Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 10 CH 10 Light
Class 10 CH 10 Light
Uploaded by
Pankaj Chhabra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views44 pages1) Light is a form of energy that allows us to see objects when light reflects off of them and into our eyes.
2) Light travels in a straight line and common phenomena involving light include shadows, reflections in mirrors and lenses, bending of light, twinkling stars, and rainbows.
3) Images formed by lenses and mirrors can be real or virtual, erect or inverted, and magnified or diminished. A real image occurs when light rays actually converge while a virtual image is where diverging light rays seem to converge.
Original Description:
Original Title
Class 10 ch 10 light
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Light is a form of energy that allows us to see objects when light reflects off of them and into our eyes.
2) Light travels in a straight line and common phenomena involving light include shadows, reflections in mirrors and lenses, bending of light, twinkling stars, and rainbows.
3) Images formed by lenses and mirrors can be real or virtual, erect or inverted, and magnified or diminished. A real image occurs when light rays actually converge while a virtual image is where diverging light rays seem to converge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views44 pagesClass 10 CH 10 Light
Class 10 CH 10 Light
Uploaded by
Pankaj Chhabra1) Light is a form of energy that allows us to see objects when light reflects off of them and into our eyes.
2) Light travels in a straight line and common phenomena involving light include shadows, reflections in mirrors and lenses, bending of light, twinkling stars, and rainbows.
3) Images formed by lenses and mirrors can be real or virtual, erect or inverted, and magnified or diminished. A real image occurs when light rays actually converge while a virtual image is where diverging light rays seem to converge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 44
Chapter 10
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
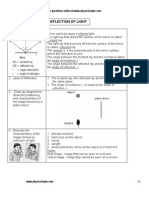
i) Light is a form of energy which helps us to see objects.
ii) When light falls on objects, it reflects the light and when
the reflected light reaches our eyes then we see the objects.
iii) Light travels in straight line.
iv) The common phenomena of light are formation of
shadows, formation of images by mirrors and lenses,
bending of light by a medium, twinkling of stars, formation of
rainbow etc.
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Characteristics of images
Images can be real or virtual, erect or inverted, magnified or
diminished.
A real image is formed by the actual convergence of light rays. A
virtual image is the apparent convergence of diverging light rays.
If an image formed is upside down then it is called inverted or else it
is an erect image. If the image formed is bigger than the object, then
it is called magnified. If the image formed is smaller than the object,
then it is diminished Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Terms used in the study of spherical mirrors :-
i) Center of curvature :- is the centre of the sphere of which the mirror
is a part (C).
ii) Radius of curvature :- is the radius of the sphere of which the mirror
is a part (CP).
iii) Pole :- is the centre of the spherical mirror (P).
iv) Principal axis :- is the straight line passing through the centre of
curvature and the pole (X-Y).
v) Principal focus :- In a concave mirror, rays of light parallel to the
principal axis after reflection meet at a point on the principal axis
called principal focus(F).
In a convex mirror, rays of light parallel to the principal axis after
reflection get diverged and appear to come from a point on the
principal axis behind the mirror called principal focus (F).
vi) Focal length :- is the distance between the pole and principal focus
(f). In a spherical mirror the radius of curvature is twice the focal
length. R = 2f or f = R/2 Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Wecan place the object at six
positions from the mirror:
◦ At infinity
◦ Beyond C
◦ At C
◦ Between C and F
◦ At F
◦ Between F and P
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
33
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
Dr. Pankaj Chhabra
You might also like
- Lesson Plans - LightDocument9 pagesLesson Plans - Lightjatinder kaur100% (6)
- Difference Between Service and Product QualityDocument3 pagesDifference Between Service and Product Qualityferreirae100% (3)
- AGRT02 21 Guide To Road Tunnels Part 2 Planning Design CommissioningDocument176 pagesAGRT02 21 Guide To Road Tunnels Part 2 Planning Design CommissioningALDO IDROGONo ratings yet
- CDM Maintenance Manual: Remote ServicesDocument37 pagesCDM Maintenance Manual: Remote Servicesmsalem73100% (2)
- Physics Chapter LightDocument25 pagesPhysics Chapter LightNurliyana Zairul AfendiNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionANJALI RANANo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument11 pagesCBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refractionshubham sehgalNo ratings yet
- As Phy-ProjectDocument14 pagesAs Phy-ProjectTeerth BusaNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and Refractiondjshlok359No ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesChapter - 10: Light: Reflection and Refractionismgilovamunisa150No ratings yet
- Light WavesDocument64 pagesLight Wavesceline.the988No ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesChapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionGarvit Khare75% (4)
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionAnant WatsNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesChapter - 10: Light: Reflection and Refractionuma mishraNo ratings yet
- Phy161 Lab Report 11Document10 pagesPhy161 Lab Report 11Javier Luis SantosNo ratings yet
- 10-Light-Reflection and Refraction 1Document42 pages10-Light-Reflection and Refraction 1dharmendra25112006No ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and Refractionapi-24735088292% (25)
- 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument43 pages10 Light Reflection and Refractiong8one2020No ratings yet
- 77 Topper 21 101 2 4 62 Light Reflection and Refraction Up201807101458 1531214913 5575 PDFDocument10 pages77 Topper 21 101 2 4 62 Light Reflection and Refraction Up201807101458 1531214913 5575 PDFsudhaNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionShubham Jain100% (1)
- 2 Out 2 PDFDocument426 pages2 Out 2 PDFSwapnil MaladkarNo ratings yet
- 10 Science TP 10 1Document8 pages10 Science TP 10 1Ajjuu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Group - 1 X-GDocument26 pagesGroup - 1 X-GRaunak ShekharNo ratings yet
- Chapter Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument1 pageChapter Light-Reflection and RefractionVIDYA MNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Chapter 12 LightDocument12 pagesClass 7 Chapter 12 Lightsiddharthsg37No ratings yet
- Workbook Solution LightDocument6 pagesWorkbook Solution Lightsmi_santhosh0% (1)
- RRB NTPC - Physics - LightDocument5 pagesRRB NTPC - Physics - LightAkella LokeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Light-3Document4 pagesChapter 16 Light-3sabreenaapNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument52 pagesNotesSwati SinghNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and Refraction PPT 1Document42 pagesLight-Reflection and Refraction PPT 1api-285160905100% (1)
- OpticsDocument89 pagesOpticsKarunya nidhi100% (1)
- Physics Class X Reference Study Material Pages DeletedDocument174 pagesPhysics Class X Reference Study Material Pages DeletedRastogi.sachin08No ratings yet
- Support material, X, Chapter- LightDocument12 pagesSupport material, X, Chapter- Lightaestheticmax23No ratings yet
- Jee Advanced Optics Revision NotesDocument34 pagesJee Advanced Optics Revision NotesarasadadhanalaxmiNo ratings yet
- Formation of Images by A Plane MirrorsDocument4 pagesFormation of Images by A Plane MirrorsAmir FaheemNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics NotesDocument23 pagesGrade 12 Physics NotesAlphonso TulayNo ratings yet
- Our Eye As A Camera Refraction, Errors and Solutions.: DR - Ali.A.Taqi Fifth Year StudentsDocument44 pagesOur Eye As A Camera Refraction, Errors and Solutions.: DR - Ali.A.Taqi Fifth Year Studentsabigail100% (1)
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument41 pagesLight-Reflection and Refractionapi-268345960No ratings yet
- Brilliant Public School, Sitamarhi: X - Physics Chapter NotesDocument21 pagesBrilliant Public School, Sitamarhi: X - Physics Chapter NotesSUSHIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Phy161 Lab Report 11Document9 pagesPhy161 Lab Report 11Javier Luis SantosNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment For CA - 3Document38 pagesPhysics Assignment For CA - 3Kshitij ChandelNo ratings yet
- Light ReflectionDocument48 pagesLight Reflectionsmi.29981No ratings yet
- Science10 Q2 Mod5 v4Document6 pagesScience10 Q2 Mod5 v4Kim TaehyungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Light Class 8Document15 pagesChapter 16 Light Class 8Amaira KalsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Class 10thDocument32 pagesChapter 12 Class 10thMN AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 10 - Light Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pages10 - Light Reflection and RefractionsamNo ratings yet
- SG - Session2 Opticsphys - RealingoDocument15 pagesSG - Session2 Opticsphys - RealingoJudarlyn Madria100% (1)
- Delhi Public School Nadergul GRADE-10 Physical Science Light - NotesDocument17 pagesDelhi Public School Nadergul GRADE-10 Physical Science Light - Notesbaby doodlesNo ratings yet
- Physics-6 LightDocument132 pagesPhysics-6 LightsamNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of A Plane MirrorJazelle PaciaNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument22 pagesLight-Reflection and Refractionregis100% (1)
- Light Lesson 1 - MergedDocument94 pagesLight Lesson 1 - Mergedrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument56 pagesOpticsahsan shahNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument19 pagesLight - Reflection and RefractionShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- Light Notebook Q/A - Grade 8Document2 pagesLight Notebook Q/A - Grade 8Prateek VatsNo ratings yet
- Wa0058.Document38 pagesWa0058.yadavdaksh986No ratings yet
- Class 8 - Chapter 16 - LightDocument30 pagesClass 8 - Chapter 16 - LightsanaNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light FINALDocument8 pagesReflection of Light FINALPrakritiNo ratings yet
- Phenomenal Vision Eyesight to Life SightFrom EverandPhenomenal Vision Eyesight to Life SightNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight LineDocument31 pagesChapter 3 Motion in A Straight LinePankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Laws of MotionDocument50 pagesChapter 5 Laws of MotionPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 MOTION IN A PLANEDocument52 pagesChapter 4 MOTION IN A PLANEPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementsDocument53 pagesChapter 2 Units and MeasurementsPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physical WorldDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Physical WorldPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- GovernorsDocument49 pagesGovernorsPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physical WorldDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Physical WorldPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Weight Calculation SheetDocument6 pagesWeight Calculation SheetPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Tom NumericalsDocument6 pagesTom NumericalsPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalworking: ©2002 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. M. P. Groover, "Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 2/e"Document34 pagesSheet Metalworking: ©2002 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. M. P. Groover, "Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 2/e"Himanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Clutch and BrakesDocument29 pagesClutch and BrakesPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Cadcam Geometric ModelingDocument31 pagesCadcam Geometric ModelingPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 - CountinuedDocument16 pagesCHP 2 - CountinuedPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Edu Crafter For PresenationDocument30 pagesEdu Crafter For PresenationPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Design and Computer Aided Manufacturing Introduction To CAD/CAMDocument28 pagesComputer Aided Design and Computer Aided Manufacturing Introduction To CAD/CAMPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CAD/CAM: Pankaj Chhabra Cad/Ca MDocument22 pagesIntroduction To CAD/CAM: Pankaj Chhabra Cad/Ca MPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics: Concept of Pressure,: Pascal's Law and Its Engineering Applications, Hydrostatic ParadoxDocument8 pagesFluid Statics: Concept of Pressure,: Pascal's Law and Its Engineering Applications, Hydrostatic ParadoxPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Length Power Dynamic Viscosity Heat FluxDocument2 pagesLength Power Dynamic Viscosity Heat FluxPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Model Based Strategies For An Optimised Ribbing Design of Large Forming ToolsDocument6 pagesModel Based Strategies For An Optimised Ribbing Design of Large Forming ToolsPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Concurrent Design and Prototyping of Composite Accelerlator PedalDocument29 pagesConcurrent Design and Prototyping of Composite Accelerlator PedalPankaj Chhabra67% (3)
- Steering PartsDocument9 pagesSteering PartsPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Concurrent Design and Prototyping of Composite Accelerlator PedalDocument29 pagesConcurrent Design and Prototyping of Composite Accelerlator PedalPankaj Chhabra67% (3)
- Instantaneous CentreDocument15 pagesInstantaneous CentrePankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Production Technology-I Unit No. 1: Cutting ToolDocument15 pagesProduction Technology-I Unit No. 1: Cutting ToolPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- "Smart Materials & Systems": Technical Seminar OnDocument20 pages"Smart Materials & Systems": Technical Seminar OnPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument1 pagePosterTalha HanifNo ratings yet
- Fenwick - The Failure of The League of NationsDocument5 pagesFenwick - The Failure of The League of NationsEmre CinarNo ratings yet
- The Minimum Mean Dominating Energy of GraphsDocument5 pagesThe Minimum Mean Dominating Energy of GraphsiirNo ratings yet
- PDF of Dental Radiography DEGOTZEN XGENUS ACDocument55 pagesPDF of Dental Radiography DEGOTZEN XGENUS ACaillNo ratings yet
- ENGL 102 Mixed Tense Exercises (8 Tenses)Document22 pagesENGL 102 Mixed Tense Exercises (8 Tenses)na-labbadNo ratings yet
- FIFA 19 Squad Builder - FUTBINDocument2 pagesFIFA 19 Squad Builder - FUTBINMauro Vázquez RebolloNo ratings yet
- 30 Must Read Bestsellers in Infographics by HeadwayDocument69 pages30 Must Read Bestsellers in Infographics by HeadwaykateNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Fluid Purpose & Properties: (Chapter 2)Document29 pagesHydraulic Fluid Purpose & Properties: (Chapter 2)christodoulos charalambousNo ratings yet
- Tinjauan Aspek Tata Ruang Perkembangan Kawasan Tawang Mas Kota SemarangDocument16 pagesTinjauan Aspek Tata Ruang Perkembangan Kawasan Tawang Mas Kota SemarangNajwa KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Effective CommunicationDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Effective CommunicationtaherzamanratherNo ratings yet
- G. Monofilament Extrusion Process.Document18 pagesG. Monofilament Extrusion Process.yohannesafework07No ratings yet
- Bag Technique Rationale BaldadoDocument2 pagesBag Technique Rationale Baldadolea mae andoloyNo ratings yet
- Ingress Protection-IP66-IEC60529Document12 pagesIngress Protection-IP66-IEC60529tushar2.khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Smart Adjustable Bridge PresentationDocument18 pagesSmart Adjustable Bridge PresentationDeshmukh AshwiniNo ratings yet
- General Geology of RomaniaDocument27 pagesGeneral Geology of RomaniaDana PrisacNo ratings yet
- Ryna Du PlooyDocument8 pagesRyna Du PlooyRosel.RamosNo ratings yet
- T 87 PG 101-102 PDFDocument2 pagesT 87 PG 101-102 PDFJossimar PerezNo ratings yet
- Cellules À ConcentrationDocument12 pagesCellules À Concentrationmohamed ikbalNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 109Document3 pagesProf Ed 109Nadnad DomingoNo ratings yet
- Test Erm T The Second:: MarkDocument2 pagesTest Erm T The Second:: Markkaimero changNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Minerals and Rocks S11 12ES Ia 9Document8 pagesLesson 6 Minerals and Rocks S11 12ES Ia 9Christine CayosaNo ratings yet
- Scenario-Based Strategic Planning and Strategic Management in Family Firms, 2013Document118 pagesScenario-Based Strategic Planning and Strategic Management in Family Firms, 2013taghavi1347No ratings yet
- ELA Syllabus Grade 2Document19 pagesELA Syllabus Grade 2Farzam GarshasbiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EarthquakesDocument13 pagesIntroduction To EarthquakesSheikh_MutaharNo ratings yet
- 2017 Target2017 AbstractsDocument177 pages2017 Target2017 AbstractsLaraNigroNo ratings yet
- Manual Instruction For Propeller Fan (APL-APN)Document4 pagesManual Instruction For Propeller Fan (APL-APN)Adi HardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Dermatosis in Children With Oedematous Malnutrition (Kwashiorkor) : A Review of The LiteratureDocument7 pagesDermatosis in Children With Oedematous Malnutrition (Kwashiorkor) : A Review of The LiteratureMariaNo ratings yet