Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsGEC253 BioEnergy 2020 Edited
GEC253 BioEnergy 2020 Edited
Uploaded by
Ndapiwa KengaletsweBioenergy currently makes up 14% of the global renewable energy mix, the largest share. Biomass can be used directly as fuel or processed into solid, liquid, or gaseous biofuels through various biological, chemical, and thermal processes. Common biofuels include bioethanol produced through fermentation of carbohydrates, and biogas produced through anaerobic digestion of organic waste. While biomass is a renewable source that does not increase atmospheric CO2, overuse or improper management can impact soil fertility and forests.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 5 Min Scalping FOREX StrategyDocument3 pages5 Min Scalping FOREX StrategyzooorNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument5 pagesBiomassbabeNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Designing of A Biogas PlantDocument11 pagesA Project Report On Designing of A Biogas PlantJafar JilaniNo ratings yet
- Bio MassDocument23 pagesBio MassTrash MailNo ratings yet
- Biomass Energy Group-2Document27 pagesBiomass Energy Group-2Sam OmpadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document55 pagesLecture 5Kauthar MaalimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document42 pagesLecture 5Kauthar MaalimNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy: Biomass: Alternative Energy Engineering ME Elective 1Document46 pagesRenewable Energy: Biomass: Alternative Energy Engineering ME Elective 1MelbertNo ratings yet
- 4.energy From Biomass NotesDocument10 pages4.energy From Biomass Notesjayasruthyk6No ratings yet
- CH-9 BiomassDocument23 pagesCH-9 Biomassaman jainNo ratings yet
- Biomass Energ Final1)Document19 pagesBiomass Energ Final1)Bishal BNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three 3. Project Title (Case Study) Assessing The Advantage of Using Biomass As Fuel Over Furnace Oil To Produce Steam in BoilerDocument8 pagesChapter Three 3. Project Title (Case Study) Assessing The Advantage of Using Biomass As Fuel Over Furnace Oil To Produce Steam in BoileretayhailuNo ratings yet
- Biogas From HuskDocument10 pagesBiogas From HuskRaghavendra Raghav0% (1)
- Power Plants Lab: Assignment 2Document7 pagesPower Plants Lab: Assignment 2Faseeh GhaziNo ratings yet
- EEE 483 (BIo Energy)Document26 pagesEEE 483 (BIo Energy)Sanjoy SanaNo ratings yet
- Biomass. It Refers To Substances That Are Produced From Living or Once-Living Organisms andDocument4 pagesBiomass. It Refers To Substances That Are Produced From Living or Once-Living Organisms andAnonymous 5ZR8rH3No ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument6 pagesBiomass EnergyStevenNo ratings yet
- What Is BiomassDocument19 pagesWhat Is BiomassWrenhartingNo ratings yet
- Energy From BiomassDocument10 pagesEnergy From BiomassPrudhvi PokuruNo ratings yet
- Bio GasDocument8 pagesBio GasammumNo ratings yet
- Unit 4&5Document28 pagesUnit 4&52k21cse093No ratings yet
- RER Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument28 pagesRER Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inrahulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Principle of Bionergy PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 6 - Principle of Bionergy PDFNazAsyrafNo ratings yet
- Biomass: (Renewable Energy For The Future)Document11 pagesBiomass: (Renewable Energy For The Future)nizom90No ratings yet
- Bio Pallets Advantages & DisadvantagesDocument3 pagesBio Pallets Advantages & DisadvantagesImran HaqNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On BioenergyDocument30 pagesA Presentation On BioenergyDaniel DadzieNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument6 pagesBiomassSaddang SaputraNo ratings yet
- Renewable Biomass A Candidate For Mitigating Global WarmingDocument13 pagesRenewable Biomass A Candidate For Mitigating Global WarmingAndreas AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Document 13 1Document7 pagesDocument 13 1Shalltear TVNo ratings yet
- Chapter II RedgeDocument7 pagesChapter II RedgeNet VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- EEM 701 BioenergyDocument26 pagesEEM 701 BioenergyUmed PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Frontline Bioenergy, LLC: What Is Biomass?Document5 pagesFrontline Bioenergy, LLC: What Is Biomass?Armando HernandezNo ratings yet
- SacrotasDocument3 pagesSacrotasm taqqi abbasNo ratings yet
- Biomass Energy: Mubashir Imdad 02-134191-118 BS (CS) - 1BDocument4 pagesBiomass Energy: Mubashir Imdad 02-134191-118 BS (CS) - 1BMubashir ImdadNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument6 pagesReview of Related Literaturenouny234No ratings yet
- Biogas and BiomassDocument20 pagesBiogas and BiomassparvezalamkhanNo ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument9 pagesBiomass EnergyHj JayatheerthaNo ratings yet
- Biomass As An Energy SourceDocument24 pagesBiomass As An Energy Sourceodebunmi taiwoNo ratings yet
- Biogas Production and UtilizationDocument98 pagesBiogas Production and UtilizationAhmed AwadenNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument2 pagesBiomassAmir AuzaNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument2 pagesBiomasstandat20092002No ratings yet
- 9.1 Biomass Production: 9.1.1 Direct MethodsDocument18 pages9.1 Biomass Production: 9.1.1 Direct MethodssahitNo ratings yet
- BiogasDocument26 pagesBiogasTALLURI LAKSHMI PRASANNANo ratings yet
- Report Ecology 20213116Document17 pagesReport Ecology 20213116Ayush kumarNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument12 pagesResearch ProposalSyedMmohammadKashanNo ratings yet
- Non Food Base Biomass: Group # 11 Roll# 2011-ch-238 2011-ch-244 2011-ch-268Document19 pagesNon Food Base Biomass: Group # 11 Roll# 2011-ch-238 2011-ch-244 2011-ch-268Anonymous b9fcR5No ratings yet
- MENG 3026 Renewable Energy - 2 Credits: Course Lecturer Dr. K. ManoharDocument63 pagesMENG 3026 Renewable Energy - 2 Credits: Course Lecturer Dr. K. ManoharRiaz JokanNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument3 pagesBiomassgeeturamchandani198877No ratings yet
- Biomass Is Defined As The Biological Degradable Fraction of Products, Waste and ResiduesDocument9 pagesBiomass Is Defined As The Biological Degradable Fraction of Products, Waste and Residuesadil malikNo ratings yet
- Biogas Biogas BiogasDocument32 pagesBiogas Biogas Biogasvishnu0751No ratings yet
- Energy From BiomassDocument30 pagesEnergy From BiomassRehman ManiNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument2 pagesBiomassJasmine AustriaNo ratings yet
- BIOFUELSDocument9 pagesBIOFUELSGeorgette RepunteNo ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument13 pagesBiomass EnergySuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument14 pagesBiomassabmtestlab82No ratings yet
- BiomassDocument5 pagesBiomassAkshara K VijayNo ratings yet
- c1 PDFDocument42 pagesc1 PDFNagendrababu RamisettyNo ratings yet
- Biomass 230916 144312Document51 pagesBiomass 230916 144312reefanyyNo ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument12 pagesBiomass Energymaria yvonne camilotesNo ratings yet
- Biomass Energy ProcessesDocument2 pagesBiomass Energy Processesmitali01sarda01No ratings yet
- Understanding Biomass Energy - Importance of Biofuels | Biomass Energy for Kids | Children's Ecology BooksFrom EverandUnderstanding Biomass Energy - Importance of Biofuels | Biomass Energy for Kids | Children's Ecology BooksNo ratings yet
- Crudeoilpetrolium 2022Document30 pagesCrudeoilpetrolium 2022Ndapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- GEC253 2018 Geothermal 2022Document18 pagesGEC253 2018 Geothermal 2022Ndapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- Solar Case Study Botswana 2022Document11 pagesSolar Case Study Botswana 2022Ndapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy - 2022FDocument23 pagesNuclear Energy - 2022FNdapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- Energy UnitsUnits Conversion 2022Document12 pagesEnergy UnitsUnits Conversion 2022Ndapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- SOLAR ENERGY - 2022 - UpdatedDocument54 pagesSOLAR ENERGY - 2022 - UpdatedNdapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary For Text Analysis and Text ProductionDocument2 pagesVocabulary For Text Analysis and Text ProductionchloNo ratings yet
- Jaworski Vs Pagcor DigestDocument1 pageJaworski Vs Pagcor Digestmegzycutes3871No ratings yet
- CE0515 4.0v1 An Introduction To Sophos Synchronized SecurityDocument20 pagesCE0515 4.0v1 An Introduction To Sophos Synchronized Securitydanielfdiaz97No ratings yet
- Solid Waste Action PlanDocument2 pagesSolid Waste Action PlanJocel Baran Macoy100% (1)
- Geography of EquadorDocument16 pagesGeography of EquadorAre JibNo ratings yet
- Poverty Alleviation & Employment Generation Descriptive Answer WritingDocument6 pagesPoverty Alleviation & Employment Generation Descriptive Answer WritingmbsyNo ratings yet
- A Disaster Is A SuddenDocument3 pagesA Disaster Is A Suddenzitadewi435No ratings yet
- ENG-101 Presentation On The Short Story "The Gift of Magi"Document15 pagesENG-101 Presentation On The Short Story "The Gift of Magi"নরকেররাজপুত্র100% (1)
- Gramatika Holandskog JezikaDocument59 pagesGramatika Holandskog JezikaNikola LučićNo ratings yet
- The Coinage of Two Hundred Rupees and Ten Rupees Coins To Commemorate The Occasion of 200 H BIRTH ANNIVERSARY of TATYA TOPE Rules, 2015.Document6 pagesThe Coinage of Two Hundred Rupees and Ten Rupees Coins To Commemorate The Occasion of 200 H BIRTH ANNIVERSARY of TATYA TOPE Rules, 2015.Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid (CH: B A B ADocument2 pagesAcetic Acid (CH: B A B APuwala ArdhanaNo ratings yet
- EcowasDocument5 pagesEcowasshubhamNo ratings yet
- Go 2Document4 pagesGo 2farhahNo ratings yet
- Diterima Oleh Yang BersangkutanDocument3 pagesDiterima Oleh Yang BersangkutanDT Dyah TetiyanaNo ratings yet
- 61 Fieldmen's Insurance v. Vda de SongcoDocument1 page61 Fieldmen's Insurance v. Vda de SongcoSIPC PSA Applications 2020No ratings yet
- Econ 122 Week 1 9 by DwexDocument19 pagesEcon 122 Week 1 9 by DwexDestinyNo ratings yet
- Bar Ops 2 - 1ST Wave Cases 1 34Document30 pagesBar Ops 2 - 1ST Wave Cases 1 34Shane Fernandez JardinicoNo ratings yet
- CJL 5000 Hsa Plan 2024 SBC Final 10182023Document8 pagesCJL 5000 Hsa Plan 2024 SBC Final 10182023dominicvjohnson03No ratings yet
- Right To EducationDocument11 pagesRight To EducationPrateek KulhariNo ratings yet
- Woyzeck Study GuideDocument9 pagesWoyzeck Study GuideShanghaï LiNo ratings yet
- 2-Self-Assessment ChecklistDocument2 pages2-Self-Assessment ChecklistFlorante De LeonNo ratings yet
- A-Morally-Defensible Noddings PDFDocument8 pagesA-Morally-Defensible Noddings PDFHazel QuinanteNo ratings yet
- ARTID121 - Enlightenment and NeoclassicismDocument79 pagesARTID121 - Enlightenment and Neoclassicismarkiosk100% (1)
- Amortization of A 30-Year, $130,000 Loan at 8.5%Document10 pagesAmortization of A 30-Year, $130,000 Loan at 8.5%Ponleu MamNo ratings yet
- Adr ReviewDocument4 pagesAdr ReviewJoseph Emanuel PunioNo ratings yet
- PPM Sudha Murty LeadreshipDocument14 pagesPPM Sudha Murty LeadreshipDevshri UmaleNo ratings yet
- ISISDocument3 pagesISISJehann DenisseNo ratings yet
- 020-500-Summary of Control WeaknessesDocument5 pages020-500-Summary of Control WeaknessesKris Anne SamudioNo ratings yet
- Oilgram Price Report: Valero Makes Big Splash Into MethanolDocument25 pagesOilgram Price Report: Valero Makes Big Splash Into MethanolPaolo Del Aguila RojasNo ratings yet
GEC253 BioEnergy 2020 Edited
GEC253 BioEnergy 2020 Edited
Uploaded by
Ndapiwa Kengaletswe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views20 pagesBioenergy currently makes up 14% of the global renewable energy mix, the largest share. Biomass can be used directly as fuel or processed into solid, liquid, or gaseous biofuels through various biological, chemical, and thermal processes. Common biofuels include bioethanol produced through fermentation of carbohydrates, and biogas produced through anaerobic digestion of organic waste. While biomass is a renewable source that does not increase atmospheric CO2, overuse or improper management can impact soil fertility and forests.
Original Description:
Original Title
GEC253_BioEnergy_2020_edited
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBioenergy currently makes up 14% of the global renewable energy mix, the largest share. Biomass can be used directly as fuel or processed into solid, liquid, or gaseous biofuels through various biological, chemical, and thermal processes. Common biofuels include bioethanol produced through fermentation of carbohydrates, and biogas produced through anaerobic digestion of organic waste. While biomass is a renewable source that does not increase atmospheric CO2, overuse or improper management can impact soil fertility and forests.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views20 pagesGEC253 BioEnergy 2020 Edited
GEC253 BioEnergy 2020 Edited
Uploaded by
Ndapiwa KengaletsweBioenergy currently makes up 14% of the global renewable energy mix, the largest share. Biomass can be used directly as fuel or processed into solid, liquid, or gaseous biofuels through various biological, chemical, and thermal processes. Common biofuels include bioethanol produced through fermentation of carbohydrates, and biogas produced through anaerobic digestion of organic waste. While biomass is a renewable source that does not increase atmospheric CO2, overuse or improper management can impact soil fertility and forests.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
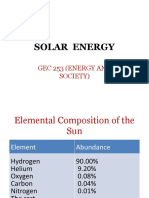
GEC 253 (ENERGY AND SOCIETY)
It is a term that refers to fuel derived
from vegetative and animal matter,
that is not embedded in geological
formations. It is a renewable energy
resource which can always be
provided by means of growing trees.
Bioenergy is currently the largest global
contributor of renewable energy mix.
The contribution of all renewable energy
resources to global energy is currently 18 %.
Bioenergy takes the lion share of 14% out of
the 18% (78 % in renewable energy mix),
followed by hydropower at 3%.
All other renewables which include Solar,
Tidal, Geothermal and Wind share the
remaining 1%.
Solar energy from the sun is converted
to chemical potential energy(biomass)
through the process called
photosynthesis, i.e.,
CO2 + H2O +Light = O2 + Carbohydrates
The carbohydrates is the biomass
(vegetative matter)
.
During grazing, animals get the stored
energy (carbohydrates) from plants and
transform it into other forms (animal matter)
through respiration.
Bioenergy fuels are produced from various
forms of Biomass.
Biomass supply is from:
Natural Forests: Brazil (Amazon forests),
Australia and Russia have largest forests.
Forests represents 90 % of biomass resource.
Agricultural Waste: Straw from harvested
grain or crops, domestic vegetative waste
Energy Planting:
Energy planting is where selected species of
plants are grown and harvested on regular
basis for provision of energy. Often the
plantation are made near a power plant. This
type of Biomass is also referred to as Morden
Biomass.
Biomass can be used without any processing
as is common with woody biomass. But
biomass can be processed into various
biofuels in the form of Solids, Liquids, or
gases. These controlled processes are classed
according to the nature of the process.
(1). Biological processes: This includes
production of Bioethanol (liquid biofuel) and
Biogas (gaseous biofuel).
Bioethanol is produced from fermentation of
carbohydrate in the presence of a catalyst
(e.g. yeast) to produce ethanol.
C6 H 12O6 2CH 3CH 2OH 2CO2
carbohydrates Ethanol Carbon dioxide
The formation is done in the absence of
oxygen (anaerobic process). Common plants
used as feedstock for the process are: sugar
cane, sweet corn etc
BIOGAS:This is a biofuel produced from
fermentation of organic matter (manure
and biodegradable waste). It is mainly
composed of carbon dioxide and
methane. It is used to power vehicles
and provide electricity. Depending on
where the gas is produced, it can be
called landfill gas, swamp gas and
digestion gas..
The simplified equation for the
anaerobic reaction is:
C6H12O6 = 3 CO2 + 3CH4 (methane)
N.B the process is also fermentation of biomass
just like for production of bioethanol but here
no catalyst is used.
The digester is normally placed below the
ground and two pipelines leads to its bottom.
One for feeding animal waste called slurry
The other for spent slurry called sludge
Sludge is also usable as it still retains all the
nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium and is
An excellent source of fertilisers.
(2) Chemical Processes:
Biodiesel Production; biodiesel is
produced by transesterification
(chemical process) of plant oil (plant
seeds) and animal fats. The biodiesel
can be used to replace the diesel obtain
from crude oil.
(3) Thermal Processes:
Biomass is often converted to other forms of
biofuel through thermal processes. These
include;
(a)Production of Synthesis Gas (SYNGAS).
Catalytic thermal cracking of Biomass
Produces Syngas. Syngas is a
combustible gasesous mixture of
Hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
(b) Pyrolysis (production of charcoal):In its
simplest form, pyrolysis represents heating the
biomass to drive off the volatile matter and
leaving behind the
charcoal. This process has doubled the energy
density of the original material because charcoal,
which is half the weight of
the original biomass, contains the same amount
of energy, making the fuel more transportable.
The charcoal also burns at
a much higher temperature than the original
biomass, making it more useful for
manufacturing processes.
Biomass does not increase carbon dioxide
level in the atmosphere as it absorbs the
same amount of carbon in growing as it
releases when consumed as a fuel.
It can cheaply replace fossil fuels. The same
power plants that are now burning fossil fuels
can be used to burn biomass to generate
electricity
Biomass is easily available and can be grown
with relative ease in all parts of the world.
Growing plants for biomass fuel may help to reduce
greenhouse gases, since plants use carbon dioxide and
produce oxygen as they
grow. Carbon dioxide is considered an important
greenhouse gas.
Decrease soil fertility, When plant and animal
wastes are used as fuel, they cannot be added to
the soil as fertilizer. Soil without fertilizer is
depleted of nutrients and produce fewer crops.
Not easy to store biomass in raw form as like
e.g. coal.
Over-collecting wood can destroy forests. Soils
bared of trees erode easily and do not hold
rainfall. Increased runoff can cause flooding
downstream
You might also like
- 5 Min Scalping FOREX StrategyDocument3 pages5 Min Scalping FOREX StrategyzooorNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument5 pagesBiomassbabeNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Designing of A Biogas PlantDocument11 pagesA Project Report On Designing of A Biogas PlantJafar JilaniNo ratings yet
- Bio MassDocument23 pagesBio MassTrash MailNo ratings yet
- Biomass Energy Group-2Document27 pagesBiomass Energy Group-2Sam OmpadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document55 pagesLecture 5Kauthar MaalimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document42 pagesLecture 5Kauthar MaalimNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy: Biomass: Alternative Energy Engineering ME Elective 1Document46 pagesRenewable Energy: Biomass: Alternative Energy Engineering ME Elective 1MelbertNo ratings yet
- 4.energy From Biomass NotesDocument10 pages4.energy From Biomass Notesjayasruthyk6No ratings yet
- CH-9 BiomassDocument23 pagesCH-9 Biomassaman jainNo ratings yet
- Biomass Energ Final1)Document19 pagesBiomass Energ Final1)Bishal BNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three 3. Project Title (Case Study) Assessing The Advantage of Using Biomass As Fuel Over Furnace Oil To Produce Steam in BoilerDocument8 pagesChapter Three 3. Project Title (Case Study) Assessing The Advantage of Using Biomass As Fuel Over Furnace Oil To Produce Steam in BoileretayhailuNo ratings yet
- Biogas From HuskDocument10 pagesBiogas From HuskRaghavendra Raghav0% (1)
- Power Plants Lab: Assignment 2Document7 pagesPower Plants Lab: Assignment 2Faseeh GhaziNo ratings yet
- EEE 483 (BIo Energy)Document26 pagesEEE 483 (BIo Energy)Sanjoy SanaNo ratings yet
- Biomass. It Refers To Substances That Are Produced From Living or Once-Living Organisms andDocument4 pagesBiomass. It Refers To Substances That Are Produced From Living or Once-Living Organisms andAnonymous 5ZR8rH3No ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument6 pagesBiomass EnergyStevenNo ratings yet
- What Is BiomassDocument19 pagesWhat Is BiomassWrenhartingNo ratings yet
- Energy From BiomassDocument10 pagesEnergy From BiomassPrudhvi PokuruNo ratings yet
- Bio GasDocument8 pagesBio GasammumNo ratings yet
- Unit 4&5Document28 pagesUnit 4&52k21cse093No ratings yet
- RER Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument28 pagesRER Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inrahulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Principle of Bionergy PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 6 - Principle of Bionergy PDFNazAsyrafNo ratings yet
- Biomass: (Renewable Energy For The Future)Document11 pagesBiomass: (Renewable Energy For The Future)nizom90No ratings yet
- Bio Pallets Advantages & DisadvantagesDocument3 pagesBio Pallets Advantages & DisadvantagesImran HaqNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On BioenergyDocument30 pagesA Presentation On BioenergyDaniel DadzieNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument6 pagesBiomassSaddang SaputraNo ratings yet
- Renewable Biomass A Candidate For Mitigating Global WarmingDocument13 pagesRenewable Biomass A Candidate For Mitigating Global WarmingAndreas AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Document 13 1Document7 pagesDocument 13 1Shalltear TVNo ratings yet
- Chapter II RedgeDocument7 pagesChapter II RedgeNet VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- EEM 701 BioenergyDocument26 pagesEEM 701 BioenergyUmed PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Frontline Bioenergy, LLC: What Is Biomass?Document5 pagesFrontline Bioenergy, LLC: What Is Biomass?Armando HernandezNo ratings yet
- SacrotasDocument3 pagesSacrotasm taqqi abbasNo ratings yet
- Biomass Energy: Mubashir Imdad 02-134191-118 BS (CS) - 1BDocument4 pagesBiomass Energy: Mubashir Imdad 02-134191-118 BS (CS) - 1BMubashir ImdadNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument6 pagesReview of Related Literaturenouny234No ratings yet
- Biogas and BiomassDocument20 pagesBiogas and BiomassparvezalamkhanNo ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument9 pagesBiomass EnergyHj JayatheerthaNo ratings yet
- Biomass As An Energy SourceDocument24 pagesBiomass As An Energy Sourceodebunmi taiwoNo ratings yet
- Biogas Production and UtilizationDocument98 pagesBiogas Production and UtilizationAhmed AwadenNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument2 pagesBiomassAmir AuzaNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument2 pagesBiomasstandat20092002No ratings yet
- 9.1 Biomass Production: 9.1.1 Direct MethodsDocument18 pages9.1 Biomass Production: 9.1.1 Direct MethodssahitNo ratings yet
- BiogasDocument26 pagesBiogasTALLURI LAKSHMI PRASANNANo ratings yet
- Report Ecology 20213116Document17 pagesReport Ecology 20213116Ayush kumarNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument12 pagesResearch ProposalSyedMmohammadKashanNo ratings yet
- Non Food Base Biomass: Group # 11 Roll# 2011-ch-238 2011-ch-244 2011-ch-268Document19 pagesNon Food Base Biomass: Group # 11 Roll# 2011-ch-238 2011-ch-244 2011-ch-268Anonymous b9fcR5No ratings yet
- MENG 3026 Renewable Energy - 2 Credits: Course Lecturer Dr. K. ManoharDocument63 pagesMENG 3026 Renewable Energy - 2 Credits: Course Lecturer Dr. K. ManoharRiaz JokanNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument3 pagesBiomassgeeturamchandani198877No ratings yet
- Biomass Is Defined As The Biological Degradable Fraction of Products, Waste and ResiduesDocument9 pagesBiomass Is Defined As The Biological Degradable Fraction of Products, Waste and Residuesadil malikNo ratings yet
- Biogas Biogas BiogasDocument32 pagesBiogas Biogas Biogasvishnu0751No ratings yet
- Energy From BiomassDocument30 pagesEnergy From BiomassRehman ManiNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument2 pagesBiomassJasmine AustriaNo ratings yet
- BIOFUELSDocument9 pagesBIOFUELSGeorgette RepunteNo ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument13 pagesBiomass EnergySuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument14 pagesBiomassabmtestlab82No ratings yet
- BiomassDocument5 pagesBiomassAkshara K VijayNo ratings yet
- c1 PDFDocument42 pagesc1 PDFNagendrababu RamisettyNo ratings yet
- Biomass 230916 144312Document51 pagesBiomass 230916 144312reefanyyNo ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument12 pagesBiomass Energymaria yvonne camilotesNo ratings yet
- Biomass Energy ProcessesDocument2 pagesBiomass Energy Processesmitali01sarda01No ratings yet
- Understanding Biomass Energy - Importance of Biofuels | Biomass Energy for Kids | Children's Ecology BooksFrom EverandUnderstanding Biomass Energy - Importance of Biofuels | Biomass Energy for Kids | Children's Ecology BooksNo ratings yet
- Crudeoilpetrolium 2022Document30 pagesCrudeoilpetrolium 2022Ndapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- GEC253 2018 Geothermal 2022Document18 pagesGEC253 2018 Geothermal 2022Ndapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- Solar Case Study Botswana 2022Document11 pagesSolar Case Study Botswana 2022Ndapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy - 2022FDocument23 pagesNuclear Energy - 2022FNdapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- Energy UnitsUnits Conversion 2022Document12 pagesEnergy UnitsUnits Conversion 2022Ndapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- SOLAR ENERGY - 2022 - UpdatedDocument54 pagesSOLAR ENERGY - 2022 - UpdatedNdapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary For Text Analysis and Text ProductionDocument2 pagesVocabulary For Text Analysis and Text ProductionchloNo ratings yet
- Jaworski Vs Pagcor DigestDocument1 pageJaworski Vs Pagcor Digestmegzycutes3871No ratings yet
- CE0515 4.0v1 An Introduction To Sophos Synchronized SecurityDocument20 pagesCE0515 4.0v1 An Introduction To Sophos Synchronized Securitydanielfdiaz97No ratings yet
- Solid Waste Action PlanDocument2 pagesSolid Waste Action PlanJocel Baran Macoy100% (1)
- Geography of EquadorDocument16 pagesGeography of EquadorAre JibNo ratings yet
- Poverty Alleviation & Employment Generation Descriptive Answer WritingDocument6 pagesPoverty Alleviation & Employment Generation Descriptive Answer WritingmbsyNo ratings yet
- A Disaster Is A SuddenDocument3 pagesA Disaster Is A Suddenzitadewi435No ratings yet
- ENG-101 Presentation On The Short Story "The Gift of Magi"Document15 pagesENG-101 Presentation On The Short Story "The Gift of Magi"নরকেররাজপুত্র100% (1)
- Gramatika Holandskog JezikaDocument59 pagesGramatika Holandskog JezikaNikola LučićNo ratings yet
- The Coinage of Two Hundred Rupees and Ten Rupees Coins To Commemorate The Occasion of 200 H BIRTH ANNIVERSARY of TATYA TOPE Rules, 2015.Document6 pagesThe Coinage of Two Hundred Rupees and Ten Rupees Coins To Commemorate The Occasion of 200 H BIRTH ANNIVERSARY of TATYA TOPE Rules, 2015.Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid (CH: B A B ADocument2 pagesAcetic Acid (CH: B A B APuwala ArdhanaNo ratings yet
- EcowasDocument5 pagesEcowasshubhamNo ratings yet
- Go 2Document4 pagesGo 2farhahNo ratings yet
- Diterima Oleh Yang BersangkutanDocument3 pagesDiterima Oleh Yang BersangkutanDT Dyah TetiyanaNo ratings yet
- 61 Fieldmen's Insurance v. Vda de SongcoDocument1 page61 Fieldmen's Insurance v. Vda de SongcoSIPC PSA Applications 2020No ratings yet
- Econ 122 Week 1 9 by DwexDocument19 pagesEcon 122 Week 1 9 by DwexDestinyNo ratings yet
- Bar Ops 2 - 1ST Wave Cases 1 34Document30 pagesBar Ops 2 - 1ST Wave Cases 1 34Shane Fernandez JardinicoNo ratings yet
- CJL 5000 Hsa Plan 2024 SBC Final 10182023Document8 pagesCJL 5000 Hsa Plan 2024 SBC Final 10182023dominicvjohnson03No ratings yet
- Right To EducationDocument11 pagesRight To EducationPrateek KulhariNo ratings yet
- Woyzeck Study GuideDocument9 pagesWoyzeck Study GuideShanghaï LiNo ratings yet
- 2-Self-Assessment ChecklistDocument2 pages2-Self-Assessment ChecklistFlorante De LeonNo ratings yet
- A-Morally-Defensible Noddings PDFDocument8 pagesA-Morally-Defensible Noddings PDFHazel QuinanteNo ratings yet
- ARTID121 - Enlightenment and NeoclassicismDocument79 pagesARTID121 - Enlightenment and Neoclassicismarkiosk100% (1)
- Amortization of A 30-Year, $130,000 Loan at 8.5%Document10 pagesAmortization of A 30-Year, $130,000 Loan at 8.5%Ponleu MamNo ratings yet
- Adr ReviewDocument4 pagesAdr ReviewJoseph Emanuel PunioNo ratings yet
- PPM Sudha Murty LeadreshipDocument14 pagesPPM Sudha Murty LeadreshipDevshri UmaleNo ratings yet
- ISISDocument3 pagesISISJehann DenisseNo ratings yet
- 020-500-Summary of Control WeaknessesDocument5 pages020-500-Summary of Control WeaknessesKris Anne SamudioNo ratings yet
- Oilgram Price Report: Valero Makes Big Splash Into MethanolDocument25 pagesOilgram Price Report: Valero Makes Big Splash Into MethanolPaolo Del Aguila RojasNo ratings yet