Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0116 Extra-Criterion Saf 4
0116 Extra-Criterion Saf 4
Uploaded by
Santiago RivadeneiraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Case StudyDocument35 pagesCase StudysamanNo ratings yet
- Banaskewiz 2017Document967 pagesBanaskewiz 2017Avishek Ray Ghatak100% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy of Upper Limb (KLM)Document4 pagesClinical Anatomy of Upper Limb (KLM)Ceo MedComNo ratings yet
- Abstracts / Atherosclerosis 252 (2016) E1 Ee196 E185Document2 pagesAbstracts / Atherosclerosis 252 (2016) E1 Ee196 E185MaulNo ratings yet
- Lupus Myocarditis A Rare CaseDocument3 pagesLupus Myocarditis A Rare Casea.rohman2700No ratings yet
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Secondary To Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis in A 12-Year-Old GirlDocument2 pagesPosterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Secondary To Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis in A 12-Year-Old GirlwawaningNo ratings yet
- Severe Pericardial Effusion Heralding Scleroderma Renal Crisis: A Case Report and The Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesSevere Pericardial Effusion Heralding Scleroderma Renal Crisis: A Case Report and The Literature ReviewJimmy Oi SantosoNo ratings yet
- Artigo Base SimoneDocument5 pagesArtigo Base SimoneWolfgang ThyerreNo ratings yet
- Síncope en EAo SeveraDocument8 pagesSíncope en EAo Severareymistery10No ratings yet
- Dilemmas in The Diagnosis and Management of Antiphospholipid SyndromeDocument15 pagesDilemmas in The Diagnosis and Management of Antiphospholipid Syndromeanna531No ratings yet
- 10.1007@s42399 021 01027 7Document9 pages10.1007@s42399 021 01027 7firstia anugerah1No ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury and Proteinuria in A Man With HemoptysisDocument3 pagesAcute Kidney Injury and Proteinuria in A Man With HemoptysisChe GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal HemoglobinuriaDocument11 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuriaida ayu agung WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Research On Post Reversible Encephalopathy Due To Blood TransfusionsDocument7 pagesResearch On Post Reversible Encephalopathy Due To Blood TransfusionsAnkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Following Blood Transfusion in The Setting of Possible Rheumatoid-Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesReversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Following Blood Transfusion in The Setting of Possible Rheumatoid-Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Doruk Erkan Expert Perspective Management ofDocument26 pagesDoruk Erkan Expert Perspective Management ofSrinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Annals of Neurology - 2022 - Gollion - Unilateral Leukoencephalopathy Revealing Cerebral Autosomal Dominant ArteriopathyDocument2 pagesAnnals of Neurology - 2022 - Gollion - Unilateral Leukoencephalopathy Revealing Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathyalex mondomobeNo ratings yet
- 2021 Special Care in Dentistry Detection of Calcified AtheromasDocument6 pages2021 Special Care in Dentistry Detection of Calcified AtheromasNATALIA SILVA ANDRADENo ratings yet
- A Review of The Management of Cerebral Vasospasm After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument15 pagesA Review of The Management of Cerebral Vasospasm After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid HemorrhageAlanNo ratings yet
- Gfy104 fp526Document1 pageGfy104 fp526spraptamaNo ratings yet
- Posttransfusion Refractory ThrombocytopeniaDocument19 pagesPosttransfusion Refractory ThrombocytopeniaKyla ValenciaNo ratings yet
- A Clinical and Echocardiographic Approach To Evaluation of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm InfantsDocument6 pagesA Clinical and Echocardiographic Approach To Evaluation of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm InfantsAfi ArdineNo ratings yet
- Cirugi A Espan Ola: Meso-Cava Bypass As An Alternative To Multivisceral TransplantationDocument2 pagesCirugi A Espan Ola: Meso-Cava Bypass As An Alternative To Multivisceral TransplantationHưng Nguyễn KiềuNo ratings yet
- Granulomatose Eosinophilique Avec Polyangeite: Presentations Inhabituelles. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis: Unusual PresentationsDocument5 pagesGranulomatose Eosinophilique Avec Polyangeite: Presentations Inhabituelles. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis: Unusual PresentationsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ceccarelli2017 HyponatremiafollowingacerebralabscessDocument3 pagesCeccarelli2017 HyponatremiafollowingacerebralabscessMario AlexanderNo ratings yet
- A Case of Male Sle: An Unusual PresentationDocument4 pagesA Case of Male Sle: An Unusual PresentationIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Shang2012 PDFDocument9 pagesShang2012 PDFManuel ArenasNo ratings yet
- A Pregnant Woman With Gross Hematuria and Acute Kidney InjuryDocument2 pagesA Pregnant Woman With Gross Hematuria and Acute Kidney InjuryChe GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Majluf Cruz1996Document1 pageMajluf Cruz1996Araceli Enríquez OvandoNo ratings yet
- Poster Viewing I: Case ReportsDocument39 pagesPoster Viewing I: Case ReportsGaurav SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Fatigability - From Concept To Clinical Profile. Case ReportDocument7 pagesFatigability - From Concept To Clinical Profile. Case ReportdianaNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Hydrocephalus After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDocument9 pagesReview Article: Hydrocephalus After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDewi DewiNo ratings yet
- Simon 2016Document12 pagesSimon 2016yoNo ratings yet
- P4 Budd-Chiari Syndrome As Initial Presentation ofDocument2 pagesP4 Budd-Chiari Syndrome As Initial Presentation ofVictor JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Aortitis, Causas Infrecuentes en Reumatología: Presentación de CasosDocument6 pagesAortitis, Causas Infrecuentes en Reumatología: Presentación de CasosNatalia TexidorNo ratings yet
- Art15 PDFDocument6 pagesArt15 PDFNatalia TexidorNo ratings yet
- BCR 2012 007205Document4 pagesBCR 2012 007205shofidhiaaaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Pulmonary Medicine: ClinmedDocument3 pagesRespiratory and Pulmonary Medicine: ClinmedGrace Yuni Soesanti MhNo ratings yet
- Muthu Et Al 2015 Image Diagnosis Weber Syndrome A Rare Presentation of Acute Leukemia A Case Report and Review of TheDocument3 pagesMuthu Et Al 2015 Image Diagnosis Weber Syndrome A Rare Presentation of Acute Leukemia A Case Report and Review of TheManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Endomyocardial Biopsy Facilitates Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis (EGPA) : A Case ReportDocument5 pagesEndomyocardial Biopsy Facilitates Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis (EGPA) : A Case Reportjinmao1010No ratings yet
- 121 Anaesthesia For VP Shunt InsertionDocument8 pages121 Anaesthesia For VP Shunt InsertionMohammed ElSayedNo ratings yet
- Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis A Genetic ConditioDocument5 pagesCerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis A Genetic Conditioangelluis1980No ratings yet
- HIE and CVSDocument11 pagesHIE and CVSakshayajainaNo ratings yet
- HIV Hemicorea CNS Histoplasmosis 2016Document3 pagesHIV Hemicorea CNS Histoplasmosis 2016Juan Salazar PajaresNo ratings yet
- Noc110069 346 351Document6 pagesNoc110069 346 351Carlos AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Aliment Pharmacol Ther - 2022 - Tergast - Home Based Tunnelled Peritoneal Drainage System As An Alternative TreatmentDocument11 pagesAliment Pharmacol Ther - 2022 - Tergast - Home Based Tunnelled Peritoneal Drainage System As An Alternative TreatmentTens AiepNo ratings yet
- CardioNET 2022 Book of AbstractDocument16 pagesCardioNET 2022 Book of AbstractSTOCARE DATENo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal HemoglobinuriaDocument12 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal HemoglobinuriaTowhidulIslamNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of PNHDocument12 pagesDiagnosis and Management of PNHapi-26302710No ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Case Study and Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesSubarachnoid Haemorrhage Case Study and Literature ReviewafmzxpqoizljqoNo ratings yet
- 61a Woman LES N Chest PainDocument6 pages61a Woman LES N Chest PainGabriel MouraNo ratings yet
- CateterixareDocument4 pagesCateterixareClaudia IrimieNo ratings yet
- Lactato y Hemorragia SaDocument6 pagesLactato y Hemorragia Samariafernandasv98No ratings yet
- Gum Disease May Be A Risk Factor For Heart ArrythmiaDocument11 pagesGum Disease May Be A Risk Factor For Heart Arrythmiaapi-708498453No ratings yet
- Diagnosis, Management, and Outcomes of Patients With Syncope and Bundle Branch BlockDocument7 pagesDiagnosis, Management, and Outcomes of Patients With Syncope and Bundle Branch BlockPaul CalbureanNo ratings yet
- Ehx493 P5438Document1 pageEhx493 P5438Anonymous NeRC5JYiSNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Aplasia: A Rare Complication of Disseminated TuberculosisDocument3 pagesBone Marrow Aplasia: A Rare Complication of Disseminated TuberculosisayuNo ratings yet
- Yagmur Et Al 2013 Platelet Hyperaggregability Is Highly Prevalent in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease AnDocument7 pagesYagmur Et Al 2013 Platelet Hyperaggregability Is Highly Prevalent in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease AnMister FannaniNo ratings yet
- Arteriovenous Fistula Creation For End-Stage Renal Disease May Worsen Pulmonary HypertensionDocument3 pagesArteriovenous Fistula Creation For End-Stage Renal Disease May Worsen Pulmonary HypertensionLuis Rodriguez PratoNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Neuroradiological Procedures Premalatha SDocument48 pagesAnaesthesia For Neuroradiological Procedures Premalatha SPrema LathaNo ratings yet
- Posterior Circulation Stroke: Advances in Understanding and ManagementFrom EverandPosterior Circulation Stroke: Advances in Understanding and ManagementJong S. KimNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Blood and Bone Marrow DisordersFrom EverandDiagnosis of Blood and Bone Marrow DisordersSa A. WangNo ratings yet
- Best Practices of Apheresis in Hematopoietic Cell TransplantationFrom EverandBest Practices of Apheresis in Hematopoietic Cell TransplantationSyed A. AbutalibNo ratings yet
- Surgery and Post OpDocument96 pagesSurgery and Post OpNguyễn Nhật HoàngNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Chap6. Bacterial Infections of Skin 2020-3-23Document368 pagesDermatology Chap6. Bacterial Infections of Skin 2020-3-23Mohsin Tanmoy100% (1)
- Melphalan (AHFS DI)Document10 pagesMelphalan (AHFS DI)maryNo ratings yet
- Senile DementiaDocument11 pagesSenile DementiaSubha MaheswariNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine Major CaseDocument25 pagesOral Medicine Major Case0030-GRETANZA HENDRAT MONICANo ratings yet
- Levenson - Psychosomatic Medicines - 3 Ed - 2019-289-313Document25 pagesLevenson - Psychosomatic Medicines - 3 Ed - 2019-289-313yennifer hoyos mendezNo ratings yet
- Eruptive Disorders of Permanent TeethDocument6 pagesEruptive Disorders of Permanent Teethtaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- PhotodermatosesDocument8 pagesPhotodermatosesIvan KurniadiNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis DiarrheaDocument2 pagesUlcerative Colitis DiarrheateuuuuNo ratings yet
- Table S1 English Translation of The MIR ExaminationDocument43 pagesTable S1 English Translation of The MIR Examinationهادي تركي شنبارةNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Embolotherapy in Interventional Oncology - Technology, Techniques, and ApplicationsDocument15 pagesHepatic Embolotherapy in Interventional Oncology - Technology, Techniques, and ApplicationsVeronica AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Assistant Surgeon Exam PDFDocument9 pagesSyllabus Assistant Surgeon Exam PDFMaguNo ratings yet
- 2Nd Year BS-MLT Course ContentsDocument13 pages2Nd Year BS-MLT Course ContentsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic TumourDocument4 pagesInflammatory Myofibroblastic TumourThiruNo ratings yet
- PCEP-PC Module 4 (Pain) NotesDocument12 pagesPCEP-PC Module 4 (Pain) NotesMan MedNo ratings yet
- 2 Intestinal-ObstructionDocument5 pages2 Intestinal-ObstructionMyrtle Yvonne RagubNo ratings yet
- Personal Social HistoryDocument1 pagePersonal Social HistoryledfielcastilloNo ratings yet
- Kussmaul BreathingDocument3 pagesKussmaul BreathingsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- OSCE Final 1 PDFDocument204 pagesOSCE Final 1 PDFamalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Medical Mycoloy - AspergillosisDocument17 pagesLecture 10 - Medical Mycoloy - AspergillosisXavier DharmaNo ratings yet
- Burn PathophysiologyDocument14 pagesBurn PathophysiologyAgung Widya PramanaNo ratings yet
- The Gems Brain Change ModelDocument9 pagesThe Gems Brain Change Modelapi-324897890100% (4)
- Kode Icd 10Document536 pagesKode Icd 10AkbarisArisNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agonists: Dr. Mohamed Samai BSC (Hons), MSC, MBBS, PGCRM, PHD Head, Department of Pharmacology Comahs, UslDocument31 pagesCholinergic Agonists: Dr. Mohamed Samai BSC (Hons), MSC, MBBS, PGCRM, PHD Head, Department of Pharmacology Comahs, Uslmatchees-gone rogue100% (1)
- How I Treat Anemia in Pregnancy: Iron, Cobalamin, and FolateDocument11 pagesHow I Treat Anemia in Pregnancy: Iron, Cobalamin, and FolateAgungBudiPamungkasNo ratings yet
- хвороби птиці 981103673X PDFDocument311 pagesхвороби птиці 981103673X PDFIgor Yuskiv100% (1)
- Small Animal Emergency and Critical Care MedicineDocument193 pagesSmall Animal Emergency and Critical Care MedicineYaiza Garcia CasadoNo ratings yet
0116 Extra-Criterion Saf 4
0116 Extra-Criterion Saf 4
Uploaded by
Santiago RivadeneiraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
0116 Extra-Criterion Saf 4
0116 Extra-Criterion Saf 4
Uploaded by
Santiago RivadeneiraCopyright:
Available Formats
0116 - "EXTRA-CRITERION" MANIFESTATIONS DUE TO NEPHROPATHY DUE TO APS: CASE
REPORT
Authors: Rivadeneira CS¹, Guevara-pacheco DG¹, Lamos-duarte AF¹, Buitrago JF¹, Gallego-cardona L¹, Cajamarca-baron JH², Cubides HH², Arredondo AM², Escobar A².
1.Rheumatology Fellow - Fundación Universitaria Ciencias de la Salud –Hospital de San José, Bogotá
2.Rheumatology instructor- Fundación Universitaria Ciencias de la Salud - Hospital de San José, Bogotá
Correspondence contact: Carlos Rivadeneira, csrivadeneira@fucsalud.edu.co
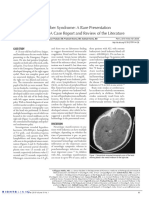
Image 1. Brain magnetic resonance
Purpose or objective: Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an acquired autoimmune thrombophilia
characterized by recurrent vascular thrombosis and/or pregnancy morbidity, in the presence of persistent
antiphospholipid (aPL) titers.
Clinical phenotypes outside the Sapporo classification criteria have been evaluated, clinical profiles:
1. Obstetric APS
2. Thrombotic APS
3. Microvascular APS
4. Catastrophic APS (CAPS)
5. Nonthrombotic APS: thrombocytopenia, skin, heart valve disease and nephropathy
Patients and methods: Case report and literature review a) FLAIR sequence axial section; b) Multiple left frontoparietal hyperintensities (LMCA) with white matter
involvement; c) Hyperintensity in the caudate and lenticular nuclei.
Table 1. Laboratory tests
Results: A 42-year-old man, with high blood pressure, chronic kidney disease and myocardial infarction, was
admitted to the emergency room due to a 3-day history of dysarthria, motor aphasia, dysgraphia associated with
right hemiparesis and syncopal episodes; normotensive physical examination, no arrhythmias, no skin lesions,
neurological examination with mental examination with motor aphasia, agraphia, alexia, strength and reflexes 4
limbs normal; brain magnetic resonance observed a acute ischemic event (Image 1), with extension studies with
thrombocytopenia, positive aPL , and proteinuria (Table 1); renal biopsy was taken with findings of
membranoproliferative nephropathy and thrombotic microangiopathy.
With the studies obtained, stroke of the left middle cerebral artery (LMCA) was considered as a thrombotic
manifestation of APS with a first triple positive set and "extra-criterion" manifestations due to severe
thrombocytopenia and nephrotic syndrome secondary to APS nephropathy.
Anticoagulation is started, but a decrease in platelets to 1,500 is documented, steroid pulses are indicated,
without response. Subsequently, he presented a new acute event with right hemiparesis, with MRI with stroke in
new territories of the LMCA with hemorrhagic transformation, immunoglobulin was indicated due to
refractoriness to steroids with recovery of platelet count, and initiation of cyclophosphamide due to renal
involvement, presenting adequate medical evolution.
Keywords: Antiphospholipid syndrome; nephropathy, thrombocytopenia
Conclusions: The extra-criterion nontrombotic manifestations of APS include kidney involvement due to aPL nephropathy, it has a low prevalence, it is characterized
as a vascular nephropathy with occlusive lesions of small vessels, related to refractory arterial hypertension, CKD, hematuria, proteinuria associated with positivity of
lupus anticoagulant, hypocomplementemia, with indication of immunomodulation.
You might also like
- Case StudyDocument35 pagesCase StudysamanNo ratings yet
- Banaskewiz 2017Document967 pagesBanaskewiz 2017Avishek Ray Ghatak100% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy of Upper Limb (KLM)Document4 pagesClinical Anatomy of Upper Limb (KLM)Ceo MedComNo ratings yet
- Abstracts / Atherosclerosis 252 (2016) E1 Ee196 E185Document2 pagesAbstracts / Atherosclerosis 252 (2016) E1 Ee196 E185MaulNo ratings yet
- Lupus Myocarditis A Rare CaseDocument3 pagesLupus Myocarditis A Rare Casea.rohman2700No ratings yet
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Secondary To Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis in A 12-Year-Old GirlDocument2 pagesPosterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Secondary To Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis in A 12-Year-Old GirlwawaningNo ratings yet
- Severe Pericardial Effusion Heralding Scleroderma Renal Crisis: A Case Report and The Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesSevere Pericardial Effusion Heralding Scleroderma Renal Crisis: A Case Report and The Literature ReviewJimmy Oi SantosoNo ratings yet
- Artigo Base SimoneDocument5 pagesArtigo Base SimoneWolfgang ThyerreNo ratings yet
- Síncope en EAo SeveraDocument8 pagesSíncope en EAo Severareymistery10No ratings yet
- Dilemmas in The Diagnosis and Management of Antiphospholipid SyndromeDocument15 pagesDilemmas in The Diagnosis and Management of Antiphospholipid Syndromeanna531No ratings yet
- 10.1007@s42399 021 01027 7Document9 pages10.1007@s42399 021 01027 7firstia anugerah1No ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury and Proteinuria in A Man With HemoptysisDocument3 pagesAcute Kidney Injury and Proteinuria in A Man With HemoptysisChe GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal HemoglobinuriaDocument11 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuriaida ayu agung WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Research On Post Reversible Encephalopathy Due To Blood TransfusionsDocument7 pagesResearch On Post Reversible Encephalopathy Due To Blood TransfusionsAnkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Following Blood Transfusion in The Setting of Possible Rheumatoid-Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesReversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome Following Blood Transfusion in The Setting of Possible Rheumatoid-Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Doruk Erkan Expert Perspective Management ofDocument26 pagesDoruk Erkan Expert Perspective Management ofSrinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Annals of Neurology - 2022 - Gollion - Unilateral Leukoencephalopathy Revealing Cerebral Autosomal Dominant ArteriopathyDocument2 pagesAnnals of Neurology - 2022 - Gollion - Unilateral Leukoencephalopathy Revealing Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathyalex mondomobeNo ratings yet
- 2021 Special Care in Dentistry Detection of Calcified AtheromasDocument6 pages2021 Special Care in Dentistry Detection of Calcified AtheromasNATALIA SILVA ANDRADENo ratings yet
- A Review of The Management of Cerebral Vasospasm After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument15 pagesA Review of The Management of Cerebral Vasospasm After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid HemorrhageAlanNo ratings yet
- Gfy104 fp526Document1 pageGfy104 fp526spraptamaNo ratings yet
- Posttransfusion Refractory ThrombocytopeniaDocument19 pagesPosttransfusion Refractory ThrombocytopeniaKyla ValenciaNo ratings yet
- A Clinical and Echocardiographic Approach To Evaluation of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm InfantsDocument6 pagesA Clinical and Echocardiographic Approach To Evaluation of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm InfantsAfi ArdineNo ratings yet
- Cirugi A Espan Ola: Meso-Cava Bypass As An Alternative To Multivisceral TransplantationDocument2 pagesCirugi A Espan Ola: Meso-Cava Bypass As An Alternative To Multivisceral TransplantationHưng Nguyễn KiềuNo ratings yet
- Granulomatose Eosinophilique Avec Polyangeite: Presentations Inhabituelles. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis: Unusual PresentationsDocument5 pagesGranulomatose Eosinophilique Avec Polyangeite: Presentations Inhabituelles. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis: Unusual PresentationsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ceccarelli2017 HyponatremiafollowingacerebralabscessDocument3 pagesCeccarelli2017 HyponatremiafollowingacerebralabscessMario AlexanderNo ratings yet
- A Case of Male Sle: An Unusual PresentationDocument4 pagesA Case of Male Sle: An Unusual PresentationIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Shang2012 PDFDocument9 pagesShang2012 PDFManuel ArenasNo ratings yet
- A Pregnant Woman With Gross Hematuria and Acute Kidney InjuryDocument2 pagesA Pregnant Woman With Gross Hematuria and Acute Kidney InjuryChe GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Majluf Cruz1996Document1 pageMajluf Cruz1996Araceli Enríquez OvandoNo ratings yet
- Poster Viewing I: Case ReportsDocument39 pagesPoster Viewing I: Case ReportsGaurav SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Fatigability - From Concept To Clinical Profile. Case ReportDocument7 pagesFatigability - From Concept To Clinical Profile. Case ReportdianaNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Hydrocephalus After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDocument9 pagesReview Article: Hydrocephalus After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDewi DewiNo ratings yet
- Simon 2016Document12 pagesSimon 2016yoNo ratings yet
- P4 Budd-Chiari Syndrome As Initial Presentation ofDocument2 pagesP4 Budd-Chiari Syndrome As Initial Presentation ofVictor JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Aortitis, Causas Infrecuentes en Reumatología: Presentación de CasosDocument6 pagesAortitis, Causas Infrecuentes en Reumatología: Presentación de CasosNatalia TexidorNo ratings yet
- Art15 PDFDocument6 pagesArt15 PDFNatalia TexidorNo ratings yet
- BCR 2012 007205Document4 pagesBCR 2012 007205shofidhiaaaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Pulmonary Medicine: ClinmedDocument3 pagesRespiratory and Pulmonary Medicine: ClinmedGrace Yuni Soesanti MhNo ratings yet
- Muthu Et Al 2015 Image Diagnosis Weber Syndrome A Rare Presentation of Acute Leukemia A Case Report and Review of TheDocument3 pagesMuthu Et Al 2015 Image Diagnosis Weber Syndrome A Rare Presentation of Acute Leukemia A Case Report and Review of TheManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Endomyocardial Biopsy Facilitates Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis (EGPA) : A Case ReportDocument5 pagesEndomyocardial Biopsy Facilitates Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis (EGPA) : A Case Reportjinmao1010No ratings yet
- 121 Anaesthesia For VP Shunt InsertionDocument8 pages121 Anaesthesia For VP Shunt InsertionMohammed ElSayedNo ratings yet
- Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis A Genetic ConditioDocument5 pagesCerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis A Genetic Conditioangelluis1980No ratings yet
- HIE and CVSDocument11 pagesHIE and CVSakshayajainaNo ratings yet
- HIV Hemicorea CNS Histoplasmosis 2016Document3 pagesHIV Hemicorea CNS Histoplasmosis 2016Juan Salazar PajaresNo ratings yet
- Noc110069 346 351Document6 pagesNoc110069 346 351Carlos AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Aliment Pharmacol Ther - 2022 - Tergast - Home Based Tunnelled Peritoneal Drainage System As An Alternative TreatmentDocument11 pagesAliment Pharmacol Ther - 2022 - Tergast - Home Based Tunnelled Peritoneal Drainage System As An Alternative TreatmentTens AiepNo ratings yet
- CardioNET 2022 Book of AbstractDocument16 pagesCardioNET 2022 Book of AbstractSTOCARE DATENo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal HemoglobinuriaDocument12 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Paroxysmal Nocturnal HemoglobinuriaTowhidulIslamNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of PNHDocument12 pagesDiagnosis and Management of PNHapi-26302710No ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Case Study and Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesSubarachnoid Haemorrhage Case Study and Literature ReviewafmzxpqoizljqoNo ratings yet
- 61a Woman LES N Chest PainDocument6 pages61a Woman LES N Chest PainGabriel MouraNo ratings yet
- CateterixareDocument4 pagesCateterixareClaudia IrimieNo ratings yet
- Lactato y Hemorragia SaDocument6 pagesLactato y Hemorragia Samariafernandasv98No ratings yet
- Gum Disease May Be A Risk Factor For Heart ArrythmiaDocument11 pagesGum Disease May Be A Risk Factor For Heart Arrythmiaapi-708498453No ratings yet
- Diagnosis, Management, and Outcomes of Patients With Syncope and Bundle Branch BlockDocument7 pagesDiagnosis, Management, and Outcomes of Patients With Syncope and Bundle Branch BlockPaul CalbureanNo ratings yet
- Ehx493 P5438Document1 pageEhx493 P5438Anonymous NeRC5JYiSNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Aplasia: A Rare Complication of Disseminated TuberculosisDocument3 pagesBone Marrow Aplasia: A Rare Complication of Disseminated TuberculosisayuNo ratings yet
- Yagmur Et Al 2013 Platelet Hyperaggregability Is Highly Prevalent in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease AnDocument7 pagesYagmur Et Al 2013 Platelet Hyperaggregability Is Highly Prevalent in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease AnMister FannaniNo ratings yet
- Arteriovenous Fistula Creation For End-Stage Renal Disease May Worsen Pulmonary HypertensionDocument3 pagesArteriovenous Fistula Creation For End-Stage Renal Disease May Worsen Pulmonary HypertensionLuis Rodriguez PratoNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Neuroradiological Procedures Premalatha SDocument48 pagesAnaesthesia For Neuroradiological Procedures Premalatha SPrema LathaNo ratings yet
- Posterior Circulation Stroke: Advances in Understanding and ManagementFrom EverandPosterior Circulation Stroke: Advances in Understanding and ManagementJong S. KimNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Blood and Bone Marrow DisordersFrom EverandDiagnosis of Blood and Bone Marrow DisordersSa A. WangNo ratings yet
- Best Practices of Apheresis in Hematopoietic Cell TransplantationFrom EverandBest Practices of Apheresis in Hematopoietic Cell TransplantationSyed A. AbutalibNo ratings yet
- Surgery and Post OpDocument96 pagesSurgery and Post OpNguyễn Nhật HoàngNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Chap6. Bacterial Infections of Skin 2020-3-23Document368 pagesDermatology Chap6. Bacterial Infections of Skin 2020-3-23Mohsin Tanmoy100% (1)
- Melphalan (AHFS DI)Document10 pagesMelphalan (AHFS DI)maryNo ratings yet
- Senile DementiaDocument11 pagesSenile DementiaSubha MaheswariNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine Major CaseDocument25 pagesOral Medicine Major Case0030-GRETANZA HENDRAT MONICANo ratings yet
- Levenson - Psychosomatic Medicines - 3 Ed - 2019-289-313Document25 pagesLevenson - Psychosomatic Medicines - 3 Ed - 2019-289-313yennifer hoyos mendezNo ratings yet
- Eruptive Disorders of Permanent TeethDocument6 pagesEruptive Disorders of Permanent Teethtaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- PhotodermatosesDocument8 pagesPhotodermatosesIvan KurniadiNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis DiarrheaDocument2 pagesUlcerative Colitis DiarrheateuuuuNo ratings yet
- Table S1 English Translation of The MIR ExaminationDocument43 pagesTable S1 English Translation of The MIR Examinationهادي تركي شنبارةNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Embolotherapy in Interventional Oncology - Technology, Techniques, and ApplicationsDocument15 pagesHepatic Embolotherapy in Interventional Oncology - Technology, Techniques, and ApplicationsVeronica AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Assistant Surgeon Exam PDFDocument9 pagesSyllabus Assistant Surgeon Exam PDFMaguNo ratings yet
- 2Nd Year BS-MLT Course ContentsDocument13 pages2Nd Year BS-MLT Course ContentsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic TumourDocument4 pagesInflammatory Myofibroblastic TumourThiruNo ratings yet
- PCEP-PC Module 4 (Pain) NotesDocument12 pagesPCEP-PC Module 4 (Pain) NotesMan MedNo ratings yet
- 2 Intestinal-ObstructionDocument5 pages2 Intestinal-ObstructionMyrtle Yvonne RagubNo ratings yet
- Personal Social HistoryDocument1 pagePersonal Social HistoryledfielcastilloNo ratings yet
- Kussmaul BreathingDocument3 pagesKussmaul BreathingsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- OSCE Final 1 PDFDocument204 pagesOSCE Final 1 PDFamalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Medical Mycoloy - AspergillosisDocument17 pagesLecture 10 - Medical Mycoloy - AspergillosisXavier DharmaNo ratings yet
- Burn PathophysiologyDocument14 pagesBurn PathophysiologyAgung Widya PramanaNo ratings yet
- The Gems Brain Change ModelDocument9 pagesThe Gems Brain Change Modelapi-324897890100% (4)
- Kode Icd 10Document536 pagesKode Icd 10AkbarisArisNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agonists: Dr. Mohamed Samai BSC (Hons), MSC, MBBS, PGCRM, PHD Head, Department of Pharmacology Comahs, UslDocument31 pagesCholinergic Agonists: Dr. Mohamed Samai BSC (Hons), MSC, MBBS, PGCRM, PHD Head, Department of Pharmacology Comahs, Uslmatchees-gone rogue100% (1)
- How I Treat Anemia in Pregnancy: Iron, Cobalamin, and FolateDocument11 pagesHow I Treat Anemia in Pregnancy: Iron, Cobalamin, and FolateAgungBudiPamungkasNo ratings yet
- хвороби птиці 981103673X PDFDocument311 pagesхвороби птиці 981103673X PDFIgor Yuskiv100% (1)
- Small Animal Emergency and Critical Care MedicineDocument193 pagesSmall Animal Emergency and Critical Care MedicineYaiza Garcia CasadoNo ratings yet