيم التي تمت صياغتها باستخدام الحاسب:التطبيق
5. Testing: The knowledge engineer tests the model in the
following ways:
-Application correct
: يقوم مهندس المعرفة باختبار النموذج من النواحي التالية:االختبار
صحة التطبيق
-The efficiency and completeness of drafting rules .
كفاءة واكتمال صياغة القواعد
- The solutions it offers are matched by expert solutions in
the same field .
. تتطابق الحلول التي يقدمها مع حلول خبير في نفس المجال
:Areas of expert systems
Expert systems have entered into several fields such as
medicine, agriculture, electronics, computers, geology,
engineering, education, law, trade, economics and many
more.
النظ م الخ بيرة دخل ت ف ي عدة مجاالت كالط ب والزراع ة واإللكترونيات والحاس بات
. والجيولوجيا والهندسة والتعليم والقانون والتجارة واالقتصاد وغيرها الكثير
The following example illustrates a rule with introductions
and results:
IF
The car engine starts turning and the car does not move
And the battery is charged
And the Starter is good
THEN
The car is free of fuel (Petrol)
: إذا كان
محرك السيارة يبدأ الدوران والسيارة ال تتحرك
و البطارية مشحونة
) جيدStarter( و مبدئ الحركة
إذن فالسيارة خالية من الوقود
Example: How to build knowledge bases ?
Rule 1: If a burning substance is poured, it causes fire
Rule 2: If the chemical concentration of the substance is less
than 6, the substance is acidic.
Rule 3: If the substance is acidic and its smells like vinegar, it is
acetic acid.
Rule 4: If the substance is acetic acid it is a non-incendiary
material.
. إذا سكبت مادة حارقة قد تسبب بالحريق:1قاعد
. فان المادة تمثل حامضا6 إذا كان التركيز الكيمائي للمادة أقل من:2قاعدة
. إذا كانت المادة المسكوبة حامضا ورائحتها مثل الخل فإنها حامض الخليك:3قاعدة
. إذا كانت المادة حامض الخليك فإنها مادة غير حارقة:4 قاعدة
If one of them pours a substance, the following facts are
available:
Fact 1: Its chemical concentration is less than 6
.Fact 2: It smells like vinegar
:وإذا سكب احدهم مادة توفرت فيها الحقائق التالية
6 أن تركيزها الكيمائي أقل من:1حقيقة
. أن رائحتها تشبه الخل:2حقيقة
When we compare the facts with the rules, we find a
correlation between fact 1 and rule 2, which results in a new
fact:
Fact 3: That the substance is acid.
مع ا ينتج2 والقاعدة1 فعن د مقارن ة الحقائ ق بالقواع د حي ث نج د مطابق ة بي ن الحقيق ة
:عن ذلك حقيقة جديدة هي
. أن المادة هي حامض:3حقيقة
When the comparison process is reconciled we find a
correspondence between facts 2 and 3 and rule 2 together
produces a new fact:
معا ينتج حقيقة2 والقاعدة3و2 وعند إعادة عملية المقارنة نجد تطابقا بين الحقائق
: جديدة
Thus we produce a new fifth fact:
Fact 5: The material is not incendiary
Therefore they do not cause fire
:وهكذا تنتج لدينا حقيقة خامسة جديدة هي
. أن المادة ليست حارقة:5حقيقة
وبالتالي فهي ال تسبب الحريق
You might also like
- Sowa - J. F. (2000) - Knowledge RepresentationDocument610 pagesSowa - J. F. (2000) - Knowledge RepresentationRaghuPatilNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 5Document13 pagesUNIT - 5nitinsingaur.bizNo ratings yet
- Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence: "Can Machines Think?"Document11 pagesIntelligence: Artificial Intelligence: "Can Machines Think?"api-26830587No ratings yet
- Expert Systems: Unit-VDocument24 pagesExpert Systems: Unit-VasarvigaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document25 pagesUnit 5skraoNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document51 pagesUnit 5shreya kharolaNo ratings yet
- Expert Systems: AbstractDocument15 pagesExpert Systems: Abstractapi-26830587No ratings yet
- AI Mod-4Document5 pagesAI Mod-4Shashank chowdary DaripineniNo ratings yet
- AI Mod-4Document5 pagesAI Mod-4Shashank chowdary DaripineniNo ratings yet
- CS6659 UNIT 5 NotesDocument25 pagesCS6659 UNIT 5 NotesprofBalamurugan89% (9)
- Artificial Intelligence Notes Unit-4 Lecture-1 Expert SystemsDocument7 pagesArtificial Intelligence Notes Unit-4 Lecture-1 Expert SystemsShivangi ThakurNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Artificial Intelligence AssignmentDocument13 pagesUnit - 4 Artificial Intelligence AssignmentVishalNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemDocument65 pagesExpert SystemBharathi ArikerieNo ratings yet
- Expert Systems - MergedDocument39 pagesExpert Systems - MergedMansi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Part 1Document13 pagesUnit IV Part 1dheerajNo ratings yet
- Knowledge-Based Expert System in Traffic Signal Control SystemsDocument9 pagesKnowledge-Based Expert System in Traffic Signal Control SystemsSudi ForFrndzNo ratings yet
- 15 - Clinical Decision Support Systems. Health Forecasting. Modeling of Decision Support Systems 1Document13 pages15 - Clinical Decision Support Systems. Health Forecasting. Modeling of Decision Support Systems 1Harshit SodhiNo ratings yet
- Ai Unit-5 (Part-1)Document11 pagesAi Unit-5 (Part-1)Kank FaizNo ratings yet
- Expert System: Artificial IntelligenceDocument16 pagesExpert System: Artificial IntelligenceAkhil DhingraNo ratings yet
- CH 10: Expert Systems:: Representing Using Domain Knowledge Expert System Shells Explanation, Knowledge AcquisitionDocument22 pagesCH 10: Expert Systems:: Representing Using Domain Knowledge Expert System Shells Explanation, Knowledge AcquisitionAMI CHARADAVANo ratings yet
- Unit 4 NotesDocument16 pagesUnit 4 NotesRamya F100% (2)
- Expert Systems: Representing and Using Domain Knowledge Expert System Shells Explanation Knowledge AcquisitionDocument25 pagesExpert Systems: Representing and Using Domain Knowledge Expert System Shells Explanation Knowledge AcquisitionAsfia Mehjabeen MohammadNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5Document8 pagesUnit - 5skraoNo ratings yet
- Expert System Week 3-4Document6 pagesExpert System Week 3-4treeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-20 (Expert Systems)Document4 pagesChapter-20 (Expert Systems)Radisson TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- RuleBased IA TIPDocument68 pagesRuleBased IA TIPmarlon_tayagNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Representation and Expert SystemDocument36 pagesKnowledge Representation and Expert SystemJiawei TanNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionsDocument15 pagesRevision QuestionsSamwelNo ratings yet
- Expert Systems NotesDocument15 pagesExpert Systems NotesJoe S0% (1)
- Expert SystemDocument47 pagesExpert SystemBin Zhang100% (1)
- AI Chapter 4 5 6 Combined NoteDocument27 pagesAI Chapter 4 5 6 Combined Noteblahhwhocares69No ratings yet
- What Is An Expert System?Document35 pagesWhat Is An Expert System?Sandeep MalikNo ratings yet
- Ai R16 - Unit-5Document13 pagesAi R16 - Unit-5Simran Reyaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Expert System 1680197669658Document27 pagesChapter 7 - Expert System 1680197669658RAʜʋɭ SʋɓɘɗɩNo ratings yet
- App of AI - Week-2Document6 pagesApp of AI - Week-2Idrees KhanafridiNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Expert SystemDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of Expert SystemghulamishaqNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemsDocument35 pagesExpert SystemsRammah YusufNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Business and Information Science Assignment Cover PageDocument6 pagesFaculty of Business and Information Science Assignment Cover PageBogati ArzoonNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument6 pagesProject ProposalMelina Ya manNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV: Expert SystemsDocument29 pagesUnit - IV: Expert SystemsBhargavNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Based SystemsDocument39 pagesKnowledge Based SystemsRuby FreshNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems: Submitted byDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Expert Systems: Submitted byRoshani KamathNo ratings yet
- Applications of AIDocument6 pagesApplications of AIkulpaudel88No ratings yet
- MIS AssignmentDocument3 pagesMIS AssignmentMNaveed OfficialNo ratings yet
- Expert Systems AIDocument16 pagesExpert Systems AIANAKHA R MScAI23-25No ratings yet
- Expert Systems and AIDocument17 pagesExpert Systems and AIPallavi PradhanNo ratings yet
- AN Expert Systems FOR Diagnosing Tractor Failure AND MalfunctionDocument7 pagesAN Expert Systems FOR Diagnosing Tractor Failure AND MalfunctionAhmed MyNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemsDocument9 pagesExpert Systemsأحمد عدلي المحتسبNo ratings yet
- EXPERT SYSTEM Is An Interactive and Reliable Computer-Based DecisionDocument8 pagesEXPERT SYSTEM Is An Interactive and Reliable Computer-Based DecisionC V M JAHNAVINo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Expert SystemsDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Expert SystemsManish Kumar KashyapNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Part 2Document22 pagesUnit 5 Part 2abhinav vuppalaNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemsDocument29 pagesExpert SystemsKeith Tanaka MagakaNo ratings yet
- 03a04chapter2v4 2Document50 pages03a04chapter2v4 2api-3738694No ratings yet
- Unit-V SyllabusDocument10 pagesUnit-V SyllabusDr-Kiran Sree PokkuluriNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 AiDocument48 pagesUnit 5 AiRamNo ratings yet
- BEU 5173 Artificial Intelligence: Rule Based Expert SystemsDocument33 pagesBEU 5173 Artificial Intelligence: Rule Based Expert SystemsMuhammad Aiman AwaludinNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemsDocument13 pagesExpert SystemsGaurav kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Part 111Document13 pagesUnit IV Part 111raghu RamNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Expert SystemsDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence Expert SystemsSri VardhanNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence - Expert SystemsDocument8 pagesArtificial Intelligence - Expert SystemsRainrock BrillerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Digital Systems and Information: Logic and Computer Design FundamentalsDocument55 pagesChapter 1 - Digital Systems and Information: Logic and Computer Design FundamentalsAbbas AlMoussawiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam-Reading and Writing-2Document6 pagesFinal Exam-Reading and Writing-2h_shatNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 09-28-2022 15.51Document1 pageCamScanner 09-28-2022 15.51h_shatNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Learning Objectives Learning ObjectivesDocument22 pagesUnit 2: Learning Objectives Learning Objectivesh_shatNo ratings yet
- Name: ID:: 50.530: Software Engineering (2014) Final ExamDocument13 pagesName: ID:: 50.530: Software Engineering (2014) Final Examh_shatNo ratings yet
- Kingdom of Saudi Arabia The National Commission For Academic Accreditation & AssessmentDocument15 pagesKingdom of Saudi Arabia The National Commission For Academic Accreditation & Assessmenth_shatNo ratings yet
- 2006-1733: Designing and Implementing A Parallel Computing Curriculum Based On Beowulf ClusteringDocument10 pages2006-1733: Designing and Implementing A Parallel Computing Curriculum Based On Beowulf Clusteringh_shatNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks: Edge Detection ExampleDocument4 pagesConvolutional Neural Networks: Edge Detection Exampleh_shatNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks: Pooling LayersDocument5 pagesConvolutional Neural Networks: Pooling Layersh_shatNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks: Edge Detection ExampleDocument4 pagesConvolutional Neural Networks: Edge Detection Exampleh_shatNo ratings yet
- مقرر شهادات مهنيةDocument1 pageمقرر شهادات مهنيةh_shatNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks: Computer VisionDocument3 pagesConvolutional Neural Networks: Computer Visionh_shatNo ratings yet
- Book IP2364 File For Review Round 9Document115 pagesBook IP2364 File For Review Round 9h_shatNo ratings yet
- Smart Machine: ComputerDocument9 pagesSmart Machine: Computerh_shatNo ratings yet
- First Term English Worksheet 2016-2017: 1.make SentencesDocument19 pagesFirst Term English Worksheet 2016-2017: 1.make Sentencesh_shatNo ratings yet
- Network Causality Structures Among Bitcoin and Other FinancialassetsDocument11 pagesNetwork Causality Structures Among Bitcoin and Other Financialassetsh_shatNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Computer Engineering Dept - Computer Skills II First ExamDocument1 pageElectrical & Computer Engineering Dept - Computer Skills II First Examh_shatNo ratings yet
- New CS432 - Module 01 - Computer Abstractions and TechnologyDocument75 pagesNew CS432 - Module 01 - Computer Abstractions and Technologyh_shatNo ratings yet
- FAI Unit 1Document40 pagesFAI Unit 1DhyeayaNo ratings yet
- AKTU IT 4th YrDocument19 pagesAKTU IT 4th YrMahak SinghNo ratings yet
- Software Systems Analysis - A Research Area Overview: Reema Al-KamhaDocument14 pagesSoftware Systems Analysis - A Research Area Overview: Reema Al-KamhaPrabhakar Srinivas GarapatiNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Representation: Unit-6Document101 pagesKnowledge Representation: Unit-6Tariq IqbalNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Lecture 1 - Chapter 1Document54 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Lecture 1 - Chapter 1Zeeshan Bhatti100% (1)
- AIMag07 02 007 PDFDocument10 pagesAIMag07 02 007 PDFRohit DNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence (Open Elective) : Unit-IiDocument1 pageArtificial Intelligence (Open Elective) : Unit-IiRadha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 7th Sem SyllabusDocument11 pages7th Sem SyllabusShobhit SinhaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Artificial Intelligence in HCL Info SystemDocument67 pagesA Study On Artificial Intelligence in HCL Info Systempiyushsharma_231093No ratings yet
- Course Overview and IntroductionDocument22 pagesCourse Overview and IntroductionJavaD AlidoustiNo ratings yet
- BIT 2319 Lab Practical II - Research LabDocument1 pageBIT 2319 Lab Practical II - Research Labgeebush60No ratings yet
- AI Notes Jagdish BhattaDocument152 pagesAI Notes Jagdish Bhattajames smithNo ratings yet
- AI Book3Document446 pagesAI Book3Super GamerNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Assignment 1: 13) Construct The Partitioned Semantic Net Representations For The FollowingDocument4 pagesArtificial Intelligence Assignment 1: 13) Construct The Partitioned Semantic Net Representations For The FollowingJasmin YadavNo ratings yet
- CSE - VI Sem 21 SeriesDocument23 pagesCSE - VI Sem 21 SeriesSafia AnjumNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Knowledge and Information?Document2 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Knowledge and Information?Brijesh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Application of First-Order Logic in Knowledge Based Systems PDFDocument7 pagesApplication of First-Order Logic in Knowledge Based Systems PDFLidya SeptianieNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Knowledge Representation BTech MS N HI L14 L22 PDFDocument91 pagesUnit-3 Knowledge Representation BTech MS N HI L14 L22 PDFshushant kumarNo ratings yet
- FMTH0301/Rev.5.3 Course Plan: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument15 pagesFMTH0301/Rev.5.3 Course Plan: Department of Electrical & Electronics EngineeringMohanNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument10 pagesArtificial IntelligenceAdarsh KannanNo ratings yet
- Logic Representation and Reasoning For Automated BIM Analysis To Support Automation in Offsite ConstructionDocument16 pagesLogic Representation and Reasoning For Automated BIM Analysis To Support Automation in Offsite ConstructionLOVELL WILDER TORPOCO LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Expert SystemsDocument31 pagesKnowledge and Expert SystemsAnurag PatidarNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial IntelligenceAbhi AndhariyaNo ratings yet
- Sia Fna MLDocument33 pagesSia Fna MLJoshua DavidNo ratings yet
- Jumping NLP Curves PDFDocument10 pagesJumping NLP Curves PDFAngelRibeiro10No ratings yet
- Semantic Web and OntologiesDocument61 pagesSemantic Web and OntologiesNaglaa FathyNo ratings yet
- F030 - The Evolution of Expert System by NoranDocument25 pagesF030 - The Evolution of Expert System by Noranism4ilyusufNo ratings yet
- CBR SystemDocument94 pagesCBR SystemJose Rafael CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 2-1Document69 pagesModule 2-1Manjunath ShenoyNo ratings yet