Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Cambridge IX Chem Unit 10.2 Redox Reactions
1 Cambridge IX Chem Unit 10.2 Redox Reactions
Uploaded by
Srihaan Mathur0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views32 pagesThe document provides information about redox reactions through examples and definitions. It discusses two examples of redox reactions where aluminium reacts with zinc oxide and carbon monoxide reacts with iron(III) oxide. It defines redox reactions as oxidation-reduction reactions involving the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions. The document also provides definitions and explanations of key terms related to redox reactions including oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents.
Original Description:
Original Title
PPT 1 Cambridge IX Chem Unit 10.2 Redox Reactions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information about redox reactions through examples and definitions. It discusses two examples of redox reactions where aluminium reacts with zinc oxide and carbon monoxide reacts with iron(III) oxide. It defines redox reactions as oxidation-reduction reactions involving the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions. The document also provides definitions and explanations of key terms related to redox reactions including oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views32 pages1 Cambridge IX Chem Unit 10.2 Redox Reactions
1 Cambridge IX Chem Unit 10.2 Redox Reactions
Uploaded by
Srihaan MathurThe document provides information about redox reactions through examples and definitions. It discusses two examples of redox reactions where aluminium reacts with zinc oxide and carbon monoxide reacts with iron(III) oxide. It defines redox reactions as oxidation-reduction reactions involving the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions. The document also provides definitions and explanations of key terms related to redox reactions including oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 32
Subject: Chemistry
Topic: Redox reactions
Standard: IX
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 1Of 32
Quick Review time - 90 secs
Aluminium reacts with zinc oxide:
aluminium + zinc oxide → aluminium oxide + zinc
Name:
1. which substance is oxidised
2. which substance acts as an oxidising agent
Carbon monoxide reacts with iron(III) oxide:
carbon monoxide + iron(III) oxide → carbon dioxide + iron
Name:
3. which substance is reduced
4. which substance acts as a reducing agent
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 2 Of 32
Quick Review time - Answers
1. Aluminium is oxidised because it gains oxygen to
form aluminium oxide.
2. Zinc oxide acts as an oxidising agent because it
can oxidise aluminium.
3. Iron(III) oxide is reduced because it loses oxygen
to form iron.
4. Carbon monoxide acts as a reducing agent
because it can reduce iron(III) oxide.
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 3 Of 32
Memory Aid
LEO OIL
GRE RIG
• L osing • O xidation
• E lectrons • Is
• O xidation • L oss of electrons
• G ains • R eduction
• E lectrons • Is
• R educed • G ain of electrons
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 4 Of 32
Redox Reactions
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 5 Of 32
Redox – Electron Transfer
• Redox Reaction = Oxidation-Reduction Reaction
• During Oxidation, the oxidation numbers of the
oxidised species goes up.
• During Reduction, the oxidation numbers of the
reduced species goes down.
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 6 Of 32
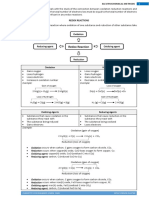
REDOX REACTIONS
An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction is a type of
chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons
between two atoms or ions.
OR
An oxidation-reduction reaction is any
chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of a
molecule, atom, or ion changes by gaining or losing an
electron.
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 7 Of 32
IMPORTANT TERMS
Oxidised: A substance that gains oxygen or loses electrons during a
reaction.
Reduced : A substance that loses oxygen or gains electrons during a
reaction.
Reducing agent : An element or compound that will remove oxygen
from the other substance.
Oxidising agent : An element or compound that will add oxygen to
another substance
Oxidation: is the increase in oxidation state of an atom or ion.
Reduction: is the decrease in oxidation state of an atom or ion.
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 8 Of 32
Quick Recall -90 seconds
Zinc reacts with copper(II) sulfate solution:
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Name, in terms of electrons, which substance is oxidised.
Zinc is oxidised because zinc atoms lose electrons to form zinc
ions, Zn2+.
Chlorine reacts with sodium bromide solution:
Cl2 + 2NaBr → 2Cl- + Br2
Name, in terms of electrons, which substance is reduced.
Chlorine is reduced because it gains electrons to form chloride
ions, Cl-.
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 9 Of 32
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
1. The oxidation number of an uncombined element is
zero.
2. The oxidation number of an element in a simple
monoatomic ion is the charge on the ion.
3. The oxidation number of hydrogen is usually +1.
4. The oxidation number of oxygen is usually -2.
5. The sum of oxidation numbers in a compound is
zero.
6. The sum of oxidation numbers in a compound ion
(molecular ion) is the charge on the ion.
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 10 Of 32
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
• The oxidation number of an atom is zero in a neutral substance
that contains atoms of only one element. For example the atoms
in O2, O3, P4, S8, and aluminum metal all have an oxidation
number of 0.
• The oxidation number of simple ions is equal to the charge on
the ion. For example the oxidation number of sodium in the
Na+ ion is +1, and the oxidation number of chlorine in the
Cl- ion is -1.
• The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 for example in CH4, NH3,
H2O, and HCl.
• Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2. For example in
SO2, CO2, and NO2 .
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 11 Of 32
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
The sum of the oxidation numbers in a neutral
compound is zero.
H2O: 2(+1) + (-2) = 0
The sum of the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is
equal to the charge on the ion.
The oxidation number of the sulfur atom in the SO42- ion
must be +6, for example, because the sum of the oxidation
numbers of the atoms in this ion must equal -2.
SO42-: (+6) + 4(-2) = -2
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 12 Of 32
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
In assigning oxidation states always go with the elements in the
compound you are sure off and then work out the rest.
Elements you can be sure of:
Group 1 metals +1
Group 2 metals +2
Aluminium +3
Group 7 elements (when not combined with oxygen) -1
Oxygen (except in peroxides) -2
If oxidation states change during a reaction it is a redox reaction.
Oxidation leads to an increase in oxidation number and reduction
leads to a decrease in oxidation number
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 13 Of 32
Redox Reactions–Oxidation Numbers
Redox reaction - electrons are transferred between reactants
• The magnesium atom changes to a magnesium ion by losing 2
electrons, and is thus oxidised
• The sulfur atom is changed to a sulfide ion by gaining 2
electrons, and is thus reduced.
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 14 Of 32
Redox Reactions–Oxidation Numbers
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 15 Of 32
Redox Reactions–Oxidation Numbers
Magnesium metal, lost electrons to form Mg2+ ions when it reacted
with oxygen.
By convention, the element or compound that gained these electrons
was said to undergo reduction.
In this case, O2 molecules were said to be reduced to form O2- ions.
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 16 Of 32
Redox Reactions–Oxidation Numbers
Cu(s) + 2 Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2 Ag(s)
The reaction involves the net transfer of electrons
from copper metal to Ag+ ions to produce whiskers
of silver metal that grow out from the copper wire
and Cu2+ ions.
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 17 Of 32
Redox Reactions–Oxidation Numbers
+4 0 +2 +1
CO2 is reduced when it reacts with hydrogen because
the oxidation number of the carbon decreases from +4
to +2.
Hydrogen is oxidised in this reaction because its
oxidation number increases from 0 to +1.
Video 4: https://www.youtube.com/embed/iSAwDJTLIKY
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 18 Of 32
Oxidation Numbers
Another method to write oxidation numbers is by using
Roman numerals
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 19 Of 32
Oxidation Numbers
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 20 Of 32
Oxidation Numbers
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 21 Of 32
QUIZ
Complete the following table:
Formula Element Oxidation Element Oxidation
number number
KCl K Cl
NH3 N H
NO2 N O
H2O H O
MnCl2 Mn Cl
FeO Fe O
Fe2O3 Fe O
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 22 Of 32
QUIZ
Complete the following table:
Formula Element Oxidation Element Oxidation
number number
KCl K +1 Cl -1
NH3 N -3 H +1
NO2 N +4 O -2
H 2O H +1 O -2
MnCl2 Mn +2 Cl -1
FeO Fe +2 O -2
Fe2O3 Fe +3 O -2
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 23 Of 32
Reducing Agent and Oxidizing Agent
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 24 Of 32
Oxidising and Reducing Agents
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 25 Of 32
Potassium Iodide
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 26 Of 32
Oxidising and Reducing Agents
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 27 Of 32
Quiz
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 28 Of 32
1. When electrons are gained:
A. Oxidation
B. Reduction
2. When electrons are lost:
A. Oxidation
B. Reduction
3. Another name for oxidation-reduction reaction is:
A. Neutralisation
B. Redox
4. When oxygen is removed:
A. Oxidation
B. Reduction
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 29 Of 32
5. Substance that loses electrons:
A. Oxidising agent
B. Reducing agent
6. Another name for charge:
A. Oxidation state
B. Reduction state
7. Substance that gains electrons:
A. Oxidising agent
B. Reducing agent
8. When oxygen is added:
A. Oxidation
B. Reduction
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 30 Of 32
Answers to the Quiz
1. Reduction
2. Oxidation
3. Redox
4. Reduction
5. Reducing agent
6. Oxidation state
7. Oxidising agent
8. Oxidation
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 30 Of 32
3-2-1
Instruct the learners:
to write 3 things they learned today,
2 interesting facts they learnt about redox reactions,
1 thing they still have a question about, in their
notebook.
Randomly call out learners and ask them to share what
they have written. Clarify any doubts
Cambridge/2122 Redox reactions 32 Of 32
You might also like
- FWD Analysis Jaipur-Reengus Report RevisedDocument69 pagesFWD Analysis Jaipur-Reengus Report RevisedPremNo ratings yet
- Siemens Gas Turbine For Mechanical Drive SGT-400Document4 pagesSiemens Gas Turbine For Mechanical Drive SGT-400arm1346No ratings yet
- Ch. 7 redox-22-23-IGDocument16 pagesCh. 7 redox-22-23-IGvfdfdNo ratings yet
- REDOKSDocument72 pagesREDOKSShirley Simon100% (1)
- Chapter 20 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDocument43 pagesChapter 20 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsTegar MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 11.4A Redox Reaction and ElectrochemistryDocument98 pages11.4A Redox Reaction and ElectrochemistryЕлнур ИкимбаевNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument92 pagesRedoxMollel TajiriNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions Grade 11Document69 pagesRedox Reactions Grade 11RahulNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument20 pagesRedox ReactionsChavi PundirNo ratings yet
- REDOX Reaction: CombustionDocument13 pagesREDOX Reaction: Combustionanwar9602020No ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document22 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Ck OoiNo ratings yet
- Oxidation AND ReductionDocument60 pagesOxidation AND ReductionSofea Alya SuhaiziNo ratings yet
- REDOX REACTIONS NOTES-Unit 8Document13 pagesREDOX REACTIONS NOTES-Unit 8muralidharhegdenorthsquareNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument14 pagesOxidation and ReductionAsik ShabickNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument80 pagesRedox ReactionsShashwatNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction ReactionsDocument33 pagesOxidation and Reduction ReactionsAl Christian YaboNo ratings yet
- Unit 15: Redox: RED Reduction OX OxidationDocument18 pagesUnit 15: Redox: RED Reduction OX Oxidationoliver abramsNo ratings yet
- Redox ChemistryDocument5 pagesRedox Chemistryibrahim ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chap 20 RedoxDocument45 pagesChap 20 RedoxJimini KimNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reaction Mechanism: Prepared By: Ms - Sumina IbrahimDocument17 pagesInorganic Reaction Mechanism: Prepared By: Ms - Sumina IbrahimTuba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Medical ChemistryDocument61 pagesLecture 4 Medical ChemistryCypher Soth ViNo ratings yet
- 1.redox IntroDocument20 pages1.redox Introshuhan.yeNo ratings yet
- Redox Titration KDBDocument45 pagesRedox Titration KDBKiranNo ratings yet
- 12 Topic 9 Reduction and OxidationDocument94 pages12 Topic 9 Reduction and OxidationyourstrulyrahulNo ratings yet
- 8oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument50 pages8oxidation Reduction ReactionsMohamed AlQallafNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reductionreactions 100429191952 Phpapp01Document24 pagesOxidation Reductionreactions 100429191952 Phpapp01Anna AnnaNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument24 pagesRedox ReactionBatrisyia RozhanNo ratings yet
- chm022L Redox LecDocument39 pageschm022L Redox LeckeishasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Oxidation & Reduction: Redox ReactionsDocument5 pagesOxidation & Reduction: Redox ReactionsVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- C12 Notes S RedoxDocument40 pagesC12 Notes S RedoxSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Topic 6-L6-RedoxDocument23 pagesTopic 6-L6-Redoxhaotongxu14No ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument31 pagesRedox ReactionEmaan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationDocument5 pagesChemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Document18 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Aidah Amir100% (2)
- Introductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Document26 pagesIntroductory Chemistry - SCH0201 - Lec10Ayanthi ShashikalaNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa FauziahDocument28 pagesExplanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa Fauziahsyifa fauziahNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions Cycle 9 (Autosaved)Document31 pagesRedox Reactions Cycle 9 (Autosaved)Azain CardenasNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction - Chemical Reactions in Which Both Oxidation and Reduction Occur SimultaneouslyDocument17 pagesRedox Reaction - Chemical Reactions in Which Both Oxidation and Reduction Occur SimultaneouslyJoanne SiaNo ratings yet
- REDOXDocument67 pagesREDOXLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- C5 ElectrochemistryDocument87 pagesC5 ElectrochemistryLily Anth100% (1)
- 5olasa 2022Document11 pages5olasa 2022volcano netNo ratings yet
- F5C1 Redox EquilibriumDocument15 pagesF5C1 Redox EquilibriumthilagaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument28 pagesOxidation and ReductionCharlene LowNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicDocument60 pagesClass XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicBaljit Singh100% (1)
- Chemistry Chapter 8.ABakshDocument10 pagesChemistry Chapter 8.ABakshNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3oxidation and ReductionDocument7 pagesChapter 3oxidation and ReductionLaven LeiNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrochemical MethodsDocument17 pages1 Electrochemical MethodsJames BombitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Electrochemistry - Redox ReactionDocument37 pagesChapter 7 Electrochemistry - Redox ReactionZuhailimuna MudaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReductionDocument47 pagesOxidation ReductionAbdulraqeb AlawadhiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry RedoxDocument57 pagesElectrochemistry RedoxMontes Arianne A.No ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Introduction To Redox Reactions: Redox Chemistry and ElectrochemistryDocument100 pagesLesson 1-Introduction To Redox Reactions: Redox Chemistry and ElectrochemistryZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document17 pagesChapter 2Mustafidzul MustaphaNo ratings yet
- GeneralChemistry 11Document81 pagesGeneralChemistry 11NAM TRƯƠNG HOÀINo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ElectrochemistryDocument74 pagesChapter 4 - Electrochemistryhoboslayer97No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - F4Document5 pagesElectrochemistry - F4felixNo ratings yet
- Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox Reactions)Document39 pagesOxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox Reactions)Thea RamosNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument2 pagesRedox Reactionschong56No ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Revision Book 2017 2018 Chapter 8Document7 pages11 Chemistry Revision Book 2017 2018 Chapter 8Gyani ChachaNo ratings yet
- Redox ChemistryDocument20 pagesRedox ChemistryNisidini JasingheNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions Part 1Document46 pagesRedox Reactions Part 1Adrian ChombaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Matlab Simulation SemiconductorsDocument10 pagesMatlab Simulation SemiconductorsGeorge VartanovNo ratings yet
- Interactive Water FountainsDocument4 pagesInteractive Water FountainsmohammudpNo ratings yet
- Buckling PinDocument6 pagesBuckling Pinwsjouri2510No ratings yet
- Galvanic Series (Electrochemical Series)Document3 pagesGalvanic Series (Electrochemical Series)chockanan suwanprasertNo ratings yet
- Impedance Control: Robotics 2Document16 pagesImpedance Control: Robotics 2Karen ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Microemulsion Based Transdermal Drug Delivery of Tea Tree OilDocument8 pagesMicroemulsion Based Transdermal Drug Delivery of Tea Tree Oiladhi wilaksonoNo ratings yet
- Manual For Design of Concrete Structures ICE 2002 PDFDocument95 pagesManual For Design of Concrete Structures ICE 2002 PDFsitheeqNo ratings yet
- Han 2016Document20 pagesHan 2016Sourabh GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Hook TheoryDocument25 pagesHook TheoryNyu123456No ratings yet
- TransmissibilityDocument15 pagesTransmissibilityHimanshuNo ratings yet
- Describing Weather B 12-22Document10 pagesDescribing Weather B 12-22Mita Isnaini HarahapNo ratings yet
- Wilsons LTD - Copper and Copper Alloys Introduction To Copper and Its Alloys - 68Document5 pagesWilsons LTD - Copper and Copper Alloys Introduction To Copper and Its Alloys - 68Juan BonottiNo ratings yet
- Civil - Highway Lab Manual - 2018Document17 pagesCivil - Highway Lab Manual - 2018Altamash NadimallaNo ratings yet
- Explain The Concepts Behind Bradford Method in Measuring Protein Concentration in A SolutionDocument4 pagesExplain The Concepts Behind Bradford Method in Measuring Protein Concentration in A SolutionRiri ShinNo ratings yet
- Plate Heat Exchanger: Applications Standard DesignDocument2 pagesPlate Heat Exchanger: Applications Standard DesignjuguenriNo ratings yet
- The Duality of Matter and WavesDocument4 pagesThe Duality of Matter and WavesNullpunktsenergie100% (5)
- MANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Prof. Suvranu deDocument30 pagesMANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Prof. Suvranu deIsrar UllahNo ratings yet
- Parul University: Subject: PHYSICS Semester: I - Academic Year 2017-18Document1 pageParul University: Subject: PHYSICS Semester: I - Academic Year 2017-18Trilok AkhaniNo ratings yet
- The Tides PhenomenonDocument155 pagesThe Tides PhenomenonDavid Hernández DomínguezNo ratings yet
- Curtain WallDocument9 pagesCurtain WallHansanee MagoNo ratings yet
- Biochem PH and BuffersDocument9 pagesBiochem PH and BuffersKurtNo ratings yet
- Kalrez Semicon Selection GuideDocument4 pagesKalrez Semicon Selection GuideSofwat SanjayaNo ratings yet
- VIP 1 Thermodynamics ExamDocument10 pagesVIP 1 Thermodynamics ExamJaybee LabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Introduction2Document78 pagesChapter 2 Introduction2Omer IkhlasNo ratings yet
- Particle CharacterizationDocument27 pagesParticle CharacterizationDANIELA HUERFANO BARRERANo ratings yet
- Science 10 LAS Q4Document73 pagesScience 10 LAS Q4Nenbon NatividadNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 4.36: X Q KL T T yDocument7 pagesPROBLEM 4.36: X Q KL T T yAnish PalNo ratings yet
- Niels BohrDocument2 pagesNiels Bohrmr personalNo ratings yet