Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
182 viewsAbout France - La Culture Francaise
About France - La Culture Francaise
Uploaded by
Hakkim shajahanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Reading Process Worksheet PalenciaDocument4 pagesReading Process Worksheet PalenciaFranz PalenciaNo ratings yet
- French Culture and Civilization PDFDocument7 pagesFrench Culture and Civilization PDFJenyNo ratings yet
- France - Culture Smart!: The Essential Guide to Customs & CultureFrom EverandFrance - Culture Smart!: The Essential Guide to Customs & CultureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nutritional Foundations and Clinical Applications 5th Edition Grodner Test BankDocument10 pagesNutritional Foundations and Clinical Applications 5th Edition Grodner Test BankKareemNo ratings yet
- Giraffe Blood CirculationDocument9 pagesGiraffe Blood Circulationthalita asriandinaNo ratings yet
- CRPC Project Sem 8thDocument11 pagesCRPC Project Sem 8thAbhay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Culture of France.1Document30 pagesCulture of France.1Rho naNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument4 pagesCulture of FranceEnrique MirazoNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument4 pagesCulture of FranceRohit SikriNo ratings yet
- French (French Culture) : Project Based ONDocument10 pagesFrench (French Culture) : Project Based ONbhadmejaNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument20 pagesCulture of FranceKUMAR HARSHNo ratings yet
- France: Scented Candles Advertising in Contemporary SocietyDocument21 pagesFrance: Scented Candles Advertising in Contemporary SocietyvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Kirit P Mehta School of Law: B.B.A, LL.B (Hons.) Third SemesterDocument25 pagesKirit P Mehta School of Law: B.B.A, LL.B (Hons.) Third SemesterSaurabh Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- FRANCEDocument9 pagesFRANCEfalak chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Cross Culture Understanding FranceDocument9 pagesCross Culture Understanding FranceFian SansNo ratings yet
- French Culture: Customs & Traditions: LanguagesDocument3 pagesFrench Culture: Customs & Traditions: LanguagesLaura VelandiaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledVioteers :3No ratings yet
- Cross Culture Understanding FranceDocument10 pagesCross Culture Understanding FranceKaviya KaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cultures of Berlin Et AlDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Cultures of Berlin Et AlAngelica CocaNo ratings yet
- Cultural A Ctivity: Valentina B Allén Anyelina Lo Mbana Angie Verg ARADocument15 pagesCultural A Ctivity: Valentina B Allén Anyelina Lo Mbana Angie Verg ARAEmily Anyelina Lombana Cifuentes100% (1)
- CULTURE (Abong, Enoc) : French Cuisine (NIEVA, ODSINADA)Document4 pagesCULTURE (Abong, Enoc) : French Cuisine (NIEVA, ODSINADA)MARIAH KNOWELLE JOSENo ratings yet
- Customs of France 1Document16 pagesCustoms of France 1Juan BorregalesNo ratings yet
- FranceDocument8 pagesFranceAnarjingoo .BNo ratings yet
- About The Country As Importan As The Culture The White Color Represents The King The Red and Blue Color Represents The Paris CityDocument5 pagesAbout The Country As Importan As The Culture The White Color Represents The King The Red and Blue Color Represents The Paris CityYireth HincapieNo ratings yet
- PMPPTDocument10 pagesPMPPThiteshkhullar33No ratings yet
- France: by Melwin MarkDocument21 pagesFrance: by Melwin MarkMelwinNo ratings yet
- FranceDocument13 pagesFranceAsma MajidNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument6 pagesCultureArushi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Singapore City: Consumer BehaviorDocument14 pagesSingapore City: Consumer BehaviorVivek AnandNo ratings yet
- France: By:Jawad Nadeem Bba 1CDocument10 pagesFrance: By:Jawad Nadeem Bba 1CJawad NadeemNo ratings yet
- France: Cultural Variety in FranceDocument5 pagesFrance: Cultural Variety in FranceIRISH GENEVIEVE DE VERANo ratings yet
- FranceDocument15 pagesFranceАртём СтроковNo ratings yet
- French AssignmentDocument14 pagesFrench AssignmentAjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- France Culture EssayDocument3 pagesFrance Culture Essayapi-267990745No ratings yet
- Comida Típica de Francia: La Quiche LorraineDocument2 pagesComida Típica de Francia: La Quiche LorraineAlejandro CanoNo ratings yet
- FranceDocument20 pagesFranceMuhammadyusuf MominovNo ratings yet
- FRANCE - SummaryDocument48 pagesFRANCE - SummaryMohd FaisalNo ratings yet
- FranceDocument2 pagesFranceranjamarioNo ratings yet
- France: BY Maria Fernanda Zapata Ruiz Luisa Fernanda Tilano PatiñoDocument9 pagesFrance: BY Maria Fernanda Zapata Ruiz Luisa Fernanda Tilano PatiñoJosue Rodrigo Caballero TamaraNo ratings yet
- Self Work in EnglishDocument6 pagesSelf Work in EnglishFatyaNo ratings yet
- Ken Ken PurposiveDocument11 pagesKen Ken Purposiveken gilosNo ratings yet
- 69 Fun Facts About France: LanguageDocument28 pages69 Fun Facts About France: Languagekashikamahajan1993100% (1)
- Traducción France Capital City: Paris Current Chairman: Emmanuel MacronDocument7 pagesTraducción France Capital City: Paris Current Chairman: Emmanuel MacronMarcelaVelasquezNo ratings yet
- France National DayDocument8 pagesFrance National DayPriti SinghNo ratings yet
- The Paris Conservatory, A Music School of The French Revolutionary MovementDocument14 pagesThe Paris Conservatory, A Music School of The French Revolutionary MovementJasonVerzolaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de FranciaDocument6 pagesTrabajo de FranciaDaniela AvalosNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate French Phrasebook: Your Valuable Trip CompanionFrom EverandThe Ultimate French Phrasebook: Your Valuable Trip CompanionNo ratings yet
- Core Debate: (Political, Economic and Socio-Cultural)Document3 pagesCore Debate: (Political, Economic and Socio-Cultural)Mahmoud HosnyNo ratings yet
- France PPT FinalDocument85 pagesFrance PPT Finalrhythm chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- People, Places, and Cultures: A Changing WorldDocument3 pagesPeople, Places, and Cultures: A Changing WorldRichard ShiauNo ratings yet
- Pro Yec To InglesDocument11 pagesPro Yec To Inglesvictor roquelNo ratings yet
- Customs and Traditions in FranceDocument4 pagesCustoms and Traditions in FranceElena CiocNo ratings yet
- The routes to exile: France and the Spanish Civil War refugees, 1939–2009From EverandThe routes to exile: France and the Spanish Civil War refugees, 1939–2009No ratings yet
- FranceDocument1 pageFranceFenicottero BluNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument30 pagesCulture of Francerazaforkamal913088% (8)
- France - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument103 pagesFrance - Britannica Online EncyclopediaLin MatsushitaNo ratings yet
- Unity in Diversity: Elev: Anton Marina Feraru Ana-Maria Mustocea Alexandra Radu FlorentinaDocument15 pagesUnity in Diversity: Elev: Anton Marina Feraru Ana-Maria Mustocea Alexandra Radu FlorentinaMarina AntonNo ratings yet
- Ani Julianthi SitorusDocument5 pagesAni Julianthi Sitorusana_51031110232960No ratings yet
- History of ParisDocument19 pagesHistory of ParisAllyNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument11 pagesCulture of FrancePutri SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Jeanjean PaperDocument14 pagesJeanjean PapernycNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics On Banking SectorDocument6 pagesDissertation Topics On Banking SectorWriteMyPaperIn3HoursCanada100% (1)
- IMC 151 - PAIR AssignmentDocument37 pagesIMC 151 - PAIR Assignmentfarishaemylia40No ratings yet
- Course Code: MCS-011 Course Title: Problem Solving and ProgrammingDocument9 pagesCourse Code: MCS-011 Course Title: Problem Solving and Programminggrvs0No ratings yet
- SPM Unit 4 Notes-1Document27 pagesSPM Unit 4 Notes-1Ibrahim GadliNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning in GeoscienceDocument22 pagesMachine Learning in GeoscienceAde PrayudaNo ratings yet
- Tiago Tigor Infotainment GuideDocument2 pagesTiago Tigor Infotainment GuidejotowekidNo ratings yet
- Psycosocial Activities Day 3Document40 pagesPsycosocial Activities Day 3John Briane CapiliNo ratings yet
- Meng 310 Exam 01 Spring 2010Document4 pagesMeng 310 Exam 01 Spring 2010Abdulrahman AlzahraniNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound in Obstretics PDFDocument40 pagesUltrasound in Obstretics PDFcarcobe3436100% (1)
- First Semester Summary ReportDocument21 pagesFirst Semester Summary ReportAkhila JoseNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae (CV) : Data PribadiDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae (CV) : Data Pribadingurah.gde.ariNo ratings yet
- Bhaktisiddhanta Appearance DayDocument5 pagesBhaktisiddhanta Appearance DaySanjeev NambalateNo ratings yet
- Modern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4Th Edition Anderson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesModern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4Th Edition Anderson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjerryholdengewmqtspaj100% (11)
- Sikolohiyang Pilipino Midterm Summary OlfuDocument10 pagesSikolohiyang Pilipino Midterm Summary OlfuMark ShelloNo ratings yet
- Transformer Is Gassing-What To DoDocument24 pagesTransformer Is Gassing-What To DoengrsurifNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Diet - What To Eat For A Healthy Pregnancy PDFDocument9 pagesGestational Diabetes Diet - What To Eat For A Healthy Pregnancy PDFJibin John JacksonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 18EC61Document93 pagesUnit 1 - 18EC61Pritam SarkarNo ratings yet
- 01 eLMS Activity 1 Network TechnologyDocument2 pages01 eLMS Activity 1 Network Technologybasahara sengokuNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety - Wikipedia PDFDocument29 pagesFire Safety - Wikipedia PDFAld rich NuñezNo ratings yet
- DisabilityDocument34 pagesDisabilitymeghnaumNo ratings yet
- 1850 Firstphasepgmedicaldegreediplomacollegewiseallotments201920Document59 pages1850 Firstphasepgmedicaldegreediplomacollegewiseallotments201920krishnaNo ratings yet
- Belzona 5111 Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesBelzona 5111 Product Data SheetPeter RhoadsNo ratings yet
- Unit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)Document43 pagesUnit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)UpasnaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Hyundai Grand I10 Magna 1.2 VTVT: Great DealDocument4 pages2016 Hyundai Grand I10 Magna 1.2 VTVT: Great DealBoby VillariNo ratings yet
- Request of Price Quotation 20212ND QUARTER 1Document2 pagesRequest of Price Quotation 20212ND QUARTER 1mary jean sumalinogNo ratings yet
- Management Science: Definition, Characteristics and ToolsDocument6 pagesManagement Science: Definition, Characteristics and ToolsAmzelle Diego LaspiñasNo ratings yet
About France - La Culture Francaise
About France - La Culture Francaise
Uploaded by
Hakkim shajahan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
182 views14 pagesOriginal Title
About France - La Culture francaise
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
182 views14 pagesAbout France - La Culture Francaise
About France - La Culture Francaise
Uploaded by
Hakkim shajahanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
INTRODUCTION
France, and in particular Paris has played an
important role as a center of high culture and
of decorative arts since the seventeenth century
France has also played an important role in cinema,
fashion and cuisine.
The importance of French culture has waxed and
waned over the centuries, depending on its
economic, political and military importance.
LANGUAGE
France counts many regional
languages, some of them being
very different from standard French
such as Breton and Alsatian.
Some regional languages are Roman, like French.
English is taught in schools as a second language.
RELIGION
France is a secular country where freedom of
thought and of religion is preserved, by virtue of
the 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man and of
the Citizen.
The Republic is based on the principle of laïcité,
that is of freedom of religion enforced by the Jules
Ferry laws and the 1905 law on the separation of
the State and the Church.
EDUCATION
The French educational system is highly
centralized, organized, and ramified. It is divided
into three different stages:
Primary education; secondary education and
higher education
Primary and secondary education is predominantly
public while higher education has both public and
private elements.
MINISTER OF CULTURE
The Minister of Culture is, in the Government of France,
the cabinet member in charge of national museums and
monuments; promoting and protecting the arts in
France and abroad; and managing the national archives
and regional “Maison de culture”
The Ministry of Culture is located on the Palais
Royal in Paris.
ACADÉMIE FRANÇAISE
The Académie française, or the French Academy, is the pre-
eminent French learned body on matters about the French
language.
The Académie consists of forty members, known as immortels.
New members are elected by the members of the Académie
itself.
Academicians hold office for life but may be removed for
misconduct.
The body has the task of acting as an official authority on the
language; it is charged with publishing an official dictionary of
the language.
LABOUR
In France the first labour laws were Waldeck
Rousseau's laws passed in 1884. Between 1936 and
1938 the Popular Front enacted a law mandating 12
days each year of paid vacation for worker.
Five years later, conservative prime
minister Dominique de Villepin enacted the New
Employment Contract (CNE)
In 2006 he then attempted to pass the First
Employment Contract (CPE) through a vote by
emergency procedure
SOCIAL WELFARE
The French are profoundly committed to the public
healthcare system and to their "pay-as-you-go"
social welfare system.
In 1998, 75% of health payments in France were paid
through the public healthcare system. Since 27 July
1999, France has a universal medical coverage for
permanent residents in France.
FOOD
Traditional French culture places a high priority on
the enjoyment of food.
Ingredients and dishes vary by region .
There are many significant regional dishes that have
become both national and regional.
Many dishes that were once regional, however, have
proliferated in different variations across the country
in the present day.
Cheese and wine are also a major part of the cuisine,
playing different roles both regionally and nationally
with their many variations
SPORTS
The French "national" sport is football.
The most-watched sports in France.
are football, rugby, cycling, tennis, handball,
basketball.
France is notable for holding the football World Cup in
1998, for holding the annual cycling race Tour de
France, and the tennis Grand Slam tournament Roland
Garros, or the French Open.
ART
The first paintings of France are those that are
from prehistoric times, painted
in the caves.
The Louvre in Paris is one of the most famous
and the largest art museums in the world,
created by the new revolutionary regime in
1793 in the former royal palace.
EXAMPLES- the Mona Lisa, by Leonardo da
Vinci, and classical Greek Venus de Milo.
MUSIC
France boasts a wide variety of indigenous folk music,
as well as styles played by immigrants
from Africa, Latin America, and Asia.
In the field of classical music, France has produced a
number of legendary composers, like Gabriel Faure,
while modern pop music has seen the rise of
popular French hip-hop, French rock, techno,
and turntablists.
The Fête de la Musique was created in France, as a
music festival, which has since become worldwide.
MERCI
You might also like
- Reading Process Worksheet PalenciaDocument4 pagesReading Process Worksheet PalenciaFranz PalenciaNo ratings yet
- French Culture and Civilization PDFDocument7 pagesFrench Culture and Civilization PDFJenyNo ratings yet
- France - Culture Smart!: The Essential Guide to Customs & CultureFrom EverandFrance - Culture Smart!: The Essential Guide to Customs & CultureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nutritional Foundations and Clinical Applications 5th Edition Grodner Test BankDocument10 pagesNutritional Foundations and Clinical Applications 5th Edition Grodner Test BankKareemNo ratings yet
- Giraffe Blood CirculationDocument9 pagesGiraffe Blood Circulationthalita asriandinaNo ratings yet
- CRPC Project Sem 8thDocument11 pagesCRPC Project Sem 8thAbhay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Culture of France.1Document30 pagesCulture of France.1Rho naNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument4 pagesCulture of FranceEnrique MirazoNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument4 pagesCulture of FranceRohit SikriNo ratings yet
- French (French Culture) : Project Based ONDocument10 pagesFrench (French Culture) : Project Based ONbhadmejaNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument20 pagesCulture of FranceKUMAR HARSHNo ratings yet
- France: Scented Candles Advertising in Contemporary SocietyDocument21 pagesFrance: Scented Candles Advertising in Contemporary SocietyvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Kirit P Mehta School of Law: B.B.A, LL.B (Hons.) Third SemesterDocument25 pagesKirit P Mehta School of Law: B.B.A, LL.B (Hons.) Third SemesterSaurabh Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- FRANCEDocument9 pagesFRANCEfalak chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Cross Culture Understanding FranceDocument9 pagesCross Culture Understanding FranceFian SansNo ratings yet
- French Culture: Customs & Traditions: LanguagesDocument3 pagesFrench Culture: Customs & Traditions: LanguagesLaura VelandiaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledVioteers :3No ratings yet
- Cross Culture Understanding FranceDocument10 pagesCross Culture Understanding FranceKaviya KaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cultures of Berlin Et AlDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Cultures of Berlin Et AlAngelica CocaNo ratings yet
- Cultural A Ctivity: Valentina B Allén Anyelina Lo Mbana Angie Verg ARADocument15 pagesCultural A Ctivity: Valentina B Allén Anyelina Lo Mbana Angie Verg ARAEmily Anyelina Lombana Cifuentes100% (1)
- CULTURE (Abong, Enoc) : French Cuisine (NIEVA, ODSINADA)Document4 pagesCULTURE (Abong, Enoc) : French Cuisine (NIEVA, ODSINADA)MARIAH KNOWELLE JOSENo ratings yet
- Customs of France 1Document16 pagesCustoms of France 1Juan BorregalesNo ratings yet
- FranceDocument8 pagesFranceAnarjingoo .BNo ratings yet
- About The Country As Importan As The Culture The White Color Represents The King The Red and Blue Color Represents The Paris CityDocument5 pagesAbout The Country As Importan As The Culture The White Color Represents The King The Red and Blue Color Represents The Paris CityYireth HincapieNo ratings yet
- PMPPTDocument10 pagesPMPPThiteshkhullar33No ratings yet
- France: by Melwin MarkDocument21 pagesFrance: by Melwin MarkMelwinNo ratings yet
- FranceDocument13 pagesFranceAsma MajidNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument6 pagesCultureArushi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Singapore City: Consumer BehaviorDocument14 pagesSingapore City: Consumer BehaviorVivek AnandNo ratings yet
- France: By:Jawad Nadeem Bba 1CDocument10 pagesFrance: By:Jawad Nadeem Bba 1CJawad NadeemNo ratings yet
- France: Cultural Variety in FranceDocument5 pagesFrance: Cultural Variety in FranceIRISH GENEVIEVE DE VERANo ratings yet
- FranceDocument15 pagesFranceАртём СтроковNo ratings yet
- French AssignmentDocument14 pagesFrench AssignmentAjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- France Culture EssayDocument3 pagesFrance Culture Essayapi-267990745No ratings yet
- Comida Típica de Francia: La Quiche LorraineDocument2 pagesComida Típica de Francia: La Quiche LorraineAlejandro CanoNo ratings yet
- FranceDocument20 pagesFranceMuhammadyusuf MominovNo ratings yet
- FRANCE - SummaryDocument48 pagesFRANCE - SummaryMohd FaisalNo ratings yet
- FranceDocument2 pagesFranceranjamarioNo ratings yet
- France: BY Maria Fernanda Zapata Ruiz Luisa Fernanda Tilano PatiñoDocument9 pagesFrance: BY Maria Fernanda Zapata Ruiz Luisa Fernanda Tilano PatiñoJosue Rodrigo Caballero TamaraNo ratings yet
- Self Work in EnglishDocument6 pagesSelf Work in EnglishFatyaNo ratings yet
- Ken Ken PurposiveDocument11 pagesKen Ken Purposiveken gilosNo ratings yet
- 69 Fun Facts About France: LanguageDocument28 pages69 Fun Facts About France: Languagekashikamahajan1993100% (1)
- Traducción France Capital City: Paris Current Chairman: Emmanuel MacronDocument7 pagesTraducción France Capital City: Paris Current Chairman: Emmanuel MacronMarcelaVelasquezNo ratings yet
- France National DayDocument8 pagesFrance National DayPriti SinghNo ratings yet
- The Paris Conservatory, A Music School of The French Revolutionary MovementDocument14 pagesThe Paris Conservatory, A Music School of The French Revolutionary MovementJasonVerzolaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de FranciaDocument6 pagesTrabajo de FranciaDaniela AvalosNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate French Phrasebook: Your Valuable Trip CompanionFrom EverandThe Ultimate French Phrasebook: Your Valuable Trip CompanionNo ratings yet
- Core Debate: (Political, Economic and Socio-Cultural)Document3 pagesCore Debate: (Political, Economic and Socio-Cultural)Mahmoud HosnyNo ratings yet
- France PPT FinalDocument85 pagesFrance PPT Finalrhythm chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- People, Places, and Cultures: A Changing WorldDocument3 pagesPeople, Places, and Cultures: A Changing WorldRichard ShiauNo ratings yet
- Pro Yec To InglesDocument11 pagesPro Yec To Inglesvictor roquelNo ratings yet
- Customs and Traditions in FranceDocument4 pagesCustoms and Traditions in FranceElena CiocNo ratings yet
- The routes to exile: France and the Spanish Civil War refugees, 1939–2009From EverandThe routes to exile: France and the Spanish Civil War refugees, 1939–2009No ratings yet
- FranceDocument1 pageFranceFenicottero BluNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument30 pagesCulture of Francerazaforkamal913088% (8)
- France - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument103 pagesFrance - Britannica Online EncyclopediaLin MatsushitaNo ratings yet
- Unity in Diversity: Elev: Anton Marina Feraru Ana-Maria Mustocea Alexandra Radu FlorentinaDocument15 pagesUnity in Diversity: Elev: Anton Marina Feraru Ana-Maria Mustocea Alexandra Radu FlorentinaMarina AntonNo ratings yet
- Ani Julianthi SitorusDocument5 pagesAni Julianthi Sitorusana_51031110232960No ratings yet
- History of ParisDocument19 pagesHistory of ParisAllyNo ratings yet
- Culture of FranceDocument11 pagesCulture of FrancePutri SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Jeanjean PaperDocument14 pagesJeanjean PapernycNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics On Banking SectorDocument6 pagesDissertation Topics On Banking SectorWriteMyPaperIn3HoursCanada100% (1)
- IMC 151 - PAIR AssignmentDocument37 pagesIMC 151 - PAIR Assignmentfarishaemylia40No ratings yet
- Course Code: MCS-011 Course Title: Problem Solving and ProgrammingDocument9 pagesCourse Code: MCS-011 Course Title: Problem Solving and Programminggrvs0No ratings yet
- SPM Unit 4 Notes-1Document27 pagesSPM Unit 4 Notes-1Ibrahim GadliNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning in GeoscienceDocument22 pagesMachine Learning in GeoscienceAde PrayudaNo ratings yet
- Tiago Tigor Infotainment GuideDocument2 pagesTiago Tigor Infotainment GuidejotowekidNo ratings yet
- Psycosocial Activities Day 3Document40 pagesPsycosocial Activities Day 3John Briane CapiliNo ratings yet
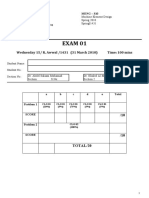
- Meng 310 Exam 01 Spring 2010Document4 pagesMeng 310 Exam 01 Spring 2010Abdulrahman AlzahraniNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound in Obstretics PDFDocument40 pagesUltrasound in Obstretics PDFcarcobe3436100% (1)
- First Semester Summary ReportDocument21 pagesFirst Semester Summary ReportAkhila JoseNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae (CV) : Data PribadiDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae (CV) : Data Pribadingurah.gde.ariNo ratings yet
- Bhaktisiddhanta Appearance DayDocument5 pagesBhaktisiddhanta Appearance DaySanjeev NambalateNo ratings yet
- Modern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4Th Edition Anderson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesModern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4Th Edition Anderson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjerryholdengewmqtspaj100% (11)
- Sikolohiyang Pilipino Midterm Summary OlfuDocument10 pagesSikolohiyang Pilipino Midterm Summary OlfuMark ShelloNo ratings yet
- Transformer Is Gassing-What To DoDocument24 pagesTransformer Is Gassing-What To DoengrsurifNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Diet - What To Eat For A Healthy Pregnancy PDFDocument9 pagesGestational Diabetes Diet - What To Eat For A Healthy Pregnancy PDFJibin John JacksonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 18EC61Document93 pagesUnit 1 - 18EC61Pritam SarkarNo ratings yet
- 01 eLMS Activity 1 Network TechnologyDocument2 pages01 eLMS Activity 1 Network Technologybasahara sengokuNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety - Wikipedia PDFDocument29 pagesFire Safety - Wikipedia PDFAld rich NuñezNo ratings yet
- DisabilityDocument34 pagesDisabilitymeghnaumNo ratings yet
- 1850 Firstphasepgmedicaldegreediplomacollegewiseallotments201920Document59 pages1850 Firstphasepgmedicaldegreediplomacollegewiseallotments201920krishnaNo ratings yet
- Belzona 5111 Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesBelzona 5111 Product Data SheetPeter RhoadsNo ratings yet
- Unit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)Document43 pagesUnit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)UpasnaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Hyundai Grand I10 Magna 1.2 VTVT: Great DealDocument4 pages2016 Hyundai Grand I10 Magna 1.2 VTVT: Great DealBoby VillariNo ratings yet
- Request of Price Quotation 20212ND QUARTER 1Document2 pagesRequest of Price Quotation 20212ND QUARTER 1mary jean sumalinogNo ratings yet
- Management Science: Definition, Characteristics and ToolsDocument6 pagesManagement Science: Definition, Characteristics and ToolsAmzelle Diego LaspiñasNo ratings yet