Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practice Occupational Health and Safety Procedures .
Practice Occupational Health and Safety Procedures .
Uploaded by
Jean Aireen Bonalos Espra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views22 pagesThe document discusses occupational health and safety procedures, including identifying various workplace hazards like physical, biological, ergonomic, chemical, and psychological hazards that caregivers may face. It also covers recognizing hazards and risks in the workplace, as well as controlling hazards and risks through methods like eliminating hazards, substituting hazardous agents, engineering controls, administrative controls, and using personal protective equipment. The overall goal is to provide guidance on maintaining a safe working environment and protecting workers from illness or injury.
Original Description:
Original Title
PRACTICE OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY PROCEDURES⛑️.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses occupational health and safety procedures, including identifying various workplace hazards like physical, biological, ergonomic, chemical, and psychological hazards that caregivers may face. It also covers recognizing hazards and risks in the workplace, as well as controlling hazards and risks through methods like eliminating hazards, substituting hazardous agents, engineering controls, administrative controls, and using personal protective equipment. The overall goal is to provide guidance on maintaining a safe working environment and protecting workers from illness or injury.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views22 pagesPractice Occupational Health and Safety Procedures .
Practice Occupational Health and Safety Procedures .
Uploaded by
Jean Aireen Bonalos EspraThe document discusses occupational health and safety procedures, including identifying various workplace hazards like physical, biological, ergonomic, chemical, and psychological hazards that caregivers may face. It also covers recognizing hazards and risks in the workplace, as well as controlling hazards and risks through methods like eliminating hazards, substituting hazardous agents, engineering controls, administrative controls, and using personal protective equipment. The overall goal is to provide guidance on maintaining a safe working environment and protecting workers from illness or injury.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 22
PRACTICE OCCUPATIONAL
HEALTH AND SAFETY
PROCEDURES
HAZARDS AND RISKS
• Hazard is anything that may cause harm to an
individual such as chemicals, electricity, open drawers,
and inadequate ventilation.
• Risk is the possibility that somebody could be harmed
by these and other hazards and the indication of how
serious the harm can be.
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND
SAFETY
• Occupational Health and Safety is the campaign and
maintenance of the well being of workers in every
occupation. It talks about providing a safe working
environment to achieve and injury-free workplace and a
healthy atmosphere that protects every worker against
illness. As an effect, it may also protect co-workers,
family members, clients and other members of the
community who are affected by the workplace
environment.
TYPES OF HAZARDS
• Physical Hazards are the most normal
occurences in workplaces. They are usually easy
to detect, however very often are neglected
because people are too accustomed to them.
Another reason may be due to lack of
knowledge or people do not see situations as
hazards.
Examples of physical hazards that a caregiver
may be exposed to:
• Biological Hazards comes from working with
animals, people or infectious materials. This is,
therefore one of the most common hazards that
a caregiver faces. If one is working in a day care
hospital, hotel, laundry, nursing home,
laboratories, he/she may be exposed to
biological hazards.
• Ergonomic Hazards occur when a caregivers
nature of work, body position and working
conditions put pressure on his/her body. It is
difficult to spot this type of hazard, because
caregivers do not immediately notice the effect
to their bodies. At first, sore muscles may be
exrerienced. But long term exposure to this type
of hazard can cause muscoskeletal problems.
• Chemical Hazards are present when a worker is
exposed to any chemical preparation in the
workplace in any form (solid, liquid, or gas).
There may be chemicals which are safe, but
some caregivers who are sensitive to solutions
may cause skin irritation, illness or breathing
problems.
P Y S C HO L O G I CA L H A Z A R D S TA KE S P L AC E W H E N
A C A R E G I V E R S W O R K E N V I R ON M E NT B E C OM E S
STRESSFUL OR DEMANDING.
RECOGNIZING HAZARDS AND RISKS
IN THE WORKPLACE
• Hazards and Risks vary from one workplace to another. Even in a
day care or nursing homes where work routines may be the same,
hazards will differ depending on the type of building the
establishment is situated, and the attitudes of caregivers, clients, or
employers.
1. A caregiver should observe the workplace .
2. A caregiver may examine complaints from his/her co-workers.
3. A caregiver should check accident records
4. A caregiver should examine chart on results of inspections done
by the employers or private organizations.
5. A caregiver may use checklist and inspect the workplace.
6. A caregiver may study reports on any other vital information
about the nursing home.
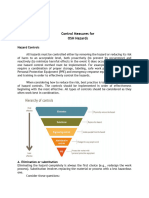
CONTROL HAZARDS AND RISKS
• It is possible that workplace hazards can be controlled by a variety
of methods. Of course, the very reason why hazards should be
controlled is to prevent workers from being exposed to
occupational hazards. Hazard control comes in different processes.
But one method may be more effective than the others.
FIVE (5) MAJOR CATEGORIES OF
CONTROL MEASURES
1. Eliminating- a hazard means removing it completely.
2. Substitution- is replqcing or substituting a hazardous agent or works
process with a less dangerous one
3. An engineering control may mean changing a piece of machinery (for
example using proper machine guards) or a work process to reduce
exposure to a hazard .
4. An administrative control may mean working a limited number of hours
in a hazards area is an example of an administrative control (for example
job rotation)
5. Personal Protective Equipment includes ear and eye protection,
respirators nad protective clothing .
PRACTICAL WAYS TO PREVENT
HAZARDS AND RISKS
You might also like
- 4 Appendix C Clarification of The Standardisation of Employment Contracts in Maintenance Works Delivery To Carillion - GTRM Imc25Document18 pages4 Appendix C Clarification of The Standardisation of Employment Contracts in Maintenance Works Delivery To Carillion - GTRM Imc25Stoyan SarovNo ratings yet
- Mother Tongue and K-12 Curriculum Content and PedagogyDocument41 pagesMother Tongue and K-12 Curriculum Content and PedagogyJean Aireen Bonalos Espra86% (7)
- Math FinanceDocument30 pagesMath FinanceAntoni AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Accounting For LaborDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Accounting For LaborIrish Jane Patricio Acuman100% (1)
- Grade 7 Hazards and RisksDocument27 pagesGrade 7 Hazards and RisksPEMAR ACOSTA75% (4)
- Tle Lesson 3 - Group 3Document35 pagesTle Lesson 3 - Group 3Sharmaine BalmoresNo ratings yet
- PRATICE OCCUPATIONAL Health and Safety ProceduresDocument27 pagesPRATICE OCCUPATIONAL Health and Safety ProceduresCherry Mae MalimaNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes: Identify Hazards and RisksDocument3 pagesConcept Notes: Identify Hazards and RisksAbigail AngcaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Hazaed and RiskDocument60 pagesLesson 5 Hazaed and RiskROWEL T. REYESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Control (Hirarc)Document13 pagesChapter 6-Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Control (Hirarc)Daisy Hayani88% (8)
- Occupational Health and Safety in CaregivingDocument38 pagesOccupational Health and Safety in Caregivinggia100% (1)
- First Aid in WorkplaceDocument21 pagesFirst Aid in WorkplaceMiroNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresDocument29 pagesOccupational Health and Safety ProceduresEila Roshame PinedaNo ratings yet
- Q2 MODULE7 G7-OR-8 COOKERY BautistaNHSDocument10 pagesQ2 MODULE7 G7-OR-8 COOKERY BautistaNHSDirty Sam LicudoNo ratings yet
- Mefc 103 Module 1 Lesson 1 2Document24 pagesMefc 103 Module 1 Lesson 1 2VELASCO JULIE-ANN G.No ratings yet
- File - PDF 20240206 170736 0000Document21 pagesFile - PDF 20240206 170736 0000Biboy MontañoNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIALDocument29 pagesINDUSTRIALMeverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Module7 g7 or 8 Cookery BautistanhsDocument12 pagesModule7 g7 or 8 Cookery BautistanhsSyruseJayLacuataNo ratings yet
- Occupational HealthDocument59 pagesOccupational HealthJoseph Nathan MarquezNo ratings yet
- Q2 MODULE6 G7-OR-8 COOKERY BautistaNHSDocument11 pagesQ2 MODULE6 G7-OR-8 COOKERY BautistaNHSDirty Sam LicudoNo ratings yet
- M2-Lessons 1&2Document10 pagesM2-Lessons 1&2zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- UC7.BASIC Practicing OSH Policies and Procedures PTC-DDNDocument57 pagesUC7.BASIC Practicing OSH Policies and Procedures PTC-DDNRomally Antonette TagnipezNo ratings yet
- Control Measures and Occupational HealthDocument8 pagesControl Measures and Occupational HealthElyk TakataNo ratings yet
- Ohes4411 - 5Document28 pagesOhes4411 - 5Emre ParlakNo ratings yet
- TLE-Caregiving7 Q3M4Week5 OKDocument12 pagesTLE-Caregiving7 Q3M4Week5 OKAmelita Benignos OsorioNo ratings yet
- Physical Hazards: Chemical HazardDocument9 pagesPhysical Hazards: Chemical HazardHarpreet Kaur MatharuNo ratings yet
- Hazard - CaregivingDocument36 pagesHazard - CaregivingamitafcragereyesNo ratings yet
- Occupational Hazards and Risk Management in Nursing PracticeDocument27 pagesOccupational Hazards and Risk Management in Nursing PracticeMelly SumardiNo ratings yet
- Hazards and RisksDocument7 pagesHazards and Riskskielaustin1968No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Safety in The WorkplaceDocument38 pagesModule 4 - Safety in The WorkplaceMariella Criscel AdonaisNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety ScopeDocument12 pagesHealth and Safety ScopeMuhammad Shahood JamalNo ratings yet
- 16.a Hazards in Health Care WorkplacesDocument4 pages16.a Hazards in Health Care WorkplacesRofida AhmedNo ratings yet
- TLE8 Q0 Mod5 Cookery v2Document14 pagesTLE8 Q0 Mod5 Cookery v2Lauro Jr. AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Elec 102 Module IDocument9 pagesElec 102 Module IKylle Bryan AranceNo ratings yet
- Health Consideration at Work Place: Airborne DiseasesDocument12 pagesHealth Consideration at Work Place: Airborne DiseasesvishwaNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Prevention: (Ndlon-Osha)Document12 pagesHazard Identification and Prevention: (Ndlon-Osha)Eugine BalomagaNo ratings yet
- Practicing Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresDocument19 pagesPracticing Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresIvy Macairan - RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Health Consideration at Work Place and PPE's: Airborne DiseasesDocument12 pagesHealth Consideration at Work Place and PPE's: Airborne DiseasesRafa AnanNo ratings yet
- Control of Work Environment: Reporters: Emie Duhaylungsod Jecris Velarde Mark Sabay-SabayDocument15 pagesControl of Work Environment: Reporters: Emie Duhaylungsod Jecris Velarde Mark Sabay-SabayRaymond FuentesNo ratings yet
- OH & SafetyDocument31 pagesOH & SafetyMadhusmita RoutNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3: Caregiving: Teacher: Jolina Mae C. Anit, LPTDocument15 pagesQuarter 3: Caregiving: Teacher: Jolina Mae C. Anit, LPTJolina AnitNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 and 2Document37 pagesCHAPTER 1 and 2Jaimie Del MundoNo ratings yet
- For Module 1Document51 pagesFor Module 1Jin Gumahin BanhaoNo ratings yet
- Practice Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresDocument37 pagesPractice Occupational Health and Safety ProceduresLudivina GalinganNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Security, and SanitationDocument24 pagesReviewer in Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Security, and Sanitationnicole kuyaNo ratings yet
- Hazardidentificationriskassessment 221203161833 f78f65bfDocument112 pagesHazardidentificationriskassessment 221203161833 f78f65bfspkpalkuNo ratings yet
- Industrial Hygiene1Document14 pagesIndustrial Hygiene1Jhynne Xalve PorcionculaNo ratings yet
- Osh Mod. Household ServicesDocument11 pagesOsh Mod. Household ServicesRustom BelandresNo ratings yet
- Work Safety Powerpoint TemplateDocument68 pagesWork Safety Powerpoint TemplateJennelyn SantosNo ratings yet
- CAREGIVING-7 Q3 Mod5 USLeM-RTPDocument10 pagesCAREGIVING-7 Q3 Mod5 USLeM-RTPKathleen LlanesNo ratings yet
- 1 HLTWHS002 PPSlides V1.0.pptx (Autosaved)Document145 pages1 HLTWHS002 PPSlides V1.0.pptx (Autosaved)Leanne EvansNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Occupational Health - NoDocument14 pagesModule 5 Occupational Health - Noangeh morilloNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument39 pagesRisk AssessmenttaylansheilaNo ratings yet
- Industrial and Environmental Safety Lec 1Document53 pagesIndustrial and Environmental Safety Lec 1AnnieMalikNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (HSS)Document6 pagesLesson 1 (HSS)Niña Mae C. QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Occupational Hazards MidtermDocument13 pagesOccupational Hazards MidtermJhonry DemerinNo ratings yet
- Hazards and Risks In' A WorkplaceDocument48 pagesHazards and Risks In' A WorkplaceCorey MaddoxNo ratings yet
- Test S&HDocument5 pagesTest S&HHf CreationNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Risk ManagementDocument36 pagesUNIT 3 Risk Managemente smithNo ratings yet
- Occupational Safety and HealthDocument4 pagesOccupational Safety and HealthCatiereign VerdeNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome 4: Maintaining Occupational Safety and Health AwarenessDocument4 pagesLearning Outcome 4: Maintaining Occupational Safety and Health AwarenessBrenNan ChannelNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health & Safety: by Assist. Prof. Maytham AL-NasrawiiDocument18 pagesOccupational Health & Safety: by Assist. Prof. Maytham AL-Nasrawiiمحمد محمدNo ratings yet
- The Construction Safety Guide: Injury and Illness Prevention through DesignFrom EverandThe Construction Safety Guide: Injury and Illness Prevention through DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- NHA Phlebotomy Exam 2022-2023: Study Guide with 400 Practice Questions and Answers for National Healthcareer Association Certified Phlebotomy Technician ExaminationFrom EverandNHA Phlebotomy Exam 2022-2023: Study Guide with 400 Practice Questions and Answers for National Healthcareer Association Certified Phlebotomy Technician ExaminationNo ratings yet
- Letters Final Na GyudDocument4 pagesLetters Final Na GyudJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- The Symbiotic Relationship Between Literature Abd LanguageDocument12 pagesThe Symbiotic Relationship Between Literature Abd LanguageJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- DEMODocument8 pagesDEMOJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Levels and PathwaysDocument22 pagesLevels and PathwaysJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Espra Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in PeDocument4 pagesEspra Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in PeJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Ged 102: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: (Physics, Earth and Space Science)Document9 pagesGed 102: Teaching Science in The Elementary Grades: (Physics, Earth and Space Science)Jean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Habitats of Animals????.Document23 pagesHabitats of Animals????.Jean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Ged 105 Technology For Teaching Elementary GradesDocument3 pagesGed 105 Technology For Teaching Elementary GradesJean Aireen Bonalos Espra100% (2)
- OERsDocument1 pageOERsJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Research Methods Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesResearch Methods Lecture NotesJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Technology For Teaching - ELEMENTARYfor Elementary GradesDocument1 pageTechnology For Teaching - ELEMENTARYfor Elementary GradesJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Arts EspraDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Arts EspraJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Stewardship and AccountabilityDocument23 pagesLesson 3: Stewardship and AccountabilityJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Second Language AcquisitionDocument41 pagesSecond Language AcquisitionJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Mother Tongue Policy Report AbanteDocument28 pagesMother Tongue Policy Report AbanteJean Aireen Bonalos Espra100% (1)
- Mother Tounge and Language TeachersDocument27 pagesMother Tounge and Language TeachersJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Peace Concepts in Islam, Other Faiths and Spiritual TraditionsDocument15 pagesPeace Concepts in Islam, Other Faiths and Spiritual TraditionsJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- "Fundamental Teachings of Islam": - Farhana A. Gandarosa Beed-IiiDocument21 pages"Fundamental Teachings of Islam": - Farhana A. Gandarosa Beed-IiiJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Steawardship and Accountability at The End of The Session The Students Are Able ToDocument27 pagesLesson 3 Steawardship and Accountability at The End of The Session The Students Are Able ToJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Language Teachers' Professional Knowledge and Standards For Language Teaching: A Review of The LiteratureDocument29 pagesLanguage Teachers' Professional Knowledge and Standards For Language Teaching: A Review of The LiteratureJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Demonstration - Teaching: 4 Physical Education: Learning OutcomesDocument7 pagesLesson Demonstration - Teaching: 4 Physical Education: Learning OutcomesJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Extract From Appointment RegulationsDocument3 pagesExtract From Appointment RegulationsJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Mother Tounge and Language TeachersDocument27 pagesMother Tounge and Language TeachersJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Language Culture: Language Acquisition & Language LearningDocument22 pagesLanguage Culture: Language Acquisition & Language LearningJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- A Helpful Guide To Basic Muslim Etiquette: Greetings and HandshakesDocument2 pagesA Helpful Guide To Basic Muslim Etiquette: Greetings and HandshakesJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- Mother Tongue and Language CurriculumDocument31 pagesMother Tongue and Language CurriculumJean Aireen Bonalos EspraNo ratings yet
- MSC HandbookDocument93 pagesMSC HandbookdanielcmartNo ratings yet
- QSO 510, Employee BurnoutDocument3 pagesQSO 510, Employee BurnoutPJ kaurNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFA BALARAJUNo ratings yet
- 02 MonikaaaaaDocument70 pages02 MonikaaaaaMonika VermaNo ratings yet
- Job Application: Letter WritingDocument9 pagesJob Application: Letter WritingAkhil Jeikar P.MNo ratings yet
- Journal Entry QuestionsDocument5 pagesJournal Entry QuestionsFareeha NazNo ratings yet
- Cutlerhodgman AgreementDocument10 pagesCutlerhodgman AgreementkevinhfdNo ratings yet
- Rodriguez Vs Park N Ride IncDocument1 pageRodriguez Vs Park N Ride IncIan Van MamugayNo ratings yet
- Site Engineer 1 Site Engineer 2Document2 pagesSite Engineer 1 Site Engineer 2Yam BalaoingNo ratings yet
- Victoria Peralta CVDocument3 pagesVictoria Peralta CVPrestige GlamNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning (Food and Beverage Services)Document23 pagesFacilitating Learning (Food and Beverage Services)joylorenzo100% (1)
- An Insight of Artificial Intelligence (AI) On The Recruitment IndustryDocument4 pagesAn Insight of Artificial Intelligence (AI) On The Recruitment IndustrysoniasNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 OB NotesDocument11 pagesChapter-2 OB NotesManik SharmaNo ratings yet
- OM Lecture 4 Capacity PlanningDocument30 pagesOM Lecture 4 Capacity PlanningDawit HusseinNo ratings yet
- BIO0916ra MLA e PDFDocument77 pagesBIO0916ra MLA e PDFPhilBoardResultsNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyMD75% (8)
- BES HandoutDocument8 pagesBES HandoutFat AjummaNo ratings yet
- Solar EngineeringDocument12 pagesSolar EngineeringShiva Krishna BhagavatulaNo ratings yet
- Disciplinary ProceduresDocument28 pagesDisciplinary ProceduresMoreTechniqueNo ratings yet
- Prashanti Technologies: A Workplace Romance Ethical DilemmaDocument6 pagesPrashanti Technologies: A Workplace Romance Ethical Dilemmasahibakhurana12No ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting (3) (Etagenehu)Document18 pagesIntroduction To Accounting (3) (Etagenehu)Nigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- BP Form 204: Staffing Summary of Non-Permanent Positions DepartmentDocument1 pageBP Form 204: Staffing Summary of Non-Permanent Positions DepartmentRocky MontañerNo ratings yet
- Log Sheet Internship HRDocument2 pagesLog Sheet Internship HRAtluri HaricharanNo ratings yet
- CP 1Document23 pagesCP 1Zoren Clyde AlinanNo ratings yet
- Government Job Vs Private JobDocument1 pageGovernment Job Vs Private JobTitoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Discusion QuestionsDocument4 pagesAssignment Discusion QuestionsBusteD WorlD0% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Business PlanDocument22 pagesChapter 4 - Business PlanEizanie MuhamadNo ratings yet