Professional Documents
Culture Documents
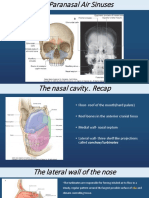
Paranasal Sinuses
Paranasal Sinuses
Uploaded by
Sridevi K0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesThe document describes the paranasal sinuses, which are air-filled spaces within bones around the nasal cavity. There are four main pairs of paranasal sinuses: frontal, maxillary, sphenoidal, and ethmoidal. The sinuses lighten the skull, warm and humidify inhaled air, and add resonance to the voice. Each sinus has a specific location, openings, blood supply, drainage, and innervation. The maxillary sinus is the largest, while the ethmoidal sinus consists of several small interconnecting air cells.
Original Description:
Original Title
PARANASAL SINUSES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the paranasal sinuses, which are air-filled spaces within bones around the nasal cavity. There are four main pairs of paranasal sinuses: frontal, maxillary, sphenoidal, and ethmoidal. The sinuses lighten the skull, warm and humidify inhaled air, and add resonance to the voice. Each sinus has a specific location, openings, blood supply, drainage, and innervation. The maxillary sinus is the largest, while the ethmoidal sinus consists of several small interconnecting air cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesParanasal Sinuses
Paranasal Sinuses
Uploaded by
Sridevi KThe document describes the paranasal sinuses, which are air-filled spaces within bones around the nasal cavity. There are four main pairs of paranasal sinuses: frontal, maxillary, sphenoidal, and ethmoidal. The sinuses lighten the skull, warm and humidify inhaled air, and add resonance to the voice. Each sinus has a specific location, openings, blood supply, drainage, and innervation. The maxillary sinus is the largest, while the ethmoidal sinus consists of several small interconnecting air cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
PARANASAL SINUSES
• These are air filled spaces present within some bones of
nasal cavities.
• Sinuses – FRONTAL , MAXILARY , SPHENOIDAL &
ETHMOIDAL
• Open – in nasal cavity through its lateral wall
• Function – make skull lighter
warm up & humidify the inspired air
add resonance to voice
• In sinusitis , the voice is altered
• Sinuses are rudimentary or absent at birth
• Enlarge rapidly at 6-7 yrs i.e. time of eruption of permanent
teeth & after puberty
FRONTAL SINUS
• Lie in frontal bone, deep to superciliary arch
• Extends – upwards – above medial end of eyebrow
backwards – into medial part of roof of orbit.
• Opens – into middle meatus of nose at anterior end of
hiatus semilunaris through infundibulum or frontonasal
duct
• Average height, width & anteroposterior depth – 2.5cm
• Sinuses are better developed in males
• Right & left sinuses are unequal in size & rarely both
absent
FRONTAL SINUS
• Rudimentary or absent at birth
• Well developed at 7-8 yrs of age & reach full size
after puberty
• Arterial supply : Supraorbital artery
• Venous drainage : into supraorbital & superior
ophthalmic veins
• Lymphatic drainage : to submandibular nodes
• Nerve supply : Supraorbital nerve
MAXILLARY SINUS
• Largest of all paranasal sinuses
• First paranasal sinus to develop
• Lie in body of the maxilla
• Pyramidal in shape – base – medially toward the lateral wall of nose
apex – laterally in zygomatic process of maxilla
• Opens – middle meatus of nose in lower part of hiatus semilunaris
• In an isolated maxilla, opening / hiatus of maxillary sinus is large
• But the size of opening is reduced to 3/4mm as it is overlapped by
• A)above – uncinate process of ethmoid
descending part of lacrimal bone
B)below – inferior nasal concha
C)behind – perpendicular plate of palatine bone
• Further reduced by thick mucosa of nose
MAXILLARY SINUS
• Measurements – height – 3.5 width – 2.5cm
anteroposterior depth – 3.5cm
• Formations
• ROOF – by floor of orbit & traversed by infraorbital nerve & artery
• FLOOR – by alveolar process of maxilla & lies 1cm below level of floor of
nose which corresponds to lower level of ala of nose
• Floor is marked by conical elevations produced by roots of upper molar
& premolar. Roots even penetrate bony floor to lie beneath mucousa
lining
• Arterial supply – facial , infraorbital & greater palatine arteries
• Venous drainage – into facial vein & pterygoid venous plexus
• Lymphatic drainage – submandibuar nodes
• Nerve supply – posterior superior alveolar branches of maxillary nerve
anterior & middle superior alveolar branches of
infraorbital nerve
SPHENOIDAL SINUS
• Lie within the sphenoidal bone
• Right & left sinuses are separated by septum & unequal in
size
• Opens – into sphenoethmoidal recess of corresponding half
of nasal cavity
• Relations – superiorly – optic chiasma & hypophysis cerebri
laterally – ICA & cavernous sinus
• Arterial supply – posterior ethmoidal artery & ICA
• Venous drainage - into pterygoid venous plexus &
cavernous sinus
• Lymphatic drainage – Retropharyngeal nodes
• Nerve supply – posterior ethmoidal nerve
orbital branches of pterygopalatine
ETHMOIDAL SINUS
• Numerous small inter-communicating spaces
• Lie within the labyrinth of ethmoid bone
• Completed by – above – by orbital plate of frontal
bone
behind – sphenoidal conchae &
orbital process of palatine bone
anteriorly – by lacrimal bone
• Sinuses are divided into anterior, middle &
posterior
• ANTERIOR ETHMOIDA L SINUS
Made of 1-11 air cells
Opens – into anterior part of hiatus semilunaris of nose
Supplied by anterior ethmoidal nerve & vessels
Lymphatic drainage – submandibular nodes
• MIDDLE ETHMOIDAL SINUS
Consists of 1-7 air cells
Opens – into middle meatus of nose
Supplied by anterior ethmoidal nerve & vessels & orbital branches of
pterygopalatine ganglion
Lymphatic drainage – submandibular nodes
• POSTERIOR ETHMOIDAL SINUS
Consists of 1-7 air cells
Opens – into superior meatus of nose
Supplied by posterior ethmoidal nerve & vessels & orbital branches of
pterygopalatine ganglion
You might also like
- GMB Isp PDFDocument29 pagesGMB Isp PDFmarkNo ratings yet
- Aiims Srship OMFSDocument31 pagesAiims Srship OMFSNikita Samal100% (1)
- Summative-Test in Science 10Document8 pagesSummative-Test in Science 10trexia autida0% (1)
- Autopsy Report FinalDocument3 pagesAutopsy Report Finalapi-358121439No ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi HidungDocument39 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi HidungHerman YosefNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi HidungDocument39 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi HidungHerman YosefNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1 Rhinorrhoea Nasal Airway ObstructionDocument399 pagesSeminar 1 Rhinorrhoea Nasal Airway ObstructionKasey ChaseNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Maxilla and MandibleDocument56 pagesAnatomy of Maxilla and Mandiblesoni bistaNo ratings yet
- The Nasal CavityDocument43 pagesThe Nasal CavityYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- 02 The Nose and The Associated StructuresDocument72 pages02 The Nose and The Associated Structuresmalaths757No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nose: Dr. Ra. Shivaraman Postgraduate in Plastic Surgery Govt. Kilpauk Medical CollegeDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Nose: Dr. Ra. Shivaraman Postgraduate in Plastic Surgery Govt. Kilpauk Medical CollegeShivaramanRamachandranNo ratings yet
- Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument35 pagesNose and Paranasal SinusesReham QueNo ratings yet
- Paranasal Air Sinuses: Presented By:-Dr. Sushma Tomar Associate Professor Department of AnatomyDocument38 pagesParanasal Air Sinuses: Presented By:-Dr. Sushma Tomar Associate Professor Department of AnatomyAbishek JNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Air Sinus (Antrum of Highmore)Document19 pagesMaxillary Air Sinus (Antrum of Highmore)giner1No ratings yet
- The Paranasal SinusesDocument13 pagesThe Paranasal SinusesAllen Bajeta CajucomNo ratings yet
- 1st SeminarDocument85 pages1st SeminarVeena GoudNo ratings yet
- Facial BonesDocument146 pagesFacial BonesPavan100% (1)
- Surgical Anatomy of JawsDocument71 pagesSurgical Anatomy of JawsBhanu Praseedha100% (2)
- Anatomy of NoseDocument31 pagesAnatomy of Nosekaruparthi sripravallikaNo ratings yet
- Salome Gvidiani For European University 2020Document32 pagesSalome Gvidiani For European University 2020Tarun SinghNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Nose & Paranasal SinusesDocument33 pagesAnatomy - Nose & Paranasal SinusesHetvi ParmarNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument351 pagesIlovepdf MergedSwara SawantNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nose and Paranasal Sinus: By: Dr. Mohammed AloulahDocument33 pagesAnatomy of Nose and Paranasal Sinus: By: Dr. Mohammed AloulahfouadNo ratings yet
- The Nose 2Document27 pagesThe Nose 2Ahmed JawdetNo ratings yet
- Sinonasal AnatomyDocument33 pagesSinonasal Anatomy李丞永No ratings yet
- Max SinusDocument97 pagesMax SinusAishwarya DesaiNo ratings yet
- Ear & Pathway of Hearing and BalanceDocument38 pagesEar & Pathway of Hearing and Balancedush35No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Respiratory System: Moderator: Dr. Aruna Speaker:Dr - Vipin KR - SinghDocument69 pagesAnatomy of Respiratory System: Moderator: Dr. Aruna Speaker:Dr - Vipin KR - SinghAnshul JainNo ratings yet
- ENDOSCOPIC ANATOMY of NOSE & PNS.Document57 pagesENDOSCOPIC ANATOMY of NOSE & PNS.Prasanna DattaNo ratings yet
- The Paranasal SinusesDocument15 pagesThe Paranasal SinusesSimphiwe CebisaNo ratings yet
- Anatomyofnoseandparanasalsinus 100616084243 Phpapp02Document33 pagesAnatomyofnoseandparanasalsinus 100616084243 Phpapp02Igor Quarmina HesseNo ratings yet
- 1.salivary Gland-AnatomyDocument42 pages1.salivary Gland-AnatomyDrbarathirajaNo ratings yet
- Final01 - Anatomi Fisiologi HidungDocument82 pagesFinal01 - Anatomi Fisiologi Hidungkurnia sariNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument58 pagesAnatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinuseschambhaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Hidung Baru BGTDocument48 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Hidung Baru BGTDzulfiqarNo ratings yet
- NaaaaaaaaaaaDocument64 pagesNaaaaaaaaaaaRhea RaveloNo ratings yet
- Paranasal Sinuses: By: Student at Faculty of Dentistry Ahram Canadian UniversityDocument20 pagesParanasal Sinuses: By: Student at Faculty of Dentistry Ahram Canadian Universityمحمد نعيمNo ratings yet
- Lec8 Sem2 Hnsweek3 20110822Document9 pagesLec8 Sem2 Hnsweek3 20110822Sazter AthiraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument43 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemChristina GonezNo ratings yet
- Telinga Hidung TenggorokanDocument111 pagesTelinga Hidung Tenggorokanharyo wiryantoNo ratings yet
- Musculos de La CaraDocument37 pagesMusculos de La Carazuri90No ratings yet
- Nasal Cavity and Oral Cavity OUTLINEDocument4 pagesNasal Cavity and Oral Cavity OUTLINEAnna AyumNo ratings yet
- External Nose AnatomyDocument17 pagesExternal Nose AnatomyAnonymous avOsNPcNo ratings yet
- Scalp and OsteologyDocument116 pagesScalp and Osteologychynne ongNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument54 pagesRespiratory SystemEndin Nokik StujannaNo ratings yet
- Middle EarDocument60 pagesMiddle EarPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy EarDocument18 pagesAnatomy EarJenu SuwalNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument65 pagesOral Cavityugwuokeprince4No ratings yet
- ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY OF THE EARDocument101 pagesANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY OF THE EARsnpshubh444No ratings yet
- Presentation, Skull, by DR Iram IqbalDocument68 pagesPresentation, Skull, by DR Iram Iqbalimmmi100% (1)
- Ontogeny of Respiratory System: Abd. Razak RatuDocument43 pagesOntogeny of Respiratory System: Abd. Razak RatuNur AnniesaNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandDocument16 pagesSalivary GlandSurvey IndiaNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument13 pagesAnatomyAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Embryology of The EarDocument35 pagesAnatomy and Embryology of The EarVictor EnachiNo ratings yet
- Nasal Cavity, Larynx PDFDocument71 pagesNasal Cavity, Larynx PDFĄå DìNo ratings yet
- Good Afternoon EverybodyDocument131 pagesGood Afternoon EverybodyIhsan HanifNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Nose 2Document23 pagesAnatomy Nose 2Max Fax100% (1)
- Extra HepaticDocument56 pagesExtra HepaticBonzowoNo ratings yet
- Aj Anatomy - and - Physiology - of - Nose - & - Paranasal - SinusDocument117 pagesAj Anatomy - and - Physiology - of - Nose - & - Paranasal - SinusTradigrade PukarNo ratings yet
- Maxillary SinusDocument67 pagesMaxillary SinusDR. NEETI TATIYANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Scalp by DR YekyeDocument32 pagesAnatomy of The Scalp by DR YekyeYEKOYENo ratings yet
- Nose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018Document63 pagesNose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018yasrul izadNo ratings yet
- H & N - Pharynx& Deglutition PDFDocument17 pagesH & N - Pharynx& Deglutition PDFRamin AmirkhiziNo ratings yet
- Cavernous SinusDocument11 pagesCavernous SinusSridevi KNo ratings yet
- 9bd9a56d3aeeedff9ee0d1d0d1f410ceDocument61 pages9bd9a56d3aeeedff9ee0d1d0d1f410ceSridevi KNo ratings yet
- HNF - Parasympathetic GangliaDocument15 pagesHNF - Parasympathetic GangliaSridevi KNo ratings yet
- Mandibular NerveDocument8 pagesMandibular NerveSridevi KNo ratings yet
- Maxillary ArteryDocument11 pagesMaxillary ArterySridevi KNo ratings yet
- Kontraksi Dan Eksitasi Otot Polos Sistem Muskuloskletal FREEDocument35 pagesKontraksi Dan Eksitasi Otot Polos Sistem Muskuloskletal FREENovita DamaiyantiNo ratings yet
- Intrusion With Mini ImplantDocument13 pagesIntrusion With Mini Implantdrzana78100% (1)
- Iliotibial Band SyndromeDocument15 pagesIliotibial Band SyndromeYuni IsmulyatiNo ratings yet
- NBSS AIA - Ivan Christian ChannelDocument128 pagesNBSS AIA - Ivan Christian ChannelASTAGINA NAURAHNo ratings yet
- ZIP 3 PowerPoint PresentationDocument46 pagesZIP 3 PowerPoint PresentationShereen FaeNo ratings yet
- Kinesio Taping 2Document137 pagesKinesio Taping 2abdul haseebNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The AbdomenDocument22 pagesAssessment of The AbdomenTerence Shane AcodNo ratings yet
- Endotracheal IntubationDocument7 pagesEndotracheal Intubationsimonjosan75% (4)
- Dave's 12 Week Muscle Building RoutineDocument26 pagesDave's 12 Week Muscle Building RoutineRyan Pan100% (1)
- CH 9 ArticulationsDocument40 pagesCH 9 ArticulationsRobin ToneyNo ratings yet
- Ch20 Answer Key 12edition CorrectedDocument11 pagesCh20 Answer Key 12edition CorrectedTeuku Muhammad LizarNo ratings yet
- Mirror Book Therapy For The Treatment of Idiopathic Facial PalsyDocument5 pagesMirror Book Therapy For The Treatment of Idiopathic Facial PalsyKhusnah KhauliyaNo ratings yet
- Textbook An Illustrated Terminologia Neuroanatomica Hans J Ten Donkelaar Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook An Illustrated Terminologia Neuroanatomica Hans J Ten Donkelaar Ebook All Chapter PDFandrew.trotter860100% (23)
- Anatomy Best Short Notes and Flow ChartDocument5 pagesAnatomy Best Short Notes and Flow ChartNikhilNo ratings yet
- LAB - Fish DissectionDocument4 pagesLAB - Fish DissectionPearl Angel May Alcon100% (2)
- Vendajes en MEd Deportiva PDFDocument474 pagesVendajes en MEd Deportiva PDFJUAN DAVID MELENDEZ MOLANONo ratings yet
- Peshab Mein Jalan Aur Dard Ka Ilaj Ke Gharelu Upay in HindiDocument3 pagesPeshab Mein Jalan Aur Dard Ka Ilaj Ke Gharelu Upay in HindiGovindNo ratings yet
- Training ProgramDocument31 pagesTraining ProgramBroadway Blues100% (1)
- Module 1: Care For Clients With Cognitive and Perceptual Disorder 1Document93 pagesModule 1: Care For Clients With Cognitive and Perceptual Disorder 1Woot RootNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cad Cam Nasoalveolar Molding ADocument6 pagesEffect of Cad Cam Nasoalveolar Molding Aisha MehtaNo ratings yet
- Protocol For Symptoms HomeopathyDocument17 pagesProtocol For Symptoms HomeopathyUmer Shahzad ANSERNo ratings yet
- Nonextraction Treatment of An Adult With Class Ii Division 2 MalocclusionDocument9 pagesNonextraction Treatment of An Adult With Class Ii Division 2 MalocclusionDrManem Jaganath VenkatNo ratings yet
- Subacromial BursitisDocument4 pagesSubacromial Bursitisfashionhub.jfNo ratings yet
- The Use of Cephalometrics As An Aid To Planning and Assessing Orthodontic Treatment, - American Journal of Orthodontics, Vol. 46, Pp. 721-735, 1960 C.C. SteinerDocument15 pagesThe Use of Cephalometrics As An Aid To Planning and Assessing Orthodontic Treatment, - American Journal of Orthodontics, Vol. 46, Pp. 721-735, 1960 C.C. SteinerMiguel Jaèn100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument35 pagesEndocrine SystemLinkNo ratings yet
- Exercise 22 Serial Section of A 10 MM Pig Embryo PDFDocument16 pagesExercise 22 Serial Section of A 10 MM Pig Embryo PDFMichaela Faye100% (1)