Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 viewsThe Process of Conception
The Process of Conception
Uploaded by
Jobelyn Dela CruzWhen sperm swims up through the vagina and fertilizes an egg in the fallopian tube, conception occurs. It happens within hours or days of having unprotected sex. The fertilized egg implants into the uterus after conception, and a pregnancy begins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Types of Microscopes Comparison Chart 4 Linear Venn Edit Answer KeyDocument2 pagesTypes of Microscopes Comparison Chart 4 Linear Venn Edit Answer KeyKLRSantosNo ratings yet
- CARIOLOGYDocument77 pagesCARIOLOGYteklay100% (3)
- 3 Fertilization and Implantation ProcessDocument83 pages3 Fertilization and Implantation ProcessMarie Cecille Soliven VarillaNo ratings yet
- 4 FertilizationDocument389 pages4 FertilizationAngel Gabriel Fornillos100% (1)
- Fertilization 1 1Document219 pagesFertilization 1 1Edwin TiuNo ratings yet
- Fetus Development From Conception To Birth Part2Document40 pagesFetus Development From Conception To Birth Part2jeremyzucker321No ratings yet
- Placenta UpdatedDocument49 pagesPlacenta UpdatedSaad HasanNo ratings yet
- Three Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pagesThree Stages of Fetal DevelopmentmellowlilydeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Conception and Fetal DevelopmentDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Conception and Fetal DevelopmentRoneshia Michelle Rudolph100% (1)
- Ovulation Fertilisation Division and ImplantationDocument35 pagesOvulation Fertilisation Division and Implantationpsy9kfd4d7No ratings yet
- Embryology - The First WeekDocument51 pagesEmbryology - The First WeekLugembe MasolaNo ratings yet
- 7 Perkembangan EMbrio Manusia PDFDocument57 pages7 Perkembangan EMbrio Manusia PDFFadhilah SiregarNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument3 pagesFertilizationbinsaalimustapha91No ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 - 3 - Goal - Fertilization - Placentation - LactationDocument4 pagesLecture - 2 - 3 - Goal - Fertilization - Placentation - LactationAPOORVA SHANDILYANo ratings yet
- Embryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesDocument13 pagesEmbryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesAudrey100% (5)
- Embryological and Fetal Development:-Fertilization - It Is The Process of Fusion of Spermatozoon With The Mature Ovum. ItDocument19 pagesEmbryological and Fetal Development:-Fertilization - It Is The Process of Fusion of Spermatozoon With The Mature Ovum. ItRaman SamraoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - 3 Placenta and Umbilical Cord: Group 4 MED 114 PresentationDocument69 pagesWeek 1 - 3 Placenta and Umbilical Cord: Group 4 MED 114 PresentationVidur S SinghNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument54 pagesFertilization & ImplantationMarvelousNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document37 pagesLec 2ibrahim.21hm32No ratings yet
- The Growing FetusDocument62 pagesThe Growing Fetuscoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- File 2Document104 pagesFile 2Djo RamNo ratings yet
- FertlizationDocument5 pagesFertlizationgallardo.bettinarose.iNo ratings yet
- Placenta Development.Document6 pagesPlacenta Development.abdurrehman4198No ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument61 pagesFertilization & ImplantationchidimmaNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument60 pagesEmbryologyDaniella AwurumibeNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument18 pagesFertilization & ImplantationRESHMA AJAYNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation-1Document9 pagesFertilization and Implantation-1hussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Practice Teaching On Fertilization and Implantation.Document20 pagesPractice Teaching On Fertilization and Implantation.RDi JNo ratings yet
- The Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 7Document75 pagesThe Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 795kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- 10 Kuliah PLACENTADocument33 pages10 Kuliah PLACENTAAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument42 pagesStages of Fetal DevelopmentKara Ashleigh0% (1)
- Fertilization-fetal Period (1)Document108 pagesFertilization-fetal Period (1)amanamare10No ratings yet
- FERTILIZATIONDocument9 pagesFERTILIZATIONRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentDocument25 pagesModule 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- THE Process OF Conceptio NDocument21 pagesTHE Process OF Conceptio NGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesHistology of The Female Reproductive Systemdavidatuluku0No ratings yet
- Implantation, Conception, Development of PlacentaDocument40 pagesImplantation, Conception, Development of PlacentaSuad jakalatNo ratings yet
- 5.implantasi & PlasentasiDocument111 pages5.implantasi & PlasentasiherdhikaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and ImplantationDocument3 pagesFertilization and ImplantationTandingco, Olivia Mari H.No ratings yet
- 02 Fertilization & ImplantationDocument24 pages02 Fertilization & ImplantationAugust Ridlof RiwuNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Part 2Document12 pagesReproduction Part 2Yuh moddaNo ratings yet
- Ncm213 Unit 1Document12 pagesNcm213 Unit 1Jan Marsha Marie DomiquelNo ratings yet
- OB 1st SemDocument4 pagesOB 1st SemMai CarbonNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Document37 pagesMaternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Bolangir Biology Assingment Guided by - Swastitapa Kar Prepared by - Sujata Goud Class - Xii Section-A Roll No. - 16Document19 pagesJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Bolangir Biology Assingment Guided by - Swastitapa Kar Prepared by - Sujata Goud Class - Xii Section-A Roll No. - 16preetamgoud225No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityDocument62 pagesUnit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityN. Siva100% (1)
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument32 pagesFetal DevelopmentSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Ferterlization and ImplantationDocument113 pagesFerterlization and Implantationmoreen kipkemoiNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec - Chapter 3Document18 pagesMCN Lec - Chapter 3David LomentigarNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument18 pagesFertilization & ImplantationReshma AjayNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation: Dr. Madhan KumarDocument47 pagesFertilization and Implantation: Dr. Madhan KumarTan DesmondNo ratings yet
- Embriologie 2017Document100 pagesEmbriologie 2017Irina LutcanNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document21 pagesDay 1Ahmed DorghamNo ratings yet
- Fetal and Embryonic DevelopmentDocument29 pagesFetal and Embryonic Developmentshan mackNo ratings yet
- Week 3 The Hormonal CyclesDocument32 pagesWeek 3 The Hormonal CyclesMutai KiprotichNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period For Medical StudentDocument43 pagesEmbryonic Period For Medical StudentMohan Prasad GuptaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy by DR - Jalal (Embryo)Document25 pagesAnatomy by DR - Jalal (Embryo)lorenoh21No ratings yet
- Conception and Fetal DevelopmentDocument22 pagesConception and Fetal DevelopmentChari RivoNo ratings yet
- Femalereprod (Author T.globa)Document56 pagesFemalereprod (Author T.globa)Angelina BulaiNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentDocument9 pages1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentElla DionedaNo ratings yet
- FERTILIZATIONDocument73 pagesFERTILIZATIONSavita Hanamsagar100% (1)
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet
- Revision Ch-Ii (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)Document11 pagesRevision Ch-Ii (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)Sahil GautamNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesFood Chemistry: Sciencedirectratri nurNo ratings yet
- 07-Detection of E. Coli O157H7 and Other Verocytotoxin-Producing E. ColiDocument15 pages07-Detection of E. Coli O157H7 and Other Verocytotoxin-Producing E. ColiNguyễn Hữu ToànNo ratings yet
- Blood DonationDocument24 pagesBlood DonationKris NNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemSubatomoNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Pneumonae: Pathophysiology of CopdDocument1 pageStreptococcus Pneumonae: Pathophysiology of CopdDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Biology Photosynthesis CourseworkDocument7 pagesBiology Photosynthesis Courseworkbdg72wjj100% (2)
- Human Development and LearningDocument36 pagesHuman Development and LearningBahasa KuNo ratings yet
- CVS 217 QaDocument125 pagesCVS 217 QaDoaa Zakaria AliNo ratings yet
- Understanding Nutrition 13th Edition Whitney Test Bank DownloadDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Nutrition 13th Edition Whitney Test Bank DownloadMichael Lozano100% (19)
- Activity Science 9 First QuarterDocument11 pagesActivity Science 9 First QuarterCristian PortugalNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Developmental Cognitive NeuroscienceDocument41 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Developmental Cognitive NeuroscienceNazım Abdurrahim NayırNo ratings yet
- Handwriting Saying - OralDocument1 pageHandwriting Saying - OralEsther FernandezNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange 2 QPDocument6 pagesGas Exchange 2 QPSyakir FahmieNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Human Health and DiseaseDocument11 pagesBiology Project Human Health and Diseasesonidipanshu66No ratings yet
- Natural Regeneration: Don Minore Robert J. LaackeDocument26 pagesNatural Regeneration: Don Minore Robert J. LaackeAngela Marie AlducenteNo ratings yet
- Body System Card SortDocument4 pagesBody System Card Sortapi-567473277No ratings yet
- Descriptions of 16 Arthropods Pests On Potato in South Africa 16may2017Document44 pagesDescriptions of 16 Arthropods Pests On Potato in South Africa 16may2017vishal37256No ratings yet
- Ra 9279Document5 pagesRa 9279lchieSNo ratings yet
- Mold and Mildew QA Understanding Mold in Your HousevnoznDocument3 pagesMold and Mildew QA Understanding Mold in Your Housevnoznliftvision70No ratings yet
- EMBL-EBI Train OnlineDocument19 pagesEMBL-EBI Train OnlineThyagoNo ratings yet
- Stainning 2019Document29 pagesStainning 2019Almoatazbellah AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Saloni Chaudhary 2019659564Document3 pagesAssignment 2 Saloni Chaudhary 2019659564Saloni ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Detection of AdulterationDocument21 pagesDetection of AdulterationDR.U.Srinivasa0% (1)
- GP Dorsal Pain Case June 2021Document5 pagesGP Dorsal Pain Case June 2021Lisa NurhasanahNo ratings yet
- EcoCRM A Recombinant CRM197 Carrier ProteinDocument1 pageEcoCRM A Recombinant CRM197 Carrier ProteinRamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument5 pagesJurnalQorin Diin ArifniNo ratings yet
- 2007 Bakker y Demorouti State of The ArtDocument120 pages2007 Bakker y Demorouti State of The ArtScott SommerNo ratings yet
The Process of Conception
The Process of Conception
Uploaded by
Jobelyn Dela Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views15 pagesWhen sperm swims up through the vagina and fertilizes an egg in the fallopian tube, conception occurs. It happens within hours or days of having unprotected sex. The fertilized egg implants into the uterus after conception, and a pregnancy begins.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWhen sperm swims up through the vagina and fertilizes an egg in the fallopian tube, conception occurs. It happens within hours or days of having unprotected sex. The fertilized egg implants into the uterus after conception, and a pregnancy begins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views15 pagesThe Process of Conception
The Process of Conception
Uploaded by
Jobelyn Dela CruzWhen sperm swims up through the vagina and fertilizes an egg in the fallopian tube, conception occurs. It happens within hours or days of having unprotected sex. The fertilized egg implants into the uterus after conception, and a pregnancy begins.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
The process of
conception
PRESENTED BY: GROUP 4
Objective
• Identify the process of conception.
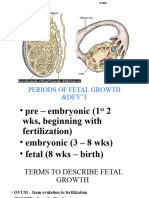
What is the process of conception?
Conception happens when sperm swims up through the vagina
and fertilizes an egg in the fallopian tube. It happens in the hours
or days after you have unprotected sex. After conception, the
fertilized egg implants into the uterus and a pregnancy begins.
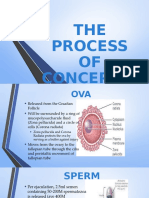
OVA
• Released from the Graafian Follicle
• Will be surrounded by a ring of mucopolysaccharide fluid
(Zona pellucida) and a circle of cells (Corona radiata)
Zona pellucida and Corona Radiata protects the ova by
serving as a buffer against injury.
• Moves from the ovary to the fallopian tube through the cilia
and peristaltic movement of the fallopian tube .
Sperm
•is the male sex cell it has a head, a
short neck, and a thin motile tail. It is
formed through spermatogenesis.
The purpose of a sperm cell is to be
released during sexual intercourse
and eventually meet with an egg cell.
•Per ejaculation, 2.5 ml semen
containing 50-200M spermatozoa is
released (ave 400M
sperm/ejaculation)
•Moves through the cervix, uterus,
and fallopian because of flagella and
uterine contractions.
•Undergoes CAPACITATION ( changes
in the plasma membrane of the
sperm head to reveal sperm binding
receptor sites) before penetrating
into the corona.
•Sperm clusters around coronal cells.
•Will release HYALURONIDASE
( proteolytic enzyme) to dissolve the
corona radiata.
•Sperm penetrates the cell; the cell
membrane of ova changes
composition to become
impenetrable to other sperm.
•Sperm and ova fuse carrying 23 pairs of
chromosomes each
•If sperm carries X sex chromosome paired with
the ovum X chromosome = female zygote
•If sperm carries Y sex chromosome paired with
the ovum X chromosome = male zygote
IMPLANTATION
•Zygote moves from fallopian tube
to uterus
•It will undergo series of mitotic
divisions resulting in a cleavage
formation, 1 in every 22 hours, with
the cleavage division happening 24
hours after fertilization
•Once it reaches the uterus zygote
is now composed of 32-50 balls of
cells termed as MORULA
• In Another 3 – 4 days, morula becomes a
BLASTOCYST consisting of:
An inner cell mass that will become the
future embryo
Trophoblast which will become the placenta
and membranes.
• At approximately 8-10 days after
fertilization, the blastocyst attaches to the
endometrium
Sheds off last residues of corona radiata
zona pellucida
Brushes against endometrium ( apposition)
and settles down
• A slight vaginal bleeding is experienced
during the implantation stage because
capillaries are ruptured by the
implanting trophoblast cells.
EMBRYONIC & FETAL STRUCTURES
DECIDUA – a uterus that has grown thick and vascular
3 areas
Decidua basalis – lies directly under the embryo
( portion where the trophoblast establishes
communication with maternal blood vessel )
Decidua capsularis – the portion that stretches or
encapsulates the surface of the trophoblast
Decidua vera – the remaining portion of the uterine
lining
CHORIONIC VILLI
Miniature villi similar to
probing fingers that appear
on the 11th or 12th day
They begin the formation of
the placenta
Consists of a central core of
connective tissue and fetal
capillaries
2 LAYERS OF
TROPHOBLAST
CELLS
• Syncytiotrophoblast(syncytial layer ) –
produces HCG, somatomammotropin
( human placental lactogen), estrogen,
and progesterone
• Cytotrophoblast (middle or Langhan’s
layer) – functions in early pregnancy to
protect the embryo and fetus from
infection.
You might also like
- Types of Microscopes Comparison Chart 4 Linear Venn Edit Answer KeyDocument2 pagesTypes of Microscopes Comparison Chart 4 Linear Venn Edit Answer KeyKLRSantosNo ratings yet
- CARIOLOGYDocument77 pagesCARIOLOGYteklay100% (3)
- 3 Fertilization and Implantation ProcessDocument83 pages3 Fertilization and Implantation ProcessMarie Cecille Soliven VarillaNo ratings yet
- 4 FertilizationDocument389 pages4 FertilizationAngel Gabriel Fornillos100% (1)
- Fertilization 1 1Document219 pagesFertilization 1 1Edwin TiuNo ratings yet
- Fetus Development From Conception To Birth Part2Document40 pagesFetus Development From Conception To Birth Part2jeremyzucker321No ratings yet
- Placenta UpdatedDocument49 pagesPlacenta UpdatedSaad HasanNo ratings yet
- Three Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pagesThree Stages of Fetal DevelopmentmellowlilydeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Conception and Fetal DevelopmentDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Conception and Fetal DevelopmentRoneshia Michelle Rudolph100% (1)
- Ovulation Fertilisation Division and ImplantationDocument35 pagesOvulation Fertilisation Division and Implantationpsy9kfd4d7No ratings yet
- Embryology - The First WeekDocument51 pagesEmbryology - The First WeekLugembe MasolaNo ratings yet
- 7 Perkembangan EMbrio Manusia PDFDocument57 pages7 Perkembangan EMbrio Manusia PDFFadhilah SiregarNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument3 pagesFertilizationbinsaalimustapha91No ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 - 3 - Goal - Fertilization - Placentation - LactationDocument4 pagesLecture - 2 - 3 - Goal - Fertilization - Placentation - LactationAPOORVA SHANDILYANo ratings yet
- Embryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesDocument13 pagesEmbryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesAudrey100% (5)
- Embryological and Fetal Development:-Fertilization - It Is The Process of Fusion of Spermatozoon With The Mature Ovum. ItDocument19 pagesEmbryological and Fetal Development:-Fertilization - It Is The Process of Fusion of Spermatozoon With The Mature Ovum. ItRaman SamraoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - 3 Placenta and Umbilical Cord: Group 4 MED 114 PresentationDocument69 pagesWeek 1 - 3 Placenta and Umbilical Cord: Group 4 MED 114 PresentationVidur S SinghNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument54 pagesFertilization & ImplantationMarvelousNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document37 pagesLec 2ibrahim.21hm32No ratings yet
- The Growing FetusDocument62 pagesThe Growing Fetuscoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- File 2Document104 pagesFile 2Djo RamNo ratings yet
- FertlizationDocument5 pagesFertlizationgallardo.bettinarose.iNo ratings yet
- Placenta Development.Document6 pagesPlacenta Development.abdurrehman4198No ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument61 pagesFertilization & ImplantationchidimmaNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument60 pagesEmbryologyDaniella AwurumibeNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument18 pagesFertilization & ImplantationRESHMA AJAYNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation-1Document9 pagesFertilization and Implantation-1hussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Practice Teaching On Fertilization and Implantation.Document20 pagesPractice Teaching On Fertilization and Implantation.RDi JNo ratings yet
- The Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 7Document75 pagesThe Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 795kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- 10 Kuliah PLACENTADocument33 pages10 Kuliah PLACENTAAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument42 pagesStages of Fetal DevelopmentKara Ashleigh0% (1)
- Fertilization-fetal Period (1)Document108 pagesFertilization-fetal Period (1)amanamare10No ratings yet
- FERTILIZATIONDocument9 pagesFERTILIZATIONRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentDocument25 pagesModule 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- THE Process OF Conceptio NDocument21 pagesTHE Process OF Conceptio NGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesHistology of The Female Reproductive Systemdavidatuluku0No ratings yet
- Implantation, Conception, Development of PlacentaDocument40 pagesImplantation, Conception, Development of PlacentaSuad jakalatNo ratings yet
- 5.implantasi & PlasentasiDocument111 pages5.implantasi & PlasentasiherdhikaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and ImplantationDocument3 pagesFertilization and ImplantationTandingco, Olivia Mari H.No ratings yet
- 02 Fertilization & ImplantationDocument24 pages02 Fertilization & ImplantationAugust Ridlof RiwuNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Part 2Document12 pagesReproduction Part 2Yuh moddaNo ratings yet
- Ncm213 Unit 1Document12 pagesNcm213 Unit 1Jan Marsha Marie DomiquelNo ratings yet
- OB 1st SemDocument4 pagesOB 1st SemMai CarbonNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Document37 pagesMaternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Bolangir Biology Assingment Guided by - Swastitapa Kar Prepared by - Sujata Goud Class - Xii Section-A Roll No. - 16Document19 pagesJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Bolangir Biology Assingment Guided by - Swastitapa Kar Prepared by - Sujata Goud Class - Xii Section-A Roll No. - 16preetamgoud225No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityDocument62 pagesUnit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityN. Siva100% (1)
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument32 pagesFetal DevelopmentSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Ferterlization and ImplantationDocument113 pagesFerterlization and Implantationmoreen kipkemoiNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec - Chapter 3Document18 pagesMCN Lec - Chapter 3David LomentigarNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument18 pagesFertilization & ImplantationReshma AjayNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation: Dr. Madhan KumarDocument47 pagesFertilization and Implantation: Dr. Madhan KumarTan DesmondNo ratings yet
- Embriologie 2017Document100 pagesEmbriologie 2017Irina LutcanNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document21 pagesDay 1Ahmed DorghamNo ratings yet
- Fetal and Embryonic DevelopmentDocument29 pagesFetal and Embryonic Developmentshan mackNo ratings yet
- Week 3 The Hormonal CyclesDocument32 pagesWeek 3 The Hormonal CyclesMutai KiprotichNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period For Medical StudentDocument43 pagesEmbryonic Period For Medical StudentMohan Prasad GuptaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy by DR - Jalal (Embryo)Document25 pagesAnatomy by DR - Jalal (Embryo)lorenoh21No ratings yet
- Conception and Fetal DevelopmentDocument22 pagesConception and Fetal DevelopmentChari RivoNo ratings yet
- Femalereprod (Author T.globa)Document56 pagesFemalereprod (Author T.globa)Angelina BulaiNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentDocument9 pages1-4 Fertilization & Fetal DevelopmentElla DionedaNo ratings yet
- FERTILIZATIONDocument73 pagesFERTILIZATIONSavita Hanamsagar100% (1)
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet
- Revision Ch-Ii (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)Document11 pagesRevision Ch-Ii (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)Sahil GautamNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesFood Chemistry: Sciencedirectratri nurNo ratings yet
- 07-Detection of E. Coli O157H7 and Other Verocytotoxin-Producing E. ColiDocument15 pages07-Detection of E. Coli O157H7 and Other Verocytotoxin-Producing E. ColiNguyễn Hữu ToànNo ratings yet
- Blood DonationDocument24 pagesBlood DonationKris NNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemSubatomoNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Pneumonae: Pathophysiology of CopdDocument1 pageStreptococcus Pneumonae: Pathophysiology of CopdDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Biology Photosynthesis CourseworkDocument7 pagesBiology Photosynthesis Courseworkbdg72wjj100% (2)
- Human Development and LearningDocument36 pagesHuman Development and LearningBahasa KuNo ratings yet
- CVS 217 QaDocument125 pagesCVS 217 QaDoaa Zakaria AliNo ratings yet
- Understanding Nutrition 13th Edition Whitney Test Bank DownloadDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Nutrition 13th Edition Whitney Test Bank DownloadMichael Lozano100% (19)
- Activity Science 9 First QuarterDocument11 pagesActivity Science 9 First QuarterCristian PortugalNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Developmental Cognitive NeuroscienceDocument41 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Developmental Cognitive NeuroscienceNazım Abdurrahim NayırNo ratings yet
- Handwriting Saying - OralDocument1 pageHandwriting Saying - OralEsther FernandezNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange 2 QPDocument6 pagesGas Exchange 2 QPSyakir FahmieNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Human Health and DiseaseDocument11 pagesBiology Project Human Health and Diseasesonidipanshu66No ratings yet
- Natural Regeneration: Don Minore Robert J. LaackeDocument26 pagesNatural Regeneration: Don Minore Robert J. LaackeAngela Marie AlducenteNo ratings yet
- Body System Card SortDocument4 pagesBody System Card Sortapi-567473277No ratings yet
- Descriptions of 16 Arthropods Pests On Potato in South Africa 16may2017Document44 pagesDescriptions of 16 Arthropods Pests On Potato in South Africa 16may2017vishal37256No ratings yet
- Ra 9279Document5 pagesRa 9279lchieSNo ratings yet
- Mold and Mildew QA Understanding Mold in Your HousevnoznDocument3 pagesMold and Mildew QA Understanding Mold in Your Housevnoznliftvision70No ratings yet
- EMBL-EBI Train OnlineDocument19 pagesEMBL-EBI Train OnlineThyagoNo ratings yet
- Stainning 2019Document29 pagesStainning 2019Almoatazbellah AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Saloni Chaudhary 2019659564Document3 pagesAssignment 2 Saloni Chaudhary 2019659564Saloni ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Detection of AdulterationDocument21 pagesDetection of AdulterationDR.U.Srinivasa0% (1)
- GP Dorsal Pain Case June 2021Document5 pagesGP Dorsal Pain Case June 2021Lisa NurhasanahNo ratings yet
- EcoCRM A Recombinant CRM197 Carrier ProteinDocument1 pageEcoCRM A Recombinant CRM197 Carrier ProteinRamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument5 pagesJurnalQorin Diin ArifniNo ratings yet
- 2007 Bakker y Demorouti State of The ArtDocument120 pages2007 Bakker y Demorouti State of The ArtScott SommerNo ratings yet