Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Los Tiempos Verbales
Los Tiempos Verbales
Uploaded by
Naos Schwa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesThis document discusses Spanish verb tenses, including:
1) It describes the uses of the present simple, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous tenses.
2) It then explains the past simple, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous tenses and provides examples of their uses.
3) Finally, it outlines the future simple, future continuous, future perfect, and future perfect continuous tenses and how they are used to describe future actions and situations.
Original Description:
Original Title
Los Tiempos Verbales Ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses Spanish verb tenses, including:
1) It describes the uses of the present simple, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous tenses.
2) It then explains the past simple, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous tenses and provides examples of their uses.
3) Finally, it outlines the future simple, future continuous, future perfect, and future perfect continuous tenses and how they are used to describe future actions and situations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesLos Tiempos Verbales
Los Tiempos Verbales
Uploaded by
Naos SchwaThis document discusses Spanish verb tenses, including:
1) It describes the uses of the present simple, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous tenses.
2) It then explains the past simple, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous tenses and provides examples of their uses.
3) Finally, it outlines the future simple, future continuous, future perfect, and future perfect continuous tenses and how they are used to describe future actions and situations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
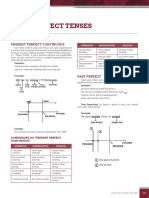
LOS TIEMPOS VERBALES
Dr. Dario Vasquez Estela
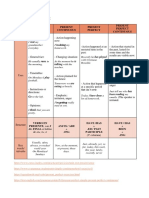
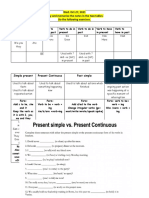
PRESENT
TIEMPO VERBAL USOS AFIRMATIVO NEGATIVO INTERROGATIVO
. is used to talk about repeated - You live in Lima - You do not live in Lima - Do you live in Lima?
activities, such as habits, - He plays the piano - She doesn’t play the piano - Does he play the piano?
PRESENT routines, or scheduled events. - They have a house - They don’t have a house - Do they have a house?
SIMPLE Adverbs of frequency and time Routines: | usually drink two cups of
expressions (such as usually and coffee in the morning. Schedules: The bus
every hour) often occur with the comes every hour.
simple present. -describe factual information, such as
- general truths or definitions. General
Truths
Indica una acción que se está
realizando en un momento
PRESENT específico.
- He is studying today -He isn’t studying today -Is he studying today?
CONTINUOUS
Este tiempo conecta el pasado
con el presente para hablar de
PRESENT una acción pasada se usa “have” - You have read this book - You haven’t read this book - Have you read this book?
PERFECT “has”
Sirve para hablar de acciones
que han comenzado en el
PRESENT pasado, pero continúan en el
- He has been working - He hasn’t been working hard - Has he been working hard?
PERFECT presente hard
CONTINUOUS
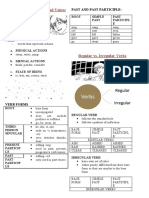
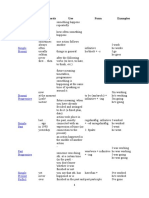
PAST
TIEMPO VERBAL
DEFINICIÓN AFIRMATIVO NEGATIVO INTERROGATIVO
Indica una acción que se realizó - I went to Lima yesterday - You didn’t go to Lima yesterday - Did you go to lima yesterday?
PAST SIMPLE en el pasado. - They watched a film - They didn´t watch a film - Did they watch a film?
- He read the book - She did not read the book - Did she read the book?
Aquello que ya aconteció forma
PAST CONTINUOUS parte del pasado. - It was raining - It wasn´t raining - Was it raining?
Se utiliza para referirse a una
PAST acción que tuvo lugar en un - She had eaten sushi - She hadn´t eaten sushi - Had she eaten sushi?
PERFECT momento anterior a otra acción.
Es el tiempo verbal del pasado que
nos indica que una acción estaba - She had been waiting for us - She hadn´t been waiting for us - Had he been waiting for us?
PAST PERFECT realizándose hasta que otra acción
CONTINUOUS ocurrió. Se forma conjugando los
verbos auxiliares "had", "been"
con el verbo principal
acompañado del gerundio "-ing".
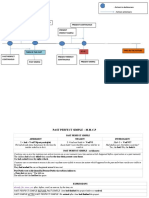
FUTURE
TIEMPO VERBAL
DEFINICIÓN AFIRMATIVO NEGATIVO INTERROGATIVO
Se utiliza para describir acciones
FUTURE SIMPLE que se van a desarrollar en un - He will go to the office - He won´t go to the office - will he go to the office ?
futuro, se usa - She will travel to Spain - she will not travel to Spain - Will she travel to Spain?
“shall-will”
Es un tiempo verbal del idioma
FUTURE inglés que expresa que una acción - We will be travelling - We won´t be travelling - Will We be travelling?
CONTINUOUS tendrá lugar en el futuro y seguirá
desarrollándose por un periodo de
tiempo determinado.
Denota una acción futura ocurrida
FUTURE con anterioridad a otra también - He will have arrived - He won´t have arrived - Will he have arrived?
PERFECT futura.
Se usa para expresar cuánto
tiempo habrá durado una acción - You will have been working - You won´t have been working - Will you have been working?
en un determinado momento
FUTURE PERFECT del futuro. Este tiempo verbal
CONTINUOUS enfatiza la continuidad de un
acontecimiento en un momento
futuro.
You might also like
- Gambier - 2003 - Introduction Screen Transadaptation Perception and ReceptionDocument20 pagesGambier - 2003 - Introduction Screen Transadaptation Perception and ReceptionGabrielaCosteira50% (2)
- Unit 5 Relative ClauseDocument7 pagesUnit 5 Relative ClauseGiang NguyenNo ratings yet
- English Verb Tenses PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish Verb Tenses PDFDenise DillonNo ratings yet
- All Tenses Infographics PDFDocument4 pagesAll Tenses Infographics PDFamajida fadia rNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review DaniDocument10 pagesGrammar Review Danidanicorrales.ibanezNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument1 pagePast ContinuousMaye OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Ingles PAST CONTINUOUSDocument4 pagesIngles PAST CONTINUOUSDavid Robles HerreraNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument6 pagesPresent PerfectBethania NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument20 pagesVerb Tensesvpetrovaa23No ratings yet
- VERBS (English)Document7 pagesVERBS (English)Kelly Calingasan100% (1)
- Present Perfect - 20240220 - 200341 - 0000Document16 pagesPresent Perfect - 20240220 - 200341 - 0000valeriaaguirreburneoNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses:: Present Simple Present Continuous Present Perfect Present Perfect ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent Tenses:: Present Simple Present Continuous Present Perfect Present Perfect ContinuousItziar Romera CatalanNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument2 pagesTensesAnuka AnuNo ratings yet
- Grid of TensesDocument2 pagesGrid of TensesKevin Yeshúa Reyes Mendez100% (1)
- 2 Bachiller Grammar and ExercisesDocument154 pages2 Bachiller Grammar and ExercisesrosarioNo ratings yet
- Simple Tenses: The Present The Past The Future Simple Continuous PerfectDocument5 pagesSimple Tenses: The Present The Past The Future Simple Continuous PerfectGetu BogaleNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect SimpleDocument2 pagesPast Perfect SimpleIanGiorgianaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Full ExplanationDocument8 pagesPresent Perfect Full ExplanationCelia IndiraNo ratings yet
- Review Tenses: Rains ArrivesDocument2 pagesReview Tenses: Rains ArrivesPhươngg ThảoNo ratings yet
- Seminário - Tense and Aspect SystemDocument46 pagesSeminário - Tense and Aspect SystemIgor BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs, Present Perfect, Present Perfect Simple Passive, Present Perfect ContinuousDocument10 pagesAdverbs, Present Perfect, Present Perfect Simple Passive, Present Perfect ContinuouslealtorresalejandroNo ratings yet
- TENSES ReviewDocument2 pagesTENSES ReviewElePra23No ratings yet
- English Tenses - ChartDocument4 pagesEnglish Tenses - Chartalicia.castroNo ratings yet
- Talent L3 Grammar MapsDocument5 pagesTalent L3 Grammar MapsCihan ÖzdemirciNo ratings yet
- MAPADocument1 pageMAPAErick EscobarNo ratings yet
- Tense Form Use Wordsrelated: Present SimpleDocument3 pagesTense Form Use Wordsrelated: Present SimplenewjanerNo ratings yet
- Wed. Oct.27, 2021 Copy and Memorize The Notes in The Two Tables. Do The Following ExercisesDocument2 pagesWed. Oct.27, 2021 Copy and Memorize The Notes in The Two Tables. Do The Following ExercisesSahar malaebNo ratings yet
- Tenses OverviewDocument1 pageTenses OverviewThijs van der KleinNo ratings yet
- Tiempos VerbalesDocument6 pagesTiempos VerbalesMaria Ines RoqueNo ratings yet
- Año de La Universalizacion de La SaludDocument3 pagesAño de La Universalizacion de La SaludLesly Nole SosaNo ratings yet
- RECAP Tenses Review Les Temps CONJUGAISONDocument12 pagesRECAP Tenses Review Les Temps CONJUGAISONSDubNo ratings yet
- Review of Verb Tenses. Edición March de 2017. Página 1 de 2Document5 pagesReview of Verb Tenses. Edición March de 2017. Página 1 de 2PepeNo ratings yet
- British English: Past TensesDocument18 pagesBritish English: Past TensesMiriam CondoriNo ratings yet
- Tense Signal Words Use Form Examples: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Signal Words Use Form Examples: Simple Presentmadalin0000No ratings yet
- Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal Words: Simple Presentsalbina arabiNo ratings yet
- 12 Different Verb TensesDocument6 pages12 Different Verb Tensessalbina arabiNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechNishath KhanNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past Continuous.: Nillireth Presutti HalubDocument12 pagesPast Simple Vs Past Continuous.: Nillireth Presutti HalubDaniela AngelNo ratings yet
- Pasado Simple y Pasado ContinuoDocument3 pagesPasado Simple y Pasado ContinuoMargarita BuenoNo ratings yet
- Tenses USE Afirmative Negative Interrogative Key WordsDocument2 pagesTenses USE Afirmative Negative Interrogative Key WordsSebastià Bennàsser BibiloniNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses: Key WordsDocument4 pagesVerb Tenses: Key WordsjoaquimNo ratings yet
- Tenses AspectsDocument8 pagesTenses AspectsUlises GallardoNo ratings yet
- B1 Book FinalDocument33 pagesB1 Book FinaljuliaNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses AllDocument14 pagesPast Tenses AllElena TkachevaNo ratings yet
- Progressive Tenses WorksheetDocument1 pageProgressive Tenses WorksheetayayaNo ratings yet
- Basic English TensesDocument1 pageBasic English TenseskarinaNo ratings yet
- Tenses ChartDocument5 pagesTenses ChartpfrecareyNo ratings yet
- Tabla InglesDocument2 pagesTabla InglesNatalia FernandezNo ratings yet
- Past Handout 1Document3 pagesPast Handout 1Катя ПрофатилоNo ratings yet
- Past Simple & ContinuousDocument7 pagesPast Simple & ContinuoussolodeilseNo ratings yet
- Tempos Verbales en InglésDocument2 pagesTempos Verbales en InglésLorys RuizNo ratings yet
- Articles: Kinds of AdjectivesDocument29 pagesArticles: Kinds of AdjectivesKostis SNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Verb TensesDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Verb Tensesakshatsahni425No ratings yet
- Verbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SDocument19 pagesVerbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SametgembulNo ratings yet
- Pasado Simple y Pasado ContinuoDocument3 pagesPasado Simple y Pasado ContinuoNuria Jimenez MirandaNo ratings yet
- 12 Verb TensesDocument2 pages12 Verb TensesfaniNo ratings yet
- Tenses Page 2Document1 pageTenses Page 2setyani dwiningsihNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument1 pageInglesJoseranny EspinozaNo ratings yet
- PPC PPS PPDocument15 pagesPPC PPS PPkarla AtaurimaNo ratings yet
- Engl111 Week 5Document53 pagesEngl111 Week 5Angelyn Grace TanNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: Types of Taboo Words Are Used in What Is The Function of Taboo Words Are Used inDocument3 pagesResearch Methodology: Types of Taboo Words Are Used in What Is The Function of Taboo Words Are Used inR RamdaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson - My Family and IDocument19 pagesLesson - My Family and IScarlet Valdés QuijadaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Communication ManagementDocument6 pagesLiterature Review Communication Managementafmzwflmdnxfeb100% (1)
- Bond Fourth 11+ ComprehensionDocument11 pagesBond Fourth 11+ Comprehensionfour forty100% (2)
- 12 Lingking R and Intrusive R by Group 2Document11 pages12 Lingking R and Intrusive R by Group 2Arya Wiranda100% (1)
- Unit Planner Understanding Poetry Unit 2, Grade 8 Q-1 AliDocument7 pagesUnit Planner Understanding Poetry Unit 2, Grade 8 Q-1 AliAli Al ShehabNo ratings yet
- Learning Module in Creative Writing: Senior High SchoolDocument7 pagesLearning Module in Creative Writing: Senior High SchoolBokuto KotaroNo ratings yet
- Articles - All-In-One Worksheets 6Document1 pageArticles - All-In-One Worksheets 6imparthi MNo ratings yet
- Verbs and GerundsDocument2 pagesVerbs and Gerundsdiegomauro1098No ratings yet
- B. Inggris Kel.1 (Skil 20 - 25)Document26 pagesB. Inggris Kel.1 (Skil 20 - 25)handaNo ratings yet
- Article 4 - SummaryDocument7 pagesArticle 4 - SummaryPhong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- Learning Area English Learning Delivery of Modality On Line LearningDocument8 pagesLearning Area English Learning Delivery of Modality On Line LearningVergel Bacares BerdanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 English BOWDocument2 pagesGrade 9 English BOWRowell Digal Bain100% (1)
- Homework For The Week 2Document10 pagesHomework For The Week 2Leyla AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Tabel 16 Tenses Bahasa InggrisDocument8 pagesTabel 16 Tenses Bahasa InggrisHrp TVNo ratings yet
- Tes TOEFL ResultDocument19 pagesTes TOEFL ResultRia SintikahNo ratings yet
- Group The Time Adverb Into The Relevant TensesDocument4 pagesGroup The Time Adverb Into The Relevant Tenseslavinia diaconu100% (1)
- Reading Lesson Plan Practica 4Document10 pagesReading Lesson Plan Practica 4ELISABETH FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- First Term English Exam: 2019/2020 Class: 3 LVDocument2 pagesFirst Term English Exam: 2019/2020 Class: 3 LVMãč Bøühëdjãr100% (1)
- Icebreaker Games ESLDocument9 pagesIcebreaker Games ESLEliana SpinaNo ratings yet
- Tong Hop de Thi Tuyen Sinh Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Cac TinhDocument25 pagesTong Hop de Thi Tuyen Sinh Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Cac TinhNhân Văn Hebe HerculesNo ratings yet
- The Phantom of The Opera WordlistDocument5 pagesThe Phantom of The Opera Wordlistglombardo412No ratings yet
- English Daily Test Short Functional Text Nine GradeDocument2 pagesEnglish Daily Test Short Functional Text Nine GradeWatu LintangNo ratings yet
- The Verb To Eat in ArabicDocument40 pagesThe Verb To Eat in ArabicAl-Andalus Academy100% (2)
- ELT6Module8 Bernardo, Danizelle Kaye C. BSED ENG2ADocument6 pagesELT6Module8 Bernardo, Danizelle Kaye C. BSED ENG2ADanizelle Kaye Cadocoy BernardoNo ratings yet
- Dialog Simple Past TenseDocument5 pagesDialog Simple Past TenseDewi Sri RezekiNo ratings yet
- Class IiiDocument4 pagesClass IiiSanjay SoniNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument39 pagesResearch PaperIra EaglesNo ratings yet