Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water?
Water?
Uploaded by
Lei Yamin Chit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views20 pagesWater is made of hydrogen and oxygen atoms bonded together to form H2O molecules. It exists in solid, liquid, and gas forms and has unique properties due to its polarity. Water molecules are polar, with slightly positive hydrogen atoms and slightly negative oxygen atoms, allowing them to bond together through hydrogen bonding. This gives water high surface tension, ability to dissolve many substances, and properties like cohesion and adhesion that allow it to move through narrow spaces and cling to other materials. Water also has a high heat capacity and freezing point, making it stable at Earth's temperatures.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWater is made of hydrogen and oxygen atoms bonded together to form H2O molecules. It exists in solid, liquid, and gas forms and has unique properties due to its polarity. Water molecules are polar, with slightly positive hydrogen atoms and slightly negative oxygen atoms, allowing them to bond together through hydrogen bonding. This gives water high surface tension, ability to dissolve many substances, and properties like cohesion and adhesion that allow it to move through narrow spaces and cling to other materials. Water also has a high heat capacity and freezing point, making it stable at Earth's temperatures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views20 pagesWater?
Water?
Uploaded by
Lei Yamin ChitWater is made of hydrogen and oxygen atoms bonded together to form H2O molecules. It exists in solid, liquid, and gas forms and has unique properties due to its polarity. Water molecules are polar, with slightly positive hydrogen atoms and slightly negative oxygen atoms, allowing them to bond together through hydrogen bonding. This gives water high surface tension, ability to dissolve many substances, and properties like cohesion and adhesion that allow it to move through narrow spaces and cling to other materials. Water also has a high heat capacity and freezing point, making it stable at Earth's temperatures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
Water💧
Present by-
Lei Yamin Chit & Myint Mo Htet
What is WATER?
• Water also known as H2O is a molecule.
• Water is made of non-metals.
• Inorganic Compound – derived from non-living things
• Most abundant compound on Earth
• Found in nearly every living things
About “WATER”
Water is a chemical compound consisting of two
hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
The bond that
forms water is a
covalent bond.
FIVE MAJOR PROPERTIES OF WATER
Water has three phases:
Solid(ice),Liquid(water),Gas(water vapour)
1. Water is liquid at room temperature, boiling point
is high at 100° C; low molecular weight molecules are
usually gaseous.
Water resists temperature change (insulator) .
2. Water has a high freezing point and ice is less
dense than water. (Thus, ice floats in water.)
3. Water is the universal solvent for polar and ionic
molecules (means it dissolves things).
• Hydrophilic: means “water-loving”, molecules that interact
with water, soluble in water.
• Hydrophobic: means “water-fearing”, insoluble in water
• Polar: Means it has a slightly positive (+) end and a
slightly negative (-) end.
4. Water has high surface tension
• water is more attracted to itself than to the air
around it Sticks together (+ and – attract.)
5.Water is sticky:
• • Hydrogen bonds keep water together (polar areas attract)
• Slightly negative (-) Oxygen end is attracted to the slightly positive
(+) Hydrogen ends.
•Cohesion: attraction of water to other water molecules.
• Adhesion: attraction of water to other types of molecules.
• Capillary Action: Can adhere creep up tubes. Ability of a substance
to draw another substance into it.
Examples: - The meniscus in a graduated cylinder.
Water up a tree.
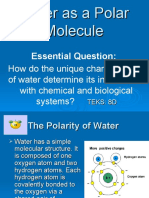
WATER Is Polar Compound
• Electrical charge is
unevenly distributed
• Chemical Formula = H2O
Polar Molecule
• Molecule that has electrically charged areas.
• Also called a polar substance or polar compound.
• Non-polar substances DO NOT HAVE charged ends.
• Water is polar because oxygen and hydrogen have
different electronegativity values.
Polar Molecule
• The positive hydrogen ends of 1 molecule are attracted to
the negative end of the oxygen of another molecule.
POLAR MOLECULE THE PROPERTIES OF:
Cohesion, adhesion, specific heat, universal solvent,
capillary action, surface tension
ALL HAPPEN BECAUSE WATER IS A POLAR SUBSTANCE!
Electrical Charge Of Water
Hydrogen = positive charge
Oxygen = negative charge
Hydrogen Bonding
• Hydrogen of one water molecule is attracted to
the oxygen of another water molecule.
• Partial charges cause water molecules to “stick”
together.
•This bonding gives water some of it’s unique
properties.
Cohesion
• Because water is a polar molecule, it is attracted to
itself.
•Cohesion is the attractive force between water
molecules.
• In chemistry, cohesion is a measure of how well molecules stick
to each other or group together.
•It is caused by the cohesive attractive force between like
molecules.
Adhesion
• Because water is a polar molecule, it is
attracted to other substances.
•Adhesion occurs when molecules of
water are attracted to other substances.
(Both Cohesion and Adhesion cause
surface tension and capillary action)
Surface Tension
• Water has a high surface tension.
• Because water is a polar molecule;
it easily attracts other water
molecules.
• This attraction causes the surface
layer of water molecules to act as a
stretched film over the surface of the
water.
• This property is known as surface
tension.
Capillary Action
Capillary action is the process of liquid flowing in narrow
space without the assistance of ,or even in opposition, any
external forces like gravity.
Capillary action is important for moving water around.
Universal Solvent
• Water is the universal solvent because more substance
dissolve in water than in any chemical .
•This has to do with the polarity of each water molecules. •
The hydrogen side of each water (H2O)molecules carries a
slight positive electric charge, while the oxygen side carries
a slight negative electric charge.
High Heat Capacity
•High heat capacity Water has the highest heat capacity of all
liquid Oceans cool shower than the land due to the high heat
capacity of water.
•To change the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree
Celsius, it takes 1.00 calories.
Mixture, solutions and suspensions
• A mixture is a combination of substance where both substances
keep their original properties.
• Types of mixture They can be divided into two types
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous.
• Solution-one or more substance are distributed evenly in another
substance (solvent).
• All solutions are examples of Homogeneous mixture.
•Suspension is a Heterogeneous mixture of two or more
substances.
• Substances that don't dissolve but separate into tiny pieces.
PH Scale
• PH scale Water is the basic necessity for all living
organisms
• Completely pure water has a pH level of 7.
• The usual pH range of surface water system is 6.5 to 8.5
whereas the pH range of ground water system is 6 to
8.5.pH and Drinking water.
• The U.S Environmental Protection Agency
(EPA)recommends a pH between 6.5 and 8.5 for drinking
water.
• Since metals dissolve readily in acidic water,dissolved metal
may be present in drinking water with a low pH level.
• pH and groundwater- Groundwater flows through rocks and soil that can
affect the water's pH level. For example, contact with sandstone results in a
nearly neutral pH between 6.5 and 7.5.
• Limestone,on the other hand can result in a alkaline pH of 8.5.pH and
streams and lakes.
• The pH level in a lake or stream is crucial for the survival of the fish and
aquatic plants.
• Freshwater lakes and streams typically have pH levels between 6.0 and 8.5 .
• Deeper lakes usually have a higher pH near the surface.
• Accurate pH testing helps keep drinking water and groundwater safe and
helps protect aquatic plants and animals.
Myint Mo Htet
&
Lei Yamin Chit
You might also like
- Renaissance Woman: Fat Loss, Muscle Growth & Performance Through Scientific EatingDocument20 pagesRenaissance Woman: Fat Loss, Muscle Growth & Performance Through Scientific EatingBenedict Ray Andhika33% (3)
- Lecture 1 Introduction PDFDocument31 pagesLecture 1 Introduction PDFAbo-Khaled Mohammed100% (1)
- Remembering, Bartlett (1932)Document11 pagesRemembering, Bartlett (1932)andreea4etc100% (1)
- 2.3 Water and Solutions: Unit 2: Chemistry of LifeDocument27 pages2.3 Water and Solutions: Unit 2: Chemistry of Lifeapi-520057338100% (1)
- Water: The Solvent of Life Where There Is Water, There Is LifeDocument18 pagesWater: The Solvent of Life Where There Is Water, There Is LifeIsaiah Fidelis Maji100% (1)
- BIOCHEMISTRY 106 Lecture RevisedDocument46 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY 106 Lecture Revisedjoanbless79No ratings yet
- Water, PH and BuffersDocument43 pagesWater, PH and BuffersDaniel LuchendoNo ratings yet
- Water 1Document9 pagesWater 1Michael Nyaongo100% (1)
- Lecture 9: Water For Life: SCCH 100 Integrated ChemistryDocument39 pagesLecture 9: Water For Life: SCCH 100 Integrated ChemistryNutt ChanchalitNo ratings yet
- Seawater Density & SalinityDocument3 pagesSeawater Density & SalinityKarthik Mathivanan100% (1)
- Lecture 10 &11 Water TreatmentDocument33 pagesLecture 10 &11 Water Treatmentanantlakhotiya.11No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Solubility & SolventsDocument105 pagesUnit 4 Solubility & SolventskloaizarNo ratings yet
- Water NotesDocument5 pagesWater NotesYaron SaksNo ratings yet
- Basic Water PropertiesDocument12 pagesBasic Water PropertiesBryan GraczykNo ratings yet
- Solution, Suspension, ColloidsDocument149 pagesSolution, Suspension, ColloidsApril Eballena100% (1)
- Water Treatment Water Treatment: Lecture 6: SofteningDocument29 pagesWater Treatment Water Treatment: Lecture 6: SofteningAbo-Khaled MohammedNo ratings yet
- Why Does Water Have A High and Specific Heat CapacityDocument6 pagesWhy Does Water Have A High and Specific Heat Capacitypangaroad200No ratings yet
- Solutions and ConcentrationDocument18 pagesSolutions and Concentrationapi-483662721No ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of WaterDocument4 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of WaterSifatNo ratings yet
- Unusual Properties of WaterDocument44 pagesUnusual Properties of WaterHanan ShehaNo ratings yet
- The Biological Importance of WaterDocument2 pagesThe Biological Importance of WaterRenee RoSe100% (1)
- WATER TREATMENT TECHNOLOGY (TAS 3010) LECTURE NOTES 3b - Water Chemistry ExtendedDocument12 pagesWATER TREATMENT TECHNOLOGY (TAS 3010) LECTURE NOTES 3b - Water Chemistry Extendedmamat88100% (2)
- Chapter 6 Coagulation WER260S 2024Document15 pagesChapter 6 Coagulation WER260S 2024leahsmith1821No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dab 30102Document75 pagesChapter 3 Dab 30102Muhammad Fazlan AliffNo ratings yet
- Salt HydrolysisDocument1 pageSalt HydrolysisnuramiraazizanNo ratings yet
- G2 SolubilityDocument3 pagesG2 SolubilityBryan AliNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: WaterDocument34 pagesBiological Molecules: WaterYing Shuang100% (1)
- Detoxification Water Enhancer (20june12)Document4 pagesDetoxification Water Enhancer (20june12)rodonetNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - Chemical Elements and WaterDocument5 pages3.1 - Chemical Elements and WaterAlvin JovanNo ratings yet
- SEV455 Assignment 1A-BusikuDocument7 pagesSEV455 Assignment 1A-BusikuBusiku SilengaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and Water TreatmentDocument16 pagesElectrochemistry and Water TreatmentSarkuvi ProdNo ratings yet
- Solubility Question 2Document14 pagesSolubility Question 2Unidentified Person100% (1)
- Removal of Heavy Metal Pollutants by Wetland PlantsDocument18 pagesRemoval of Heavy Metal Pollutants by Wetland Plantsjcool_dn100% (1)
- The Motivational Power of Science Discrepant EventsDocument8 pagesThe Motivational Power of Science Discrepant EventsJennifer Owens100% (1)
- Properties of Water Notes: Honors BiologyDocument15 pagesProperties of Water Notes: Honors BiologyPavanNo ratings yet
- Classified - Internal UseDocument18 pagesClassified - Internal UseNandha KumarNo ratings yet
- Water As A Polar MoleculeDocument13 pagesWater As A Polar MoleculeAyaan Asim KhanNo ratings yet
- 11.3 Powerpoint - Net Ionic Equations CE 2Document25 pages11.3 Powerpoint - Net Ionic Equations CE 2Lauren BoersmaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument15 pagesElectrochemistrySakshi TamshettiNo ratings yet
- ElectrodialysisDocument6 pagesElectrodialysisstevenspillkumar100% (2)
- Lab 5 Drinking Water Treatment PDFDocument10 pagesLab 5 Drinking Water Treatment PDFgagileNo ratings yet
- Ecw331 Chapter 10 FinalDocument34 pagesEcw331 Chapter 10 FinalNaqib KamarozamanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Iii Cve 503 Biological Treatment of Wastewater1Document41 pagesLecture Iii Cve 503 Biological Treatment of Wastewater1James Korbla Dodzi Hills100% (1)
- Predicting Products of Precipitation ReactionsDocument16 pagesPredicting Products of Precipitation ReactionsFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Waste Water TreatmentDocument93 pagesChapter 6 Waste Water Treatmentshiksha gauliNo ratings yet
- Theory of Practice WaterDocument5 pagesTheory of Practice WaterTemimi Feras0% (1)
- Chapter ThreeDocument20 pagesChapter ThreeKasozi Bateesa ShafickNo ratings yet
- Application of Water Quality Index To Assess The Potability of Some Domestic Water Supply Sources in Mubi North Nigeria IJERTV9IS080335 PDFDocument13 pagesApplication of Water Quality Index To Assess The Potability of Some Domestic Water Supply Sources in Mubi North Nigeria IJERTV9IS080335 PDFHyellamada DanielNo ratings yet
- Electrodialysis ReportDocument8 pagesElectrodialysis Reportblackbeauty14No ratings yet
- Conductivity, Salinity & Total Dissolved Solids - Environmental Measurement SystemsDocument13 pagesConductivity, Salinity & Total Dissolved Solids - Environmental Measurement SystemsMiguelNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Water: Its Properties and Purification ADocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Water: Its Properties and Purification Aapple bottom jeansNo ratings yet
- Solubility CurveDocument2 pagesSolubility CurveDanni SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal - THMDocument16 pagesProject Proposal - THMAnjali KotheNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification NotesDocument38 pagesPeriodic Classification NotesSantosh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Hard Water, Soft WaterDocument16 pagesHard Water, Soft WaterMark Abion ValladolidNo ratings yet
- Hard Water LabDocument6 pagesHard Water Labapi-317559664No ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument29 pagesWater TreatmentSubhamay BarmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Water QualityDocument26 pagesLecture 6 Water QualitySimphiweNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Water PPT 1Document19 pagesCH 16 Water PPT 1Sandarbh Jain100% (1)
- Determination of Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) in Waste Water - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDocument3 pagesDetermination of Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) in Waste Water - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesIrfan SalimNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCDocument42 pagesBiomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCAmon SangulubeNo ratings yet
- Properties of WaterDocument43 pagesProperties of WaterJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- PGDRD Mail Assignment 26 Feb PalitDocument8 pagesPGDRD Mail Assignment 26 Feb PalitDeepak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten HandbookDocument5 pagesKindergarten HandbookElizabeth MoorlagNo ratings yet
- GLS-LS40GW Specification 20200902Document5 pagesGLS-LS40GW Specification 20200902houyamelkandoussiNo ratings yet
- Design and Synthesis of Zinc (Ii) Complexes With Schiff Base Derived From 6-Aminopenicillanic Acid and Heterocyclic AldehydesDocument6 pagesDesign and Synthesis of Zinc (Ii) Complexes With Schiff Base Derived From 6-Aminopenicillanic Acid and Heterocyclic AldehydesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- R30 CFA Level 3Document19 pagesR30 CFA Level 3Ashna0188No ratings yet
- Cutoff1 101020 0Document3 pagesCutoff1 101020 0ghi98183No ratings yet
- Furosemide DSDocument2 pagesFurosemide DSjhanrey0810_18768No ratings yet
- English Curriculum Reforminthe PhilippinesDocument18 pagesEnglish Curriculum Reforminthe PhilippinesLanping FuNo ratings yet
- A Bravo Delta Lancaster Model Worth 329: 38 Paralle L Paralle LDocument116 pagesA Bravo Delta Lancaster Model Worth 329: 38 Paralle L Paralle LAnonymous 7Je2SSU100% (2)
- A320 PedestalDocument14 pagesA320 PedestalAiman ZabadNo ratings yet
- Minimal Stimulation IVF Vs Conventional IVFDocument8 pagesMinimal Stimulation IVF Vs Conventional IVFpolygoneNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets-Empirical - Molecular-FormulaDocument1 pageChemsheets-Empirical - Molecular-FormulaMouli MishraNo ratings yet
- Deed of DonationDocument2 pagesDeed of DonationMary RockwellNo ratings yet
- CAD1501 Notes: Unit 1: What You Can Expect To See in The Summary/Notes For This UnitDocument9 pagesCAD1501 Notes: Unit 1: What You Can Expect To See in The Summary/Notes For This UnitSimone BreetNo ratings yet
- DS Masteri An PhuDocument174 pagesDS Masteri An PhuPhong PhuNo ratings yet
- Muscle Memo Workout - Guitar Coach MagDocument28 pagesMuscle Memo Workout - Guitar Coach Magpeterd87No ratings yet
- GIS Based Analysis On Walkability of Commercial Streets at Continuing Growth Stages - EditedDocument11 pagesGIS Based Analysis On Walkability of Commercial Streets at Continuing Growth Stages - EditedemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Stones Unit 2bDocument11 pagesStones Unit 2bJamal Al-deenNo ratings yet
- Dual-Band Wearable Rectenna For Low-Power RF Energy HarvestingDocument10 pagesDual-Band Wearable Rectenna For Low-Power RF Energy HarvestingbabuNo ratings yet
- Iii Iihiiiiiiiiiiii 111111: Does User-Oriented Gas Turbine Research Pay Off?Document7 pagesIii Iihiiiiiiiiiiii 111111: Does User-Oriented Gas Turbine Research Pay Off?Morteza YazdizadehNo ratings yet
- Enya Ukuleles - Enya Music UsaDocument1 pageEnya Ukuleles - Enya Music Usav9zmmt9g7hNo ratings yet
- Leo HistoryDocument14 pagesLeo HistoryJeamil Esthiff Terán ToledoNo ratings yet
- Task Force On Sexual Assault and Interpersonal Violence Final Report 2014-15Document16 pagesTask Force On Sexual Assault and Interpersonal Violence Final Report 2014-15Fourth EstateNo ratings yet
- SB KarbonDocument3 pagesSB KarbonAbdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Print - Udyam Registration CertificateDocument2 pagesPrint - Udyam Registration CertificatesahityaasthaNo ratings yet
- Not in His Image (15th Anniversary Edition) - Preface and IntroDocument17 pagesNot in His Image (15th Anniversary Edition) - Preface and IntroChelsea Green PublishingNo ratings yet
- OX App Suite User Guide English v7.6.0Document180 pagesOX App Suite User Guide English v7.6.0Ranveer SinghNo ratings yet
- SG Unit5progresscheckfrq 5e815f88c4fb70Document9 pagesSG Unit5progresscheckfrq 5e815f88c4fb70api-485795043No ratings yet