Professional Documents
Culture Documents
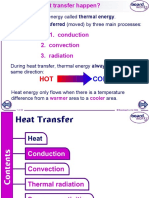
Transfer of Thermal Energy
Transfer of Thermal Energy
Uploaded by
Arzou Nawaz Virk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesThis document summarizes three main mechanisms of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the transfer of kinetic energy between adjacent particles through molecular vibration, while convection relies on the bulk movement of heated fluids to transfer thermal energy. Radiation emits infrared waves directly from hot surfaces through empty space without a medium. Metals are good conductors due to their free electrons, while heat transfer in liquids and gases occurs through molecular collisions. Convection currents only occur in fluids as they involve the bulk fluid movement carrying heat.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes three main mechanisms of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the transfer of kinetic energy between adjacent particles through molecular vibration, while convection relies on the bulk movement of heated fluids to transfer thermal energy. Radiation emits infrared waves directly from hot surfaces through empty space without a medium. Metals are good conductors due to their free electrons, while heat transfer in liquids and gases occurs through molecular collisions. Convection currents only occur in fluids as they involve the bulk fluid movement carrying heat.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy
Transfer of Thermal Energy
Uploaded by
Arzou Nawaz VirkThis document summarizes three main mechanisms of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the transfer of kinetic energy between adjacent particles through molecular vibration, while convection relies on the bulk movement of heated fluids to transfer thermal energy. Radiation emits infrared waves directly from hot surfaces through empty space without a medium. Metals are good conductors due to their free electrons, while heat transfer in liquids and gases occurs through molecular collisions. Convection currents only occur in fluids as they involve the bulk fluid movement carrying heat.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Transfer of thermal energy
Made by: Arzou Nawaz Virk
Class 9s
Conduction
• It is the transfer of energy without any flow of the medium.
• Heat flows through the materials of the rods without any flow of the material.
The process of transfer of thermal energy without any flow of medium is thereby
called conduction.
• Different materials conduct heat at different rates. Since the lengths of the
unmelted wax left is shortest for copper and the longest for wood we can say that
copper is a good conductor and wood is a poor conductor of heat in other words
we can say that wood is an insulator.
• In general, metals such as copper, silver, steel and iron are good conductors of
heat while non-metals (such as glass, plastic, wood, brick), gases (such as air) and
liquids (such as water) are poor conductors of heat.
Mechanisms of Conduction
• All solids (metals or non-metal) are made up of tiny particles called atoms, or
groups of atoms called molecules. However, there is one important difference b/w
metals and non-metals: metals contain many free electrons which are able to
move randomly b/w the molecules. For non-metals there are a few free electrons.
• When heat is supplied to one end of a rod, the molecules at the end vibrate
vigorously and jostle neighbouring molecules, making them vibrate as well. Thus,
some of the kinetic energy of the vibrate molecules at the hot end gets transferred
to their neighbours.
• The process of passing heat from the hot end to the cold end by molecular
vibration is common to both copper (metal) and wood (non-metal. It is relatively
slow mechanism of heat transfer compared to other mechanism of heat transfer
that was taking place in metals: free-electron diffusion.
Continued……….
• When the rods are heated, the free electrons in the copper move faster as a result
of having more kinetic energy. These fast moving energy-carrying electrons diffuse
or spread into the cooler parts of the metal and then transfer their kinetic energy
to the molecules by colliding with them. This explains why the rate of heat transfer
in good conductors (metals) is much faster than that in insulators (non-metals).
• CONDUCTION OF HEAT THROUGH LIQUIDS AND GASES:
• In liquids and gases, heat can also be conducted from a hotter to a cooler region.
However, the process of conduction in liquids and gases is insufficient. Heat
conduction in liquids and gases involve the transfer of kinetic energy from fast-
moving atoms or molecules to slow-moving ones through the process of collisions.
Collisions b/w atom and molecules are extremely frequent in liquids and even less
frequent in gases where atoms and molecules are far apart.
Convection
• It is the transfer of thermal energy by means of currents in the material medium
(liquids or gas).
• It is heat transfer through bulk movement of fluid itself. A convection current is the
movement of fluid caused by the change in densities in various parts of the fluid.
• MECHANISM OF CONVECTION:
• The circulation of the purple streams of water in figure 12.6 (in book physics a
course for o´levels) or the flow of smoke in figure 12.7 (in book a course for o´levels)
represents a convection current. When the water at the bottom of the round
bottomed flask (or the air above the candle) is heated, it expands. The fluid is now
less dense than the surrounding fluid so it starts to rise. In doing so, the cooler
regions of the fluid in the upper part of the flask, being denser, now descend. This
movement of fluid due to a difference in densities sets up a convectional current.
Continued…………
• Convection currents occur only in fluids (i.e. in liquids and gases) but
not in solids. This is because convection involves the bulk movement
of the fluids which carry heat with them. For solids, the heat is
transferred from one molecule t another without any movement of
the molecules themselves.
Radiation
• It is the continual emission of infra-red waves from the surfaces of all
bodies, transmitted through space, without the aid of a material
medium.
• For example: heat from the sun reaches the earth by the process
You might also like
- A320 HydraulicsystemDocument2 pagesA320 HydraulicsystemMinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ProjectDocument68 pagesHeat Transfer ProjectsubratorajNo ratings yet
- SPP Pumps - Mod. TD15F - Información TécnicaDocument7 pagesSPP Pumps - Mod. TD15F - Información TécnicaGabriel LopezNo ratings yet
- Blind Flange With StiffenersDocument4 pagesBlind Flange With Stiffenersshahid khan100% (1)
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument15 pagesConduction Convection Radiationsalmanismart123No ratings yet
- Document 10Document5 pagesDocument 10shookookie 101No ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument9 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energycontroller playerNo ratings yet
- Flow of Heat: Chapter 6 (Physics)Document56 pagesFlow of Heat: Chapter 6 (Physics)Pratham KanwraniNo ratings yet
- Thermal ProcessesDocument5 pagesThermal Processestrsilas24No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Methods 2017 Class Notes AutosavedDocument39 pagesHeat Transfer Methods 2017 Class Notes AutosavedItsMe SirMJNo ratings yet
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 1Document75 pagesLecture No 1Raza AnsariNo ratings yet
- ConductionDocument9 pagesConductionaneeqa StudentNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Transfer: ConductionDocument2 pagesThermal Energy Transfer: ConductionJaniah Aaliyah M. DrakesNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection Radiation PowerpointDocument27 pagesConduction Convection Radiation PowerpointApet Satusembilansembilan JieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document10 pagesChapter 11ranaaNo ratings yet
- Transmission of Heat: Presented by V.Rajalakshmi II-B.Sc (Physics) 13UPHY024Document11 pagesTransmission of Heat: Presented by V.Rajalakshmi II-B.Sc (Physics) 13UPHY024shajmalikNo ratings yet
- Physics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8Document9 pagesPhysics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8dhureyaaNo ratings yet
- Sci101 - 23 05 08Document22 pagesSci101 - 23 05 08koalibrahimNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection Radiation PowerpointDocument18 pagesConduction Convection Radiation PowerpointRavichandran G100% (1)
- Conduction, Convection, RadiationDocument4 pagesConduction, Convection, RadiationChloe LiewNo ratings yet
- AND Modes of Heat TransferDocument41 pagesAND Modes of Heat TransferKushNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Thermal ProcessesDocument6 pages2.3 Thermal ProcesseshaiderNo ratings yet
- Physics STPM HEAT TRANSFERDocument23 pagesPhysics STPM HEAT TRANSFERRed Jagung Fish100% (3)
- Heat TransferDocument27 pagesHeat TransferOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer PDFDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer PDFTahmeed AzizNo ratings yet
- Modes of Heat TransferDocument25 pagesModes of Heat TransferMD. Humayun KobirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document10 pagesLecture 3Aarzoo JobanputraNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 5-Lesson 4-Determining Conductors of Heat and ElectricityDocument67 pagesScience Grade 5-Lesson 4-Determining Conductors of Heat and Electricityclyde domingo100% (4)
- Thermal Effects Part 2Document8 pagesThermal Effects Part 2xbmqzqnqg4No ratings yet
- Silver Oak University: Mahirkhan I. PathanDocument26 pagesSilver Oak University: Mahirkhan I. PathanMahir Khan PathanNo ratings yet
- Research: Conductivity, in General, Is The Capacity To Transmit Something, Such As Electricity or HeatDocument2 pagesResearch: Conductivity, in General, Is The Capacity To Transmit Something, Such As Electricity or HeatanayahNo ratings yet
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationDocument25 pagesUnderstanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationMahir Khan PathanNo ratings yet
- IMPRESS Education - Heat TransferDocument2 pagesIMPRESS Education - Heat TransferJA KNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferSquidward TentaclesNo ratings yet
- Conduction Notes PDFDocument5 pagesConduction Notes PDFgodaxonNo ratings yet
- Test ContentDocument45 pagesTest ContentAtifa OmerNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection Radiation NotesDocument13 pagesConduction Convection Radiation Notesch_ymyaa100% (3)
- Rohit Rajput PhysicsDocument17 pagesRohit Rajput Physicsuchiha3993No ratings yet
- Week 6 and 7 Thermal TransferDocument25 pagesWeek 6 and 7 Thermal TransferdrishtiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer and Expansion NotesDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer and Expansion NotesmelissaNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection and Radiation-1Document19 pagesConduction, Convection and Radiation-1Alvin JacobNo ratings yet
- Warmer Cooler: © Boardworks LTD 2006 1 of 32Document7 pagesWarmer Cooler: © Boardworks LTD 2006 1 of 32Bboatb PpbblNo ratings yet
- CH 12 SciDocument8 pagesCH 12 SciHend HamedNo ratings yet
- Course: Heat Transfer (MEC301)Document13 pagesCourse: Heat Transfer (MEC301)wonderNo ratings yet
- Hello The WorldDocument55 pagesHello The Worldvincent02hk_57881301No ratings yet
- PhysicsrevisionnotesDocument12 pagesPhysicsrevisionnotesapi-253698991No ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument11 pagesHeat TransferArnab HazraNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument3 pagesTransfer of Thermal EnergyPeter KachouhNo ratings yet
- Heat Enegy TransferDocument6 pagesHeat Enegy TransferManya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sci Oly 2.0Document12 pagesSci Oly 2.0arinaitwejoshua24No ratings yet
- 1 Fundamental of Heat TransferDocument20 pages1 Fundamental of Heat Transferred18ggmuNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationDocument29 pagesModule 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationVishnupriya B.No ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument3 pagesHeat Transferjaivik230No ratings yet
- Alnukhba College NoryDocument8 pagesAlnukhba College NoryHaitham AliNo ratings yet
- Task: Hypothesis and Table in BookDocument9 pagesTask: Hypothesis and Table in BookKiLlmEEEplz XDNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument2 pagesHeat TransferRitishBoodhunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Heat TransferDivya DevhariNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Is The Transition ofDocument11 pagesHeat Transfer Is The Transition of3m3hNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: Physics Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument20 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: Physics Notes GCE Study Buddyanwar9602020No ratings yet
- The Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- 047 - CE6501 Structural Analysis I - Question BankDocument17 pages047 - CE6501 Structural Analysis I - Question BankGERARD HAULENo ratings yet
- TFG SARA CHARCO INIESTA ADocument231 pagesTFG SARA CHARCO INIESTA AGowtham SinghNo ratings yet
- Savier CanardDocument41 pagesSavier CanardSattar Al-JabairNo ratings yet
- UTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp12Document7 pagesUTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp12Izykiel EdwardNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Chip Formation in Machining Process.: Presented byDocument19 pagesMechanism of Chip Formation in Machining Process.: Presented byShraddha SangoleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Physiological and Toxicologica - 2020 - Industrial Ventilation DesigDocument116 pagesChapter 5 - Physiological and Toxicologica - 2020 - Industrial Ventilation DesigRichardNo ratings yet
- Selection of Equation of State Models For Process SimulatorsDocument18 pagesSelection of Equation of State Models For Process Simulatorssuratiningrum100% (1)
- Tieback Wall Design and ConstructionDocument184 pagesTieback Wall Design and Constructionlaporpo123100% (1)
- Combined Gas LawsDocument7 pagesCombined Gas LawsGabriela UnoNo ratings yet
- Strengthening of RC Columns by Steel Angles and StripsDocument12 pagesStrengthening of RC Columns by Steel Angles and StripsGema Putra PratamaNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document8 pagesHW 5Anonymous AjrDxGNo ratings yet
- Heat Mass TransferDocument221 pagesHeat Mass Transferjeas grejoyNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress Model: Transforming Stress Components and DirectionsDocument7 pagesPlane Stress Model: Transforming Stress Components and DirectionsEngr Aizaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hydrate Plug MechanismsDocument10 pagesHydrate Plug Mechanismsrjehanathan7098No ratings yet
- SSC Je Civil 2016 Set 6.pdf 50Document12 pagesSSC Je Civil 2016 Set 6.pdf 50Sameer bhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties of Dupont Opteon YfDocument15 pagesThermodynamic Properties of Dupont Opteon Yffederiko86No ratings yet
- Week 3 Lecture Material - WatermarkDocument53 pagesWeek 3 Lecture Material - WatermarkVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Geostatic StressesDocument10 pagesGeostatic StressesMadhuNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 473 6071 PDFDocument8 pages10 1 1 473 6071 PDFSaddy KhanNo ratings yet
- Vip 02 Pipe Looks FamDocument65 pagesVip 02 Pipe Looks FamUllyses SebialNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Fatigue: SciencedirectDocument21 pagesInternational Journal of Fatigue: SciencedirectolavusNo ratings yet
- Concrete LectureDocument4 pagesConcrete LectureAndrea ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Exercises of ch3 (w4) - AnswerDocument6 pagesExercises of ch3 (w4) - AnswerNguyễn Nam AnhNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document109 pagesUnit 5Mithila100% (2)
- OCR A Chemistry A-Level - Chapter 9 - Enthalpy - Keywords & DefinitionsDocument1 pageOCR A Chemistry A-Level - Chapter 9 - Enthalpy - Keywords & DefinitionsTemi BalogunNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Exam MCQ'sDocument2 pagesMid Term Exam MCQ'sAbdul Khaliq KhanNo ratings yet
- Heat and Temperature Activity 1 Explaining Hotness and ColdnessDocument21 pagesHeat and Temperature Activity 1 Explaining Hotness and ColdnessChristopher M. CasuguidNo ratings yet