Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative Reproduction
Uploaded by
Jane Sandra LimOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative Reproduction
Uploaded by
Jane Sandra LimCopyright:
Available Formats
Asexual reproduction in plants involving the vegetative structures the roots, stems, and leaves.
. Vegetative structures normally play a part in the nutrition & growth of plants. When these parts give rise to new plants, it is called vegetative reproduction or propagation.
Two Types of Vegetative Reproduction Natural
Bulb Corm Tuber Stolon Rhizome
Artificial
Stem Cutting Leaf Cutting Layering Grafting
A bulb is really an underground storehouse and flower factory. Bulbs planted in the autumn will produce beautiful flowers the following spring.
Cross-section
Longitudinal -section
In this red onion cross section, you can clearly see the round tubular leaves develop inside each other. There are two flowering stalks in the middle of this bulb.
Note the prominent basal plate to which the remains of the previous seasons root system are attached.
This tulip bulb, like the onion bulb, has a preformed flower in the center.
Many bulbs reproduce themselves asexually by forming offsets on the basal plate.
Garlic is also a bulb in which axillary buds grow to form many offsets (cloves).
Greenhouse lilies are one of the most difficult crops to grow. The only market is Easter and Easter comes at a different time each year. Many factors such as day length,temperature and sunny days are involved.
The corm is a relatively solid modified stem that has a few fleshy leaves. In the photo, the upside down crocus corm has a black line drawn on it to emphasize the point of attachment of a leaf. The papery tunic on the outside of the crocus corm is the dead petiole (leaf stem) from last years leaf. The crocus flower often pops through the snow in March offering the first sign of spring. To insure another season of flowers, the foliage of all bulbs should be left in place after flowering.
The potato is an underground stem known as a tuber. It is a stem because it has many nodes called eyes with spaces between the eyes known as internodes.
Most potatoes are treated with growth inhibitors to retard their eyes from sprouting during storage.
The sweet potato is not a tuber like a white potato. Instead, it is a tuberous root.
The sweet potato reproduces itself by producing adventitious shoots called slips.
A stolon is a stem that grows sideways and has buds. Usually the stolon grows along the surface of the ground. Stolons can be seen on grasses and strawberries.
A rhizome is a large, fleshy underground stem that runs parallel with the soil. Iris plants grow from rhizomes. These plants can be propagated by cutting the rhizome into pieces to which a piece of foliage is attached.
Ginger, used in cooking, is a rhizome.
In plants such as Bryophyllum (also known as mother of thousands) or the piggyback plant, the leaf supports development of tiny shoot buds. These buds may begin to form roots at their base. As these shoots break off from the original leaf, they fall onto the ground and take root. Cytokinins accumulating at the leaf margins stimulate cell division in the notches to produce these adventitious shoots.
Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
Leaf Cuttings
Many plants, like the African Violet shown here, can be artificially cloned by leaf cuttings.
Hormones, known as IAA (auxin) & Ck (cytokinins) are involved in this process. The callus that forms is a mixture of meristematic and parenchyma cells that do not have a determined fate. It is possible to influence these cells to differentiate into various tissues.
Stem Cuttings
Many species cannot be propagated from leaves alone. The leaf may root but shoots do not form, or form so slowly that it is impractical. Instead, a stem cutting can be made. A stem cutting grows more rapidly than a leaf cutting because auxin and glucose (made by photosynthesis) is contributed from several leaves. Geraniums can be artificially propagated by stem cuttings.
Black raspberry and blackberry plants (among other species) can spread by having arching shoots that ultimately touch-down onto the soil. The rubbing of the stem on the soil and the horizontal position of the stem along the soil surface cause auxins to build up there. The auxins induce root formation.
The developing roots produce lots of cytokinins. These chemicals induce more shoot formation. The tangle of arching shoots & tip rooting result in a very dense briar patch without the spines.
Grafting is the process of removing a stem or bud from one plant and joining it permanently to the stem of a closely related plant. The part of the plant providing the roots is called the stock. The added piece of plant material is the scion.
The cambium layers (growing region) of the scion and stock must be held in close contact. Grafts are usually held together with a material to help prevent water loss. After awhile, the cambiums of the 2 pieces form new xylem and phloem which grow together and connect the scion with the stock. Stock nourishes scion; scion keeps its own characteristics.
You might also like
- Celery Osmosis LabDocument3 pagesCelery Osmosis Labmommy72100% (1)
- 1.0 Fe - 202201 Mpob7113-202201f0712Document15 pages1.0 Fe - 202201 Mpob7113-202201f0712Jessy SimonNo ratings yet
- Allocation Translocation and Partitioning of PhotoassimilatesDocument69 pagesAllocation Translocation and Partitioning of Photoassimilatesfitri100% (2)
- Translocation of SolutesDocument22 pagesTranslocation of Solutesmanojtbgri5793No ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument62 pagesPlant ReproductionAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- 4th Grading Classification of PlantsDocument57 pages4th Grading Classification of PlantsAlea DuqueNo ratings yet
- Soil Structure and FabricDocument33 pagesSoil Structure and FabricVigknaraja JagathesanNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 10 Organic Matter DecompositionDocument3 pagesEXERCISE 10 Organic Matter DecompositionKobe Conrad AbelleraNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 8 How Do Organism ReproduceDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 8 How Do Organism ReproduceAVIRUP DASNo ratings yet
- Soil ReactionDocument30 pagesSoil ReactionVetri Vel PrakashNo ratings yet
- Sexual Propagation in Plants: Most Higher Plants Start Their Life As Vegetative Prop UnitDocument41 pagesSexual Propagation in Plants: Most Higher Plants Start Their Life As Vegetative Prop UnitDoni DarimastNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument15 pagesClassification of PlantsKielNo ratings yet
- Soil Science Sample Ale Review Questions 081408Document53 pagesSoil Science Sample Ale Review Questions 081408Kay Ponilas100% (1)
- The Effect of Depth On Onion Seed GerminationDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Depth On Onion Seed GerminationBurhan RiazNo ratings yet
- 4-Plant Structure and FunctionDocument7 pages4-Plant Structure and FunctionfebrimetrinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Chemistry SPECTRUM Lecture 1Document18 pagesPrinciples of Chemistry SPECTRUM Lecture 1Mei Chin LyeNo ratings yet
- Field Problems of Important CropsDocument70 pagesField Problems of Important CropsAnuragBhatnagar100% (2)
- Control and Coordination NotesDocument5 pagesControl and Coordination NotesNyra HillsNo ratings yet
- Flowering PlantsDocument43 pagesFlowering Plantskingbanakon100% (1)
- Latihan Soal Metode Ilmiah Beserta Kunci JawabannyaDocument4 pagesLatihan Soal Metode Ilmiah Beserta Kunci JawabannyaTiaNo ratings yet
- All About FlowersDocument43 pagesAll About FlowersjeffinjoffiNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower To FruitDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Pollination: Flower To FruitcesarNo ratings yet
- Adaptations in Plants - Terrestrial HabitatDocument20 pagesAdaptations in Plants - Terrestrial Habitatatbatcha batNo ratings yet
- Growth Response in PlantsDocument31 pagesGrowth Response in PlantsShahab Akhtar100% (1)
- Major Classification of PlantsDocument19 pagesMajor Classification of PlantsJhoy Angeles PinlacNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument40 pagesLecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- Photoperiodism Powerpoint EduDocument12 pagesPhotoperiodism Powerpoint EduAlabi FauziatBulalaNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination Lab WorkDocument3 pagesSeed Germination Lab Workashwathimahendran100% (1)
- Chapter 7: Energy and Ecosystems: SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 7: Energy and Ecosystems: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Digestion - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesIGCSE Digestion - Print - Quizizzjv peridoNo ratings yet
- Plant FamiliesDocument2 pagesPlant FamiliesZahid Mehmood100% (1)
- 01-g Cell Fractionation - Definition, Steps MethodsDocument6 pages01-g Cell Fractionation - Definition, Steps MethodsCaffe AncaeusNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDocument18 pagesClass 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDianna josephNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method Test Study Guide2Document4 pagesScientific Method Test Study Guide2Gabriel TaylorNo ratings yet
- Moisture Stress of PlantDocument30 pagesMoisture Stress of PlantHassen100% (1)
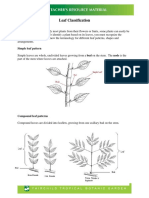
- Leaf ClassificationDocument4 pagesLeaf ClassificationSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Document7 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Jann LarNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument11 pagesAsexual ReproductionKoushik KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Green Algae - ChlorophytaDocument16 pagesGreen Algae - ChlorophytaAbhishek Isaac MathewNo ratings yet
- The Continuity of LifeDocument29 pagesThe Continuity of LifeI Gede MahardikaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionsarNo ratings yet
- Plants Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesPlants Reproduction and DevelopmentAlwìn GarciaNo ratings yet
- CRP 101 Lecture No. 13Document10 pagesCRP 101 Lecture No. 13AnandKuttiyanNo ratings yet
- Soil Structure, Density, and Porosity: Laboratory #4Document32 pagesSoil Structure, Density, and Porosity: Laboratory #4ZevanyaRolandTualakaNo ratings yet
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- Botany Lec 2-truePLANT SYSTEMATICSDocument105 pagesBotany Lec 2-truePLANT SYSTEMATICSDANIEL LANCE NEVADONo ratings yet
- Different Modes of Fossil PreservationDocument2 pagesDifferent Modes of Fossil Preservationrajat100% (2)
- 8384 ST PDFDocument20 pages8384 ST PDFJohn Dave Francisco100% (1)
- Running Head: Effect of Magnesium Chloride On Seed Germination 1Document9 pagesRunning Head: Effect of Magnesium Chloride On Seed Germination 1George AbuorNo ratings yet
- Physiological Disorders in Fruit CropsDocument8 pagesPhysiological Disorders in Fruit CropsMohamed BahgatNo ratings yet
- The Factors That Affect Plant Growth Can Be Classified As Genetic or EnvironmentalDocument16 pagesThe Factors That Affect Plant Growth Can Be Classified As Genetic or EnvironmentalshadoworacleNo ratings yet
- SalinityDocument5 pagesSalinityhemant8988100% (1)
- Plant Tissues: PBOT 111: Lecture 5Document42 pagesPlant Tissues: PBOT 111: Lecture 5Cham RosarioNo ratings yet
- Bryophytes To Gymnosperms PDFDocument101 pagesBryophytes To Gymnosperms PDFRyan Merza100% (1)
- FRUITS SEEDS and GERMINATION ReviewerDocument4 pagesFRUITS SEEDS and GERMINATION ReviewerRona Mae JavateNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet - Docx-2Document6 pagesRevision Sheet - Docx-2mofid monirNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertility Management TechniqueDocument74 pagesSoil Fertility Management TechniqueslimsimoNo ratings yet
- Consortium For Educational Communication: Dr. Abdul Rashid DarDocument12 pagesConsortium For Educational Communication: Dr. Abdul Rashid DarChoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument8 pagesIntroductionBanana LatteNo ratings yet
- Basic Botany 2Document92 pagesBasic Botany 2Michael OduorNo ratings yet
- The Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Senescence Dan Absisi Lia MociDocument19 pagesSenescence Dan Absisi Lia MociNahla FaridaNo ratings yet
- Second Term Science 5 Modules 5-8Document18 pagesSecond Term Science 5 Modules 5-8Kathleen FernandezNo ratings yet
- SQP Science Vii Kvs Ro LkoDocument25 pagesSQP Science Vii Kvs Ro Lkotharishr@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- 1 Reproduction in OrganismsDocument9 pages1 Reproduction in OrganismsTanya PasrichaNo ratings yet
- Gene BanksDocument13 pagesGene BanksHARSHIT MAHESHWARINo ratings yet
- Tea ImprovementDocument58 pagesTea ImprovementSanthosh K. V. ThoshNo ratings yet
- Report HANSRAREDocument46 pagesReport HANSRAREfaco260869No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 7 - QUARTER 2 - WEEK 5 - WORKSHEET 1 - Vegetative PropagationDocument2 pagesSCIENCE 7 - QUARTER 2 - WEEK 5 - WORKSHEET 1 - Vegetative Propagationjaychel Delos reyes100% (1)
- Effect of Exogenous Hormone and Rooting Medium On Cutting Propagation of Golden Camellia (Camellia Impressinervis)Document5 pagesEffect of Exogenous Hormone and Rooting Medium On Cutting Propagation of Golden Camellia (Camellia Impressinervis)Shailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 6 Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 6 Asexual and Sexual ReproductionPinky Vitalicio Seña100% (1)
- Unit 3Document11 pagesUnit 3gachatoqaNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument30 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproducethottiNo ratings yet
- TLE 101 - Unit 7 - Fruit Tree Crop ProductionDocument48 pagesTLE 101 - Unit 7 - Fruit Tree Crop ProductionAGNES TUBOLANo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument16 pagesAgricultureUmar MuhammadNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument7 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDan Pacyao Miras100% (1)
- 4.1 Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument17 pages4.1 Sexual and Asexual ReproductionRoza Roza100% (1)
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 Subtopic 1.3 Growth CurvesDocument12 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 1 Subtopic 1.3 Growth CurvesSafwan YusufNo ratings yet
- G5 Q2W5 DLL SCIENCE MELCsDocument10 pagesG5 Q2W5 DLL SCIENCE MELCsma cristina cabaya cunananNo ratings yet
- Dioscorea L. (PROSEA) - PlantUse EnglishDocument29 pagesDioscorea L. (PROSEA) - PlantUse Englishfortuna_dNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Powerpoint SlidesDocument55 pagesReproduction in Plants Powerpoint SlidesTay Kai xin (Ahs)No ratings yet
- Types of Sexual ReproductionDocument22 pagesTypes of Sexual ReproductionAndjelyn AbalosNo ratings yet
- Science Artificial Propagation Essay Agung 9Document3 pagesScience Artificial Propagation Essay Agung 9api-197385195No ratings yet
- 4.02 Plant PropagationDocument38 pages4.02 Plant Propagationjayson sorianoNo ratings yet
- GEN BIO 2 Week 1aDocument3 pagesGEN BIO 2 Week 1aNina Reca OmisolNo ratings yet
- MScHorticulture SYLLABUSDocument253 pagesMScHorticulture SYLLABUSArun Krishnan MNo ratings yet
- Marcos Thesis ProposalDocument13 pagesMarcos Thesis Proposaljan ray aribuaboNo ratings yet
- Jojoba (Simmondsia Chinensis Link Schnider) : Waseem Haider (BAGF16E247) Israr Ahmed (BAGF16E221)Document28 pagesJojoba (Simmondsia Chinensis Link Schnider) : Waseem Haider (BAGF16E247) Israr Ahmed (BAGF16E221)Waseem HaiderNo ratings yet
- Banana Tissue Culture Research Papers PDFDocument8 pagesBanana Tissue Culture Research Papers PDFgz7vhnpe100% (1)
- Asexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFDocument6 pagesAsexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFLebron DoggiNo ratings yet