Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Women and The M-WPS Office
Women and The M-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Avie Matriz Sañado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views11 pagesThis document discusses differences in how men and women gain and view knowledge. It suggests that women typically learn through association, empathy, and connecting with others by listening, while men often learn through separation from others. Five perspectives on how women know are described: through silence, received knowledge from authorities, subjective knowledge from personal experience, procedural knowledge from formal systems, and constructed knowledge by reflecting on their own views and voices. The document argues that valuing women's knowledge and including them in all aspects of society can promote gender equality and empowerment.
Original Description:
Description of the topic. Men and women's differences.
Original Title
Women and the m-WPS Office
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses differences in how men and women gain and view knowledge. It suggests that women typically learn through association, empathy, and connecting with others by listening, while men often learn through separation from others. Five perspectives on how women know are described: through silence, received knowledge from authorities, subjective knowledge from personal experience, procedural knowledge from formal systems, and constructed knowledge by reflecting on their own views and voices. The document argues that valuing women's knowledge and including them in all aspects of society can promote gender equality and empowerment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views11 pagesWomen and The M-WPS Office
Women and The M-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Avie Matriz SañadoThis document discusses differences in how men and women gain and view knowledge. It suggests that women typically learn through association, empathy, and connecting with others by listening, while men often learn through separation from others. Five perspectives on how women know are described: through silence, received knowledge from authorities, subjective knowledge from personal experience, procedural knowledge from formal systems, and constructed knowledge by reflecting on their own views and voices. The document argues that valuing women's knowledge and including them in all aspects of society can promote gender equality and empowerment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Women and the
metaphor for silence
Chapter 4
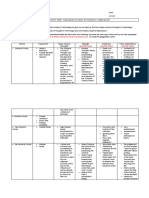
Culture
• Plays a large part • Western male
determining masculine reasoning uses image
or feminine traits. related to visual seeing
and or illumination.
Women view of
knowledge *Listening is
more
representing
how other
people
specifically to
women view
knowledge .
DIFFERENCES IN WAYS OF
KNOWING
The main difference of men and women’s way of knowing
comes from upbringing and gender socialization.
• Universal caregiving – given to women in all societies
• Differences of men and women’s way of knowing:
• Women – had their mother’s as role models
• Learned through association and connectedness
• Learned through empathy
• Men - learned through disassociation with their mother’s
role
• Learned through the separation of the self from others
HOW WOMEN KNOW
Five perspectives as to how women learned about the
world and come to conclusions about truth.
1.)Women and Silence 2.)Received Knowledge
• The absence of thought or reflection
• Developed by absorbing
• Women who lives in silence are those
who are:
knowledge
• • disconnected from their families • Silence is valued yet not
• • lives in a secluded places internal
• • victims of abuse and violence • Words – imperative to
• Their knowledge comes from learning
authorities and focuses on survival.
• Women are able to do the
• No internal voice, no self-perception
and lack of an identity separate from
right thing by following rules
what is dictated to them. • Values authority and cannot
understand paradoxes
3.)Subjective Knowledge
Women who learned through subjective
knowledge:
• learn to trust their ‘inner voice and
infallible gut’
• depends on their selves and experience
to attain truth
• uses their intuition to decipher truth from
fiction
4.)Procedural Knowledge
Procedural knowers:
• learn through processes
• learned well from formal systems (e.g.,
education)
• learn the language of experts and apply this
to their own views
• focuses more on method and less on the
problem
• believes that each person views the world
differently and is entitled to his/her own opinion
• understanding – vital aspect of knowing
• learn through acquiring the knowledge of
others
5.)Constructed Knowledge
To obtain constructed knowledge women has to:
• have the ability to reflect on and accept
themselves
• learn to value their own methods of
knowing
• listen to their voice in the world that is
domained by male
• know that “knowledge is constructed and
the knower is an intimate part of the known.
• value real-talk which is the optimum
settings for the co-creation of knowledge
We must value ourselves and see ourselves as an
indispensable part of knowledge-creation, we can
become empowered, working toward an
improvement in our lives as well as in the lives of
others.”
Meaning of Differences in Knowing:
Gender Equality – Inclusion of women in all
aspects of society; all rights afforded to men must
be afforded to women.
Exclusion of
women to
disciplines
According to a study released
in Science, women are
underrepresented in academic
disciplines that place an
emphasis on “raw intellectual
talent,” as opposed to qualities
like work ethic.It is not
surprising, then, that the case
has resulted in a rare public
airing for issues that have been
an ongoing concern for women
in philosophy. But to what
extent does this sort of
publicity further the cause of
women in philosophy
Reporters:
Avie Sañado
Michelle San juan
(BSED ENGLISH 2-A)
You might also like
- Chapter 4 WOMEN'S WAYS OF KNOWINGDocument14 pagesChapter 4 WOMEN'S WAYS OF KNOWINGFer Grace AniñonAcabalcuid Cataylo57% (7)
- NARTH Institute Practice GuidelinesDocument68 pagesNARTH Institute Practice GuidelinesDavid C. Pruden100% (1)
- Gec Elec3 - M1 03Document22 pagesGec Elec3 - M1 03daniela aquinoNo ratings yet
- Women's Ways of KnowingDocument10 pagesWomen's Ways of Knowinghoneydee21No ratings yet
- GE E2-Chapter 3-6Document9 pagesGE E2-Chapter 3-6Fherry AlarcioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Gender And...Document6 pagesReviewer Gender And...Divynne MadeloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Socialization FEB 24 New File 2020Document32 pagesLecture 5 Socialization FEB 24 New File 2020bb60536No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Understanding The SelfDocument14 pagesLesson 1 - Understanding The SelfYam YamNo ratings yet
- CH 2 B - Individual Psychology AdlerDocument40 pagesCH 2 B - Individual Psychology AdlerKaye Ann ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of SelfDocument31 pagesBasic Concepts of SelfJeanzy Anne GupitNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument33 pagesUnderstanding The SelfBrianne LlamasNo ratings yet
- UTS Module 6Document4 pagesUTS Module 6Kyle BuenoNo ratings yet
- Theories of Personality I Horney TNM0Document48 pagesTheories of Personality I Horney TNM0John Lloyd RaborNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Women's Ways of KnowingDocument16 pagesChapter 2 Women's Ways of KnowingCaptain ObviousNo ratings yet
- SOCIALIZATION AS A PROCESS OF BECOMING FULLY HUMAN - PPTX No. 2Document16 pagesSOCIALIZATION AS A PROCESS OF BECOMING FULLY HUMAN - PPTX No. 2Aquino Jomar AtosNo ratings yet
- Theories of Personality I Horney TNM0 PDFDocument48 pagesTheories of Personality I Horney TNM0 PDFGarofil, JoshNo ratings yet
- Gee 102 3Document3 pagesGee 102 3Sunshine AmaracoNo ratings yet
- GE1: Understanding The Self Philosophy of Man What Is Philosophy?Document5 pagesGE1: Understanding The Self Philosophy of Man What Is Philosophy?maria cruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document69 pagesChapter 3LisetteNo ratings yet
- Bsn3a Group 2 Speaker NotesDocument12 pagesBsn3a Group 2 Speaker NotesLoren SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- Horney PsychoanalyticDocument8 pagesHorney PsychoanalyticLourdes Jane SongkipNo ratings yet
- UTS - The Self in The Wester and Eastern ThoughtDocument18 pagesUTS - The Self in The Wester and Eastern ThoughtJhon dave SurbanoNo ratings yet
- Assertiveness: Prepared By-Chirag Solanki Wasim Kazmi Macklinbrett Veigas Mayur Veer (Se Mech-B)Document18 pagesAssertiveness: Prepared By-Chirag Solanki Wasim Kazmi Macklinbrett Veigas Mayur Veer (Se Mech-B)Kuldeep singhNo ratings yet
- Individual Psychology: Alfred AdlerDocument51 pagesIndividual Psychology: Alfred AdlerSeokWoo MinNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalytic Social TheoryDocument20 pagesPsychoanalytic Social Theorysemihaomur87No ratings yet
- Horney Psychosocial Analytic TtheoryDocument30 pagesHorney Psychosocial Analytic TtheoryElla Marie GavilenoNo ratings yet
- Personality: Lecturer Saima Azad Air University IslamabadDocument50 pagesPersonality: Lecturer Saima Azad Air University IslamabadtoobaNo ratings yet
- Adlerain Approach (Lecture 10)Document55 pagesAdlerain Approach (Lecture 10)princessriyagulNo ratings yet
- Womens Ways of KnowingDocument15 pagesWomens Ways of KnowingRonald CentinoNo ratings yet
- Sociological Self PDFDocument32 pagesSociological Self PDFJohn Jabez LuceroNo ratings yet
- ERICH-FROMM TheoriesDocument41 pagesERICH-FROMM TheoriesQueen T BallesterosNo ratings yet
- The Individual and Society: Week 8Document38 pagesThe Individual and Society: Week 8Jhonry CaalimNo ratings yet
- Student Dev Theory 01-21-2011Document4 pagesStudent Dev Theory 01-21-2011bjnpedronptrp100% (1)
- Alfred AdlerDocument16 pagesAlfred AdlerOdiesa faye CanonigoNo ratings yet
- Assignment SocializationDocument17 pagesAssignment SocializationAmna Shoukat100% (1)
- 5 Prejudice 19092023 104537amDocument51 pages5 Prejudice 19092023 104537amcaramelNo ratings yet
- Alfred Adler: Dolores Salvacion F. Tolentino, RGC Faculty, Graduate ProgramDocument46 pagesAlfred Adler: Dolores Salvacion F. Tolentino, RGC Faculty, Graduate ProgramNoemi Ruth Carrasco MesanaNo ratings yet
- Ucsp 2ND Sem MQTDocument28 pagesUcsp 2ND Sem MQTEricka ArceNo ratings yet
- Prejudice: Course Instructor: Maha Mohsin BS-2 Social PsychologyDocument45 pagesPrejudice: Course Instructor: Maha Mohsin BS-2 Social PsychologyIrzaNo ratings yet
- Personality DevelopmentDocument16 pagesPersonality DevelopmentLielane VarelaNo ratings yet
- Child Development TheoriesDocument32 pagesChild Development Theoriesapi-357233146No ratings yet
- Self From Various Perspective: Unit 1Document31 pagesSelf From Various Perspective: Unit 1Angeline LimNo ratings yet
- Sociological Perspective of The SelfDocument27 pagesSociological Perspective of The SelfIman Official (Em-J)No ratings yet
- Psychoanalytic Social Theory: Karen HorneyDocument36 pagesPsychoanalytic Social Theory: Karen HorneySeokWoo MinNo ratings yet
- Maslow Holistic Dynamic TheoryDocument4 pagesMaslow Holistic Dynamic Theorychristianlorzano8No ratings yet
- Lectre 5Document27 pagesLectre 5Sd WtNo ratings yet
- Theories of PersonalityDocument8 pagesTheories of PersonalityM-j Villafuerte ChävêżNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument2 pagesUnderstanding The SelfELMSSNo ratings yet
- ALFRED ADLER'sDocument35 pagesALFRED ADLER'sAizek HopefulNo ratings yet
- The Western and Eastern Concepts of Self: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityDocument13 pagesThe Western and Eastern Concepts of Self: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityKenneth CanceranNo ratings yet
- Theories of SocializationDocument15 pagesTheories of SocializationJodie VirayNo ratings yet
- Epistemology: Dr. Mehboob BukhariDocument20 pagesEpistemology: Dr. Mehboob BukhariYasir Ahmed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- PERDEV Q1M1P1 - Knowing and Understanding Oneself During Middle and Late AdolescenceDocument17 pagesPERDEV Q1M1P1 - Knowing and Understanding Oneself During Middle and Late AdolescenceEllize ClaireNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Understanding Self & OthersDocument17 pagesModule 2 Understanding Self & OthersPaulo Sigua100% (1)
- 5 Karen Horney Psychoanalytic Social TheoryDocument36 pages5 Karen Horney Psychoanalytic Social TheoryMae EscanillanNo ratings yet
- Individual PsychologyDocument5 pagesIndividual PsychologyRessie Joy Catherine FelicesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Tools For Self DevelopmentDocument58 pagesLecture 3 - Tools For Self DevelopmentSebastian GonzalezNo ratings yet
- FDGHJKDocument19 pagesFDGHJKJP Caballero JaoNo ratings yet
- Person#3Document41 pagesPerson#3Arumpac, Norjanah T.No ratings yet
- Dear Parents: Listen to Your Teen's Unheard Cry for True Love, Meaning & SuccessFrom EverandDear Parents: Listen to Your Teen's Unheard Cry for True Love, Meaning & SuccessNo ratings yet
- Take Home Activity No# 1: Four Major Schools of Thought in CriminologyDocument3 pagesTake Home Activity No# 1: Four Major Schools of Thought in CriminologyMarrie Eloisa Biag SaLazarNo ratings yet
- Brave New World - PropagandaDocument3 pagesBrave New World - Propagandaapi-375202554No ratings yet
- Living The Twilio Magic: Twilio Code of ConductDocument44 pagesLiving The Twilio Magic: Twilio Code of ConductnileshdalvimumbaiNo ratings yet
- Unity University Department of Mba Ethics and Legal Environment AssignmentDocument7 pagesUnity University Department of Mba Ethics and Legal Environment Assignmentአረጋዊ ሐይለማርያም100% (1)
- Mid Phi401Document7 pagesMid Phi401Tahania Afrin Chowdhury 1821943630No ratings yet
- Ethics: Christine Diane Galvan, CSPE, LPT InstructressDocument35 pagesEthics: Christine Diane Galvan, CSPE, LPT InstructressChristine DianeNo ratings yet
- Middle and Late Childhood MilestonesDocument23 pagesMiddle and Late Childhood MilestonesAlyssa ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Criminology With Psychology of Crime: A. Kalantiaw CodeDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Criminology With Psychology of Crime: A. Kalantiaw CodeGlendel Fernandez Lasam0% (1)
- Pope HappinessDocument17 pagesPope HappinessRasool Bux SaandNo ratings yet
- Community and Progress in Kant's Moral Philosophy - Kate A. MoranDocument278 pagesCommunity and Progress in Kant's Moral Philosophy - Kate A. MoranCleiton SantosNo ratings yet
- The Fiduciary Obligations of Public Officials The Fiduciary Obligations of Public OfficialsDocument44 pagesThe Fiduciary Obligations of Public Officials The Fiduciary Obligations of Public OfficialsRonald CarstarphenNo ratings yet
- Reading Questions 7Document2 pagesReading Questions 7api-338125752No ratings yet
- Historical Memory and Democratic CitizenshipDocument22 pagesHistorical Memory and Democratic Citizenshipion irauliNo ratings yet
- Leadership and EthicsDocument14 pagesLeadership and EthicsHuseyn KaNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ethics of Information and Communication Technologies 1St Edition Adriano Fabris Auth Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Ethics of Information and Communication Technologies 1St Edition Adriano Fabris Auth Ebook All Chapter PDFgeorge.mills297100% (14)
- Chapter 1 Data Handling Ethics 2022Document56 pagesChapter 1 Data Handling Ethics 2022Basel AbdulHakNo ratings yet
- Ethical Theories and Biomedical PrincipleDocument5 pagesEthical Theories and Biomedical PrincipleAlyssa Marie PepitoNo ratings yet
- Criminology 3 Police Ethics and Community Relations By: Poly D. BanaganDocument16 pagesCriminology 3 Police Ethics and Community Relations By: Poly D. BanaganAllysa Jane FajilagmagoNo ratings yet
- Leszek Kołakowski - How To Be A Conservative-Liberal-SocialistDocument3 pagesLeszek Kołakowski - How To Be A Conservative-Liberal-SocialistEliasz NiezgodaNo ratings yet
- Business EthicsDocument28 pagesBusiness EthicsSudhir PawarNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument4 pagesEthicsleonaidusNo ratings yet
- Morals Vs Values Vs EthicsDocument3 pagesMorals Vs Values Vs Ethicschilukuri sandeepNo ratings yet
- Market Research Unethical BehaviorDocument4 pagesMarket Research Unethical BehaviorSamuel KamuriNo ratings yet
- Apd 3 NotesDocument6 pagesApd 3 NotesHelios HexNo ratings yet
- Computerized Decision Making KevinDocument7 pagesComputerized Decision Making KevinKevinDennison100% (4)
- QUB-SGBV Report English WebDocument37 pagesQUB-SGBV Report English WebsofiabloemNo ratings yet
- PDF Ethics Lesson 3 Moral DilemmaDocument8 pagesPDF Ethics Lesson 3 Moral DilemmaShineeljay TumipadNo ratings yet
- Data Design - DAT7003D Report 1666Document8 pagesData Design - DAT7003D Report 1666Abner ogegaNo ratings yet
- PornographyDocument3 pagesPornographyRahul SisodiaNo ratings yet