Professional Documents
Culture Documents
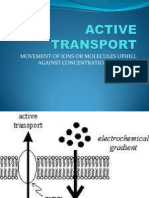
Active Transport
Active Transport
Uploaded by
Karan Bhagdev0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views31 pagesActive transport is the movement of substances against a concentration gradient using energy, usually from ATP hydrolysis. There are two main types: primary active transport which directly uses ATP, and secondary active transport which uses the energy from ion gradients. Primary transporters include the sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump, and hydrogen pump. Secondary transport mechanisms include co-transport and counter-transport which use the energy from ion gradients like sodium to transport other molecules. Special types of active transport use vesicles like endocytosis, exocytosis, and transcytosis.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentActive transport is the movement of substances against a concentration gradient using energy, usually from ATP hydrolysis. There are two main types: primary active transport which directly uses ATP, and secondary active transport which uses the energy from ion gradients. Primary transporters include the sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump, and hydrogen pump. Secondary transport mechanisms include co-transport and counter-transport which use the energy from ion gradients like sodium to transport other molecules. Special types of active transport use vesicles like endocytosis, exocytosis, and transcytosis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views31 pagesActive Transport
Active Transport
Uploaded by
Karan BhagdevActive transport is the movement of substances against a concentration gradient using energy, usually from ATP hydrolysis. There are two main types: primary active transport which directly uses ATP, and secondary active transport which uses the energy from ion gradients. Primary transporters include the sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump, and hydrogen pump. Secondary transport mechanisms include co-transport and counter-transport which use the energy from ion gradients like sodium to transport other molecules. Special types of active transport use vesicles like endocytosis, exocytosis, and transcytosis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 31
Definition
• Active transport is the movement of
substances against the chemical or
electrochemical gradient.
• Uphill transport
• Energy is obtained mainly breakdown of ATP
• A.T each carrier protein can carry one or more
substances across the cell membrane.
Substances which are transported in 2 form
• Ionic form- Na+, k+, Ca+, h+, cl+, iodine
• No ionic – glucose, amino acid, urea
Types of active substance
• Primary active transport-
1) sodium potassium pump
2) calcium pump
3) hydrogen pump
• Secondary active transport-
1)cotransport
2)counter transport
Primary active transport
• Primary active transport is one of the
transport mechanism in which the energy is
liberated directly from the breakdown of ATP
• This mechanism ionic form substances are
transported across the cell membrane
Sodium potassium pump
• Na+ k+ ATPase pump or ATPase
• This pump is transported Na+ from inside to
outside cell and k+ from outside to inside the
cell.
• This pump present in all cell of body
• This pump development of resting membrane
potential
mechanism
• 3 Na+ ions are attached to the Na+ ions receptor in
inner surface of carrier protein 2 k+ ions outside
the cell bind to the k+ receptor site on the outer
surface of a carrier protein. This ions binding to
carrier protein immediately activate the enzyme
ATPase.
• This ATPase cause the breakdown of ATP into ADP
with the release of energy
• Now energy cause change in the molecule of carrier
protein
Calcium pump
• Calcium is actively transported from inside to
outside the cell membrane by the carrier
protein called calcium pump. The energy
obtained from ATP by catalytic activity of
ATPase
• Eg. Sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle ,
mitochondria of cell
Hydrogen pump
• Hydrogen ions is actively transported across the
cell membrane by carrier protein called hydrogen
pump.
• It obtained energy by activity of ATPase
• In stomach- parietal cells of the gastric glands are
involved in formation of hydrochloric acid
• In kidney- epithelial cell of distal convoluted
tubules and collecting ducts are involved in the
secretion of hydrogen ions from blood into urine
Secondary active transport
• This mechanism in which energy is obtained
from the sources (other than ATP) for the
transportation of substances against
concentration gradient
• It include
1) co transport 2) counter transport
Sodium co transport
• It is the process in which along with
sodium ,another substances is transported by
a carrier proteins. The energy released by the
movement of sodium is utilized for the
movement of another substances.
• Substances carried by sodium co transport are
glucose, amino acid, chloride, iodine,
iron ,urate
Carrier protein for sodium cotransport
• Carrier protein for the sodium cotransport has
2 receptor site
• 1 is binding of sodium and another is binding
of other substances
• Sodium cotransport with glucose and
aminoacide
Primary secondary difference
• Transport of molecule • Transport of 2 different
against the concentration molecule across a transport
gradient by use of ATP molecule using energy in
other forms of ATP
• Single molecule is
• 2 type of molecules are
transported
transported at once
• Ionic molecule are
• Concentration gradient of
transported across the the ions provides the
cell membrane energy for the transport of
• Trans membrane protein molecules against
are unique to the ion concentration gradient
Sodium counter transport
• It is the process in which the substances are
transported across the cell membrane in exchange
for( sodium ions and another substance move in
opposite direction) by the carrier protein.
• Sodium counter transport system are sodium-
calcium, sodium- magnesium, sodium- potassium,
calcium- magnesium, calcium- potassium ,chloride
– bicarbonate and chloride -sulfate
What is S.A.T
Special type of active transport
• Primary and secondary active transport
system there are some special categories of
active transport. The substances are
transported through cell membrane in the
vesicles. This type of transport mechanism are
generally are vesicular transport
• Types- 1) endocytosis 2) exocytosis 3)
transcytosis
endocytosis
• Special type of A.T process by which large
particles move inside the cell is called
endocytosis
• Special category- pinocytosis, phagocytosis ,
receptor- mediated endocytosis
exocytosis
• The process in which cell releases undigested
material to the outside is called exocytosis
transcytosis
• Transcytosis is transport mechanism in which
an extracellular macromolecules enter
through one side of cell migrate across
cytoplasm of the cell and exit other site
eg. HIV
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Edexcel IAL BIO Question Paper (June 2020)Document36 pagesEdexcel IAL BIO Question Paper (June 2020)Meenakshie Chaudrie50% (2)
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument28 pagesTransport Across The Cell MembraneGeorge LusanaNo ratings yet
- B. Cell Physiology Transport Across CellmembraneDocument62 pagesB. Cell Physiology Transport Across Cellmembranenoahngoma41No ratings yet
- Transport Cell: Diana N. AffandiDocument36 pagesTransport Cell: Diana N. AffandiunyeNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport SystemsDocument33 pagesMembrane Transport SystemsObiajulu Crystal OnyinyechiNo ratings yet
- 1st Year 2nd Week PHYS Lecture 6 2019 2020Document14 pages1st Year 2nd Week PHYS Lecture 6 2019 2020Ahmed TarekNo ratings yet
- "In The Name Of,, .": AllahDocument28 pages"In The Name Of,, .": AllahAqsa ArifNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument7 pagesActive Transportidokofavour2015No ratings yet
- Biochem Lab For ReadingDocument57 pagesBiochem Lab For ReadingShaira Elyze GabrielNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Transport Mechanisms PDFDocument24 pagesCell Membrane and Transport Mechanisms PDFAremu AbdulwahabNo ratings yet
- MEMBRANE TRANSPORTand DISEASES MBBSDocument48 pagesMEMBRANE TRANSPORTand DISEASES MBBSAbdulateef AdebisiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document31 pagesLecture 4BlaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive TransportDocument21 pagesActive and Passive Transportm umair zahirNo ratings yet
- Lipids Biologial Membrane Transport Part II PDFDocument24 pagesLipids Biologial Membrane Transport Part II PDFJia HuiNo ratings yet
- San Pedro College: Senior High School DepartmentDocument54 pagesSan Pedro College: Senior High School DepartmentKrisha Diane FunaNo ratings yet
- Transport 2 PDF Lecture Elalamein 2021-22Document5 pagesTransport 2 PDF Lecture Elalamein 2021-22Ahmed MagdyNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument6 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membraneshekinah656No ratings yet
- 3 - kh201295 kh201295Document5 pages3 - kh201295 kh201295murtada gubaNo ratings yet
- Active Transport MechanismDocument46 pagesActive Transport MechanismnoblefxNo ratings yet
- CH - 6, Passive TransportDocument43 pagesCH - 6, Passive TransportTony StarkNo ratings yet
- Movement of Ions or Molecules Uphill Against Concentration GradientDocument32 pagesMovement of Ions or Molecules Uphill Against Concentration Gradientraanja2No ratings yet
- Cells The Living Units Opart BDocument5 pagesCells The Living Units Opart BDan Paulene AceboNo ratings yet
- Types of TransportsDocument13 pagesTypes of Transports88AKKNo ratings yet
- Secondary Active Transport EminDocument7 pagesSecondary Active Transport EminHASHIR CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport ABDocument38 pagesMembrane Transport ABdj77djcqy7No ratings yet
- Membrane Tranport 2ND Lecture by Dr. RoomiDocument32 pagesMembrane Tranport 2ND Lecture by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (2)
- 05 Membrane Transport VDocument27 pages05 Membrane Transport Vmaksud alaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Transport of Substances Across The Cell MembraneDocument24 pagesLecture 2 Transport of Substances Across The Cell MembraneEzeudu SomtoNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument14 pagesActive TransportRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Transport of Substance (Autosaved)Document32 pagesTransport of Substance (Autosaved)Mary AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Cell MembraneDocument20 pagesTransportation in Cell Membraneaditya patilNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument52 pagesCell BiologyDefensor Pison GringgoNo ratings yet
- Transport of Substances Through MembranesDocument27 pagesTransport of Substances Through MembranesjerxyxmaxNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument8 pagesActive TransportSarah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Renal Tubular Reabsorption Renal Tubular ReabsorptionDocument46 pagesRenal Tubular Reabsorption Renal Tubular ReabsorptionoldmarnerNo ratings yet
- R-Sen Lecture 01bDocument57 pagesR-Sen Lecture 01bhimanshu_agraNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDocument12 pagesTransport Across Cell Membranepetricia johnsonNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-02-07 at 9.06.14 PMDocument92 pagesScreenshot 2023-02-07 at 9.06.14 PMMohammed RamzyNo ratings yet
- Important Topics in Cell BiologyDocument108 pagesImportant Topics in Cell Biologygabbs_123No ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument46 pagesCell BiologyHajni Rizkia ZulpaNo ratings yet
- BBT221 Lecture 2Document19 pagesBBT221 Lecture 2Al Sabri Bhuiyan 1812098042No ratings yet
- Intro, Transport SysDocument44 pagesIntro, Transport Sysr74k8zgg8rNo ratings yet
- Heny Ekowati: Pharmacy Department Medicine and Health Sciences Faculty University of Jenderal Soedirman 2013Document24 pagesHeny Ekowati: Pharmacy Department Medicine and Health Sciences Faculty University of Jenderal Soedirman 2013Nisadiyah Faridatus ShahihNo ratings yet
- 3.8 Active TransportDocument12 pages3.8 Active TransportVictoria MonacelliNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 TransportDocument49 pagesWEEK 7 Transportorioluna00No ratings yet
- Heny Ekowati: Pharmacy Department Medicine and Health Sciences Faculty University of Jenderal Soedirman September 2014Document24 pagesHeny Ekowati: Pharmacy Department Medicine and Health Sciences Faculty University of Jenderal Soedirman September 2014Ghea Boriel SadochiNo ratings yet
- L3 Cell Membrane and Transport 2Document23 pagesL3 Cell Membrane and Transport 2sampsonsoo17No ratings yet
- 4-Transport Across Cell Membrane 4Document51 pages4-Transport Across Cell Membrane 4devdsantoshNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Membrane TransportDocument28 pages2.2 Membrane Transporthaiqalfariq07No ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument2 pagesTransport MechanismLeng BunthaiNo ratings yet
- CH5 Membrane TraffickingDocument48 pagesCH5 Membrane TraffickingAhmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDocument26 pagesTransport Across Cell MembraneAlhadaeel JesjNo ratings yet
- 4 - Membrane PhysiologyDocument31 pages4 - Membrane PhysiologysadaffardoosNo ratings yet
- الشيت الثالث - علم الحيوانDocument48 pagesالشيت الثالث - علم الحيوانmahmiylylylyNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane - Radiology LecDocument22 pagesPlasma Membrane - Radiology Lecsara so888No ratings yet
- Transport Across MembraneDocument13 pagesTransport Across MembraneHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- Biology I For Non-Majors: Cell MembranesDocument19 pagesBiology I For Non-Majors: Cell MembranesEmma RiftyanNo ratings yet
- Cell ExchangesDocument28 pagesCell ExchangesBenzerari ManaNo ratings yet
- DNA: Damage Types and Repair Mechanisms (With Diagram)Document7 pagesDNA: Damage Types and Repair Mechanisms (With Diagram)Biofilm NSTUNo ratings yet
- Book 2014 Samal BioinformaticsmanualDocument121 pagesBook 2014 Samal BioinformaticsmanualUttam VictoryNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument16 pagesStem CellJesse PinkmanNo ratings yet
- Thesis WholeDocument17 pagesThesis Wholeapi-431926146No ratings yet
- NGS and Sequence Analysis With Biopython For Prospective Brain Cancer Therapeutic StudiesDocument14 pagesNGS and Sequence Analysis With Biopython For Prospective Brain Cancer Therapeutic StudiesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Fan 2019Document7 pagesFan 2019amandasantanalila186No ratings yet
- Oropouche Virus As An Emerging Cause of Acute Febrile Illness in ColombiaDocument14 pagesOropouche Virus As An Emerging Cause of Acute Febrile Illness in Colombiajuliana22004No ratings yet
- Problem Statements - SBADocument3 pagesProblem Statements - SBAjbsquad007No ratings yet
- C3 Written Test Question PaperDocument1 pageC3 Written Test Question PaperPrakhar JalanNo ratings yet
- Dna ProfilingDocument19 pagesDna ProfilingAaron Janapin MirandaNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson - Dagne Beza-Protein SynthesisDocument5 pages5e Lesson - Dagne Beza-Protein Synthesisapi-528044846No ratings yet
- Gene Transfer MechanismDocument21 pagesGene Transfer MechanismNik SharmaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication - IB Biology SL Grade 11Document9 pagesDNA Replication - IB Biology SL Grade 11atharNo ratings yet
- Workshop 8 Bio 1Document2 pagesWorkshop 8 Bio 1Luis Rodriguez DiazNo ratings yet
- Remedial Worksheet Enzymes Cell Structure & MembranesDocument3 pagesRemedial Worksheet Enzymes Cell Structure & MembraneskimNo ratings yet
- JCT All India Aakash Test Series (AIATS) Planner For NEET 2024Document2 pagesJCT All India Aakash Test Series (AIATS) Planner For NEET 2024Vijaya RajuNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Cancer EngDocument11 pagesColorectal Cancer Engrinadi_aNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Composition and Functions of Cell MembraneDocument42 pagesBiochemical Composition and Functions of Cell MembraneAmir NangyalNo ratings yet
- Mutations Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesMutations Worksheet PDFNouradin Ibrahim OmerNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell StrucDocument27 pagesEukaryotic Cell StrucHari. ChadhaNo ratings yet
- GE-INCell 3000Document15 pagesGE-INCell 3000api-19762689No ratings yet
- Zoology PG Syllabus MSCDocument33 pagesZoology PG Syllabus MSCSayak MondalNo ratings yet
- Separation and Characterization Techniques For Proteins and AminoDocument34 pagesSeparation and Characterization Techniques For Proteins and AminoAnna Donato100% (2)
- Unit 1Document47 pagesUnit 1Ansh KumarNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 One-Step RT-PCR Kit - IFUDocument2 pagesCovid-19 One-Step RT-PCR Kit - IFUHarun GanićNo ratings yet
- Biology-12TH PB 2Document11 pagesBiology-12TH PB 2Rudra GourNo ratings yet
- Lectures: February 28, March 2, 7, 9 and 11, 2005 Michael Greenwood (Michael - Greenwood@mcgill - Ca)Document32 pagesLectures: February 28, March 2, 7, 9 and 11, 2005 Michael Greenwood (Michael - Greenwood@mcgill - Ca)Gent'No ratings yet
- Quality Characteristics of Chicken Burger Processed From Broiler Chicken Fed On Different Levels of Quinoa SeedsDocument9 pagesQuality Characteristics of Chicken Burger Processed From Broiler Chicken Fed On Different Levels of Quinoa SeedsMamta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences SyllabusDocument4 pagesLife Sciences SyllabusConflicted ConundrumNo ratings yet