Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 viewsSession 2 Basic Terms
Session 2 Basic Terms
Uploaded by
Sagar ParateThis document defines several basic accounting terms:
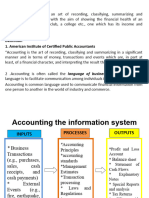
Business transactions can be cash or credit transactions. Accounts record transactions summarized by category on debit and credit sides. Capital refers to the owner's investment. Assets are resources used in operations, classified as current within one year or non-current longer-term. Liabilities are obligations to pay debts in the future, classified as current within one year or non-current longer term. Expenses are costs to earn revenue while expenditures acquire assets or services. Profit is revenue exceeding expenses and loss is expenses exceeding revenue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The World Nuclear Supply Chain: Outlook 2030 (2014)Document198 pagesThe World Nuclear Supply Chain: Outlook 2030 (2014)Greg KaserNo ratings yet
- Solution - Numericals Market Structure PDFDocument4 pagesSolution - Numericals Market Structure PDFpiyush kumarNo ratings yet
- Accounting TermsDocument37 pagesAccounting Termsmcsworkshop777No ratings yet
- Basic Acc Terms HandoutDocument3 pagesBasic Acc Terms HandoutpranjalNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermsDocument2 pagesBasic Accounting Termssatyam skNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Financial MangementDocument25 pagesAccounting and Financial MangementSHASHINo ratings yet
- Basic TermsDocument28 pagesBasic TermsShaji RarothNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terms NotesDocument5 pagesBasic Accounting Terms NotesNathan DavidNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Basic Accounting TermsDocument6 pagesChapter - 2 Basic Accounting TermsChaudhary GaylesabbNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument2 pagesTypes of Major AccountsKelsey Sofia RojasNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermsDocument16 pagesBasic Accounting TermsKusum MotwaniNo ratings yet
- EFA AssignmentDocument5 pagesEFA AssignmentDeviNo ratings yet
- 11 ACCTS theoryNOTESDocument6 pages11 ACCTS theoryNOTESDeveshi TewariNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Managers. 1pdfDocument168 pagesAccounting For Managers. 1pdfAkash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8Mrittika WadderNo ratings yet
- Accounting TermsDocument8 pagesAccounting TermsIshrit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mba Study MaterialsDocument4 pagesMba Study Materialskumar2346No ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermsDocument12 pagesBasic Accounting TermsNathan DavidNo ratings yet
- 1, Class Xi, Subject - Accountancy, Chapter - 1Document17 pages1, Class Xi, Subject - Accountancy, Chapter - 1Shoryamann SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2assets, Liabilities and CapitalDocument5 pages2assets, Liabilities and Capitaldilhani sheharaNo ratings yet
- Classification of AccountsDocument4 pagesClassification of AccountsManan MunshiNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminologies of Accounting: 1. AssetsDocument10 pagesBasic Terminologies of Accounting: 1. AssetsSophiya PrabinNo ratings yet
- Short-Questions (Accounts) 1.goodsDocument3 pagesShort-Questions (Accounts) 1.goodsUrvishNo ratings yet
- 2 Elements of AccountingDocument4 pages2 Elements of Accountingapi-299265916No ratings yet
- XI Notes of Chapter 2 Part I PDFDocument3 pagesXI Notes of Chapter 2 Part I PDFRoshanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lesson NotesDocument9 pages2nd Lesson Notesjayasandhya mNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accountancy-Basic ConceptsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Accountancy-Basic ConceptsjemrecayakNo ratings yet
- Accounting:: Capital Assets - LiabilitiesDocument3 pagesAccounting:: Capital Assets - LiabilitiesashNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument2 pagesTypes of Major Accountscristin l. viloriaNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument5 pagesTypes of Major AccountsJenny SaynoNo ratings yet
- FIA-FA1 NotesDocument37 pagesFIA-FA1 NotesAbdul Rehman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument30 pagesTypes of Major AccountsEstelle GammadNo ratings yet
- EpfoDocument6 pagesEpfoSiddharth OjhaNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermDocument4 pagesBasic Accounting Termak99archana1999No ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terms: By: Shivani ChandelDocument29 pagesBasic Accounting Terms: By: Shivani ChandelDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Tally ERP9Document68 pagesTally ERP9sah100% (11)
- Financial AccountingDocument16 pagesFinancial AccountingSNo ratings yet
- LESSON 8 - Types of Major AccountsDocument3 pagesLESSON 8 - Types of Major Accountsdrea.heart29No ratings yet
- Faa IDocument18 pagesFaa Iabhiseknanda82495No ratings yet
- Chapter-2: The Accounting Cycle: Accounting For A Service Enterprise 2.1Document19 pagesChapter-2: The Accounting Cycle: Accounting For A Service Enterprise 2.1Nigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Session 4Document12 pagesSession 4devanshk121No ratings yet
- Basic TerminologiesDocument20 pagesBasic TerminologiesMOHAMED USAIDNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks QuestionsDocument44 pages2 Marks Questionsvicky241989No ratings yet
- Account Tiltes HandoutsDocument2 pagesAccount Tiltes HandoutsSean Andreson MabalacadNo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting: Mba (HRD) Delhi School of Economics Department of Commerce University of DelhiDocument15 pagesBasics of Accounting: Mba (HRD) Delhi School of Economics Department of Commerce University of DelhiMukesh DroliaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting (Basic Terms)Document6 pagesFinancial Accounting (Basic Terms)prathampawar5912No ratings yet
- Chapter # 1 Business TransactionDocument22 pagesChapter # 1 Business TransactionWaleed NasirNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To Accounting PART 1-LLB 1Document34 pagesIntoduction To Accounting PART 1-LLB 1brandywilliam203No ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terms l1 Accountancy Class 11 Cbse by Ushank SirDocument11 pagesBasic Accounting Terms l1 Accountancy Class 11 Cbse by Ushank Sirrajput442007No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Statement of Financial PositionDocument22 pagesLesson 1 Statement of Financial PositionMylene SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Principles of AccontingDocument16 pagesPrinciples of AccontingShafqat WassanNo ratings yet
- Type of AccountsDocument35 pagesType of AccountsJennifer0% (1)
- Wa0054.Document9 pagesWa0054.Siddhi JhaNo ratings yet
- STUDY Note 3 Important Accounting TermsDocument10 pagesSTUDY Note 3 Important Accounting TermsKeerthana Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 and Ch. 3 Basic Theory and Final AccountsDocument53 pagesCH 2 and Ch. 3 Basic Theory and Final AccountssagarnarayanmundadaNo ratings yet
- Basic Terms of Accounting-1Document10 pagesBasic Terms of Accounting-1vju chauhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Asset AccountsDocument3 pages1 Asset Accountsapi-299265916No ratings yet
- Accountancy Class Xi Chapter-2 Basic Accounting TermsDocument7 pagesAccountancy Class Xi Chapter-2 Basic Accounting TermsSomari ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CMBE 2 - Lesson 3 ModuleDocument12 pagesCMBE 2 - Lesson 3 ModuleEunice AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting 3 Double Entry Book Keeping RulesDocument44 pagesBasics of Accounting 3 Double Entry Book Keeping Rulesjiten zopeNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-4Document11 pagesChap 1-47a4374 hisNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Made a Cake Walk: IGCSE Accounting theory- exam style questions and answersFrom EverandCambridge Made a Cake Walk: IGCSE Accounting theory- exam style questions and answersRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (4)
- Unit 2 Session 7 Introduction To Financial StatementsDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Session 7 Introduction To Financial StatementsSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Basic Accounting TermsDocument17 pagesSession 3 Basic Accounting TermsSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Session1 Introduction To Book KeepingDocument37 pagesSession1 Introduction To Book KeepingSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Double Entry SystemDocument19 pagesSession 5 Double Entry SystemSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Session 2 Introduction To AccountingDocument11 pagesSession 2 Introduction To AccountingSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept in Disaster ManagementDocument18 pagesBasic Concept in Disaster ManagementSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Managerial AccountingDocument16 pagesManagerial AccountingSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- PLATODocument15 pagesPLATOSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- SYBADocument335 pagesSYBASagar ParateNo ratings yet
- PCPAr Special Materials 1 1stPB PDFDocument54 pagesPCPAr Special Materials 1 1stPB PDFJessie jorgeNo ratings yet
- SCM Notes Third and Fourth ChaptersDocument27 pagesSCM Notes Third and Fourth ChaptersSameer RaiNo ratings yet
- W1 Module 1 - Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument5 pagesW1 Module 1 - Introduction To Financial ManagementDanica VetuzNo ratings yet
- CHP 6 Eko 2Document10 pagesCHP 6 Eko 2Golden Ting Chiong SiiNo ratings yet
- Depreciation ExerciseDocument7 pagesDepreciation ExerciseMuskan LohariwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Practice KEYDocument19 pagesChapter 3 Practice KEYmartinmuebejayiNo ratings yet
- CB & STPDocument20 pagesCB & STPPruthviraj RathoreNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Declarations Form (SMCI) FY 2022 2023Document1 pageIncome Tax Declarations Form (SMCI) FY 2022 2023Nitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Economic and Political History: Rajesh Bhattacharya Email: Virtual Lounge: TBADocument14 pagesIndian Economic and Political History: Rajesh Bhattacharya Email: Virtual Lounge: TBANaunihal KumarNo ratings yet
- Serghei Merjan CVDocument11 pagesSerghei Merjan CVUNIMEDIANo ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Module 3 DEMAND AND PRICINGDocument3 pagesMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Module 3 DEMAND AND PRICINGJohn DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Change in Credit PolicyDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Change in Credit PolicyJhunorlando DisonoNo ratings yet
- W11 Module 9-Aggregate and Operations SchedulingDocument11 pagesW11 Module 9-Aggregate and Operations SchedulingDanica VetuzNo ratings yet
- Negotiation and Conflict Management Vaibhav Tiwari ROLL NO.2053, MBA-II Individual Assignment Grievance Management at SwiggyDocument23 pagesNegotiation and Conflict Management Vaibhav Tiwari ROLL NO.2053, MBA-II Individual Assignment Grievance Management at SwiggyVaibhav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Batteries Company, Oil and Gas Company, Manufacturing Company DUBAIDocument28 pagesBatteries Company, Oil and Gas Company, Manufacturing Company DUBAIPacific HRNo ratings yet
- PRICELIST MRT Maret 2015 PDFDocument1 pagePRICELIST MRT Maret 2015 PDFKhryzt DiazNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Supply Chain Management: Dr.P.Nivetha Assistant Professor Department of Management StudiesDocument34 pagesUnit-I Supply Chain Management: Dr.P.Nivetha Assistant Professor Department of Management Studiesshahina begumNo ratings yet
- Economics For ManagersDocument73 pagesEconomics For ManagersSwapnil DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Saln CherryDocument3 pagesSaln CherryMARISSA MAMARILNo ratings yet
- BAM 101 Introduction To Business Administration (Shakshi Shakshi)Document10 pagesBAM 101 Introduction To Business Administration (Shakshi Shakshi)shakshiNo ratings yet
- Mcgraw Hill/IrwinDocument12 pagesMcgraw Hill/IrwinAhmed El KhateebNo ratings yet
- PPDA Contracts 2023Document56 pagesPPDA Contracts 2023richard.musiimeNo ratings yet
- The Economist 20 AprilDocument332 pagesThe Economist 20 AprilUsama hameed0% (1)
- Burfisher - Introduction To CGE ModelsDocument420 pagesBurfisher - Introduction To CGE ModelsEstudiante bernardo david romero torresNo ratings yet
- Engineering EconomicsDocument2 pagesEngineering EconomicsAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1 PracticeDocument7 pagesQuiz #1 PracticeSano ManjiroNo ratings yet
- The Composable Commerce Cheat Sheet: How To Sell The Commerce Solution of Your Dreams To Your Business PeersDocument4 pagesThe Composable Commerce Cheat Sheet: How To Sell The Commerce Solution of Your Dreams To Your Business PeersSaurabh PantNo ratings yet
- Guide Question AccountingDocument24 pagesGuide Question AccountingJUARE MaxineNo ratings yet
Session 2 Basic Terms
Session 2 Basic Terms
Uploaded by
Sagar Parate0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views23 pagesThis document defines several basic accounting terms:
Business transactions can be cash or credit transactions. Accounts record transactions summarized by category on debit and credit sides. Capital refers to the owner's investment. Assets are resources used in operations, classified as current within one year or non-current longer-term. Liabilities are obligations to pay debts in the future, classified as current within one year or non-current longer term. Expenses are costs to earn revenue while expenditures acquire assets or services. Profit is revenue exceeding expenses and loss is expenses exceeding revenue.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines several basic accounting terms:
Business transactions can be cash or credit transactions. Accounts record transactions summarized by category on debit and credit sides. Capital refers to the owner's investment. Assets are resources used in operations, classified as current within one year or non-current longer-term. Liabilities are obligations to pay debts in the future, classified as current within one year or non-current longer term. Expenses are costs to earn revenue while expenditures acquire assets or services. Profit is revenue exceeding expenses and loss is expenses exceeding revenue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views23 pagesSession 2 Basic Terms
Session 2 Basic Terms
Uploaded by
Sagar ParateThis document defines several basic accounting terms:
Business transactions can be cash or credit transactions. Accounts record transactions summarized by category on debit and credit sides. Capital refers to the owner's investment. Assets are resources used in operations, classified as current within one year or non-current longer-term. Liabilities are obligations to pay debts in the future, classified as current within one year or non-current longer term. Expenses are costs to earn revenue while expenditures acquire assets or services. Profit is revenue exceeding expenses and loss is expenses exceeding revenue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 23
Basic Terms in Accounting
Asst. Prof. Rasika Naik
Basic Terms in Accounting
Business Transaction
An Economic activity that affects financial position of the business
and can be measured in terms of money e.g., expenses etc.
Business Transaction can be Credit Transactions as well as Cash
Transactions.
Cash Transaction- Cash Transaction is the one where cash
receipts and payments is involved in the transaction.
Credit Transaction- Credit Transaction is the one where cash is
not involved immediately but will be paid or received later.
Account : Account refers to a summarized record of relevant
transactions of particular head at one place. All accounts are
divided into two sides. The left side of an account is called debit
side and the right side of an account is called credit side.
Capital: Amount invested by the owner in the firm is known as
capital. It may be brought in the form of cash or assets by the
owner.
Drawings: The money or goods or both withdrawn by owner
from business for personal use, is known as drawings.
Example: Purchase of car for wife by withdrawing money from
business.
Assets: Assets are valuable and economic resources of an
enterprise useful in its operations
• 1. Current Assets: Current Assets are those assets which are
held for short period and can be converted into cash within one
year. For example: Debtors, stock etc.
2. Non-Current Assets: Non-Current Assets are those assets
which are hold for long period and used for normal business
operation. For example: Land, Building, Machinery etc. They are
further classified into:
(a) Tangible Assets: Tangible Assets are those assets which have
physical existence and can be seen and touched. For Example:
Furniture, Machinery etc.
(b) Intangible Assets: Intangible Assets are those assets which have no
physical existence and can be felt by operation. For example: Goodwill,
Patent, Trade mark etc.
Liabilities: Liabilities are obligations or debts that an enterprise
has to pay after some time in the future.
Liabilities can be classified as:
1. Current Liabilities: Current Liabilities are obligations or
debts that are payable within a period of one year. For Example:
Creditors, Bill Payable etc.
2. Non-Current Liabilities: Non-Current Liabilities are those
obligations or debts that are payable after a period of one year.
Example: Bank Loan, Debentures etc.
Examples of Liability
Expenses: Costs incurred by a business for earning revenue are
known as expenses. For example: Rent, Wages, Salaries, Interest
etc.
Expenditure: Spending money or incurring a liability for
acquiring assets, goods or services is called expenditure.
1. Revenue Expenditure: It is the amount spent to purchase
goods and services that are used during an accounting period is
called revenue expenditure. For Example: Rent, Interest etc.
2. Capital Expenditure: If benefit of expenditure is received for
more than one year, it is called capital expenditure. Example:
Purchase of Machinery.
3.Deferred Revenue Expenditure: There are certain
expenditures which are revenue in nature but benefit of which is
derived over number of years. For Example: Huge Advertisement
Expenditure.
Profit : The excess of revenues over its related expenses during an accounting year is profit.
Profit = Revenue – Expenses
Loss: The excess of expenses of a period over its related revenues is termed as loss.
Loss = Expenses – Revenue
Goods: The products in which the business deal in. The items that are
purchased for the purpose of resale and not for use in the business are
called goods.
Thank you
You might also like
- The World Nuclear Supply Chain: Outlook 2030 (2014)Document198 pagesThe World Nuclear Supply Chain: Outlook 2030 (2014)Greg KaserNo ratings yet
- Solution - Numericals Market Structure PDFDocument4 pagesSolution - Numericals Market Structure PDFpiyush kumarNo ratings yet
- Accounting TermsDocument37 pagesAccounting Termsmcsworkshop777No ratings yet
- Basic Acc Terms HandoutDocument3 pagesBasic Acc Terms HandoutpranjalNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermsDocument2 pagesBasic Accounting Termssatyam skNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Financial MangementDocument25 pagesAccounting and Financial MangementSHASHINo ratings yet
- Basic TermsDocument28 pagesBasic TermsShaji RarothNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terms NotesDocument5 pagesBasic Accounting Terms NotesNathan DavidNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Basic Accounting TermsDocument6 pagesChapter - 2 Basic Accounting TermsChaudhary GaylesabbNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument2 pagesTypes of Major AccountsKelsey Sofia RojasNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermsDocument16 pagesBasic Accounting TermsKusum MotwaniNo ratings yet
- EFA AssignmentDocument5 pagesEFA AssignmentDeviNo ratings yet
- 11 ACCTS theoryNOTESDocument6 pages11 ACCTS theoryNOTESDeveshi TewariNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Managers. 1pdfDocument168 pagesAccounting For Managers. 1pdfAkash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8Mrittika WadderNo ratings yet
- Accounting TermsDocument8 pagesAccounting TermsIshrit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mba Study MaterialsDocument4 pagesMba Study Materialskumar2346No ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermsDocument12 pagesBasic Accounting TermsNathan DavidNo ratings yet
- 1, Class Xi, Subject - Accountancy, Chapter - 1Document17 pages1, Class Xi, Subject - Accountancy, Chapter - 1Shoryamann SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2assets, Liabilities and CapitalDocument5 pages2assets, Liabilities and Capitaldilhani sheharaNo ratings yet
- Classification of AccountsDocument4 pagesClassification of AccountsManan MunshiNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminologies of Accounting: 1. AssetsDocument10 pagesBasic Terminologies of Accounting: 1. AssetsSophiya PrabinNo ratings yet
- Short-Questions (Accounts) 1.goodsDocument3 pagesShort-Questions (Accounts) 1.goodsUrvishNo ratings yet
- 2 Elements of AccountingDocument4 pages2 Elements of Accountingapi-299265916No ratings yet
- XI Notes of Chapter 2 Part I PDFDocument3 pagesXI Notes of Chapter 2 Part I PDFRoshanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lesson NotesDocument9 pages2nd Lesson Notesjayasandhya mNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accountancy-Basic ConceptsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Accountancy-Basic ConceptsjemrecayakNo ratings yet
- Accounting:: Capital Assets - LiabilitiesDocument3 pagesAccounting:: Capital Assets - LiabilitiesashNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument2 pagesTypes of Major Accountscristin l. viloriaNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument5 pagesTypes of Major AccountsJenny SaynoNo ratings yet
- FIA-FA1 NotesDocument37 pagesFIA-FA1 NotesAbdul Rehman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Types of Major AccountsDocument30 pagesTypes of Major AccountsEstelle GammadNo ratings yet
- EpfoDocument6 pagesEpfoSiddharth OjhaNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting TermDocument4 pagesBasic Accounting Termak99archana1999No ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terms: By: Shivani ChandelDocument29 pagesBasic Accounting Terms: By: Shivani ChandelDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Tally ERP9Document68 pagesTally ERP9sah100% (11)
- Financial AccountingDocument16 pagesFinancial AccountingSNo ratings yet
- LESSON 8 - Types of Major AccountsDocument3 pagesLESSON 8 - Types of Major Accountsdrea.heart29No ratings yet
- Faa IDocument18 pagesFaa Iabhiseknanda82495No ratings yet
- Chapter-2: The Accounting Cycle: Accounting For A Service Enterprise 2.1Document19 pagesChapter-2: The Accounting Cycle: Accounting For A Service Enterprise 2.1Nigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Session 4Document12 pagesSession 4devanshk121No ratings yet
- Basic TerminologiesDocument20 pagesBasic TerminologiesMOHAMED USAIDNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks QuestionsDocument44 pages2 Marks Questionsvicky241989No ratings yet
- Account Tiltes HandoutsDocument2 pagesAccount Tiltes HandoutsSean Andreson MabalacadNo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting: Mba (HRD) Delhi School of Economics Department of Commerce University of DelhiDocument15 pagesBasics of Accounting: Mba (HRD) Delhi School of Economics Department of Commerce University of DelhiMukesh DroliaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting (Basic Terms)Document6 pagesFinancial Accounting (Basic Terms)prathampawar5912No ratings yet
- Chapter # 1 Business TransactionDocument22 pagesChapter # 1 Business TransactionWaleed NasirNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To Accounting PART 1-LLB 1Document34 pagesIntoduction To Accounting PART 1-LLB 1brandywilliam203No ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terms l1 Accountancy Class 11 Cbse by Ushank SirDocument11 pagesBasic Accounting Terms l1 Accountancy Class 11 Cbse by Ushank Sirrajput442007No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Statement of Financial PositionDocument22 pagesLesson 1 Statement of Financial PositionMylene SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Principles of AccontingDocument16 pagesPrinciples of AccontingShafqat WassanNo ratings yet
- Type of AccountsDocument35 pagesType of AccountsJennifer0% (1)
- Wa0054.Document9 pagesWa0054.Siddhi JhaNo ratings yet
- STUDY Note 3 Important Accounting TermsDocument10 pagesSTUDY Note 3 Important Accounting TermsKeerthana Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 and Ch. 3 Basic Theory and Final AccountsDocument53 pagesCH 2 and Ch. 3 Basic Theory and Final AccountssagarnarayanmundadaNo ratings yet
- Basic Terms of Accounting-1Document10 pagesBasic Terms of Accounting-1vju chauhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Asset AccountsDocument3 pages1 Asset Accountsapi-299265916No ratings yet
- Accountancy Class Xi Chapter-2 Basic Accounting TermsDocument7 pagesAccountancy Class Xi Chapter-2 Basic Accounting TermsSomari ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CMBE 2 - Lesson 3 ModuleDocument12 pagesCMBE 2 - Lesson 3 ModuleEunice AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting 3 Double Entry Book Keeping RulesDocument44 pagesBasics of Accounting 3 Double Entry Book Keeping Rulesjiten zopeNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-4Document11 pagesChap 1-47a4374 hisNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Made a Cake Walk: IGCSE Accounting theory- exam style questions and answersFrom EverandCambridge Made a Cake Walk: IGCSE Accounting theory- exam style questions and answersRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (4)
- Unit 2 Session 7 Introduction To Financial StatementsDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Session 7 Introduction To Financial StatementsSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Basic Accounting TermsDocument17 pagesSession 3 Basic Accounting TermsSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Session1 Introduction To Book KeepingDocument37 pagesSession1 Introduction To Book KeepingSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Double Entry SystemDocument19 pagesSession 5 Double Entry SystemSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Session 2 Introduction To AccountingDocument11 pagesSession 2 Introduction To AccountingSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept in Disaster ManagementDocument18 pagesBasic Concept in Disaster ManagementSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- Managerial AccountingDocument16 pagesManagerial AccountingSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- PLATODocument15 pagesPLATOSagar ParateNo ratings yet
- SYBADocument335 pagesSYBASagar ParateNo ratings yet
- PCPAr Special Materials 1 1stPB PDFDocument54 pagesPCPAr Special Materials 1 1stPB PDFJessie jorgeNo ratings yet
- SCM Notes Third and Fourth ChaptersDocument27 pagesSCM Notes Third and Fourth ChaptersSameer RaiNo ratings yet
- W1 Module 1 - Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument5 pagesW1 Module 1 - Introduction To Financial ManagementDanica VetuzNo ratings yet
- CHP 6 Eko 2Document10 pagesCHP 6 Eko 2Golden Ting Chiong SiiNo ratings yet
- Depreciation ExerciseDocument7 pagesDepreciation ExerciseMuskan LohariwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Practice KEYDocument19 pagesChapter 3 Practice KEYmartinmuebejayiNo ratings yet
- CB & STPDocument20 pagesCB & STPPruthviraj RathoreNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Declarations Form (SMCI) FY 2022 2023Document1 pageIncome Tax Declarations Form (SMCI) FY 2022 2023Nitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Economic and Political History: Rajesh Bhattacharya Email: Virtual Lounge: TBADocument14 pagesIndian Economic and Political History: Rajesh Bhattacharya Email: Virtual Lounge: TBANaunihal KumarNo ratings yet
- Serghei Merjan CVDocument11 pagesSerghei Merjan CVUNIMEDIANo ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Module 3 DEMAND AND PRICINGDocument3 pagesMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Module 3 DEMAND AND PRICINGJohn DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Change in Credit PolicyDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Change in Credit PolicyJhunorlando DisonoNo ratings yet
- W11 Module 9-Aggregate and Operations SchedulingDocument11 pagesW11 Module 9-Aggregate and Operations SchedulingDanica VetuzNo ratings yet
- Negotiation and Conflict Management Vaibhav Tiwari ROLL NO.2053, MBA-II Individual Assignment Grievance Management at SwiggyDocument23 pagesNegotiation and Conflict Management Vaibhav Tiwari ROLL NO.2053, MBA-II Individual Assignment Grievance Management at SwiggyVaibhav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Batteries Company, Oil and Gas Company, Manufacturing Company DUBAIDocument28 pagesBatteries Company, Oil and Gas Company, Manufacturing Company DUBAIPacific HRNo ratings yet
- PRICELIST MRT Maret 2015 PDFDocument1 pagePRICELIST MRT Maret 2015 PDFKhryzt DiazNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Supply Chain Management: Dr.P.Nivetha Assistant Professor Department of Management StudiesDocument34 pagesUnit-I Supply Chain Management: Dr.P.Nivetha Assistant Professor Department of Management Studiesshahina begumNo ratings yet
- Economics For ManagersDocument73 pagesEconomics For ManagersSwapnil DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Saln CherryDocument3 pagesSaln CherryMARISSA MAMARILNo ratings yet
- BAM 101 Introduction To Business Administration (Shakshi Shakshi)Document10 pagesBAM 101 Introduction To Business Administration (Shakshi Shakshi)shakshiNo ratings yet
- Mcgraw Hill/IrwinDocument12 pagesMcgraw Hill/IrwinAhmed El KhateebNo ratings yet
- PPDA Contracts 2023Document56 pagesPPDA Contracts 2023richard.musiimeNo ratings yet
- The Economist 20 AprilDocument332 pagesThe Economist 20 AprilUsama hameed0% (1)
- Burfisher - Introduction To CGE ModelsDocument420 pagesBurfisher - Introduction To CGE ModelsEstudiante bernardo david romero torresNo ratings yet
- Engineering EconomicsDocument2 pagesEngineering EconomicsAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1 PracticeDocument7 pagesQuiz #1 PracticeSano ManjiroNo ratings yet
- The Composable Commerce Cheat Sheet: How To Sell The Commerce Solution of Your Dreams To Your Business PeersDocument4 pagesThe Composable Commerce Cheat Sheet: How To Sell The Commerce Solution of Your Dreams To Your Business PeersSaurabh PantNo ratings yet
- Guide Question AccountingDocument24 pagesGuide Question AccountingJUARE MaxineNo ratings yet