Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cellular Respiration
Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
Mary Cris Tandoc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
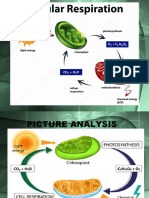
5 views11 pagesCellular respiration involves three main stages - glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain - to break down glucose and generate ATP, the energy currency of cells. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate, the Krebs cycle further breaks down pyruvate and acetyl CoA molecules, and the electron transport chain uses oxygen to harvest energy from NADH and FADH2 to power the synthesis of large amounts of ATP. Aerobic respiration generates 36 ATP per glucose molecule with water and carbon dioxide as byproducts, while anaerobic respiration like fermentation yields less ATP without oxygen by producing other byproducts like ethanol or lactic acid.
Original Description:
Original Title
Cellular respiration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCellular respiration involves three main stages - glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain - to break down glucose and generate ATP, the energy currency of cells. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate, the Krebs cycle further breaks down pyruvate and acetyl CoA molecules, and the electron transport chain uses oxygen to harvest energy from NADH and FADH2 to power the synthesis of large amounts of ATP. Aerobic respiration generates 36 ATP per glucose molecule with water and carbon dioxide as byproducts, while anaerobic respiration like fermentation yields less ATP without oxygen by producing other byproducts like ethanol or lactic acid.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesCellular Respiration
Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
Mary Cris TandocCellular respiration involves three main stages - glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain - to break down glucose and generate ATP, the energy currency of cells. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate, the Krebs cycle further breaks down pyruvate and acetyl CoA molecules, and the electron transport chain uses oxygen to harvest energy from NADH and FADH2 to power the synthesis of large amounts of ATP. Aerobic respiration generates 36 ATP per glucose molecule with water and carbon dioxide as byproducts, while anaerobic respiration like fermentation yields less ATP without oxygen by producing other byproducts like ethanol or lactic acid.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Cellular respiration
• ATP - adenosine triphosphate - Adenosine triphosphate is an organic
compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living
cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation,
condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis.
• The food you eat is mechanically and chemically digested starting
from the mouth until it reaches the small intestine. During
digestion ,complex foods are broken into their simplest
forms,carbohydrates into simple sugar (glucose) ; proteins into amino
acids ; and lipids (fats) into fatty acids and glycerol (building blocks of
lipids). These digested foods are then absorbed by the cells from the
walls of the small intestine . They are then circulated by the blood to
different parts of the body , and thus become part of every single cell
of the body. But the cell cannot simply use the stored energy from
glucose , amino acid ,or fatty acids. The stored energy must first
converted into ATP by a series of chemical reactions via CELLULAR
RESPIRATION.
Aerobic Respiration
• Uses oxygen to produce ATPs.
• Anaerobic respiration does not involve oxygen.
• Oxygen is consumed but a large number of ATPs are generated along
with water and carbon dioxide as by-product.
• By-product an incidental or secondary product made in the
manufacture or synthesis of something else
• Involves three stages : glycolysis , Krebs Cycle and electron transport
Glycolysis : Harvesting energy by breaking
down glucose to pyruvate
• Process by which one glucose molecule is broken down into two
pyruvic acid molecules to generate two net ATPs in the process .
• Enzymes - proteins that help speed up metabolism, or the chemical
reactions in our bodies
Krebs Cycle : breaking down acetyl-CoA
completely into carbon dioxide and water
• Acetyl coa - the breakdown of both carbohydrates (by glycolysis) and
lipids (by β-oxidation)
• Acetyl coa combines with a four carbon compound to form a six carbon
compound.
• Carbon dioxide is released from the six carbon compound , resulting in
a five carbon compound
• Another molecule of carbon dioxide is released from the five carbon
compound to form a four carbon compound
• The four carbon compound is converted into a new four carbon
compound .
• The new four carbon compound is converted into a four carbon
compound similar to that of the four carbon compound at the start of
the cycle . The four carbon compound re enters the cycle .
Electron Transport Chain : Harvesting More
• The last step in cellular respiration ,called the electron transport chain
,takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria . The first two
steps in cellular respiration ,glycolysis and Krebs cycle,generate only
small amount of energy and produce NAHD and FADH molecules.
• Oxidative phosphorylation refers to a series of oxidation processes
where electrons carried by NADH and FADH are transferred to
electron acceptors. As electrons transferred ,ATPs are released, along
with water as by product . A total of three ATPs are produce for every
molecule of NADH, two ATPs for every three FADH that enter the
electron transport chain , respectedly. In sum , a total of 36 ATPs are
generated for every molecules of glucose
Anaerobic Respiration : Providing Energy
Without Oxygen
• Fermentation, a type of anaerobic respiration , breaks down pyruvic
acid without using oxygen.
• a water-soluble, organic liquid that is produced by breaking down
carbohydrates and sugars through the glycolytic pathway (glycolysis)
• Yields fewer ATPs than aerobic respiration .
• Alcoholic fermentation ethanol and carbon dioxide are produce
from pyruvic acid
• Lactic acid fermentation when lactic acid is produce from pyruvic
acid
• Muscle fatigue accumulation of lactic acid in the muscle cells .
Lesson learned : nakakapagod gumawa ng
report
You might also like
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NotesDocument18 pagesCritical Care NotesjulieNo ratings yet
- BSC 2085 Final Exam Study Guide RevisedDocument3 pagesBSC 2085 Final Exam Study Guide RevisedReymon SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Respiration in Plants - Glycoysis - Fermentation - Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument31 pagesLecture 7 Respiration in Plants - Glycoysis - Fermentation - Oxidative Phosphorylationmichael328wanjiruNo ratings yet
- Energetics PDF ResumeDocument40 pagesEnergetics PDF ResumeketyleenbNo ratings yet
- Respiration:: Glycolysis, Krebs' CycleDocument20 pagesRespiration:: Glycolysis, Krebs' CycleNikhil DeshwalNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument24 pagesCellular RespirationAdelaide CNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument33 pagesCellular RespirationAndres Maroto100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument41 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisCarissa MarchanNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument15 pagesCellular RespirationFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in PlantsDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration in PlantsMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Amelia Putri Nariya Astri Yohana Putri Gabriellia Oktaviani P. Muhammad Fauzan Safina ZahiraDocument43 pagesCellular Respiration: Amelia Putri Nariya Astri Yohana Putri Gabriellia Oktaviani P. Muhammad Fauzan Safina ZahirasafinazahiraNo ratings yet
- Respiration Part 1Document35 pagesRespiration Part 1Ashley JohnsNo ratings yet
- Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesKey ConceptsHikaru IshiiNo ratings yet
- Bio Lesson 21 RespiDocument48 pagesBio Lesson 21 RespiChlzy ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument13 pagesCellular Respirationmanojtbgri5793No ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration LECTURE 111Document47 pagesCellular - Respiration LECTURE 111Cynel DelaNo ratings yet
- HyacinthDocument52 pagesHyacinthHyacinth Rae Ramirez Aranas - LipatNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical EnergyDocument37 pagesCellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical EnergyEdward GanggangNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument51 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint Guidelaloo01No ratings yet
- Energy and Respiration - 2Document39 pagesEnergy and Respiration - 2Rohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Respiration-The Source of EnergyDocument14 pages1.4 Respiration-The Source of EnergysamiktshyagiriNo ratings yet
- Science Daily Lesson l44Document48 pagesScience Daily Lesson l44Audie Nocedo MontecastroNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism 13Document87 pagesMicrobial Metabolism 13lalithaNo ratings yet
- Science of Living SystemsDocument52 pagesScience of Living Systemshimanshu_agraNo ratings yet
- MR Jabbie GlycosisDocument48 pagesMR Jabbie Glycosisvandytommy308No ratings yet
- 4 Cell RespirationDocument20 pages4 Cell RespirationCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Fermentation: Bayas Conde de Leon Bse 41Document26 pagesFermentation: Bayas Conde de Leon Bse 41Mary Jesreth Vergara BayasNo ratings yet
- Atp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasDocument12 pagesAtp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasIan AusejoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration SummaryDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Summarylady ann jimenezNo ratings yet
- BIOL CH 9Document21 pagesBIOL CH 9Nouf AlshareefNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesCellular RespirationrhaineNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lec 4.5Document40 pagesBiochemistry Lec 4.5ao868598No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument37 pagesCellular Respirationamarali11420222No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Cuanan Manlangit MenilDocument87 pagesCellular Respiration: Cuanan Manlangit MenilChath Regalado PacunlaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Complete Reviewer JamDocument193 pagesBiochem Complete Reviewer JamArianne Jans MunarNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)Document11 pagesRespiration in Plants Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)soumyajitghosh289No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument28 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationGlena MendozaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic RespirationDocument29 pagesAerobic Respirationleeyaonde123No ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Chemical EnergyDocument43 pagesHow Cells Release Chemical EnergyDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1Document50 pagesQuarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1champimiloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Respiration A PDFDocument19 pagesLecture 5 Respiration A PDFShegNo ratings yet
- GBIO1 Week18 Energy Transformation Part 5Document25 pagesGBIO1 Week18 Energy Transformation Part 5Endeavor KutosakiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Key PointsDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Key PointsKathleen RamiloNo ratings yet
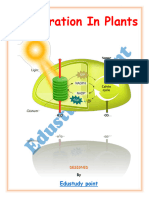
- Respiration in Plants (Edustudy Point) - UnlockedDocument6 pagesRespiration in Plants (Edustudy Point) - Unlockedkushwahvivek1028No ratings yet
- Cellular EnergeticsDocument17 pagesCellular EnergeticsdangbonlapNo ratings yet
- Unit 8-MetabolismDocument103 pagesUnit 8-Metabolismnumberr515No ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 6Document35 pagesBIOL223-Lab 6chicken friesNo ratings yet
- MetabolismeDocument31 pagesMetabolismeLalu Aldi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Notes: RespirationDocument46 pagesUnit 5 Notes: Respirationbody fayezNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument49 pagesCell RespirationJanine CambaNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationDocument28 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation Anaerobic Respiration and Fermentationcediebanaag10No ratings yet
- Final PDFDocument6 pagesFinal PDFNhư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument34 pagesCellular RespirationJonathan Blaza100% (2)
- Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument4 pagesPortal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksSHRAVYA K REDDYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7cellular Respiration 2016 To Be UsedDocument26 pagesChapter 7cellular Respiration 2016 To Be UsedMichel Jay Arguelles EspulgarNo ratings yet
- Powering The Cell-Cellular RespirationDocument37 pagesPowering The Cell-Cellular RespirationMarjorie VistaNo ratings yet
- Pearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationDocument77 pagesPearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationMetaknight360 LiveNo ratings yet
- 1.4 RespirationDocument11 pages1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNo ratings yet
- 8-C1.2 Cell RespirationDocument47 pages8-C1.2 Cell Respirationmakaya02No ratings yet
- Bioenergetics (How The Body Converts Food To Energy)Document59 pagesBioenergetics (How The Body Converts Food To Energy)Mary Rose Bobis Vicente100% (1)
- Tle 10. Week 10Document31 pagesTle 10. Week 10Mary Cris TandocNo ratings yet
- Sr. Cris Thesis Final DefenseDocument49 pagesSr. Cris Thesis Final DefenseMary Cris TandocNo ratings yet
- Theo - FrameworkDocument2 pagesTheo - FrameworkMary Cris TandocNo ratings yet
- THESISDocument47 pagesTHESISMary Cris TandocNo ratings yet
- TANDOC MARY CRIS Thesis Math Major. With Comments 1Document28 pagesTANDOC MARY CRIS Thesis Math Major. With Comments 1Mary Cris TandocNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 NetiquettesDocument44 pagesGrade 6 NetiquettesMary Cris TandocNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 Pattern of LV Diastolic FillingDocument3 pagesGrade 1 Pattern of LV Diastolic FillingNicoleNo ratings yet
- Buffer Systems in The Body: Protein Buffers in Blood Plasma and CellsDocument11 pagesBuffer Systems in The Body: Protein Buffers in Blood Plasma and CellsK Jayakumar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- ABG PRACTICE KeyDocument1 pageABG PRACTICE KeyMolly Baller100% (1)
- Sodium and Potassium - Atp Ase PumpDocument18 pagesSodium and Potassium - Atp Ase PumpYaswanthyadavNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument10 pagesBody Fluids and CirculationFree4TechNo ratings yet
- Self CareDocument27 pagesSelf CareJessa May RapadasNo ratings yet
- Reckeweg Base 10 PDFDocument2 pagesReckeweg Base 10 PDFTrikala2016No ratings yet
- Drug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLDocument3 pagesDrug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- Physiology, Lecture 4, Body Fluids and Blood (Lecture Notes)Document17 pagesPhysiology, Lecture 4, Body Fluids and Blood (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (5)
- Respi Demo Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesRespi Demo Lesson PlanBunny BansNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Circulatory SystemAndreNo ratings yet
- Inflammation & Healing of Soft & Hard TissueDocument3 pagesInflammation & Healing of Soft & Hard TissueLakshita PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Handbook For Physiology DepartmentDocument5 pagesHandbook For Physiology Departmenttriumphonyenkawen14No ratings yet
- PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST - BP TakingDocument1 pagePERFORMANCE CHECKLIST - BP TakingMarites PasionNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument54 pagesRespiratory SystemHannah YsaBelle LeguroNo ratings yet
- Module XIII - Vital Signs Behavioral Objectives Content Skills Performance Learning OpportunitiesDocument4 pagesModule XIII - Vital Signs Behavioral Objectives Content Skills Performance Learning OpportunitieskawsarmehmoodNo ratings yet
- Lesson-9 1Document26 pagesLesson-9 1Aihk kenneth BaronaNo ratings yet
- Coup de ChaleurDocument16 pagesCoup de ChaleurEric CharpentierNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The PupilDocument26 pagesDrugs Acting On The PupilAmin AllamNo ratings yet
- Raga Todi Bringing Down Blood PressureDocument8 pagesRaga Todi Bringing Down Blood Pressureami1967No ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in OxygenationDocument185 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in OxygenationAnna Michelle Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dr. RSK - Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument44 pagesDr. RSK - Cyanotic Congenital Heart Diseasemanjunath182019No ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation - NotesDocument12 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation - NotesSaloni GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of RespiratoryDocument6 pagesAssessment of RespiratoryEdraline LumawigNo ratings yet
- Sarcodes: The Important Sarcodes Are Adrenalinum Cholesterinum Insulinum Pituitarinum Pepsinum Pancreatinum ThyroidinumDocument17 pagesSarcodes: The Important Sarcodes Are Adrenalinum Cholesterinum Insulinum Pituitarinum Pepsinum Pancreatinum ThyroidinumMADHURI DHUMAKNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure in Children PDFDocument47 pagesRespiratory Failure in Children PDFOxana TurcuNo ratings yet
- Cureus 0014 00000032158Document8 pagesCureus 0014 00000032158Daniel Martinez HernándezNo ratings yet