Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 3
Topic 3
Uploaded by
Mekonnen Tariku0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views37 pagesThe document discusses hierarchical network design and modular network design approaches. It describes a hierarchical design with three layers - access, distribution, and core layers. Each layer has specific functions. The document also introduces Cisco's modular enterprise architecture, which divides the network into six functional areas or modules including campus, edge, branch, data center, and teleworker. This modular approach allows more flexible design and easier implementation and troubleshooting compared to hierarchical design alone.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses hierarchical network design and modular network design approaches. It describes a hierarchical design with three layers - access, distribution, and core layers. Each layer has specific functions. The document also introduces Cisco's modular enterprise architecture, which divides the network into six functional areas or modules including campus, edge, branch, data center, and teleworker. This modular approach allows more flexible design and easier implementation and troubleshooting compared to hierarchical design alone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views37 pagesTopic 3
Topic 3
Uploaded by
Mekonnen TarikuThe document discusses hierarchical network design and modular network design approaches. It describes a hierarchical design with three layers - access, distribution, and core layers. Each layer has specific functions. The document also introduces Cisco's modular enterprise architecture, which divides the network into six functional areas or modules including campus, edge, branch, data center, and teleworker. This modular approach allows more flexible design and easier implementation and troubleshooting compared to hierarchical design alone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 37
Topic 3
Structuring and Modularizing the Network
Outline
The Topic begins with a discussion of the
hierarchical network structure
The topic introduces a modular hierarchical
approach to network design
Using a Modular Approach to Network Design
HU IT Dep't Network Design 2
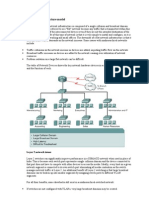
Hierarchical network design
It provides a framework that network designers can
use to help ensure that the network is flexible and
easy to implement and troubleshoot.
It is composed of the access, distribution, and core
layers.
Hierarchical network design
Each hierarchical layer focuses on specific
functions, thereby allowing the network
designer to choose
the right systems and
features based on their function within the
model.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 4
Sample Network Designed Using the
Hierarchical Model
HU IT Dep't Network Design 5
Access Layer Functionality
To grant user access to network resources
Access layer devices control traffic by localizing service requests to
the access media.
In the campus environment, the access layer typically incorporates
switched LAN devices with ports that provide connectivity for
workstations and servers.
In the WAN environment, the access layer for teleworkers or
remote sites provides access to the corporate network across some
wide-area technology (Frame Relay, MPLS, ISDN, leased line, DSL
over traditional telephone copper lines, or coaxial cable)
HU IT Dep't Network Design 6
Access Layer Connectivity in a Campus
LAN
HU IT Dep't Network Design 7
Distribution Layer Functionality
It represents both a separation between the access and core
layers and a connection point between the diverse access
sites and the core layer
It provides redundant connections for access devices
( opportunity to load-balance between devices)
It summarize routes from the access layer to improve
routing protocol performance
It implements policies for QoS, security, traffic loading, and
routing.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 8
Distribution Layer Functionality
(Policy-Based Connectivity)
Policy-based connectivity means implementing the
policies of the organization
Policy-based traffic control prioritizes traffic to
ensure the best performance for the most
time-critical and
time-dependent applications
HU IT Dep't Network Design 9
Methods for implementing
policies include the following:
Filtering by source or destination address
Filtering based on input or output ports
Hiding internal network numbers by route filtering
Security (for example, certain packets might not be allowed into a
specific part of the network)
QoS mechanisms (for example, the precedence and type of service
[ToS] values in IP packet headers can be set in routers to leverage
queuing mechanisms to prioritize traffic)
HU IT Dep't Network Design 10
Example of Distribution Layer Features
HU IT Dep't Network Design 11
Core Layer Functionality
The function of the core layer is to provide fast and efficient
data transport.
Characteristics of the core layer
It is a high-speed backbone that should be designed
to switch packets as quickly as possible to optimize
communication transport within the network.
core layer devices are expected to provide a high level of
availability and reliability.
It should not perform any packet manipulation (such as
checking access lists or filtering, which would slow down
the switching of packets)
The core layer must be manageable.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 12
Core Layer Functionality
The core devices must be able to implement scalable
protocols and technologies, and provide alternative paths and
load balancing.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 13
Today
Revise hierarchical network design
Modular Approach to network design
Security services in a modular network design
Hierarchical network design
It consists of three layers:
Access layer
Distribution layer
Core (or backbone) layer
HU IT Dep't Network Design 15
Core functions of Layers
Access To grant user access to network
Layer resources
Provides redundant connections for
Distribution
access devices
Layer Summarize routes from the access layer
provides policy-based connectivity
Core Provides high-speed transport to satisfy
Layer the connectivity and transport needs of
the distribution layer devices
Revise hierarchical network design
Modular Approach to network design
Security services in a modular network
design
Using a Modular Approach to Network Design
The modularity built into the architecture allows flexibility
in network design and facilitates implementation and
troubleshooting.
Cisco introduced the hierarchical model to divide the
enterprise network design (separately for both campus and
WAN networks) into the access, distribution, and core layers.
This solution (hierarchical model) has several weaknesses,
especially for large networks, which are difficult to
implement, manage, and, particularly, troubleshoot.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 18
Using a Modular Approach to Network Design
An efficient method of solving and scaling a complex task is
to break it into smaller, more specialized tasks.
Networks can easily be broken down smaller because they
have natural physical, logical, and functional boundaries.
If they are sufficiently large, the specialized functional
modules can then be designed hierarchically with the access,
distribution, and core layers (for design or operational
separation)
HU IT Dep't Network Design 19
Cisco Enterprise Architecture
Designing with this Cisco Enterprise Architecture is
not much different from what is already used in
practice; it formalizes current practice.
There have always been separate hierarchies for the campus
(with access, distribution, and core) and for the WAN (the
remote office was the access layer, the regional office
provided the distribution layer, and the headquarters was the
core).
HU IT Dep't Network Design 20
Cisco SONA (Service-Oriented Network Architecture)
Framework
HU IT Dep't Network Design 21
Functional Areas of the Cisco Enterprise Architecture
It comprises the following six major functional areas (also
called modules):
Enterprise Campus
Enterprise Edge
Service Provider
Enterprise Branch
Enterprise Data Center
Enterprise Teleworker
The access, distribution, and core layers can appear in any
functional area or module of the Cisco Enterprise Architecture.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 22
Cisco Enterprise Architecture
HU IT Dep't Network Design 23
Cisco Enterprise Architecture
It allows network designers to focus on only a selected
module and its functions.
Designers can describe each network application and service
on a per-module basis and validate each as part of the
complete enterprise network design.
Modules can be added to achieve scalability if necessary
HU IT Dep't Network Design 24
Sample Network Divided into Functional Areas
HU IT Dep't Network Design 25
Enterprise Campus Functional Area
Aggregates end users
from different workgroups
Aggregates the wiring
closets within a building
Provides redundant and
fast converging
connectivity between
buildings , with the Server
Farm & Enterprise Edge
provides users with
internal server resources
HU IT Dep't Network Design 26
Enterprise Edge Modules
It is composed of
four main modules:
E-commerce module
Internet Connectivity
module
Remote Access and
VPN module
WAN and MAN and
Site-to-Site VPN module
HU IT Dep't Network Design 27
E-commerce Module
To build a successful e-commerce solution, the following
network devices might be included
Web servers
Application servers
Database servers
Firewalls or firewall routers
NIDS/NIPS
Multilayer switch with IDS/IPS
Host-Based IPS
HU IT Dep't Network Design 28
Internet Connectivity Module
It provides internal users with connectivity to Internet
services, such as HTTP, FTP, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
(SMTP), and DNS.
It is not designed to serve e-commerce applications.
Major components used in the Internet Connectivity module
include the following:
SMTP mail servers
DNS servers
Public servers
Firewalls or firewall routers
Edge routers
HU IT Dep't Network Design 29
Remote Access and VPN Module
This module terminates remote access traffic and VPN traffic
that the Internet Connectivity Module forwards from remote
users and remote sites.
WAN and MAN and Site-to-Site VPN Module
This module can use traditional media and more recent
WAN physical layer technologies like
SONET/SDH , cable, DSL, MPLS, Metro Ethernet, wireless, and
service provider VPNs.
This module does not include the WAN connections or links; it
provides only the interfaces to the WAN.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 30
Service Provider Modules
The enterprise itself does not implement these modules;
however, they are necessary to enable communication with
other networks, using a variety of WAN technologies, and
with Internet service providers (ISP).
This functional area include:
Internet Service Provider module
PSTN module
Frame Relay/ATM module
HU IT Dep't Network Design 31
Remote Enterprise Modules
The three modules supporting remote enterprise locations are:-
Enterprise Branch module - by providing each location with a resilient
network architecture
Enterprise Data Center module - similar to the campus Server Farm
module
Enterprise Teleworker module - provides people in geographically
dispersed locations, such as home offices or hotels, with highly secure
access to central-site applications and network services.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 32
Revise hierarchical network design
Modular approach to network design
Secure Services in a modular network
design
Security Services in a Modular Network Design
Security is an infrastructure service that increases the
network’s integrity by protecting network resources and users
from internal and external threats.
Without a full understanding of the threats involved, network
security deployments tend to be incorrectly configured, too
focused on security devices, or lacking appropriate threat
response options.
Security both in the Enterprise Campus (internal security) and
at the Enterprise Edge (from external threats) is important.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 34
Internal Threats
In designing internal security into the network, the following
points should have to be considered at each module.
Building Access - use switch port security to control access
to the network.
Building Distribution - use access lists to provide security.
Campus Core - not to implement packet manipulation
Serve Farm - use host- and network-based IDS and IPS,
private VLANs, access control lists, secure password, use
authentication servers and logging to minimize security
threats.
HU IT Dep't Network Design 35
External Threats
When designing security in an enterprise network, the
Enterprise Edge is the first line of defense at which potential
outside attacks can be stopped.
The following four attack methods are commonly from the
outside:
IP spoofing
Password attacks
DoS attacks
Application layer attacks
HU IT Dep't Network Design 36
~ end ~
HU IT Dep't Network Design 37
You might also like
- 456029-Character Sheet DRUID EDITABLEDocument1 page456029-Character Sheet DRUID EDITABLEJarad KendrickNo ratings yet
- Learning SD-WAN with Cisco: Transform Your Existing WAN Into a Cost-effective NetworkFrom EverandLearning SD-WAN with Cisco: Transform Your Existing WAN Into a Cost-effective NetworkNo ratings yet
- Barrowmaze Players GuideDocument7 pagesBarrowmaze Players GuideFrédéric Roelandts100% (1)
- Play The Benko Gambit (PDFDrive)Document212 pagesPlay The Benko Gambit (PDFDrive)Dima100% (1)
- Network Management and Administration-NotesDocument11 pagesNetwork Management and Administration-NotesSalman Ilyas Awan71% (7)
- Chapter3.1 Designing A Network TopologyDocument49 pagesChapter3.1 Designing A Network Topologyquoc.dx.62cnttNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - LAN Design Module PDFDocument24 pagesWeek 1 - LAN Design Module PDFJacob Satorious ExcaliburNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document34 pagesCH 01mari_euNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument10 pagesChapter Threemustefa endrisNo ratings yet
- ITNE 3006 - AssignmentDocument13 pagesITNE 3006 - AssignmentSadia AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Campus Network Design Guideline - Cisco Support CommunityDocument7 pagesCampus Network Design Guideline - Cisco Support Communityamhosny64No ratings yet
- Module 001 Introduction To Scaling Networks PDFDocument34 pagesModule 001 Introduction To Scaling Networks PDFRenz RaquelNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document92 pagesChap 2Iman KhoujaNo ratings yet
- 1.borderless Switched NetworksDocument14 pages1.borderless Switched NetworksSATHISHNo ratings yet
- CCNP ROUTE Ch01Document71 pagesCCNP ROUTE Ch01kupeoNo ratings yet
- Branch-WAN Solution Overview: Executive SummaryDocument24 pagesBranch-WAN Solution Overview: Executive SummarySteveihNo ratings yet
- Data Center Design-IP Network InfrastructureDocument70 pagesData Center Design-IP Network InfrastructureDema PermanaNo ratings yet
- Unit Title: Switching Technology Unit Code: HP1L 48Document35 pagesUnit Title: Switching Technology Unit Code: HP1L 48gokuNo ratings yet
- Network Design Fundamentals: CCNP SWITCH: Implementing Cisco IP Switched NetworksDocument41 pagesNetwork Design Fundamentals: CCNP SWITCH: Implementing Cisco IP Switched NetworkszizozoroNo ratings yet
- Network Design Fundamentals: CCNP SWITCH: Implementing Cisco IP Switched NetworksDocument41 pagesNetwork Design Fundamentals: CCNP SWITCH: Implementing Cisco IP Switched NetworksSulayman AlwabelNo ratings yet
- Building Core Networks With OSPF, Is-Is, BGP, and MPLSDocument252 pagesBuilding Core Networks With OSPF, Is-Is, BGP, and MPLSWeiborao100% (1)
- Campus Area NetworkDocument4 pagesCampus Area NetworkanuyawellingNo ratings yet
- Campus NetworkDocument8 pagesCampus NetworkRebeca García FrancoNo ratings yet
- CCNA-Day1 (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)Document203 pagesCCNA-Day1 (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)khalidgabbalNo ratings yet
- 21.1 Planning For Security ServicesDocument15 pages21.1 Planning For Security ServicesRaj KaranNo ratings yet
- Path IsolDocument252 pagesPath IsolDavid HicksNo ratings yet
- CISCO Data Center Architecture OverviewDocument10 pagesCISCO Data Center Architecture OverviewTarek HniediNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document48 pagesChapter 1Syafiq OnneNo ratings yet
- Campus Network Design and Implementation Using Top Down Approach - A Case Study Tarumanagara UniDocument6 pagesCampus Network Design and Implementation Using Top Down Approach - A Case Study Tarumanagara Unikflim0% (1)
- Routing Services: CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP RoutingDocument72 pagesRouting Services: CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP RoutingLê Ngọc DũngNo ratings yet
- Acn - (Da 7650) SlidesDocument62 pagesAcn - (Da 7650) SlidesRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Exp3 AayushKumar 2022300025Document7 pagesExp3 AayushKumar 2022300025Aayush Kumar DubeyNo ratings yet
- Exploration LAN Switching Chapter1Document31 pagesExploration LAN Switching Chapter1Sahan DininduNo ratings yet
- Small Enterprise Design Profile (SEDP) - Network Foundation DesignDocument52 pagesSmall Enterprise Design Profile (SEDP) - Network Foundation DesignThinh Tien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cisco Intent-Based Networking: Detailed Report DR180830HDocument33 pagesCisco Intent-Based Networking: Detailed Report DR180830HSalma HamriNo ratings yet
- CCDP - Cisco GuidleneDocument509 pagesCCDP - Cisco Guidleneseaview1199No ratings yet
- Campus DesignDocument9 pagesCampus DesignSaffanArainNo ratings yet
- Cisco Sda Design Guide PDFDocument112 pagesCisco Sda Design Guide PDFAlemseged HabtamuNo ratings yet
- Campus Infrastructure ModelDocument244 pagesCampus Infrastructure ModelxrasnaNo ratings yet
- Training On Network: PREPARED BY: Vishal BediDocument141 pagesTraining On Network: PREPARED BY: Vishal BedidsmehlawatNo ratings yet
- Practice WordDocument25 pagesPractice WordDasale DaposNo ratings yet
- SD Access Wireless Deployment GuideDocument84 pagesSD Access Wireless Deployment GuideSalis AlvarezNo ratings yet
- SD-Access WirelessDocument118 pagesSD-Access WirelessAhmad Al-MashaikhNo ratings yet
- Seamless NetworkingDocument18 pagesSeamless NetworkingStanleyNo ratings yet
- CCNP BMSN Cap.1Document11 pagesCCNP BMSN Cap.1Vadan CorneliuNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Branch Architecture Design OverviewDocument28 pagesEnterprise Branch Architecture Design OverviewRuchir PokharnaNo ratings yet
- EnRoute500 Mesh Sample Design ReportDocument60 pagesEnRoute500 Mesh Sample Design ReportnggianglxNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Network Design and Implementations ConceptsDocument23 pagesChapter Four Network Design and Implementations ConceptsBethelhem YetwaleNo ratings yet
- CN instructorPPT Chapter1 FinalDocument31 pagesCN instructorPPT Chapter1 FinalArbias GashiNo ratings yet
- WAN Design WAN DesignDocument26 pagesWAN Design WAN DesignHarsh BhorNo ratings yet
- Report For Networking...Document194 pagesReport For Networking...Piyush AgnihotryNo ratings yet
- Main Proj - Group1Document22 pagesMain Proj - Group1ankitasinha2490No ratings yet
- CCNADocument825 pagesCCNAGirma100% (2)
- LAN Design Guide For The Midmarket: Esign Mplementation UideDocument13 pagesLAN Design Guide For The Midmarket: Esign Mplementation UideDuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Cisco Sda Design Guide PDFDocument143 pagesCisco Sda Design Guide PDFdhanraj80No ratings yet
- Telecom Network Design Final Topics FilesDocument20 pagesTelecom Network Design Final Topics FilesR Adil waheedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structured CablingDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Structured CablingSAMNo ratings yet
- 13 Designing SDN and APIC-EMDocument14 pages13 Designing SDN and APIC-EMRezaNo ratings yet
- Network Virtualization-Path Isolation Design GuideDocument252 pagesNetwork Virtualization-Path Isolation Design GuideCatalin ApostolNo ratings yet
- Next-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsFrom EverandNext-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- 34-IKLC 2019 EcolierDocument6 pages34-IKLC 2019 EcolierAnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Ramayana Book ReviewDocument8 pagesRamayana Book Reviewapi-280769193No ratings yet
- Traffic Rules and SignsDocument240 pagesTraffic Rules and Signsdhj.ind.87No ratings yet
- English CommDocument17 pagesEnglish CommastuanahNo ratings yet
- TLB Bseries 30621GBDocument16 pagesTLB Bseries 30621GBPiotr PogorzelczykNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Try It Out!Document7 pagesContemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Try It Out!Master NistroNo ratings yet
- Essay LeipzigDocument11 pagesEssay LeipzigPere Méndez MarsalNo ratings yet
- Italics vs. Quotation Marks in TitlesDocument2 pagesItalics vs. Quotation Marks in TitlesJSmith1103No ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Testjoybie loayonNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Class VIIIDocument4 pagesAssignment of Class VIIIMd A RAZZAKNo ratings yet
- Thadiyankudisai Rural TourismDocument21 pagesThadiyankudisai Rural TourismKiran KeswaniNo ratings yet
- Cruiser ManualDocument491 pagesCruiser ManualChristian HauganNo ratings yet
- Avalon Direct English Imię I Nazwisko ............................................... Tel. Kontaktowy.................. Test WstępnyDocument5 pagesAvalon Direct English Imię I Nazwisko ............................................... Tel. Kontaktowy.................. Test WstępnyMalwina HerszNo ratings yet
- CMS Manual: CMS Quick Operation GuideDocument16 pagesCMS Manual: CMS Quick Operation GuideHarvey PeñaNo ratings yet
- Details PDFDocument7 pagesDetails PDFαиgєl ѕєlєиαNo ratings yet
- 05a Tuba in CDocument49 pages05a Tuba in CMichael RogersNo ratings yet
- Peking OperaDocument2 pagesPeking OperaHEVER TORRESNo ratings yet
- RPP SpeakingDocument6 pagesRPP SpeakingOfik Taufik NNo ratings yet
- Discovering Computers 2009Document48 pagesDiscovering Computers 2009Serah JavaidNo ratings yet
- 2023 02 28 - LogDocument221 pages2023 02 28 - LogIlaaNo ratings yet
- Chennai Madhavaram Bus Terminus To Tirupathi: Cancelled Ticket DetailsDocument1 pageChennai Madhavaram Bus Terminus To Tirupathi: Cancelled Ticket DetailsraghuNo ratings yet
- Animals in Their Surroundings Book Ex Ques Ans TestDocument2 pagesAnimals in Their Surroundings Book Ex Ques Ans TestsanjoymisraNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Cold RollingDocument37 pagesPresentation of Cold Rollingmange_ram70No ratings yet
- Knee JointDocument39 pagesKnee JointPraneetha NouduriNo ratings yet
- Bom SWBD2Document2 pagesBom SWBD2Prasanna SinthajeNo ratings yet
- Speed Secrets WeeklyDocument3 pagesSpeed Secrets WeeklyMunawwar ArNo ratings yet
- Ayman Satopay - Office FileDocument14 pagesAyman Satopay - Office FileAyman SatopayNo ratings yet