Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 8 - 4
Lecture 8 - 4
Uploaded by
Rakhmeen gul0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views24 pagesThe document discusses differential amplifiers with current source loads. It describes how cascoding the amplifying transistors and current sources can increase the gain of the differential amplifier. It also examines the common-mode gain and common-mode rejection ratio of differential amplifiers. A mismatch in the drain resistances of the transistors causes the amplifier to have a finite common-mode gain, resulting in some interference appearing at the output. The ratio of the differential gain to the common-mode gain is called the common-mode rejection ratio.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lecture 8_4 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses differential amplifiers with current source loads. It describes how cascoding the amplifying transistors and current sources can increase the gain of the differential amplifier. It also examines the common-mode gain and common-mode rejection ratio of differential amplifiers. A mismatch in the drain resistances of the transistors causes the amplifier to have a finite common-mode gain, resulting in some interference appearing at the output. The ratio of the differential gain to the common-mode gain is called the common-mode rejection ratio.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views24 pagesLecture 8 - 4
Lecture 8 - 4
Uploaded by
Rakhmeen gulThe document discusses differential amplifiers with current source loads. It describes how cascoding the amplifying transistors and current sources can increase the gain of the differential amplifier. It also examines the common-mode gain and common-mode rejection ratio of differential amplifiers. A mismatch in the drain resistances of the transistors causes the amplifier to have a finite common-mode gain, resulting in some interference appearing at the output. The ratio of the differential gain to the common-mode gain is called the common-mode rejection ratio.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 24
Lecture 8_4
The Differential Amplifier with
Current-Source Loads
MOS Loads
(a) Diode-connected load
(b) Current-Source load
To obtain higher gain, the passive resistances can be replaced with current sources
Solution to low-gain problem: Cascoding
AV ,diff g m1[( g m 3 ro 3 ro1 ) || ( g m 5 ro 5 ro 7 )]
Cascode Differential Amplifier
The gain of the differential amplifier
can be increased by utilizing the
cascode configuration
A CMOS differential amplifier with cascading
applied to the amplifying transistors and via
transistors and
and to the current-source transistors and via
transistors and The differential voltage gain can
be found from the differential half-circuit shown in
Fig.
Common-Mode Gain and Common-Mode Rejection
Ratio
(CMRR)
Part 1: Effect due to
resistance of a non-ideal
current source
is usually very large, this change in dc current in each of and is usually small and we shall neglect it, thus
assuming that the two transistors continue to operate at the bias current of
consider the more
realistic situation of
the current source
having a finite
output Resistance ,
the common-mode
gain will no longer
be zero
Thus the differential output voltage will remain free of
common-mode interference
Unfortunately, however, this will
not be the
The case if the
virtual ground circuit
that develops on the is not
common-source
perfectlyeffect
symmetrical
terminal results in a zero signal current through ; hence has no
on the value of .
Effect of Mismatch
It follows that a mismatch in the drain resistances causes the differential amplifier to have a
finite common-mode gain.
Thus, a portion of the interference or noise signal will appear as a component of
A measure of the effectiveness of the differential amplifier in amplifying differential-mode
signals and rejecting common-mode interference is the ratio of the magnitude of its differential
gain to the magnitude of its common-mode gain .
This ratio is termed common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR). Thus
𝑔𝑚 𝑅 𝐷
For the case of a MOS differential amplifier with
drain resistances that exhibit a mismatch ( 𝑅𝐷
2 𝑅 𝑆𝑆 )( ∆ 𝑅𝐷
𝑅𝐷 )
You might also like
- Electrical Abbreviations and Full FormsDocument5 pagesElectrical Abbreviations and Full Formsraja.shriram89% (126)
- Design of A Single Ended Two Stage Opamp Using 90Nm Cmos GPDK TechnologyDocument8 pagesDesign of A Single Ended Two Stage Opamp Using 90Nm Cmos GPDK Technologygill6335100% (1)
- ACCESSORIES AND EQUIPMENT Park Assist Module (PAM) (PTSPAM) - Electrical Diagnostics - Ram Pickup PDFDocument175 pagesACCESSORIES AND EQUIPMENT Park Assist Module (PAM) (PTSPAM) - Electrical Diagnostics - Ram Pickup PDFcharlesNo ratings yet
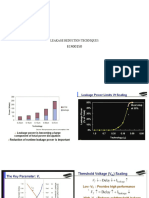
- Leakage Reduction TechniquesDocument33 pagesLeakage Reduction TechniquesIndrajeet GautamNo ratings yet
- No. Option A Option B Option C Option DDocument3 pagesNo. Option A Option B Option C Option DNevil ModiNo ratings yet
- Tuen Voltage AmplifirDocument7 pagesTuen Voltage Amplifirkaran007_mNo ratings yet
- Effect of Finite Amplifier Gain, Bandwidth, and Non-Idealities of Switches in Switched Capacitor Ladder CircuitsDocument6 pagesEffect of Finite Amplifier Gain, Bandwidth, and Non-Idealities of Switches in Switched Capacitor Ladder CircuitssdfasdfNo ratings yet
- A 50 MHZ Order Elliptic Lp-Filter Using Current Mode GM-C TopologyDocument4 pagesA 50 MHZ Order Elliptic Lp-Filter Using Current Mode GM-C TopologyYJ ZHANGNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Switching Characteristics of DC-DC Boost Converter SystemsDocument7 pagesEnhanced Switching Characteristics of DC-DC Boost Converter Systemsmhd ali mustofah nstNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Different Current Mirror Using 0.35 M and Its ApplicationDocument5 pagesComparative Analysis of Different Current Mirror Using 0.35 M and Its ApplicationaliNo ratings yet
- No. Option A Option B Potion C Option DDocument6 pagesNo. Option A Option B Potion C Option DhappyNo ratings yet
- Design and Validation of Pre-Insertion Resistor Rating For Mitigation of Zero Missing PhenomenonDocument6 pagesDesign and Validation of Pre-Insertion Resistor Rating For Mitigation of Zero Missing PhenomenonJonayed Iqbal JoyNo ratings yet
- Emitter FollowersDocument6 pagesEmitter Followersalgnben1746No ratings yet
- Differential Amplifier Using CMOS Technology: Saud Almusallam, Ali AshkananiDocument8 pagesDifferential Amplifier Using CMOS Technology: Saud Almusallam, Ali AshkananiNiranjan DaradeNo ratings yet
- Parallel RC Circuit Impedance Calculator - Electrical, RF and Electronics Calculators - Online Unit ConvertersDocument4 pagesParallel RC Circuit Impedance Calculator - Electrical, RF and Electronics Calculators - Online Unit ConvertersMRSUPERCOOLNo ratings yet
- Transformer Neutral GroundingDocument5 pagesTransformer Neutral Groundingsalemg82No ratings yet
- Single Line To Ground FaultDocument12 pagesSingle Line To Ground Faultluhusapa-1No ratings yet
- Analog Vls I ProjectDocument8 pagesAnalog Vls I ProjectLakshmi Sri Ram GannavarapuNo ratings yet
- Pilot Wires - On DRDocument6 pagesPilot Wires - On DRmarkigldmm918No ratings yet
- Ground FaultDocument27 pagesGround FaultbobyNo ratings yet
- ITEPS Lecture 2.BDocument14 pagesITEPS Lecture 2.BJin Young SongNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test 12 - Elec. CHOICESdocxDocument5 pagesMastery Test 12 - Elec. CHOICESdocxuvubwebweNo ratings yet
- Droop Control ExplanationDocument2 pagesDroop Control ExplanationAli Reza GalibNo ratings yet
- Slua 056Document9 pagesSlua 056mohamed tawfikNo ratings yet
- 4.ELEC2130 Op-Amp Characteristics - VPDocument10 pages4.ELEC2130 Op-Amp Characteristics - VPmahavir prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Instrument Transformers For Relaying: W. A. ElmoreDocument13 pagesInstrument Transformers For Relaying: W. A. ElmoreAbhishek RajputNo ratings yet
- Intermittent Line-to-Ground Faults in Generator Stator Windings and Consequences On Neutral GroundingDocument6 pagesIntermittent Line-to-Ground Faults in Generator Stator Windings and Consequences On Neutral GroundingjuanNo ratings yet
- The Inverter: Presented By: Erica Niña Ignacio Phildrick Perea Janvoi de TazaDocument19 pagesThe Inverter: Presented By: Erica Niña Ignacio Phildrick Perea Janvoi de TazaSydney BajentingNo ratings yet
- A Low Power Low Voltage Rail To Rail Constant GM Differential Amplifier With 150 DB CMRR and Enhanced Frequency PerformanceDocument11 pagesA Low Power Low Voltage Rail To Rail Constant GM Differential Amplifier With 150 DB CMRR and Enhanced Frequency Performanceersan turkmanNo ratings yet
- Voltage Controlled Oscillators v1 (March 22)Document37 pagesVoltage Controlled Oscillators v1 (March 22)소공자No ratings yet
- Answer: Electronics (Day 2) Ue Caloocan (1-5)Document6 pagesAnswer: Electronics (Day 2) Ue Caloocan (1-5)von kervy onradeNo ratings yet
- Current Transformer FundamentalDocument3 pagesCurrent Transformer FundamentalSagar DesaiNo ratings yet
- A CMOS Bandgap ReferenceDocument10 pagesA CMOS Bandgap ReferencemeslonNo ratings yet
- Operation, Design and Testing of Generator 100% Stator Earth Fault Protection Using Low Frequency InjectionDocument7 pagesOperation, Design and Testing of Generator 100% Stator Earth Fault Protection Using Low Frequency InjectionYaman ghayadNo ratings yet
- Self Biased Complementary Folded Cascode Op AmpDocument3 pagesSelf Biased Complementary Folded Cascode Op AmpCapitaneanu StefanNo ratings yet
- 5.2.3 Error AmplifierDocument8 pages5.2.3 Error AmplifierAnonymous TPVfFif6TONo ratings yet
- Areva MBCHDocument16 pagesAreva MBCHronald_chan_2100% (3)
- Conducted Emission: Electromagnetic Compatibility EngineeringDocument27 pagesConducted Emission: Electromagnetic Compatibility Engineeringyanuar1976No ratings yet
- LC Oscillator Has 1% THD: Amplifier and Comparator Circuits Signal Generation CircuitsDocument2 pagesLC Oscillator Has 1% THD: Amplifier and Comparator Circuits Signal Generation CircuitsAnonymous H3rwrtBNo ratings yet
- Gec DTT Biased Diff R 5116dDocument4 pagesGec DTT Biased Diff R 5116dfarzad dalaviNo ratings yet
- Power Quality: Expert LevelDocument55 pagesPower Quality: Expert Levelabdallah hosinNo ratings yet
- 008 - Transformer PtotectionDocument10 pages008 - Transformer PtotectionarunmozhiNo ratings yet
- Wien Bridge OscillatorDocument5 pagesWien Bridge OscillatorMarcus DavidssonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document6 pagesChapter 11vuphanhuanNo ratings yet
- An Adaptive Biased Single-Stage CMOS Operational Amplifier With A Novel Rail-To-Rail Constant-Gm Input StageDocument8 pagesAn Adaptive Biased Single-Stage CMOS Operational Amplifier With A Novel Rail-To-Rail Constant-Gm Input Stagekhausar1785No ratings yet
- 2007 Nonis TCAS CML Divider DesignDocument10 pages2007 Nonis TCAS CML Divider DesignDavidNo ratings yet
- 509RFD33Document2 pages509RFD33gary2ndhome2182No ratings yet
- A Gain Cmos: 50 MHZ Variable Amplifier Cell in 2PmDocument3 pagesA Gain Cmos: 50 MHZ Variable Amplifier Cell in 2Pmapi-19755952No ratings yet
- Harmonic Distortion in Power Stations Due To FerroresonanceDocument4 pagesHarmonic Distortion in Power Stations Due To FerroresonanceSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- C3.0 Operational Amplifiers II: Jeng-Han TsaiDocument12 pagesC3.0 Operational Amplifiers II: Jeng-Han Tsailinux14No ratings yet
- Essential Electronics: R C R 2 L 4 f L ζ = = πDocument11 pagesEssential Electronics: R C R 2 L 4 f L ζ = = πmohamadazareshNo ratings yet
- The Use of Triggered Current Limitors To Reduce The Prospective Fault Current For High Voltage SystemDocument3 pagesThe Use of Triggered Current Limitors To Reduce The Prospective Fault Current For High Voltage SystemShailesh ChettyNo ratings yet
- LCL Filter DesignDocument22 pagesLCL Filter DesignZunAib Ali100% (1)
- ELecs Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesELecs Sample QuestionsMikaela VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Tol SelectDocument4 pagesCapacitor Tol Selectwrite2arshad_mNo ratings yet
- 2marks Unit1Document4 pages2marks Unit1Sinan SinanNo ratings yet
- Consequences of Harmonic Currents in Generator PDFDocument2 pagesConsequences of Harmonic Currents in Generator PDFAshish ParasharNo ratings yet
- Half-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter For High Power DC Power Supply PDFDocument6 pagesHalf-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter For High Power DC Power Supply PDFAditya ThanawalaNo ratings yet
- Mosfet & BJT Frequency ResponseDocument18 pagesMosfet & BJT Frequency ResponseMalik JameelNo ratings yet
- LC - VCO With One Octave Tuning RangeDocument5 pagesLC - VCO With One Octave Tuning RangeGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Lecture Slides - Week-02 Review of Signals PDFDocument30 pagesLecture Slides - Week-02 Review of Signals PDFRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides - Week-04 DSB-SC and AM PDFDocument16 pagesLecture Slides - Week-04 DSB-SC and AM PDFRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides - Week-03 Fourier Series and Fourier Transform PDFDocument31 pagesLecture Slides - Week-03 Fourier Series and Fourier Transform PDFRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides - Week-05 SSB and VSB Modulation PDFDocument14 pagesLecture Slides - Week-05 SSB and VSB Modulation PDFRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides - Week-06 Angle Modulation PDFDocument14 pagesLecture Slides - Week-06 Angle Modulation PDFRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 PDFDocument18 pagesLecture 04 PDFRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Steady-State ErrorDocument53 pagesChapter 7 Steady-State ErrorRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 02 - 03 - Discrete Time Signals - 2.1-2.4 PDFDocument43 pagesLecture - 02 - 03 - Discrete Time Signals - 2.1-2.4 PDFRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Time Response of Dynamic Systems 1Document86 pagesChapter 4 Time Response of Dynamic Systems 1Rakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 Electromechanical Systems Transfer FunctionsDocument13 pagesLecture 05 Electromechanical Systems Transfer FunctionsRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06 Case Study - Antena Position ControlDocument15 pagesLecture 06 Case Study - Antena Position ControlRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Alternative Representation in State SpaceDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Alternative Representation in State SpaceRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- ECD Lab 6Document6 pagesECD Lab 6Rakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 5 8 6BJT-Differential AmplifierDocument105 pagesLec 8 5 8 6BJT-Differential AmplifierRakhmeen gulNo ratings yet
- Directional Spool Valves, Direct Operated, With Solenoid ActuationDocument12 pagesDirectional Spool Valves, Direct Operated, With Solenoid Actuationchmatias3No ratings yet
- 20LL27 19y600 7560 PDFDocument26 pages20LL27 19y600 7560 PDFAleksander AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Altivar 31Document96 pagesAltivar 31Leyre Marcilla MartínezNo ratings yet
- Esquema Motor MagneticoDocument5 pagesEsquema Motor MagneticonewTesla22No ratings yet
- Pterra ReportDocument63 pagesPterra ReportHectorNo ratings yet
- SatheeshP 15yrs Dip - Electrical C LicenseDocument5 pagesSatheeshP 15yrs Dip - Electrical C LicenseSatheesh SathyaNo ratings yet
- Daewoo Matiz 2000-2013 Airbags 1-6 PDFDocument6 pagesDaewoo Matiz 2000-2013 Airbags 1-6 PDFsheoNo ratings yet
- MC2W3C - D MPD 1306Document1 pageMC2W3C - D MPD 1306CRIS SEDANTONo ratings yet
- Octonet Catalog Section PDFDocument4 pagesOctonet Catalog Section PDFParasaram SrinivasNo ratings yet
- City and Relay Cards Installation Instructions: Topic See PageDocument12 pagesCity and Relay Cards Installation Instructions: Topic See PageMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Correction - Week 5Document35 pagesPower Factor Correction - Week 5Tayyab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Motor DrivesDocument21 pagesSynchronous Motor DrivesPathakota Sai Niranjan Kumar100% (1)
- 24VDC Address Central Battery System: Installation Programming UseDocument44 pages24VDC Address Central Battery System: Installation Programming UseThanosEleftheroudisNo ratings yet
- CD4070Document6 pagesCD4070api-3708997No ratings yet
- Yf S201CDocument4 pagesYf S201CLQ530No ratings yet
- Scania Skrzynia BiegówDocument67 pagesScania Skrzynia Biegówandrzej100% (1)
- Skil Models 77 367 825 Super Duty SawsDocument6 pagesSkil Models 77 367 825 Super Duty SawsrexNo ratings yet
- KP1, KP5 - InstallationDocument2 pagesKP1, KP5 - InstallationThùy DungNo ratings yet
- ECEN 5817 Resonant and Soft-Switching Techniques in Power ElectronicsDocument22 pagesECEN 5817 Resonant and Soft-Switching Techniques in Power ElectronicsDiego BautistaNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Indutivo m12 m18Document14 pagesCatalogo Indutivo m12 m18Carlos HuaiquinaoNo ratings yet
- 04.closure Drive Motor CylinderDocument31 pages04.closure Drive Motor CylinderThinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Tim WylieDocument33 pagesTim WyliemsiantexNo ratings yet
- Relay Trip Circuit - C16Document39 pagesRelay Trip Circuit - C16josehenriquezsotoNo ratings yet
- E-STOP Relays, Safety Gate Monitors: Pnoz X6Document8 pagesE-STOP Relays, Safety Gate Monitors: Pnoz X6muaadhNo ratings yet
- Choke Coil: FeaturesDocument2 pagesChoke Coil: FeaturesNuc LeusNo ratings yet
- 8051 ApplicationsDocument5 pages8051 Applicationsgdreddy25No ratings yet
- Saturable ReactorDocument2 pagesSaturable ReactorGilberto ManhattanNo ratings yet
- StelmecDocument2 pagesStelmecARUMUGAMNo ratings yet