Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lact 2
Lact 2
Uploaded by
Playersbattle Ground0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
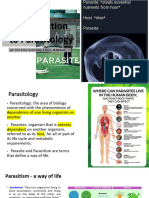
86 views14 pagesParasites are organisms that live on or inside a host organism and derive nutrients from the host. There are two main types - ectoparasites which live on the outside of the host, and endoparasites which live inside the host. Endoparasites typically cause more diseases in humans. Parasites can be obligate and dependent on the host, facultative and able to live independently at times, or accidental parasites infecting unusual hosts. Hosts play various roles including definitive hosts where sexual reproduction occurs, intermediate hosts where larvae develop, reservoir hosts that maintain infection, and transport hosts that carry larvae but cannot support development.
Original Description:
Original Title
lact 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentParasites are organisms that live on or inside a host organism and derive nutrients from the host. There are two main types - ectoparasites which live on the outside of the host, and endoparasites which live inside the host. Endoparasites typically cause more diseases in humans. Parasites can be obligate and dependent on the host, facultative and able to live independently at times, or accidental parasites infecting unusual hosts. Hosts play various roles including definitive hosts where sexual reproduction occurs, intermediate hosts where larvae develop, reservoir hosts that maintain infection, and transport hosts that carry larvae but cannot support development.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views14 pagesLact 2
Lact 2
Uploaded by
Playersbattle GroundParasites are organisms that live on or inside a host organism and derive nutrients from the host. There are two main types - ectoparasites which live on the outside of the host, and endoparasites which live inside the host. Endoparasites typically cause more diseases in humans. Parasites can be obligate and dependent on the host, facultative and able to live independently at times, or accidental parasites infecting unusual hosts. Hosts play various roles including definitive hosts where sexual reproduction occurs, intermediate hosts where larvae develop, reservoir hosts that maintain infection, and transport hosts that carry larvae but cannot support development.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Parasite
• It is an animal or plant which lives in or upon
another organism(technically called its host)
and draws its nutriment directly from it.
• By this definition all infectious agents,
viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and
helminths are parasites.
• Traditionally protozoa , helnimths and
medical arthropod are called parasites.
Types
Ectoparasites
• Ectoparasite, the parasite which lives on the outer surface or in the superficial
tissues of the host(e.g., lice).
• The infection by these parasites is called infestation.
Endoparasite
• The parasite which lives within the host is
called the endoparasite(e.g, tapeworm).
• Invasion by the parasite is called infection.
• Usually, the endoparasites cause most
human diseases.
• 3 types
• Obligative parasites
• Facultative parasite
• Accidental parasites
Obligative parasites
• They are physiologically dependent upon their hosts for its habitat and
nourishment.
• Usually cannot survive if kept isolated from them.
• The obligate parasite is also known as holoparasite.
• Example: Toxoplasma gondii (Toxoplasmosis)
Facultative parasites
• the parasite may live in the absence of a host and occasionally
become parasitic under certain conditions.
• Example: Naegleria fowleri,
• A free-living amoeba that on some occasions may infect humans.
Accidental parasites
• The parasite which attacks an unusual host.
• Accidental hosts can be any kind of host.
• Examples: humans with fish parasites (likely a result of diet)
• Ticks which can feed on humans as accidental hosts, rather than their normal
deer or forest animal hosts
• Dog tapeworm (echinococcus granulosus)
Host
• Host is defined as an organism which harbours the parasite and
provides the nourishment and shelter.
• These hosts, in comparison to their parasites are relatively larger in
size.
• The hosts may be of the following types:
• Definitive host
• Intermediate host
• Reservoir host
• Paratenic host
Definitive Host
• The hosts which harbour the adult parasites(e.G., Taenia saginata causing
intestinal taeniasis),
• Most highly developed form of the parasite(e.G., Trypanosoma cruzi causing
african sleeping sickness)
• Where the parasite replicates sexually(e.G., Paragonimus westermani) are
called the definitive hosts.
• The definitive hosts may be human or non-human living things.
Plasmodium
Hosts
Intermediate host
• The hosts which harbour the larval stages of parasite development, or
the asexual forms of the parasite are called intermediate host.
• Some times two different hosts may be required to complete different
larval stages.
• These are known as the first and second intermediate hosts
respectively
• (e.g., snails are the first intermediate hosts and fresh water fish are
the second intermediate hosts for chines liver fluke).
Reservoir host
• The animal which harbours the parasites and serves as an important
source of infection to other susceptible hosts are known as reservoir
host
• (e.g., water buffalo is the reservoir host for schistosomiasis)
Paratenic host or transport host
• The larva of some parasites can invade a non-normal host, but can
not develop, and only keep the larva stage.
• If the larva enter a normal definitive host, it can continue to develop
into adult worm.
• The non-normal host is called paratenic host or transport host.
• It functions as a transport or carrier host
You might also like
- Parasites: Tales of Humanity's Most Unwelcome GuestsFrom EverandParasites: Tales of Humanity's Most Unwelcome GuestsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Endocarditis, MyocarditisDocument37 pagesEndocarditis, MyocarditisJuma AwarNo ratings yet
- Pendahuluan ParasitologiDocument29 pagesPendahuluan ParasitologiTri Ayu Mega SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Medical-Parasitology IntroDocument39 pagesMedical-Parasitology IntrochuniadsuarNo ratings yet
- Parasite and Communicable Disease PDFDocument58 pagesParasite and Communicable Disease PDFDr Dhruva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Welcome: I'm A Great Believer in Luck, and I Find The Harder I Work The More I Have of ItDocument17 pagesWelcome: I'm A Great Believer in Luck, and I Find The Harder I Work The More I Have of ItMamunparaNo ratings yet
- Intro Parasitology 1lectureDocument79 pagesIntro Parasitology 1lectureManav VyasNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument16 pagesParasitologyRutchelNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document49 pagesPresentation 1Gift MagangaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To ParasitologyDocument71 pages1 - Introduction To Parasitologykaartikey dubeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ParasitologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Parasitologyning ningNo ratings yet
- Intro - ParasitologyDocument37 pagesIntro - ParasitologySurya L KNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1glennngugi86No ratings yet
- ParasiteDocument60 pagesParasiteJewan Ambadil SampulnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ParasitologyDocument35 pagesChapter 4 ParasitologyJuancho OsorioNo ratings yet
- Parasitology NotesDocument3 pagesParasitology NotesRizwan BalouchNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Introduction To Parasitology Symbiosis: (E.g.,dog Tapeworm)Document12 pagesChapter 11: Introduction To Parasitology Symbiosis: (E.g.,dog Tapeworm)Angelica Areola CabalceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitology: Pamanatasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Modified By: Maria Cielo B. Malijan, MD, DPPS, FPSDBPDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology: Pamanatasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Modified By: Maria Cielo B. Malijan, MD, DPPS, FPSDBP2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitology'23 230517 171647Document135 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology'23 230517 171647lawrencenandowNo ratings yet
- Intro To para CBTSDocument30 pagesIntro To para CBTSErrold Joseph LahaganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical ParasitologyDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Medical ParasitologyStephen ThiguNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Microorganisms and ParasitesDocument37 pagesEukaryotic Microorganisms and ParasitesAbd ahmadNo ratings yet
- Lecure I.introductionDocument29 pagesLecure I.introductionAdnanhaider 03049907445No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To ParasitologyDocument24 pages1 Introduction To ParasitologytheonlinegeekhubNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument37 pagesParasitologyyomifNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical ParasitologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Medical ParasitologySimone OmegaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Parasitology Part 2 PDFDocument4 pagesIntro To Parasitology Part 2 PDFsherlynmamac98No ratings yet
- Parasitology: Prepared By: Charriz A. AmoyanDocument99 pagesParasitology: Prepared By: Charriz A. AmoyanRaphylyn EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Guanzon, Assignment On Clinical ParasitologyDocument2 pagesGuanzon, Assignment On Clinical ParasitologyIan Paul GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology: Dr.B.V.RamanaDocument38 pagesMedical Parasitology: Dr.B.V.Ramanadrbvramana100% (1)
- 7-Introduction To Medical ParasitologyDocument32 pages7-Introduction To Medical Parasitologytruch 2022No ratings yet
- 05 1animal AssociationsDocument4 pages05 1animal AssociationssaadizoyasaadiNo ratings yet
- Para 311 Lec Week 2Document52 pagesPara 311 Lec Week 2jeijai0827No ratings yet
- Medical para Health-1Document504 pagesMedical para Health-1Yordanos AsmareNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument75 pagesSodapdfRachelNo ratings yet
- ParasitesDocument52 pagesParasitesAmmara NaeemNo ratings yet
- General Applied Parasitology & MycologyDocument31 pagesGeneral Applied Parasitology & MycologyRaunaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology LecDocument13 pagesParasitology LecMarisa AlmaraNo ratings yet
- 2.11 - Introduction To ParasitologyDocument2 pages2.11 - Introduction To ParasitologyLunaNo ratings yet
- Parasitic InfectionsDocument27 pagesParasitic InfectionsYsabelle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- General Properties & Classification of ParasitesDocument33 pagesGeneral Properties & Classification of Parasitesraanja2100% (1)
- Parasit OlogyDocument11 pagesParasit OlogyAhmed AzeezNo ratings yet
- 16 Medical ParasitologyDocument8 pages16 Medical Parasitologypandiwa.amNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document49 pagesUnit 1EyamgualeleNo ratings yet
- Mt639 Unit 1 For Quiz Doc YoloDocument7 pagesMt639 Unit 1 For Quiz Doc YoloJorelle NogoyNo ratings yet
- Specific Learning Objectives: at The End of This Chapter The Student Will Be Able ToDocument13 pagesSpecific Learning Objectives: at The End of This Chapter The Student Will Be Able ToNashat SaadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ParasitologyDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Parasitologyالاء جاه الرسولNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitology - B28Document23 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology - B28Heswer RajNo ratings yet
- Basics of ParasitismDocument9 pagesBasics of ParasitismIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Mrs. Mehwish ZeeshanDocument59 pagesParasitology: Mrs. Mehwish ZeeshanAlex ChagalaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology NotesDocument3 pagesParasitology NotesMyrielle Trisha SAYRENo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1.Ppt-2 ParasitologyDocument80 pagesCHAPTER 1.Ppt-2 ParasitologyhlufnegaNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument3 pagesDefinition of TermsFarlogyNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar College of Medicine and Health Sciences School of Biomedical and Laboratory Sciences Department of Medical ParasitologyDocument48 pagesUniversity of Gondar College of Medicine and Health Sciences School of Biomedical and Laboratory Sciences Department of Medical Parasitologykidus asnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical ParasitologyDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Medical ParasitologyLaila AbdulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To ParasitologyDocument9 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To ParasitologyHanz EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Trypa and LeishDocument52 pagesTrypa and LeishDenise Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To ParasitologyDocument60 pages1 - Introduction To ParasitologyThesa TagalogNo ratings yet
- Bahir Dar University College of Medicine & Health Sciences Advanced Medical ProtozoologyDocument64 pagesBahir Dar University College of Medicine & Health Sciences Advanced Medical ProtozoologyMegbaruNo ratings yet
- TO Medical ParasitologyDocument65 pagesTO Medical ParasitologyMengistu MalkeNo ratings yet
- 1b. Types of Microscopes-1Document44 pages1b. Types of Microscopes-1Playersbattle GroundNo ratings yet
- Micrometry and MorphometryDocument26 pagesMicrometry and MorphometryPlayersbattle GroundNo ratings yet
- 1a.biological TechniquesDocument23 pages1a.biological TechniquesPlayersbattle GroundNo ratings yet
- Toxicology IntroductionDocument26 pagesToxicology IntroductionPlayersbattle Ground100% (1)
- Lect 3Document13 pagesLect 3Playersbattle GroundNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument35 pages1 IntroductionPlayersbattle GroundNo ratings yet
- Lect 1Document16 pagesLect 1Playersbattle GroundNo ratings yet
- 1st CLASSDocument13 pages1st CLASSPlayersbattle GroundNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Effects of The Forward Head Posture Epidemic - Spider Tech Solution HandoutDocument1 pageTop 10 Effects of The Forward Head Posture Epidemic - Spider Tech Solution HandoutthevitalitydepotNo ratings yet
- CholecystitisDocument10 pagesCholecystitisCris Pin BumatangNo ratings yet
- MiraMate Light Pad InstructionsDocument8 pagesMiraMate Light Pad InstructionsLaurentMartinonNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 4 LifeDocument8 pagesDiabetes 4 LifeBhavin VoraNo ratings yet
- Breast Sarcoidosis An Extremely Rare Case of Idiopathic Granulomatous MastitisDocument3 pagesBreast Sarcoidosis An Extremely Rare Case of Idiopathic Granulomatous MastitisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Case Report Persistent Buccopharyngeal Membrane: Report of A Case and Review of The LiteratureDocument4 pagesCase Report Persistent Buccopharyngeal Membrane: Report of A Case and Review of The LiteratureLiviaNo ratings yet
- Physical Agent For Cancer Survvors An Updated Literatured ReviewDocument9 pagesPhysical Agent For Cancer Survvors An Updated Literatured ReviewDeborah SalinasNo ratings yet
- Genetic Counseling: Presented By: Nivedita Kochar M.Sc. Nursing 1 YearDocument17 pagesGenetic Counseling: Presented By: Nivedita Kochar M.Sc. Nursing 1 YearNivedita NivuNo ratings yet
- Top of The Foot Pain and Swelling TreatmentDocument13 pagesTop of The Foot Pain and Swelling TreatmentNyanLinKyawNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Use: Read Carefully Before UseDocument36 pagesInstructions For Use: Read Carefully Before UseCorey EasleyNo ratings yet
- Cardio NotesDocument2 pagesCardio NotesMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- WCP 2023 Program at A GlanceDocument4 pagesWCP 2023 Program at A GlanceMutiara UtamiNo ratings yet
- Virology LecturesDocument72 pagesVirology LecturesKrishma GuptaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Abnormal Psychology 7th Edition Thomas F OltmannsDocument38 pagesTest Bank For Abnormal Psychology 7th Edition Thomas F Oltmannscourtneyparkermdknscmrepzq100% (38)
- Tumori Tesuturi MoiDocument123 pagesTumori Tesuturi MoiOana BarbuNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis 2014Document13 pagesAtopic Dermatitis 2014IvanNo ratings yet
- Barium StudiesDocument89 pagesBarium StudiesManuel PoncianNo ratings yet
- Neck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Document40 pagesNeck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Hauwa shitu.B100% (1)
- Winter SwimmingDocument2 pagesWinter SwimmingKarolína Runnová100% (1)
- Introduction To Oncology and Palliative Care: Lecturer: Nadia ShamasnahDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Oncology and Palliative Care: Lecturer: Nadia ShamasnahXo Yem100% (1)
- Fix JurnalDocument12 pagesFix JurnalYolanda Qonita ShalihatNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Alcoholic Liver Diseaseshailendra tripathiNo ratings yet
- St. Alexius College: ABO Reverse GroupingDocument7 pagesSt. Alexius College: ABO Reverse GroupingSohaymeen PanontonganNo ratings yet
- ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)Document22 pagesECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)dhivya singhNo ratings yet
- A Case of Beauvieux'S Syndrome and Its EvolutionDocument7 pagesA Case of Beauvieux'S Syndrome and Its EvolutionAndrea ModestieNo ratings yet
- Strabismus: Prepared By: Ayesah Janora A. Sarip Msu-Chs BSN IiDocument14 pagesStrabismus: Prepared By: Ayesah Janora A. Sarip Msu-Chs BSN IiTni JolieNo ratings yet
- Oral Submucous Fibrosis Newer Proposed ClassificatDocument6 pagesOral Submucous Fibrosis Newer Proposed Classificatshehla khanNo ratings yet
- Soal UTS, 10 October 2020 Hari NugrahaDocument4 pagesSoal UTS, 10 October 2020 Hari NugrahaFitri RiupassaNo ratings yet
- Health Problems and RemediesDocument2 pagesHealth Problems and RemediesLuisaNo ratings yet