Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Strain Gauge Pressure Transducer
Strain Gauge Pressure Transducer
Uploaded by
dskjajkdsa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views9 pagesA strain gauge pressure transducer uses strain gauges attached to a diaphragm to measure pressure. As pressure is applied to the diaphragm, it flexes and strains the gauges, changing their resistance in a Wheatstone bridge circuit. Any imbalance in the bridge due to resistance changes produces an output voltage proportional to the measured pressure. Temperature effects all gauges equally and does not impact the pressure reading.
Original Description:
Original Title
STRAIN GAUGE PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA strain gauge pressure transducer uses strain gauges attached to a diaphragm to measure pressure. As pressure is applied to the diaphragm, it flexes and strains the gauges, changing their resistance in a Wheatstone bridge circuit. Any imbalance in the bridge due to resistance changes produces an output voltage proportional to the measured pressure. Temperature effects all gauges equally and does not impact the pressure reading.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views9 pagesStrain Gauge Pressure Transducer
Strain Gauge Pressure Transducer
Uploaded by
dskjajkdsaA strain gauge pressure transducer uses strain gauges attached to a diaphragm to measure pressure. As pressure is applied to the diaphragm, it flexes and strains the gauges, changing their resistance in a Wheatstone bridge circuit. Any imbalance in the bridge due to resistance changes produces an output voltage proportional to the measured pressure. Temperature effects all gauges equally and does not impact the pressure reading.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
STRAIN GAUGE PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
Strain gauge is a type of resistive transduction.
Pressure measurement is obtained from
displacement of elastic element.
Pressure is measured through force that is exerted
on the diaphragm where the force will be detected
by the strain gauge and resistance change will be
produced.
Wheatstone Bridge circuit is used to detect the
change in pressure and an amplifier is used to
amplify the small output signals.
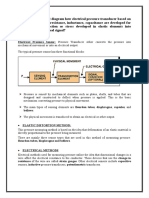
BASIC PRINCIPLE
The strain gauge is a fine wire which changes its
resistance when mechanically strained, due to physical
effects.
A strain gauge may be attached to the diaphragm so that
when the diaphragm flexes due to the process pressure
applied on it , the strain gauge stretches for compresses.
This deformation of the strain gauge causes the
variation in its length and cross sectional area due to
which its resistance also changes as shown in fig.1
The resistance changes of a strain gauge is
usually converted into voltage by connecting one
,two, or four similar gauges , as of wheatstone
bridge and applying excitation to the bridge .
The bridge output voltage is then a measure of
the pressure sensed by the strain gauges
Strain gauge transducer
Strain gauge bridge circuit
With diaphragm element
CONSTRUCTION AND WORKING
Figure 2 shows a bridge circuit with four strain
gauges , Rsg 1,Rsg 2,Rsg 3 & Rsg 4.
Two strain gauges ,Rsg 1 & Rsg 4 , are mounted so
that increasing pressure increases their resistance.
Strain gauges Rsg 2 & Rsg 3 , are mounted so that
increasing pressure decreases their resistance.
A change in temperature affects all the four strain gauges
in the same way , resulting in no change in the pressure
indication .
At balance , when there is no pressure , no current flows
through the galvanometer G and hence there will be no
deflection in the galvanometer .
As soon as the pressure is applied the strain gauge
stretches or compresses accordingly and the bridge
circuit is unbalanced due to the change in resistance of
the strain gauges.
Thus, a current flows in the galvanometer ,
which is measured by the deflection of the
galvanometer .
These changes affect the output of the bridge
circuit , which indicates a change in measured
pressure.
Now, this change in output voltage may be
calibrated for the pressure change .
ADVANTAGES
Small and easy to install.
Have good accuracy.
Good stability.
Simple to maintain .
Contain no moving parts .
Good shock and vibration characteristics.
Fast speed of response.
High output signal strength.
DISADVANTAGES
Moderate to high cost.
Electrical readout necessary.
Require constant voltage supply.
Temperature compensation required due to
problems presented by temperature variations.
You might also like
- Wma12 01 Que 20230518Document32 pagesWma12 01 Que 20230518saidieraneNo ratings yet
- Proving Ring ExperimentDocument7 pagesProving Ring ExperimentPrateek AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Lug AnalysisDocument4 pagesLug AnalysisKuldeep BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementDocument28 pagesPressure MeasurementbcramcNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics Pressure and Stress Sensor "Strain Gauge Pressure Transducer"Document3 pagesIndustrial Electronics Pressure and Stress Sensor "Strain Gauge Pressure Transducer"Ronniel VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Pressure TransducerDocument12 pagesPressure TransducerAsif BhatiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Pressure SensorsDocument5 pagesElectronic Pressure Sensorsmcbmcb159No ratings yet
- Pressure Measurement Part 3 of 3 PDFDocument37 pagesPressure Measurement Part 3 of 3 PDFSimanjuntak JulpianNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON Transducers: PowerpointDocument19 pagesPresentation ON Transducers: Powerpointapi-19822723No ratings yet
- Adith SeminarDocument2 pagesAdith SeminarJithin RajuNo ratings yet
- How Do Air Pressure Sensors WorkDocument9 pagesHow Do Air Pressure Sensors WorkjackNo ratings yet
- Pressure Gauge Bourdon Tube Pressure GaugeDocument7 pagesPressure Gauge Bourdon Tube Pressure GaugeVignesh RajanNo ratings yet
- Measurement TipsDocument14 pagesMeasurement TipsFarah DianaNo ratings yet
- The Basic Bridge CircuitDocument8 pagesThe Basic Bridge CircuitMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Load CellDocument9 pagesLoad Cellminhtrieu999No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Tanvi IsraniNo ratings yet
- Principle of The Strain GaugeDocument6 pagesPrinciple of The Strain Gaugeapi-3706095100% (1)
- Tema: Galgas Extensiométricas (Strain Gages)Document4 pagesTema: Galgas Extensiométricas (Strain Gages)Anonymous 21Y57AuNo ratings yet
- High Wire Pressure Transducers 2020uch1937 and 2020uch1936Document16 pagesHigh Wire Pressure Transducers 2020uch1937 and 2020uch1936nishantNo ratings yet
- Loadcells Quarter Half and Full BridgeDocument25 pagesLoadcells Quarter Half and Full BridgeCharles le MagneNo ratings yet
- STRAIN GageDocument5 pagesSTRAIN Gagemanoish07No ratings yet
- KSP Pressure MeasurementDocument15 pagesKSP Pressure MeasurementZulfequar R. Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Me 2221 - 3 PDFDocument16 pagesMe 2221 - 3 PDFRejaul Karim RaihanNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument67 pagesUnit IIonhaNo ratings yet
- 16md02 - Force SensorDocument13 pages16md02 - Force SensorPriyadarshini KrishnaswamyNo ratings yet
- Ans: Electrical Pressure Sensor: Pressure Transducer Either Converts The Pressure IntoDocument6 pagesAns: Electrical Pressure Sensor: Pressure Transducer Either Converts The Pressure IntoSpryknterNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measuring Instruments: Dr. Fahad Rehman CUI, Lahore CampusDocument69 pagesPressure Measuring Instruments: Dr. Fahad Rehman CUI, Lahore CampusAhmed Mustafa100% (1)
- Measurement of Force, Torque and Strain: Prepared by DrrrshahDocument84 pagesMeasurement of Force, Torque and Strain: Prepared by DrrrshahKantha RaoNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge ProjectDocument18 pagesStrain Gauge ProjectAnkit Garg100% (1)
- PI Lecture 13Document8 pagesPI Lecture 13pk2003158No ratings yet
- RecoveredDocument33 pagesRecoveredmahmoudsaeb10No ratings yet
- TRANSDUCERDocument14 pagesTRANSDUCERmicah micahNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge Connections and Bridge CircuitsDocument6 pagesStrain Gauge Connections and Bridge CircuitsFilippinNo ratings yet
- Transducer EngineeringUnit3Document58 pagesTransducer EngineeringUnit3irfanahmed7105No ratings yet
- Modified AC Wheatstone Bridge Network For Accurate Measurement of Pressure Using Strain Gauge Type Pressure SensorDocument3 pagesModified AC Wheatstone Bridge Network For Accurate Measurement of Pressure Using Strain Gauge Type Pressure SensorMukul RNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document29 pagesUnit 2nikhill kundarNo ratings yet
- CC C C CC: CCC CCCDocument7 pagesCC C C CC: CCC CCCPranay PatilNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument14 pagesStrain GaugeEngr. Abdullah100% (2)
- Strain MeasurementDocument10 pagesStrain MeasurementsivaeeinfoNo ratings yet
- Unit NotesDocument12 pagesUnit NotesAyushi ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Resistive Sensors and TrasducersDocument12 pagesResistive Sensors and TrasducersDr-Eng Imad A. ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report #04 Testing TransformersDocument5 pagesLaboratory Report #04 Testing TransformersCristian Camilo Díaz Piñeros0% (1)
- Use of Electrical Strain GaugesDocument7 pagesUse of Electrical Strain GaugesChetan B ArkasaliNo ratings yet
- StrainDocument13 pagesStrainspanandk0% (1)
- Introduction To Pressure TransducersDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Pressure TransducersTEUKUNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge: Load CellDocument33 pagesStrain Gauge: Load CellPrashant ShahNo ratings yet
- Sensors For Measurement and Control: 6.3 The Measurement of Pressure PP 452 (R.C Vol3 Chemical Engineering)Document33 pagesSensors For Measurement and Control: 6.3 The Measurement of Pressure PP 452 (R.C Vol3 Chemical Engineering)unters yayNo ratings yet
- Report 2-محولDocument14 pagesReport 2-محولKarim SakrNo ratings yet
- Measurement, Instrumentation and Computer Interfacing: A.Resistive Transducer DefinitionDocument7 pagesMeasurement, Instrumentation and Computer Interfacing: A.Resistive Transducer DefinitionqwertyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Pressure TransducersDocument2 pagesBasics of Pressure TransducersCris Vincent Rivera SedantoNo ratings yet
- Tirtharaj Pati - Details of Strain Gauge Sensor PDFDocument13 pagesTirtharaj Pati - Details of Strain Gauge Sensor PDFTirtharaj PatiNo ratings yet
- Aic Rep NewDocument10 pagesAic Rep Newj.k.boseNo ratings yet
- Wheatstone AbDocument10 pagesWheatstone AbkartheesanvNo ratings yet
- Measurements: Part 2d: Measurement of PressureDocument15 pagesMeasurements: Part 2d: Measurement of Pressureviswa37No ratings yet
- EEM Chap-5Document67 pagesEEM Chap-5patilrudreshNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Transducer: Posts Tagged: "Displacement Transducers"Document21 pagesCapacitance Transducer: Posts Tagged: "Displacement Transducers"RamNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument22 pagesStrain Gaugesel_d_bellNo ratings yet
- Strain MeasurementDocument31 pagesStrain MeasurementTejal IkharNo ratings yet
- Experimental Stress AnalysisDocument25 pagesExperimental Stress AnalysisSharjeel Ahmed ShakeelNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Iso 18164 2005 RR PDFDocument9 pagesIso 18164 2005 RR PDFdskjajkdsaNo ratings yet
- Direct Syntheses PDFDocument4 pagesDirect Syntheses PDFdskjajkdsaNo ratings yet
- Tyre RetradingDocument4 pagesTyre RetradingdskjajkdsaNo ratings yet
- Temperature SenesorDocument16 pagesTemperature SenesordskjajkdsaNo ratings yet
- PyrometerDocument7 pagesPyrometerdskjajkdsaNo ratings yet
- Ch3rolconbear1 200312773Document56 pagesCh3rolconbear1 200312773Mix TubeNo ratings yet
- Participating Institute: AriesDocument2 pagesParticipating Institute: AriesGauravPatelNo ratings yet
- Measure of Variability: For Grouped DataDocument10 pagesMeasure of Variability: For Grouped DataJake ColomaNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Math Final Revision2Document45 pagesYear 8 Math Final Revision2Amro BoudyNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry q1Document57 pagesGeneral Chemistry q1Dianna Rose QuintoNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Transmission Lines Lecture 3: Transmission Line AnalysisDocument8 pagesModule 2: Transmission Lines Lecture 3: Transmission Line Analysisjon9 snowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Pressure Vessels: Sr. No. QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - Pressure Vessels: Sr. No. Questionsdarshit dadhaniyaNo ratings yet
- Savannah Montelongo - Momentum ProblemsDocument2 pagesSavannah Montelongo - Momentum Problemssavannah67% (3)
- Sensortechnik Optical Belt Scale Tech Sheet S1400 FinalDocument1 pageSensortechnik Optical Belt Scale Tech Sheet S1400 FinalyogaNo ratings yet
- Utility Pole Brochure (CPM231-0613) LtrsizeDocument36 pagesUtility Pole Brochure (CPM231-0613) LtrsizeIman HerdyanthoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Particle Counter Sample Preparation: Best Practices For Repeatable Particle Count ResultsDocument3 pagesHydraulic Particle Counter Sample Preparation: Best Practices For Repeatable Particle Count ResultsPaula LópezNo ratings yet
- CET Crash Course Test Schedule DetailedDocument3 pagesCET Crash Course Test Schedule DetailedDbebebdNo ratings yet
- PNJunctionsI S16Document21 pagesPNJunctionsI S16puceiroaleNo ratings yet
- Elemental Mind Map Project 6th GradeDocument2 pagesElemental Mind Map Project 6th GradeTalanNo ratings yet
- Seismic Response of SDOF SystemsDocument42 pagesSeismic Response of SDOF SystemsRonnie1478No ratings yet
- WorkbookDocument78 pagesWorkbookmirfurkaan106No ratings yet
- Mid Infrared Hyperspectral Sensor Based On MEMS Fabry Pérot Interferometer For Stand Off Sensing ApplicationsDocument6 pagesMid Infrared Hyperspectral Sensor Based On MEMS Fabry Pérot Interferometer For Stand Off Sensing ApplicationsHoun SophatNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics EM 1 Mark Questions English Medium PDF DownloadDocument18 pages12th Physics EM 1 Mark Questions English Medium PDF Downloadkrajakannan1965No ratings yet
- 02 Machine Tool, Automation & Metrology Mechanical Engineering ME 3201 E3/II 23-12-2012Document3 pages02 Machine Tool, Automation & Metrology Mechanical Engineering ME 3201 E3/II 23-12-2012Chaitanya ReddyNo ratings yet
- System Components: Global Chiller TrainingDocument22 pagesSystem Components: Global Chiller TrainingSyed Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Previous Exams Questions Exercise-I: PhysicsDocument18 pagesPrevious Exams Questions Exercise-I: PhysicsSuryansh KhatiNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Packet PDFDocument6 pages5.4 Packet PDFVed PatelNo ratings yet
- 1995 - Structural Design Sensitivity - Continuum and Discrete Approaches PDFDocument24 pages1995 - Structural Design Sensitivity - Continuum and Discrete Approaches PDFGuatavo91No ratings yet
- Circuit TypeDocument4 pagesCircuit TypeSwaraj BoseNo ratings yet
- Project InformationDocument203 pagesProject InformationPaul RaduNo ratings yet
- Properties of Structure Steel As Per Limit State Method IS 800:2007, Mechanical Properties of SteelDocument19 pagesProperties of Structure Steel As Per Limit State Method IS 800:2007, Mechanical Properties of SteelRaju Sharma75% (4)
- Question Paper: Biology - 100 Chemistry - 50 Physics - 50Document24 pagesQuestion Paper: Biology - 100 Chemistry - 50 Physics - 50harita shindeNo ratings yet
- BTS - 0000 (Zero O'Clock)Document8 pagesBTS - 0000 (Zero O'Clock)Triesha SyifahatiNo ratings yet