Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hvac Unit
Hvac Unit
Uploaded by
JanakiramCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pipe Fittings Surface AreaDocument1 pagePipe Fittings Surface AreaB Girish82% (57)
- Air Curtain Guide DesignDocument8 pagesAir Curtain Guide Designanton7786No ratings yet
- JIS H 3300 - 2006 Copper Andcopper Alloy Seamless Pipes and TubesDocument35 pagesJIS H 3300 - 2006 Copper Andcopper Alloy Seamless Pipes and TubesTRONGHAI266100% (2)
- Chapter 34Document7 pagesChapter 34loise0% (1)
- Ventilation and Air-ConditioningDocument93 pagesVentilation and Air-ConditioningEmmanuel P Dube100% (2)
- 1-Air Handling and Distribution SystemsDocument32 pages1-Air Handling and Distribution SystemsKhalidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Ku Illyani Nadia BT Ku Aziz 2011478072 BCM5BDocument3 pagesTutorial - Ku Illyani Nadia BT Ku Aziz 2011478072 BCM5Bnadia0109No ratings yet
- VentilationDocument28 pagesVentilationTannum Negi0% (1)
- Ventilation SystemDocument22 pagesVentilation SystemPrakriti Goel100% (3)
- Air Distribution Sys DesignDocument6 pagesAir Distribution Sys DesignpauloNo ratings yet
- Air Distribution Sytems DesignDocument6 pagesAir Distribution Sytems Designvalentinlupascu33No ratings yet
- Air Distribution System Design: Good Duct Design Increases EfficiencyDocument6 pagesAir Distribution System Design: Good Duct Design Increases Efficiencyharoub_nasNo ratings yet
- 2 Out Ts Omm HVC Acu 3832 02 210613950 Omm of Air Curtain For BRTDocument77 pages2 Out Ts Omm HVC Acu 3832 02 210613950 Omm of Air Curtain For BRTMohamed AbdelmoneimNo ratings yet
- An Air Handling UnitDocument4 pagesAn Air Handling UnitDono WayNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: & Its SystemDocument14 pagesVentilation: & Its SystemTangha Muklom KunchaNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: & Its SystemDocument14 pagesVentilation: & Its SystemTangha Muklom KunchaNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: MDM Nurul Aini/Qus 3206Document22 pagesVentilation: MDM Nurul Aini/Qus 3206Anisha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Planning OlDocument97 pagesVentilation Planning Olenjam yasankNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Regulations On Design and Installation of Hvac SystemDocument12 pagesMechanical Regulations On Design and Installation of Hvac SystemJohn ApeladoNo ratings yet
- Ventilation SystemsDocument5 pagesVentilation SystemsnualdinNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: Types of SystemsDocument10 pagesVentilation: Types of SystemsanangwahjudiNo ratings yet
- AERECO-Demand Controlled Mechanical Extract VentilationDocument12 pagesAERECO-Demand Controlled Mechanical Extract VentilationVali GheorghisorNo ratings yet
- Air Distribution System Equipment's and Duct DesignDocument36 pagesAir Distribution System Equipment's and Duct DesignfekadeNo ratings yet
- Air Distribution SystemDocument29 pagesAir Distribution System20-06115No ratings yet
- Tutorial - Underfloor Air-ConditioningDocument8 pagesTutorial - Underfloor Air-ConditioningJasper_HVACNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY #4 - Castro, Xaira Alexa Mari L.Document19 pagesACTIVITY #4 - Castro, Xaira Alexa Mari L.Xaira Alexa Mari CastroNo ratings yet
- Dilution VentilationDocument4 pagesDilution VentilationUthman OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- ISOVERDocument35 pagesISOVERMadhu RaghuNo ratings yet
- What Is Air ConditioningDocument16 pagesWhat Is Air ConditioningCheeragNo ratings yet
- 10 - Air Distribution SystemDocument7 pages10 - Air Distribution SystemZeeshan HasanNo ratings yet
- Offshore Hvac DesignDocument6 pagesOffshore Hvac DesignAndrew Alex100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Duct Design and SealingDocument14 pagesChapter 8 Duct Design and SealingMiguel FloresNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Piping-Economic PipingDocument5 pagesCompressed Air Piping-Economic PipingMOHAMMAD ASIFNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document7 pagesExp 2Philip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- HVAC - Part-1Document63 pagesHVAC - Part-1ShubhaNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Air Filter System OptimizationDocument10 pagesGas Turbine Air Filter System Optimizationsevero97100% (2)
- Designs That Work Hot DryMixed Dry Climate AlbuquerquePr..Document8 pagesDesigns That Work Hot DryMixed Dry Climate AlbuquerquePr..Kosar MuradiNo ratings yet
- Design Guide - Humidity ControlDocument2 pagesDesign Guide - Humidity Controldzul92100% (1)
- Mechanical Ventilation Systems Are Frequently Applied To Commercial BuildingsDocument9 pagesMechanical Ventilation Systems Are Frequently Applied To Commercial BuildingsIbn Shaffee IVNo ratings yet
- EEMs To Consider 2011-09-15Document12 pagesEEMs To Consider 2011-09-15razali131266No ratings yet
- HVAC SystemDocument5 pagesHVAC SystemMrinal Kanti RoyNo ratings yet
- CR MOD 17 Heating and Cooling09Document36 pagesCR MOD 17 Heating and Cooling09MMMOH200No ratings yet
- Heat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (Hvac)Document27 pagesHeat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (Hvac)satishNo ratings yet
- Natural Ventilation PDFDocument7 pagesNatural Ventilation PDFDebasis DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Reading Lecture 5-6 Mechanical VentilationDocument13 pagesReading Lecture 5-6 Mechanical VentilationMd. Rizwan Hasan Kabir ShovonNo ratings yet
- Draw-Through or Blow-Through: Components of Air Handling UnitDocument23 pagesDraw-Through or Blow-Through: Components of Air Handling Unityousuff0% (1)
- Air HandlerDocument15 pagesAir HandlerShashank BijweNo ratings yet
- RM379 Pleura UK PASB2 PG Sept 2011 For WebDocument16 pagesRM379 Pleura UK PASB2 PG Sept 2011 For WebDissasekaraNo ratings yet
- Central Air ConditioningDocument8 pagesCentral Air ConditioningAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Passive and ACTIVE VentilationDocument12 pagesPassive and ACTIVE VentilationHimanshu Ruhilla50% (4)
- Pengantar Teknik Kimia Sesi 1 Peralatan Proses: Ir. Abdul Wahid Surhim, MTDocument14 pagesPengantar Teknik Kimia Sesi 1 Peralatan Proses: Ir. Abdul Wahid Surhim, MTAinul NasihaNo ratings yet
- DuctDocument21 pagesDuctkhanzak2009No ratings yet
- Why Is Forced Mechanical Ventilation Necessary in A Confined BuildingDocument3 pagesWhy Is Forced Mechanical Ventilation Necessary in A Confined BuildingJade Putis100% (1)
- Ventilation PDFDocument10 pagesVentilation PDFKarim Abd ElazizNo ratings yet
- Air Handling UnitDocument8 pagesAir Handling UnitSN Shuhada ZakariaNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationFrom EverandThe Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- Career as an Air Conditioning TechnicanFrom EverandCareer as an Air Conditioning TechnicanRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Inside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryFrom EverandInside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryNo ratings yet
- Mall StandardsDocument34 pagesMall StandardsJanakiramNo ratings yet
- FIRESAFETYDocument24 pagesFIRESAFETYJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Gated Community Net Case StudyDocument20 pagesGated Community Net Case StudyJanakiramNo ratings yet
- GATED COMMUNITY AnalysisDocument15 pagesGATED COMMUNITY AnalysisJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Anjaly Meera AbrahamDocument30 pagesAnjaly Meera AbrahamJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Case Study:National Institute of Fashion Technology, New DelhiDocument18 pagesCase Study:National Institute of Fashion Technology, New DelhiJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Concrete Injected ColumnsDocument26 pagesConcrete Injected ColumnsfaisaltmNo ratings yet
- Hri Am Anels: WWW Magnusinternational inDocument17 pagesHri Am Anels: WWW Magnusinternational inAvjot JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Bored PilingDocument23 pagesBored PilingRatha MenNo ratings yet
- Susan Aradeon - Summary History of Nigerian Architecture - The Last 100 YearsDocument7 pagesSusan Aradeon - Summary History of Nigerian Architecture - The Last 100 YearsAderinsola AdeagboNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, 2 and 3 - Brick - WMDocument68 pagesLecture 1, 2 and 3 - Brick - WMMehzabeen HaqueNo ratings yet
- Demag All Terrain Cranes Spec Ff4c8dDocument13 pagesDemag All Terrain Cranes Spec Ff4c8dFarag ElgarhyNo ratings yet
- Kevin John Paglinawan: Case StudyDocument2 pagesKevin John Paglinawan: Case StudyKevin John PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Continuity in RC Beams and FramesDocument80 pagesContinuity in RC Beams and Frameszeeshan68No ratings yet
- MPPWD (Piu) Nirman Bhawan, Bhopal Building Works (Errata/Ammendment/Addendum No. 01Document6 pagesMPPWD (Piu) Nirman Bhawan, Bhopal Building Works (Errata/Ammendment/Addendum No. 01ravilaad83No ratings yet
- IC50 Fortune RankDocument68 pagesIC50 Fortune RankTatak Bay AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Steel DesignDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Steel DesignRami Demachki100% (1)
- Sosialisasi Draft R1 Sni Struktur Penahan TanahDocument59 pagesSosialisasi Draft R1 Sni Struktur Penahan TanahAwang DarmawangsaNo ratings yet
- 27 Elevators Chain Shackle DIN 745 and DIN 5699Document1 page27 Elevators Chain Shackle DIN 745 and DIN 5699kariem noweerNo ratings yet
- Conplast UWL: Constructive SolutionsDocument2 pagesConplast UWL: Constructive SolutionsVincent JavateNo ratings yet
- TimberDocument24 pagesTimberflower lilyNo ratings yet
- Sikacim Pink: Liquid Integral Waterproofing Compound For Concrete, Mortar and PlasterDocument2 pagesSikacim Pink: Liquid Integral Waterproofing Compound For Concrete, Mortar and PlasterTanvir ShawonNo ratings yet
- Urban Insert: Lund Cathderal ForumDocument3 pagesUrban Insert: Lund Cathderal Forumsuhani patelNo ratings yet
- Company Logo Here: Checklist For ManagementDocument5 pagesCompany Logo Here: Checklist For ManagementAlphaNo ratings yet
- CONCEPTDocument1 pageCONCEPTTanya SirohiNo ratings yet
- Battle Deck Floors 170 3Document24 pagesBattle Deck Floors 170 3thorenNo ratings yet
- Codigos Bits IADC IIDocument69 pagesCodigos Bits IADC IIedicarlosNo ratings yet
- SIMPLIFIED CONSTRUCTION ESTIMATES TABLES-gurDocument14 pagesSIMPLIFIED CONSTRUCTION ESTIMATES TABLES-gurCelsoRapiNo ratings yet
- Request For Inspection Summary: Project Name: ClientDocument2 pagesRequest For Inspection Summary: Project Name: ClientAmit MaityNo ratings yet
- Balaram Sahoo ProjectDocument71 pagesBalaram Sahoo ProjectBalaram SahooNo ratings yet
- X94 - Gold Souq Bus Station To Dubai Investment ParkDocument3 pagesX94 - Gold Souq Bus Station To Dubai Investment ParkDubai Q&A100% (1)
- BS 1387 PDFDocument3 pagesBS 1387 PDFAngga KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Final Paper One PDFDocument33 pagesFinal Paper One PDFfrehiwotNo ratings yet
Hvac Unit
Hvac Unit
Uploaded by
JanakiramOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hvac Unit
Hvac Unit
Uploaded by
JanakiramCopyright:
Available Formats
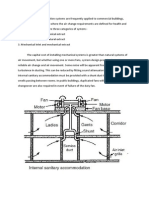
Selection of HVAC Equipment
heating and cooling needs
energy efficiency
humidity control
potential for natural ventilation
adherence to codes and standards
outdoor air quantity and quality
indoor air quality
cost
Where feasible, use central HVAC air handling units (AHUs) that serve multiple
rooms in lieu of unit ventilators or individual heat pumps
Quieter and therefore more likely to be turned on or left on by teachers and staff;
Less drafty due to multiple supplies and a return that is away from occupants;
Better at controlling humidity and condensed moisture drainage;
Easier to maintain due to reduced number of components and few units to access;
More space around units and can be accessed without interfering with class activities;
Space for higher efficiency air filters and more surface area;
Made of heavier duty components;
Less likely to have quantity of outdoor air supply inadvertently reduced.
Specify the following features for all air handling units:
Double-sloped drain pan and drain trap depth
Double-sloped drain pan - A double-sloped pan prevents water from standing and stagnating in
the pan.
Non-corroding drain pan - Made from stainless steel or plastic. Prevents corrosion that would
cause water to leak inside the AHU.
Easy access doors - All access doors are hinged and use quick release latches that do not require
tools to open. Easy access to filters, drain pans and cooling coils is imperative.
Double wall cabinet - The inner wall protects the insulation from moisture and mechanical
damage, increases sound dampening and is easier to clean.
Tightly sealed cabinet - Small yet continuous air leaks in and out of the AHU cabinet can affect
IAQ and energy. The greatest pressure differentials driving leaks occur at the AHU.
Double wall doors with gaskets - Double wall doors provide better thermal and acoustic
insulation and will remain flatter, allowing a better seal against door frame gaskets
Minimum 2 inch thick filter slots - For better protection of the indoor environment, as well as
the equipment and ducts, the filters slots should be able to accommodate 2 in. or thicker filters.
Extended surface area filter bank - To reduce the frequency of filter maintenance and the cost of
fan energy, the bank is designed to allow more filter area, such as the deep V approach or bags.
Air filter assemblies (racks & housings) designed for minimum leakage - The filter bank should
have gaskets and sealants at all points where air could easily bypass the air filters, such as
between the filter rack and the access door. Use properly gasketed manufacturer supplied filter
rack spacers.
Air filter monitor - A differential pressure gauge to indicate the static pressure drop across the
filter bank. This feature could easily be installed as an option in the field.
Corrosion resistant dampers & links - All moving parts such as pivot pins, damper actuators and
linkages are able to withstand weather and moisture-induced corrosion for the full life of the
system
Moisture and Humidity Control
Uncontrolled moisture indoors can cause major damage to the building structure, as well as to
furnishings and to finish materials like floors, walls and ceilings. Uncontrolled moisture can
trigger mold growth which not only damages the school facility, but can lead to health and
performance problems for students and staff.
Primary causes of indoor moisture problems in new schools include:
Use of building materials that were repeatedly or deeply wetted before the building was fully
enclosed
Poor control of rain and snow, resulting in roof and flashing leaks
Wet or damp construction cavities
Moisture-laden outdoor air entering the building
Condensation on cool surfaces
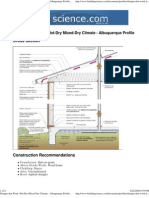
The number or name of the AHU (e.g., AHU ##, or AHU for West Wing)
The outdoor air (OA), supply air (SA), return air (RA) and exhaust or relief air (EA) connections to the AHU, each with arrows noting proper airflow directio
The access door(s) for the air filters and the minimum filter dust-spot (or MERV) efficiency (Air Filters, minimum xx% dust spot efficiency)
The filter pressure gauge and the recommended filter change pressure (Filter Pressure, max 0.x in. w.g.)
The access door(s) for the condensate drain pan (Drain Pan)
Other pertinent access doors such as to energy recovery ventilation wheels or plates (Energy Recovery Ventilation Unit)
The minimum amount of outdoor air for each AHU (### CFM minimum during occupied times)
The outdoor air damper (OA Damper), with special marks noting when the damper is in the fully closed (Closed), fully opened (open) and minimum design
If a motorized relief damper is installed (EA Damper), note the same positions as above.
The access door to any outdoor air controls (OA Control(s)) such as damper position adjustments, outdoor airflow measuring stations, resets, fuses and s
Breakers for exhaust fans (Exhaust Fan ##), AHU, unit ventilators
Access doors for inspection and maintenance of air ducts
Any dampers and controls for air side economizers (as appropriate)
The number or name of all exhaust fans, including the air quantity exhausted (EF##, ###CFM)
You might also like
- Pipe Fittings Surface AreaDocument1 pagePipe Fittings Surface AreaB Girish82% (57)
- Air Curtain Guide DesignDocument8 pagesAir Curtain Guide Designanton7786No ratings yet
- JIS H 3300 - 2006 Copper Andcopper Alloy Seamless Pipes and TubesDocument35 pagesJIS H 3300 - 2006 Copper Andcopper Alloy Seamless Pipes and TubesTRONGHAI266100% (2)
- Chapter 34Document7 pagesChapter 34loise0% (1)
- Ventilation and Air-ConditioningDocument93 pagesVentilation and Air-ConditioningEmmanuel P Dube100% (2)
- 1-Air Handling and Distribution SystemsDocument32 pages1-Air Handling and Distribution SystemsKhalidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Ku Illyani Nadia BT Ku Aziz 2011478072 BCM5BDocument3 pagesTutorial - Ku Illyani Nadia BT Ku Aziz 2011478072 BCM5Bnadia0109No ratings yet
- VentilationDocument28 pagesVentilationTannum Negi0% (1)
- Ventilation SystemDocument22 pagesVentilation SystemPrakriti Goel100% (3)
- Air Distribution Sys DesignDocument6 pagesAir Distribution Sys DesignpauloNo ratings yet
- Air Distribution Sytems DesignDocument6 pagesAir Distribution Sytems Designvalentinlupascu33No ratings yet
- Air Distribution System Design: Good Duct Design Increases EfficiencyDocument6 pagesAir Distribution System Design: Good Duct Design Increases Efficiencyharoub_nasNo ratings yet
- 2 Out Ts Omm HVC Acu 3832 02 210613950 Omm of Air Curtain For BRTDocument77 pages2 Out Ts Omm HVC Acu 3832 02 210613950 Omm of Air Curtain For BRTMohamed AbdelmoneimNo ratings yet
- An Air Handling UnitDocument4 pagesAn Air Handling UnitDono WayNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: & Its SystemDocument14 pagesVentilation: & Its SystemTangha Muklom KunchaNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: & Its SystemDocument14 pagesVentilation: & Its SystemTangha Muklom KunchaNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: MDM Nurul Aini/Qus 3206Document22 pagesVentilation: MDM Nurul Aini/Qus 3206Anisha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Planning OlDocument97 pagesVentilation Planning Olenjam yasankNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Regulations On Design and Installation of Hvac SystemDocument12 pagesMechanical Regulations On Design and Installation of Hvac SystemJohn ApeladoNo ratings yet
- Ventilation SystemsDocument5 pagesVentilation SystemsnualdinNo ratings yet
- Ventilation: Types of SystemsDocument10 pagesVentilation: Types of SystemsanangwahjudiNo ratings yet
- AERECO-Demand Controlled Mechanical Extract VentilationDocument12 pagesAERECO-Demand Controlled Mechanical Extract VentilationVali GheorghisorNo ratings yet
- Air Distribution System Equipment's and Duct DesignDocument36 pagesAir Distribution System Equipment's and Duct DesignfekadeNo ratings yet
- Air Distribution SystemDocument29 pagesAir Distribution System20-06115No ratings yet
- Tutorial - Underfloor Air-ConditioningDocument8 pagesTutorial - Underfloor Air-ConditioningJasper_HVACNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY #4 - Castro, Xaira Alexa Mari L.Document19 pagesACTIVITY #4 - Castro, Xaira Alexa Mari L.Xaira Alexa Mari CastroNo ratings yet
- Dilution VentilationDocument4 pagesDilution VentilationUthman OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- ISOVERDocument35 pagesISOVERMadhu RaghuNo ratings yet
- What Is Air ConditioningDocument16 pagesWhat Is Air ConditioningCheeragNo ratings yet
- 10 - Air Distribution SystemDocument7 pages10 - Air Distribution SystemZeeshan HasanNo ratings yet
- Offshore Hvac DesignDocument6 pagesOffshore Hvac DesignAndrew Alex100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Duct Design and SealingDocument14 pagesChapter 8 Duct Design and SealingMiguel FloresNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Piping-Economic PipingDocument5 pagesCompressed Air Piping-Economic PipingMOHAMMAD ASIFNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document7 pagesExp 2Philip Anthony MasilangNo ratings yet
- HVAC - Part-1Document63 pagesHVAC - Part-1ShubhaNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Air Filter System OptimizationDocument10 pagesGas Turbine Air Filter System Optimizationsevero97100% (2)
- Designs That Work Hot DryMixed Dry Climate AlbuquerquePr..Document8 pagesDesigns That Work Hot DryMixed Dry Climate AlbuquerquePr..Kosar MuradiNo ratings yet
- Design Guide - Humidity ControlDocument2 pagesDesign Guide - Humidity Controldzul92100% (1)
- Mechanical Ventilation Systems Are Frequently Applied To Commercial BuildingsDocument9 pagesMechanical Ventilation Systems Are Frequently Applied To Commercial BuildingsIbn Shaffee IVNo ratings yet
- EEMs To Consider 2011-09-15Document12 pagesEEMs To Consider 2011-09-15razali131266No ratings yet
- HVAC SystemDocument5 pagesHVAC SystemMrinal Kanti RoyNo ratings yet
- CR MOD 17 Heating and Cooling09Document36 pagesCR MOD 17 Heating and Cooling09MMMOH200No ratings yet
- Heat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (Hvac)Document27 pagesHeat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (Hvac)satishNo ratings yet
- Natural Ventilation PDFDocument7 pagesNatural Ventilation PDFDebasis DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Reading Lecture 5-6 Mechanical VentilationDocument13 pagesReading Lecture 5-6 Mechanical VentilationMd. Rizwan Hasan Kabir ShovonNo ratings yet
- Draw-Through or Blow-Through: Components of Air Handling UnitDocument23 pagesDraw-Through or Blow-Through: Components of Air Handling Unityousuff0% (1)
- Air HandlerDocument15 pagesAir HandlerShashank BijweNo ratings yet
- RM379 Pleura UK PASB2 PG Sept 2011 For WebDocument16 pagesRM379 Pleura UK PASB2 PG Sept 2011 For WebDissasekaraNo ratings yet
- Central Air ConditioningDocument8 pagesCentral Air ConditioningAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Passive and ACTIVE VentilationDocument12 pagesPassive and ACTIVE VentilationHimanshu Ruhilla50% (4)
- Pengantar Teknik Kimia Sesi 1 Peralatan Proses: Ir. Abdul Wahid Surhim, MTDocument14 pagesPengantar Teknik Kimia Sesi 1 Peralatan Proses: Ir. Abdul Wahid Surhim, MTAinul NasihaNo ratings yet
- DuctDocument21 pagesDuctkhanzak2009No ratings yet
- Why Is Forced Mechanical Ventilation Necessary in A Confined BuildingDocument3 pagesWhy Is Forced Mechanical Ventilation Necessary in A Confined BuildingJade Putis100% (1)
- Ventilation PDFDocument10 pagesVentilation PDFKarim Abd ElazizNo ratings yet
- Air Handling UnitDocument8 pagesAir Handling UnitSN Shuhada ZakariaNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationFrom EverandThe Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- Career as an Air Conditioning TechnicanFrom EverandCareer as an Air Conditioning TechnicanRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Inside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryFrom EverandInside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryNo ratings yet
- Mall StandardsDocument34 pagesMall StandardsJanakiramNo ratings yet
- FIRESAFETYDocument24 pagesFIRESAFETYJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Gated Community Net Case StudyDocument20 pagesGated Community Net Case StudyJanakiramNo ratings yet
- GATED COMMUNITY AnalysisDocument15 pagesGATED COMMUNITY AnalysisJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Anjaly Meera AbrahamDocument30 pagesAnjaly Meera AbrahamJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Case Study:National Institute of Fashion Technology, New DelhiDocument18 pagesCase Study:National Institute of Fashion Technology, New DelhiJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Concrete Injected ColumnsDocument26 pagesConcrete Injected ColumnsfaisaltmNo ratings yet
- Hri Am Anels: WWW Magnusinternational inDocument17 pagesHri Am Anels: WWW Magnusinternational inAvjot JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Bored PilingDocument23 pagesBored PilingRatha MenNo ratings yet
- Susan Aradeon - Summary History of Nigerian Architecture - The Last 100 YearsDocument7 pagesSusan Aradeon - Summary History of Nigerian Architecture - The Last 100 YearsAderinsola AdeagboNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, 2 and 3 - Brick - WMDocument68 pagesLecture 1, 2 and 3 - Brick - WMMehzabeen HaqueNo ratings yet
- Demag All Terrain Cranes Spec Ff4c8dDocument13 pagesDemag All Terrain Cranes Spec Ff4c8dFarag ElgarhyNo ratings yet
- Kevin John Paglinawan: Case StudyDocument2 pagesKevin John Paglinawan: Case StudyKevin John PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Continuity in RC Beams and FramesDocument80 pagesContinuity in RC Beams and Frameszeeshan68No ratings yet
- MPPWD (Piu) Nirman Bhawan, Bhopal Building Works (Errata/Ammendment/Addendum No. 01Document6 pagesMPPWD (Piu) Nirman Bhawan, Bhopal Building Works (Errata/Ammendment/Addendum No. 01ravilaad83No ratings yet
- IC50 Fortune RankDocument68 pagesIC50 Fortune RankTatak Bay AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Steel DesignDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Steel DesignRami Demachki100% (1)
- Sosialisasi Draft R1 Sni Struktur Penahan TanahDocument59 pagesSosialisasi Draft R1 Sni Struktur Penahan TanahAwang DarmawangsaNo ratings yet
- 27 Elevators Chain Shackle DIN 745 and DIN 5699Document1 page27 Elevators Chain Shackle DIN 745 and DIN 5699kariem noweerNo ratings yet
- Conplast UWL: Constructive SolutionsDocument2 pagesConplast UWL: Constructive SolutionsVincent JavateNo ratings yet
- TimberDocument24 pagesTimberflower lilyNo ratings yet
- Sikacim Pink: Liquid Integral Waterproofing Compound For Concrete, Mortar and PlasterDocument2 pagesSikacim Pink: Liquid Integral Waterproofing Compound For Concrete, Mortar and PlasterTanvir ShawonNo ratings yet
- Urban Insert: Lund Cathderal ForumDocument3 pagesUrban Insert: Lund Cathderal Forumsuhani patelNo ratings yet
- Company Logo Here: Checklist For ManagementDocument5 pagesCompany Logo Here: Checklist For ManagementAlphaNo ratings yet
- CONCEPTDocument1 pageCONCEPTTanya SirohiNo ratings yet
- Battle Deck Floors 170 3Document24 pagesBattle Deck Floors 170 3thorenNo ratings yet
- Codigos Bits IADC IIDocument69 pagesCodigos Bits IADC IIedicarlosNo ratings yet
- SIMPLIFIED CONSTRUCTION ESTIMATES TABLES-gurDocument14 pagesSIMPLIFIED CONSTRUCTION ESTIMATES TABLES-gurCelsoRapiNo ratings yet
- Request For Inspection Summary: Project Name: ClientDocument2 pagesRequest For Inspection Summary: Project Name: ClientAmit MaityNo ratings yet
- Balaram Sahoo ProjectDocument71 pagesBalaram Sahoo ProjectBalaram SahooNo ratings yet
- X94 - Gold Souq Bus Station To Dubai Investment ParkDocument3 pagesX94 - Gold Souq Bus Station To Dubai Investment ParkDubai Q&A100% (1)
- BS 1387 PDFDocument3 pagesBS 1387 PDFAngga KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Final Paper One PDFDocument33 pagesFinal Paper One PDFfrehiwotNo ratings yet