Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Circle
Introduction To Circle
Uploaded by
Matsuri Virus0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views5 pagesA circle is defined as a set of points equidistant from a fixed center point. The key parts of a circle include the radius, diameter, chord, circumference, arc, angle, and their properties. A radius connects the center to a point on the circle, while a diameter connects two points on the circle through the center. An arc is part of the circumference. Theorems and postulates describe relationships between central angles, arcs, chords, and their measures. A sector is the region between an arc and radii, and a segment is between an arc and the chord.
Original Description:
Original Title
INTRODUCTION-TO-CIRCLE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA circle is defined as a set of points equidistant from a fixed center point. The key parts of a circle include the radius, diameter, chord, circumference, arc, angle, and their properties. A radius connects the center to a point on the circle, while a diameter connects two points on the circle through the center. An arc is part of the circumference. Theorems and postulates describe relationships between central angles, arcs, chords, and their measures. A sector is the region between an arc and radii, and a segment is between an arc and the chord.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views5 pagesIntroduction To Circle
Introduction To Circle
Uploaded by
Matsuri VirusA circle is defined as a set of points equidistant from a fixed center point. The key parts of a circle include the radius, diameter, chord, circumference, arc, angle, and their properties. A radius connects the center to a point on the circle, while a diameter connects two points on the circle through the center. An arc is part of the circumference. Theorems and postulates describe relationships between central angles, arcs, chords, and their measures. A sector is the region between an arc and radii, and a segment is between an arc and the chord.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
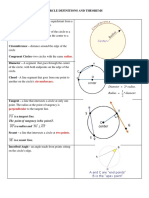
CIRCLE – is a set of points equidistant from a fixed
point called the CENTER. It is usually named by its
center (e.g. )
PRIMARY PARTS
1. Radius is a segment that connects the center and
any point on the circle. Distance between the center
and a point on the circle.
2. Diameter is a segment that connects two points on
the circle and passes through the center of the circle.
It also twice the length of the radius.
3. Chord is a segment joining two points on the circle.
4. Circumference is the distance around the circle.
5. Arc is part of the circumference of the circle.
• Minor Arc is an arc that measures less than 180 degrees.
• Major Arc is an arc that measures more than 180 degrees.
• Semicircle is an arc that measures exactly 180 degrees. Also
half the circumference of the circle.
• Intercepted Arc is an arc that is intercepted by an angle.
6. Angle is a figure formed by two rays/segments with a common
point called the vertex.
• Central Angle is an angle whose sides are the radii of a circle
and the vertex is the center. The measure of the central angle
is equal to the measure of its intercepted arc.
• Inscribed Angle is an angle whose sides are two chords and the
vertex is a point on the circle. The measure of the inscribed
angle is equal to one half the measure of its intercepted arc.
SECONDARY PARTS
1. Tangent is a line that passes through the
circle at exactly one point
2. Secant is a line that passes through the circle
in two points.
MORE TERMS ON CIRCLES
• Congruent Circles are circles whose radii are
equal.
• Concentric Circles are circles with common
center but of different radii.
• Congruent Arcs are arcs of equal measures
C. Theorems on Central Angles, Arcs and Chords.
1. In a circle or congruent circles, two minor arcs are congruent iff their
corresponding central angles are congruent.
2. In a circle or congruent circles, two minor arcs are congruent iff their
corresponding chords are congruent. In a circle the diameter bisects a chord
and an arc with the same endpoints iff it is perpendicular to that chord.
3. In a circle, a diameter bisects a chord and an arc with the same
endpoints, iff it is perpendicular to the chord.
D. Postulates on Central Angles, Arcs and Chords
1. Angle Addition Postulate The measure of an angle formed by two
adjacent angles is the sum of the measures of the two angles.
2. Arc Addition Postulate The measure of an arc formed by two adjacent
angles is the sum of the measures of the two arcs.
3. Sum of the Central Angles of the circle with no common interior points is
360 degrees.
SECTOR OF A CIRCLE is the region bounded by an arc of
the circle and two radii to the endpoints of the arc.
SEGMENT OF A CIRCLE is the region bounded by an arc
and the segment joining its endpoints.
ARC LENGTH is the linear length of the arc
You might also like
- Maths Project For Class 10Document18 pagesMaths Project For Class 10John Nguyen57% (42)
- Definitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryDocument8 pagesDefinitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Circles 230825064621 68c161e6Document36 pagesCircles 230825064621 68c161e6kian mndzNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument19 pagesCirclealexandradeleon080508No ratings yet
- Circles Review For Test 1 1Document4 pagesCircles Review For Test 1 1api-256105506No ratings yet
- Circle and TheoremsDocument32 pagesCircle and Theoremsalexandradeleon080508No ratings yet
- CircleDocument11 pagesCircleJulie Anne TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Circles and Other Related TermsDocument36 pagesCircles and Other Related TermsPatricia CadacioNo ratings yet
- Math70 F2013 Lecture Sections6 1thru6 2Document4 pagesMath70 F2013 Lecture Sections6 1thru6 2Raiel RoaNo ratings yet
- Math Subject For High School - 9th Grade - Systems of Equations and Inequalities by SlidesgoDocument24 pagesMath Subject For High School - 9th Grade - Systems of Equations and Inequalities by Slidesgolheyvin kert bautistaNo ratings yet
- Math Subject For High School - 9th Grade - Systems of Equations and Inequalities by SlidesgoDocument24 pagesMath Subject For High School - 9th Grade - Systems of Equations and Inequalities by Slidesgolheyvin kert bautistaNo ratings yet
- Circle: Section 1.6 - Circles VocabularyDocument8 pagesCircle: Section 1.6 - Circles Vocabularysullygks2092No ratings yet
- Terms Realated To CirclesDocument2 pagesTerms Realated To CirclesMilanNo ratings yet
- 2 - Chords Arcs Angles Tangents and SecantsDocument9 pages2 - Chords Arcs Angles Tangents and SecantsJoshWayne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of A CircleDocument11 pagesBasic Concepts of A CircleSudharani Sudha100% (1)
- 4 2 Properties of Circles NotesDocument10 pages4 2 Properties of Circles Notesapi-276774539No ratings yet
- Mathamatics Fest: Leaders GroupDocument14 pagesMathamatics Fest: Leaders GroupArshad PashaNo ratings yet
- Circles ModifiedDocument134 pagesCircles ModifiedHermione ClydeNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Definition of Circle and Its Parts With IllustrationsDocument6 pagesIntroduction - Definition of Circle and Its Parts With IllustrationsMikaela Angela CenaNo ratings yet
- CIrclesDocument10 pagesCIrclesMaria DzNo ratings yet
- Glossary Terms: R Is The Radius of The Circle and L Is The Arc LengthDocument4 pagesGlossary Terms: R Is The Radius of The Circle and L Is The Arc LengthBonbert LascoNo ratings yet
- Relationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central AnglesDocument45 pagesRelationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central Anglesjoshuaomnos9No ratings yet
- Circle Definitions and TheoremsDocument8 pagesCircle Definitions and TheoremsGani Almeron100% (1)
- Geom - 10.1-10.4 PowerPointDocument19 pagesGeom - 10.1-10.4 PowerPointAnanthuNo ratings yet
- Circles Arc and Cyclic PropertiesDocument3 pagesCircles Arc and Cyclic PropertiesBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Module1 1Document10 pagesModule1 1Jowelyn MaderalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 Circles Central Angle and Inscribed AngleDocument16 pagesMathematics 10 Circles Central Angle and Inscribed AngleSealthiel JacobeNo ratings yet
- Central Angle and ArcsDocument1 pageCentral Angle and ArcsTito AgooNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Mathematics Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Mathematics Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesMarieanne SantosNo ratings yet
- Firm Up: Central and Inscribed AnglesDocument4 pagesFirm Up: Central and Inscribed AnglesAnte, Jay-R B.No ratings yet
- Geometry RodriguezDocument3 pagesGeometry RodriguezVI DALAGAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Circles and Its Related TermsDocument3 pagesCircles and Its Related Termsapi-174391216No ratings yet
- Tangent and CircleDocument1 pageTangent and Circleaimgod100No ratings yet
- Vocabulary Circles 122710Document1 pageVocabulary Circles 122710pfredaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Math 3rd Year - Arcs and Angles 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesReviewer Math 3rd Year - Arcs and Angles 3rd QuarterNanay GiNo ratings yet
- Circles:: Introduction To Chords, Arcs, andDocument1 pageCircles:: Introduction To Chords, Arcs, andPatrick PelicanoNo ratings yet
- Central and Inscribed AnglesDocument41 pagesCentral and Inscribed Angleselizabethlagutin1No ratings yet
- Report On The CircleDocument8 pagesReport On The CircleZanderNo ratings yet
- Circle MathsDocument10 pagesCircle MathsAdhithy SkumarNo ratings yet
- Pink Purple Organic Abstract Group Project Presentation - 20240401 - 114155 - 0000Document22 pagesPink Purple Organic Abstract Group Project Presentation - 20240401 - 114155 - 0000MA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument49 pagesCircleMars SalazarNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument4 pagesCirclesTrendy PorlageNo ratings yet
- ADVGEOM Lecture5 Nov20Document26 pagesADVGEOM Lecture5 Nov20Ellaine LimpangogNo ratings yet
- Module1 2Document14 pagesModule1 2Jowelyn MaderalNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument16 pagesCirclesSant AshiaNo ratings yet
- MATH (Geron)Document5 pagesMATH (Geron)Chris Orlan Hilary RazonaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Math 2nd Monthly 10Document1 pageReviewer in Math 2nd Monthly 10Trixie AsistidoNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument51 pagesGeometryneerja92No ratings yet
- MATHSDocument11 pagesMATHSyogeshbhati20077No ratings yet
- Circle: Parts of A CircleDocument2 pagesCircle: Parts of A CircleChristine Joy MagtibayNo ratings yet
- A CircleDocument1 pageA CircleFrenzy SenarillosNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument23 pagesCirclesDanna Marie OlioNo ratings yet
- Topik-2 Bulatan CircleDocument36 pagesTopik-2 Bulatan Circle许如楠No ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1: CIRCLES Lesson 2.2 MISCELLANEOUS Planes: Week 3 and Week 4 Math 13 Solid MensurationDocument29 pagesLesson 2.1: CIRCLES Lesson 2.2 MISCELLANEOUS Planes: Week 3 and Week 4 Math 13 Solid MensurationDan Casurao100% (1)
- 2.6 CIRCLES and Related Segments and AnglesDocument50 pages2.6 CIRCLES and Related Segments and AnglesJamill BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- Circle Geometry NotesDocument2 pagesCircle Geometry NotesGeoffrey WongNo ratings yet
- Spherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesFrom EverandSpherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesNo ratings yet
- 3rd Unified Exam FIL10Document1 page3rd Unified Exam FIL10Matsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Parents Consent PARA MAKAPANOOD NG BOTBDocument1 pageParents Consent PARA MAKAPANOOD NG BOTBMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- The Genome Sequence of The Rice Blast Fungus Magnaporthe GriseaDocument1 pageThe Genome Sequence of The Rice Blast Fungus Magnaporthe GriseaMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument22 pagesGas LawsMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Elective Mathematics 10 Module Tangent Line of 4th QTRDocument14 pagesElective Mathematics 10 Module Tangent Line of 4th QTRMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument14 pagesConcentration of SolutionsMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Equation of Hyperbola Center at The HKDocument12 pagesEquation of Hyperbola Center at The HKMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- New Music Composers and Song ComposersDocument29 pagesNew Music Composers and Song ComposersMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LimitsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To LimitsMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Force On A Moving Charge ProblemsDocument11 pagesMagnetic Force On A Moving Charge ProblemsMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- MR and Ms HandbookDocument5 pagesMR and Ms HandbookMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 10 Class Program 2022 2023Document14 pagesGrade 9 10 Class Program 2022 2023Matsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Elective Math Week 2Document5 pagesElective Math Week 2Matsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Midpoint and SlopeDocument19 pagesMidpoint and SlopeMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- 2nd QTR English 10 LESSON 3Document27 pages2nd QTR English 10 LESSON 3Matsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- October 12 2022Document5 pagesOctober 12 2022Matsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Calamansi X Citrofortunella Microcarpa Pure Fruit Extract As An Antibacterial Hand Sanitizer Against Staphylococcus Aureus 1Document37 pagesCalamansi X Citrofortunella Microcarpa Pure Fruit Extract As An Antibacterial Hand Sanitizer Against Staphylococcus Aureus 1Matsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work For First Quarter 1Document7 pagesBudget of Work For First Quarter 1Matsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Flow Part 1Document4 pagesResearch Proposal Flow Part 1Matsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- 3RDM3WO MarcoDocument1 page3RDM3WO MarcoMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- JUNIORDocument1 pageJUNIORMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Problems On Polynomial FunctionsDocument8 pagesProblems On Polynomial FunctionsMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- FILIPINDocument7 pagesFILIPINMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- 2nd QTR Eng10 Week 1 Quarter Language Research Campaigns and AdvocaciesDocument16 pages2nd QTR Eng10 Week 1 Quarter Language Research Campaigns and AdvocaciesMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument1 pageTheoretical FrameworkMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- STEM1110 Harnessing Biofuel From Chlorophyceae MicroalgaeGreen Algae For Generators Acanto Argana Castro Gamuzaran MarcoDocument19 pagesSTEM1110 Harnessing Biofuel From Chlorophyceae MicroalgaeGreen Algae For Generators Acanto Argana Castro Gamuzaran MarcoMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Marc Conrad P. Din 9 Fleming Week 3Document2 pagesMarc Conrad P. Din 9 Fleming Week 3Matsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Q4 Math 9 LAS 3 KeyDocument1 pageQ4 Math 9 LAS 3 KeyMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Coordinate SystemDocument14 pagesRectangular Coordinate SystemMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Slem Health 9 Week 7 Q 2 FinalDocument10 pagesSlem Health 9 Week 7 Q 2 FinalMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Plane GeometryDocument24 pagesPlane GeometryEurydiceNo ratings yet
- Gened CompileDocument163 pagesGened Compilerose PlopenioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Review Vocabulary Coordinate Plane, Written in The Form (X, Y)Document9 pagesLesson 1: Review Vocabulary Coordinate Plane, Written in The Form (X, Y)Donna IllanaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Handout #6 Answers and SolutionsDocument9 pagesGeometry Handout #6 Answers and SolutionsWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Maths Text Book ReviewDocument15 pagesMaths Text Book ReviewJigna Khoyani100% (1)
- 3D Geometry FormulasDocument15 pages3D Geometry FormulasRahul ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Geometric ConstructionsDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Geometric ConstructionsArianne AtilasNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorem: Remember To Look For "Basics"Document25 pagesCircle Theorem: Remember To Look For "Basics"Carl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Bow Mathematics 7-10...Document37 pagesBow Mathematics 7-10...era resusNo ratings yet
- Form 0NE PDFDocument3 pagesForm 0NE PDFAlphonsius WongNo ratings yet
- Congruence of TriangleDocument15 pagesCongruence of TriangleShlok BaruaoleNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Mathematics Olympiads Assam Academy of MathematicsDocument5 pagesSyllabus of Mathematics Olympiads Assam Academy of MathematicsBipanchi ChekonidharaNo ratings yet
- 2023 JC HL MathsDocument23 pages2023 JC HL Mathsdavidjohnson73736No ratings yet
- 9 Maths Cbse Papers Sa 2 Cce 2012 Set 2Document4 pages9 Maths Cbse Papers Sa 2 Cce 2012 Set 2inammurad12No ratings yet
- Pure Math PDFDocument101 pagesPure Math PDFKundai Chiweshe100% (1)
- Basic Geometric ConstructionsDocument2 pagesBasic Geometric ConstructionsKitty CheungNo ratings yet
- Common ErrorsDocument16 pagesCommon ErrorsdavrangNo ratings yet
- AP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusDocument17 pagesAP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusbbbbbbbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Circle PPT Worksheet 13a 2021 - 2022Document29 pagesGrade 12 Circle PPT Worksheet 13a 2021 - 2022Devi DeviNo ratings yet
- Pembinaan 3 Calon Peserta Imo 2016: Country: A BDocument1 pagePembinaan 3 Calon Peserta Imo 2016: Country: A BValentioNo ratings yet
- Similarity and CongruencyDocument22 pagesSimilarity and CongruencyVardan BajajNo ratings yet
- VMC - SOSE IX HRT - 3 (Question Paper)Document12 pagesVMC - SOSE IX HRT - 3 (Question Paper)anshmaurya454No ratings yet
- CIMCO CNC-Calc 2 - User Guide With Tutorials 1-10Document156 pagesCIMCO CNC-Calc 2 - User Guide With Tutorials 1-10Alexandru IancuNo ratings yet
- Geometry English PDFDocument40 pagesGeometry English PDFHafizAhmad100% (2)
- 2 EuclidDocument25 pages2 EuclidLorie Mae MicarisNo ratings yet
- Theorems On ParallelogramsDocument16 pagesTheorems On ParallelogramsJerrald Meyer L. BayaniNo ratings yet
- 12 Sci 4. Pair of Straight LineDocument8 pages12 Sci 4. Pair of Straight LineAdesh GadageNo ratings yet
- EGMO 2012-19 EN With Solutions PDFDocument151 pagesEGMO 2012-19 EN With Solutions PDFgarciacapitan100% (1)
- Sei-Ccrc Model Exam: Time: 1 Hr. 30 Mins. Full Marks: 100 P.M. 40Document6 pagesSei-Ccrc Model Exam: Time: 1 Hr. 30 Mins. Full Marks: 100 P.M. 40Damodar Ghimire100% (1)
- Parallelograms: Quadrilateral Opposite Sides ParallelDocument19 pagesParallelograms: Quadrilateral Opposite Sides ParallelPenke Mejado BelenNo ratings yet