Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Strategy of IB: International Business - Chapter 13
The Strategy of IB: International Business - Chapter 13
Uploaded by
Yến Ngô Hoàng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views20 pagesThe chapter discusses International Business strategies. It explains that global expansion allows firms to benefit from location economies by performing value-creating activities in optimal locations to lower costs or differentiate products. Clear Vision, an eyewear company, faced threats from low-cost imports. Instead of lowering costs, it invested in high-quality factories abroad and differentiated its "designer" products. Experience curves show that production costs decline as cumulative output increases due to learning effects and economies of scale. Firms face the greatest pressure to reduce costs in commodity industries, when major competitors have low costs, during excess capacity, and when consumers have power and low switching costs.
Original Description:
Original Title
IB-W2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe chapter discusses International Business strategies. It explains that global expansion allows firms to benefit from location economies by performing value-creating activities in optimal locations to lower costs or differentiate products. Clear Vision, an eyewear company, faced threats from low-cost imports. Instead of lowering costs, it invested in high-quality factories abroad and differentiated its "designer" products. Experience curves show that production costs decline as cumulative output increases due to learning effects and economies of scale. Firms face the greatest pressure to reduce costs in commodity industries, when major competitors have low costs, during excess capacity, and when consumers have power and low switching costs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views20 pagesThe Strategy of IB: International Business - Chapter 13
The Strategy of IB: International Business - Chapter 13
Uploaded by
Yến Ngô HoàngThe chapter discusses International Business strategies. It explains that global expansion allows firms to benefit from location economies by performing value-creating activities in optimal locations to lower costs or differentiate products. Clear Vision, an eyewear company, faced threats from low-cost imports. Instead of lowering costs, it invested in high-quality factories abroad and differentiated its "designer" products. Experience curves show that production costs decline as cumulative output increases due to learning effects and economies of scale. Firms face the greatest pressure to reduce costs in commodity industries, when major competitors have low costs, during excess capacity, and when consumers have power and low switching costs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
Chapter 13
The strategy of IB
International Business - Chapter 13
4.Global expansion
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
Part 2. Location Economies
• Definition: economies that arise from performing a value creation
activity in the optional location
• Why? It can lower the cost of value creation and help the firm achieve a low-
cost position, and/or it can enable a firm to differentiate its products offering
those of competitors
• Kinh te dia diem: là đặt những nơi tạo ra kinh tế ở nhiều địa điểm
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
Case: Clear Vision page.372
• What is the typical team that play Clear Vision faced? how did it handle?
• Low-priced imports were taking an ever-larger share of the U.S.
• a threat from foreign competition
• growing labour shortage had pushed up wage rates because industrialization in HK
-> low-cost location no longer
• Describe the changes and their strategies throughout the case:
• Changes:
• Its objective was not to reduce production costs but to launch a line of high-quality
differentiated, “designer” eyewear.
• ClearVision invested its capital in factories in Japan, France, and Italy.
• Strategies:
• intended to lower its cost structure (lower C) -> to increase the perceived value of its product.
International Business - Chapter 13
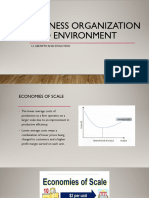
Figure 13.5 illustrates this experience curve relationship between unit production costs and cumulative
output
International Business - Chapter 13
Experience Effect
• Learning Effects: • Economies of Scale
• Labor productivity increases over • reductions in unit cost achieved by
time as individuals learn the most producing a large volume of a
efficient ways to perform product.
particular tasks. • The more rapidly that cumulative
• Production costs decline due to sales volume is built up, the more
increasing labour productivity and rapidly fixed costs can be
management efficiency, which amortized over a large production
increases the firm’s profitability. volume, and the more rapidly unit
• learning effects typically costs will fall.
• disappear after a while.
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
What is implied in the case? Page.376
• Faced with slow growth -> its local franchisees have begun to
experiment not only with the menu, but also with the layout and
theme of restaurants.
• Half of the 1,200 or so outlets in France have been upgraded to an
incredible level
=> After that, the Sale increased annually up to 3.4%
• The company must reward people for successes and not sanction
them unnecessarily for taking risks that did not pan out.
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
When are pressures for cost reductions
greatest?
• Presures for cost reductions are greatest?
1. In industries producing commodity type products that fill universisal needs
( needs that exist when the tastes and preferences of consumers in
different nations are similar if not identical) where price is the main
competitive weapon
2. When major competitors are based in low-cost locations
3. Where there is persistent excess capacity
4. Where consumer are powerful and face low switching costs
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
International Business - Chapter 13
You might also like
- IBizSim-International Business SimulationDocument30 pagesIBizSim-International Business SimulationNaresh Hingonikar100% (1)
- MMVA ZG512 Manufacturing Strategy: Rajiv Gupta BITS Pilani Session 5Document42 pagesMMVA ZG512 Manufacturing Strategy: Rajiv Gupta BITS Pilani Session 5ANIL KUMAR SINGHALNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Unit 3.5.5 - Economies and Diseconomies of Scale - Miss PatelDocument13 pagesCIE IGCSE Unit 3.5.5 - Economies and Diseconomies of Scale - Miss PatelJingyao HanNo ratings yet
- Economies of Scale: Igcse BusinessDocument38 pagesEconomies of Scale: Igcse Businessrahaf.jaradat008No ratings yet
- PLM Study Material For Assignment 2Document32 pagesPLM Study Material For Assignment 2Yash KateNo ratings yet
- Chap 11 - IBDocument17 pagesChap 11 - IBkamaruljamil4No ratings yet
- Sales and Distribution Management: Name:Shivaraj Patil G D Reg. No:19MCMS047095 Course:MBA (Marketing)Document10 pagesSales and Distribution Management: Name:Shivaraj Patil G D Reg. No:19MCMS047095 Course:MBA (Marketing)annetteNo ratings yet
- Economics IGCSE Chap 20-Firms and ProductionDocument59 pagesEconomics IGCSE Chap 20-Firms and ProductioneyshaNo ratings yet
- ProductionDocument22 pagesProductionapi-53255207No ratings yet
- Operations Management RevisionDocument36 pagesOperations Management RevisionSonca TruongNo ratings yet
- Winning in Business Lite Case Study - Read As PreworkDocument3 pagesWinning in Business Lite Case Study - Read As PreworkAgustinNo ratings yet
- BM GROWTH AND EVOLUTION (1)Document28 pagesBM GROWTH AND EVOLUTION (1)laura graceNo ratings yet
- ThegrowthoffirmsDocument12 pagesThegrowthoffirmsBlack arab GaladimaNo ratings yet
- The Strategy and Structure of International Business: Maglinte, Shela Mae L. Padron, Abigail MDocument19 pagesThe Strategy and Structure of International Business: Maglinte, Shela Mae L. Padron, Abigail MHanna Sobreviñas AmanteNo ratings yet
- The Strategy of International Business: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument37 pagesThe Strategy of International Business: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinMardhiah RamlanNo ratings yet
- Economics - Topic 8Document19 pagesEconomics - Topic 8AB RomillaNo ratings yet
- The Strategy of International BusinessDocument29 pagesThe Strategy of International Businessrittik sarkerNo ratings yet
- Business 1.6Document72 pagesBusiness 1.6samerNo ratings yet
- Erica Novianti LukasDocument16 pagesErica Novianti LukasRimeh BakirNo ratings yet
- Operations Strategy in Global EnvironmentDocument18 pagesOperations Strategy in Global EnvironmentIsha MasroorNo ratings yet
- Strategy & Policy Lecture Week 6 - CanvasDocument37 pagesStrategy & Policy Lecture Week 6 - CanvasPo Wai LeungNo ratings yet
- The Strategy of International BusinessDocument27 pagesThe Strategy of International BusinessGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- ch5. IntroDocument51 pagesch5. Intro223joemamaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management NotesDocument8 pagesStrategic Management NotesSreejith Rnair SrnNo ratings yet
- BussDocument16 pagesBusskarkam22No ratings yet
- Target CostingDocument20 pagesTarget CostinganisahNo ratings yet
- Building Competitive Advantage Through Functional Level StrategyDocument50 pagesBuilding Competitive Advantage Through Functional Level Strategykawsar_cow2819No ratings yet
- Business To Business Marketing: Strategic Planning For Global Business MarketsDocument25 pagesBusiness To Business Marketing: Strategic Planning For Global Business MarketsMd. Mehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 StrategyDocument36 pagesChapter 5 StrategyThương Huyền LêNo ratings yet
- Economies of Scale, Disconomies of Scale & Economies of ScopeDocument16 pagesEconomies of Scale, Disconomies of Scale & Economies of Scopesalman_shajiNo ratings yet
- Strategy of International BusinessDocument13 pagesStrategy of International BusinessKezzel Dannah NAPAWITNo ratings yet
- International Business: by Charles W.L. HillDocument29 pagesInternational Business: by Charles W.L. HillAshraful IslamNo ratings yet
- 0450 - 1.3 Enterprise, Business Growth and SizeDocument15 pages0450 - 1.3 Enterprise, Business Growth and SizeCherylNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Functional Level Strategy - 2023Document33 pagesChapter 4 Functional Level Strategy - 2023Mai PhươngNo ratings yet
- IB Bm2tr 5 Resources Answers5Document6 pagesIB Bm2tr 5 Resources Answers5Gabriel FungNo ratings yet
- IBM Unit III 2018 05.09.2018Document94 pagesIBM Unit III 2018 05.09.2018Arunkumar PoMNo ratings yet
- SC T9Document28 pagesSC T9Zi En AngNo ratings yet
- (L10) Managing International OperationsDocument34 pages(L10) Managing International OperationsMarvin YuNo ratings yet
- Business and Supply - 2024 - PVDocument50 pagesBusiness and Supply - 2024 - PVsilverphantom9090No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - International Business StrategyDocument33 pagesChapter 5 - International Business StrategyHoàng Trần ĐứcNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Growth and EvolutionDocument38 pages1.5 Growth and EvolutionMarina Peña BenitaNo ratings yet
- SM - 09Document26 pagesSM - 09Jithma RanawakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - International Business StrategiesDocument33 pagesChapter 7 - International Business StrategiesThanh Lam LamNo ratings yet
- Economies of Scale FinalDocument33 pagesEconomies of Scale FinalNikhil KasatNo ratings yet
- Economics (Economies and Diseconomies & BEP)Document34 pagesEconomics (Economies and Diseconomies & BEP)bhutan govtNo ratings yet
- Scales of ProductionDocument11 pagesScales of Production165Y020 SATHWICK BUJENDRA GOWDA100% (1)
- The Strategy of International BusinessDocument24 pagesThe Strategy of International BusinessZakiah Abu KasimNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Consumer BehaviorDocument41 pagesWeek 5 - Consumer BehaviorAdruffNo ratings yet
- Formulating Long Term Objectives and Grand StrategiesDocument50 pagesFormulating Long Term Objectives and Grand StrategiesNida_Basheer_206No ratings yet
- Week 6 - Behaviour of A Firm and Short Run ProductionDocument62 pagesWeek 6 - Behaviour of A Firm and Short Run ProductionAdruffNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - International Business StrategiesDocument31 pagesChapter 7 - International Business StrategiesHuyền NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Topic 1Document42 pagesChapter 9 - Topic 1Vedant NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Global Business - Unit 4Document86 pagesGlobal Business - Unit 4GauravTiwariNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Boundaries of The FirmDocument49 pagesTopic 1 Boundaries of The FirmPeter MastersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - International Business StrategyDocument32 pagesChapter 5 - International Business Strategykhanhan231204No ratings yet
- IFIS Lecture 3 Headquarter Subsidiary RelationDocument28 pagesIFIS Lecture 3 Headquarter Subsidiary RelationinkmytaskNo ratings yet
- Arun Balan Chirag Chadda Jimmey Jose Khalid Shuaib Madhumitha Sundaresan Christ University 20 July 2010Document13 pagesArun Balan Chirag Chadda Jimmey Jose Khalid Shuaib Madhumitha Sundaresan Christ University 20 July 2010Sourabh ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Grand Strategies: Zakir PatelDocument36 pagesGrand Strategies: Zakir Patelzakirno19248No ratings yet
- The Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)From EverandThe Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)No ratings yet
- Week1 - Sony CaseDocument4 pagesWeek1 - Sony CaseYến Ngô HoàngNo ratings yet
- Ib - W4Document25 pagesIb - W4Yến Ngô HoàngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15.entry ModesDocument4 pagesChapter 15.entry ModesYến Ngô HoàngNo ratings yet
- Ky Nang Viet Students Book Effective Academic WritingDocument169 pagesKy Nang Viet Students Book Effective Academic WritingYến Ngô HoàngNo ratings yet
- 2015 Atlas Copco MR Warranty Policy Rev 012Document10 pages2015 Atlas Copco MR Warranty Policy Rev 012jogremaurNo ratings yet
- IMPORTANT INFORMATION - : Baggage AllowanceDocument2 pagesIMPORTANT INFORMATION - : Baggage AllowanceHla Cho HtutNo ratings yet
- France - Airbus : A Web Based Case StudyDocument13 pagesFrance - Airbus : A Web Based Case Studyvijaysingh_83No ratings yet
- University of Hargeisa Hargeisa School eDocument22 pagesUniversity of Hargeisa Hargeisa School eamira yonisNo ratings yet
- Oracle Istore Custom Page Creation For Multiple Sites: March 2009Document7 pagesOracle Istore Custom Page Creation For Multiple Sites: March 2009NRK MurthyNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument28 pagesINTRODUCTIONKristin BactolNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting and Analysis Revsine 6th Edition Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesFinancial Reporting and Analysis Revsine 6th Edition Solutions Manualweantoss8ykg5100% (44)
- Test Bank For Cost Accounting A Managerial Emphasis 13e 9780136126638Document24 pagesTest Bank For Cost Accounting A Managerial Emphasis 13e 9780136126638AlejandraPruittarqbp100% (50)
- Forster Investment AdvisorsDocument3 pagesForster Investment AdvisorsTiến Dũng MaiNo ratings yet
- Câu H i ạ ể: Hoàn thành t i m 1,00 trên 1,00Document4 pagesCâu H i ạ ể: Hoàn thành t i m 1,00 trên 1,00Tram NguyenNo ratings yet
- A Training Proposal Submitted To The Maritime Sector of The FMTDocument11 pagesA Training Proposal Submitted To The Maritime Sector of The FMTSomkwe John-Nwosu100% (2)
- Sas#11 Bam200Document7 pagesSas#11 Bam200Mekuh Rouzenne Balisacan PagapongNo ratings yet
- A Prep Guide For Case InterviewsDocument56 pagesA Prep Guide For Case InterviewsVikramAditya Kumar TanejaNo ratings yet
- OUMH2203 English For Workplace Comm - Emay23 (CS)Document211 pagesOUMH2203 English For Workplace Comm - Emay23 (CS)suriaNo ratings yet
- 3 Self-Assessment LSADocument4 pages3 Self-Assessment LSAJELYN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Lankabangla Project by MinhazDocument40 pagesLankabangla Project by MinhazShafayet JamilNo ratings yet
- Project Case - Brannigan Foods - Financial CalculationsDocument2 pagesProject Case - Brannigan Foods - Financial CalculationsDuyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter II The Companies (Incorporation) Rules, 2014Document116 pagesChapter II The Companies (Incorporation) Rules, 2014Jitendra RavalNo ratings yet
- Music Dissertation ProposalDocument5 pagesMusic Dissertation ProposalWriteMyPersuasivePaperCanada100% (1)
- Enderes vs. Lee TSNDocument3 pagesEnderes vs. Lee TSNLowell MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- 00 - Service Operations Management OutlineDocument6 pages00 - Service Operations Management OutlineSagar BadnakheNo ratings yet
- NREL Case DigestDocument6 pagesNREL Case DigestRhengie hernandezNo ratings yet
- Oromia Int Bank Annual Report July 2014-June2015Document61 pagesOromia Int Bank Annual Report July 2014-June2015shelema lemiNo ratings yet
- SPREE - THE MARKET PLAN (Muhammad Shoaib Assignment)Document10 pagesSPREE - THE MARKET PLAN (Muhammad Shoaib Assignment)shoaibNo ratings yet
- (Eim-t222-Wsb3 - Reading Chapter 1 - Example of InnovationDocument2 pages(Eim-t222-Wsb3 - Reading Chapter 1 - Example of InnovationBaonhiiNo ratings yet
- Applicable Fees and Charges On Credit CardDocument3 pagesApplicable Fees and Charges On Credit CardAbbasNo ratings yet
- Bank of AgricultureDocument15 pagesBank of AgricultureHaidee BellaNo ratings yet
- Resume-Pramod-Bhupathi TeamconnectDocument3 pagesResume-Pramod-Bhupathi TeamconnectHaseeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Condenser Tube Leakage2Document10 pagesCondenser Tube Leakage2prakash100% (2)
- Каталог ССК и инструментаDocument162 pagesКаталог ССК и инструментаШилоNo ratings yet