Professional Documents
Culture Documents
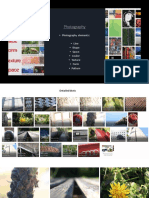
Knowledge Organisers Gcse Photography
Knowledge Organisers Gcse Photography
Uploaded by
api-563918017Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Knowledge Organisers Gcse Photography
Knowledge Organisers Gcse Photography
Uploaded by
api-563918017Copyright:
Available Formats
GCSE PHOTOGRAPHY - KNOWLEDGE ORGANISER
Assessment Objectives
- This is how you are marked for coursework and Exam.
- There are 25 marks to gain for each AO.
- 60% of your GCSE mark is coursework and 40% is your exam mark.
AO1 • Artist research pages.
Develop ideas through • Visits to exhibitions and
investigations galleries.
• Your own responses in
the style of the artist.
• Interviews with artists/
photographers.
Scan here • Annotate and analyse
for more what you have found out.
advice on
AO1
AO2 • Experimenting with a range
of different materials and
Refine work by exploring
techniques.
ideas and selecting and
experimenting with • Photo-shoots exploring
appropriate techniques. different techniques.
• Selecting best photographs
from Photo-shoots.
• Using Photo-shop to edit
photographs further in
Scan here a creative way.
for more • Using Darkroom processes to
advice on create photograms/
AO2 cyanotypes/ Double
exposures.
AO3 • Title page.
Record ideas, observations • Mind Map.
and insights relevant to • Mood-boards.
their intentions in visual • Planning Photo-shoots.
and/or other forms. • Photographs.
• Contact sheets of Photo-
shoots.
Scan here
for more
advice on
AO3
AO4 • Plans and drawings of final
piece ideas.
Present a personal, • Mini mock-ups and
informed and meaningful experiments for final piece.
response. Completing a • Creating an original final
relevant and intentional piece, that is clearly inspired
by your research and creative
final piece. journey.
Scan here • Evaluation of final piece (how
for more does your piece link to the
advice on project theme?).
AO4
GCSE PHOTOGRAPHY - KNOWLEDGE ORGANISER
Manual Camera Settings
- Gives you complete control of the camera. Can be accessed on a DSLR by selecting M.
- Involves the Exposure Triangle – Aperture / ISO/ Shutter Speed
- If one of the exposure triangle setting is changed it will affect the other two.
- For hints and tips on how to do a photo-shoot go to Student Share / Art / GCSE Photography / How to do a
photo-shoot.
Aperture: Scan here for an
• How open the lens is. introduction to
• To capture close up shots a wider lens is required. using Aperture
• To capture detail in the distance a smaller lens setting is required. settings
Shutter Speed:
• How quickly the shutter
opens and closes.
• Used for action and
movement shots.
• The slower the setting Scan here for an
the more blurred the introduction to
photograph. using Shutter
Speed settings
ISO:
• How much light is let into the camera.
• Can affect the photograph by making it grainy the higher the setting.
Scan here for an
introduction to
using ISO
settings
GCSE PHOTOGRAPHY - KNOWLEDGE ORGANISER
Compositional Elements
- Key things to consider when setting up a shot.
- Used to describe how a photograph works.
- Are not all used at the same time. However some can be more prominent than others in a photograph.
Pattern There are patterns all around us if we only learn JON MEASURES
to see them. Emphasizing and highlighting
these patterns can lead to striking shots – as
can high lighting when patterns are broken.
Texture Photographs of two dimensional objects yet with ANSEL ADAMS
the clever use of ‘texture’ they can come alive
and become almost three dimensional. You want
the viewer to imagine how the object feels.
Depth of Field The depth of field that you select when taking ELIA LOCARDI
an image will drastically impact the composition
of an image.
It can isolate a subject from its background and
foreground (when using a shallow depth of field)
or it can put the same subject in context by
revealing it’s surrounds with a larger depth of
field.
Symmetry Can create a balanced composition that leaves IRVING PENN
the viewer with a feeling the photograph is
staged in some way. Can add a striking effect
depending on the subject/ object photographed.
Rule of Thirds A 3x3 grid used by photographs to create a ERNST HAAS
composition that feels right. Objects that fall on
or near the lines are considered to have the best
impact.
Shape The way subjects connect to each other in a MAN RAY
photo forms shapes that draw the eye from
subject to subject. If your subject is already
triangular or diamond-shaped (like a pyramid),
the viewer's eye will automatically focus on that
shape.
Focal Point/ The main focus of a photograph/artwork. There is MICHAEL BOSANKO
usually a line/ shape/ space of some form leading
to it.
GCSE PHOTOGRAPHY - KNOWLEDGE ORGANISER
Compositional Elements
- Key things to consider when setting up a shot.
- Used to describe how a photograph works.
- Are not all used at the same time. However some can be more prominent than others in a photograph.
Restful / If there is space around an object in a ANNIE LEIBOVITZ
Dynamic composition then it is considered restful.
Composition Photographs that are zoomed in and objects
touch the edges of the composition are
considered dynamic. It dictates how much
the viewer’s eyes have to move around the
photograph to see everything.
Simplification When light, depth of field, positioning of an NICHOLAS
object is used to make the viewer focus on a GOODDEN
specific area of the photograph/artwork.
Lines Lines can be powerful elements in an image. They BILL BRANDT
(Horizon line) have the power to draw the eye to key focal
points in a shot and to impact the ‘feel’ of an
image greatly.
Diagonal, Horizontal, Vertical and Converging
lines all impact images differently and should be
spotted while framing a shot and then utilized to
strengthen it.
Viewpoint/ Birds- eye: From above facing downward ANTONIO JAGGIE
Perspective Worm’s – eye: From below facing upward
Eye – line: At standing height
These perspectives can have an impact on how
the viewer feels about the photograph, and how
it is perceived.
Colour A lot of colour can be overwhelming ANDY WARHOL
and considered a bold statement.
Lack of colour can focus the viewer on the
message the photographer is trying to convey.
Lack of colour can also accentuate the patterns,
shapes and textures in a photograph.
Abstract It is taking a subject and forcing the viewer to PAUL STRAND
look at it in a different way. This may cause the
subject to lose its original meaning or purpose.
It may even render the subject unreal, abnormal
and not of this world. The subject could lose all
literal meaning and be reduced to only shape,
light, texture or color.
GCSE PHOTOGRAPHY - KNOWLEDGE ORGANISER
Light Shadow Art
- Can be used to create shadow or highlight an object/person. by
- Comes in many different forms. Kumi
- Use of light can have an impact on camera settings. Yamashita
- Direction of the light source is very important.
Scan here for an
introduction to
using light in
Natural Light Artificial Light
photography
Helpful Websites for GCSE Photography
Website QR Code Summary
https://digital-photography- Really informative website with
school.com/digital-photography-tips-for- lots of easy to follow tutorials
for beginners in photography.
beginners/
https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/zg GCSE Bitesize website is great
wpnbk/revision/1 for video tutorials, subject
specific vocab and helping to
understand how GCSE
Photography course works.
https://www.tate.org.uk/ The Tate website is a fantastic
resource for finding out about
exhibitions you could visit for
primary research (AO1).
Photoshop
- Used to enhance and creatively edit digital photographs.
- Always take screenshots using the “Snipping Tool” to evidence what you have done while editing.
- Only use specific features and effects if there is a link to research. Not every Photograph needs to be edited.
- To find a digital guide to the basic skills for using Photoshop go to:
Student Share / Art / GCSE Photography / Basic Photoshop Skills
You might also like
- Fiber Chart 432 PDFDocument1 pageFiber Chart 432 PDFSrbska Muzika40% (5)
- Suzanne Saroff - Analysing A PhotographerDocument2 pagesSuzanne Saroff - Analysing A Photographerapi-565375679No ratings yet
- Understanding Photography PDFDocument35 pagesUnderstanding Photography PDFAl DenteNo ratings yet
- My English Book - KindergartenDocument95 pagesMy English Book - KindergartenAngelica Valdez100% (1)
- Canvas Size: A. Instagram Feeds: 1000 X 1000 Pixels B. Instagram Story: 1080 X 1920 Pixels 2. Theme: A. First Week: Blue, Land of OoDocument4 pagesCanvas Size: A. Instagram Feeds: 1000 X 1000 Pixels B. Instagram Story: 1080 X 1920 Pixels 2. Theme: A. First Week: Blue, Land of OoRibka NovitaNo ratings yet
- Digital Photography - Videography (Syllabus)Document6 pagesDigital Photography - Videography (Syllabus)Rizqi BaruNo ratings yet
- Theme Shoot DigitalDocument2 pagesTheme Shoot Digitalbriguy43051No ratings yet
- Que Hace Grandiosa Una Fotografia InglesDocument55 pagesQue Hace Grandiosa Una Fotografia InglesPabloGustavoG.PeñaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum - The Power of Photography Chapter 5 Pages 1-5Document5 pagesCurriculum - The Power of Photography Chapter 5 Pages 1-5Majeogbe PaulNo ratings yet
- Photography 2Document17 pagesPhotography 2api-545835776No ratings yet
- Photography - Lesson 5Document10 pagesPhotography - Lesson 5heathparkmoviesNo ratings yet
- Au Ma14 1L PDFDocument18 pagesAu Ma14 1L PDFAnonymous dSFbLxc9No ratings yet
- PhotographyDocument96 pagesPhotographyKARLVINNo ratings yet
- Photography - Lesson 4Document19 pagesPhotography - Lesson 4heathparkmoviesNo ratings yet
- Lights, Camera, Action! Becoming A Producer With Inventor StudioDocument18 pagesLights, Camera, Action! Becoming A Producer With Inventor StudioGraham MooreNo ratings yet
- Avsten3s Module 4Document14 pagesAvsten3s Module 4Arianne Joy Quiba DullasNo ratings yet
- The Visual Elements—Photography: A Handbook for Communicating Science and EngineeringFrom EverandThe Visual Elements—Photography: A Handbook for Communicating Science and EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Photography Workshop: Ximb 22 Jan 2012Document56 pagesPhotography Workshop: Ximb 22 Jan 2012Dibya Swarup Panigrahi100% (1)
- ActionCards Macro+PhotographyDocument3 pagesActionCards Macro+Photographyredbaron196750% (2)
- Camera Parts and FunctionsDocument29 pagesCamera Parts and FunctionslizaNo ratings yet
- MR BoneyVarghesePTitus PhotographyDocument31 pagesMR BoneyVarghesePTitus PhotographyEzedinim IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Photojournalism PressDocument60 pagesPhotojournalism PressMary Ann Ayson100% (1)
- PHOTOjournalismDocument96 pagesPHOTOjournalismLeoAtienza100% (3)
- PortfolioDocument21 pagesPortfolioapi-733180654No ratings yet
- Portfolio Template Part 2Document8 pagesPortfolio Template Part 2api-565692107No ratings yet
- Famous Photographer Investigation Task 2019Document3 pagesFamous Photographer Investigation Task 2019ealesc26No ratings yet
- Making Your Lenses: Work For YouDocument1 pageMaking Your Lenses: Work For YouAsif RazaNo ratings yet
- Photography Club: Bandar Penawar Sports SchoolDocument34 pagesPhotography Club: Bandar Penawar Sports SchoolzularisNo ratings yet
- If You Want More Film:: CHOOSE 3 of The Following To Shoot On B&W FilmDocument3 pagesIf You Want More Film:: CHOOSE 3 of The Following To Shoot On B&W FilmjcecilNo ratings yet
- Layering: Focusing OnDocument1 pageLayering: Focusing OnAsif RazaNo ratings yet
- Sel351 - Landscape PhotographyDocument26 pagesSel351 - Landscape Photographysyed aimanNo ratings yet
- 7304 BRIEF-4f Cinematic ReflectionsDocument3 pages7304 BRIEF-4f Cinematic ReflectionsBakka SilvaNo ratings yet
- Background Guide - PhotographyDocument12 pagesBackground Guide - PhotographyKhushi Gupta100% (1)
- Amateur Photographer - July 30, 2016Document84 pagesAmateur Photographer - July 30, 2016Voinea AndreiNo ratings yet
- Languange of The Lens: Course: Cinematography For Animation Effective Period: September 2016Document12 pagesLanguange of The Lens: Course: Cinematography For Animation Effective Period: September 2016Yuna MusicNo ratings yet
- Still Photography Lab (Subject Code: 154) Semester - IiDocument27 pagesStill Photography Lab (Subject Code: 154) Semester - IiNaman jainNo ratings yet
- Ciro Sannino - Photography and Rendering With VRay 2013Document239 pagesCiro Sannino - Photography and Rendering With VRay 2013Calvin Wong, Jr.100% (1)
- Art Parctices and Notes7Document47 pagesArt Parctices and Notes7fzlibra61002No ratings yet
- LightDocument2 pagesLightcaro sturgesNo ratings yet
- Focal Length To Effective Aperture Diameter (Inversely Proportional)Document15 pagesFocal Length To Effective Aperture Diameter (Inversely Proportional)Mj PacunayenNo ratings yet
- DISCUSS & Essential Questions Photography and Camera Skills Digital Skills (Developing Craft) Photographic ConceptsDocument11 pagesDISCUSS & Essential Questions Photography and Camera Skills Digital Skills (Developing Craft) Photographic ConceptsStojan AćimovićNo ratings yet
- What To Do Before You Start Shooting - Qué Hacer Antes de Empezar A FotografiarDocument30 pagesWhat To Do Before You Start Shooting - Qué Hacer Antes de Empezar A FotografiarEditorial JlpcNo ratings yet
- Module 8Document6 pagesModule 8Ânţhony Đełos RıosNo ratings yet
- PhotographyDocument11 pagesPhotographyHysham AliNo ratings yet
- Viplav PHOTOGRAPHY LAB EXERCISE BOOKDocument35 pagesViplav PHOTOGRAPHY LAB EXERCISE BOOKViplav BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Photography and VideographyDocument54 pagesGroup 2 - Photography and Videographyjedidiah eliotNo ratings yet
- FocusingDocument29 pagesFocusingJeric CatalanNo ratings yet
- 2152 Composition BasicsDocument64 pages2152 Composition BasicsBabielyn BelamideNo ratings yet
- Photo: GraphyDocument99 pagesPhoto: GraphyAby Mathew100% (1)
- Photography - Lesson 6Document5 pagesPhotography - Lesson 6heathparkmoviesNo ratings yet
- Pre-Session TasksDocument20 pagesPre-Session TasksGracey ElizabethNo ratings yet
- B. Where To Put The SubjectDocument45 pagesB. Where To Put The SubjectzekdazelfaNo ratings yet
- RPSA Notes For PhotographyDocument5 pagesRPSA Notes For PhotographytateamilleNo ratings yet
- Elet5100 Learningmodule Designdocument TemplateDocument3 pagesElet5100 Learningmodule Designdocument Templateapi-351479475No ratings yet
- Topaz Lens Effects: Quick Start GuideDocument16 pagesTopaz Lens Effects: Quick Start GuideAnonymous l4hJOryNo ratings yet
- Visual Media - PhotographyDocument6 pagesVisual Media - PhotographyMary Dorothy Anne OmalNo ratings yet
- Visual Elements of Photography PDFDocument3 pagesVisual Elements of Photography PDFwillywdeNo ratings yet
- Double Exposure 1Document10 pagesDouble Exposure 1api-564519569No ratings yet
- Q2 Arts L2Document30 pagesQ2 Arts L2JHerwin Dagdagan PranillaNo ratings yet
- Photography - Lesson 10Document8 pagesPhotography - Lesson 10heathparkmoviesNo ratings yet
- The Art of PhotographyDocument14 pagesThe Art of PhotographyOltag DangoNo ratings yet
- IteDocument20 pagesIteJanrei Devilla TeNo ratings yet
- Photocomposition Intro 2020 BDocument48 pagesPhotocomposition Intro 2020 Bapi-334248806No ratings yet
- Marks A01: A02: AO3: AO4:: Marks 5-8 Marks 9-12 Marks 13-16 Marks 17-18 MarksDocument2 pagesMarks A01: A02: AO3: AO4:: Marks 5-8 Marks 9-12 Marks 13-16 Marks 17-18 Marksapi-565375679No ratings yet
- Laurence DemaisonDocument1 pageLaurence Demaisonapi-565375679No ratings yet
- Light PaintingDocument1 pageLight Paintingapi-565375679No ratings yet
- Kls 9 BAB 2 Persamaan Dan Fungsi KuadratDocument27 pagesKls 9 BAB 2 Persamaan Dan Fungsi KuadratNaily SyarifahNo ratings yet
- Predefined FontDocument3 pagesPredefined FontIndustrial AutomationNo ratings yet
- Colour Properties and Colour Theory When PaintingDocument3 pagesColour Properties and Colour Theory When PaintingAmalia CandiaNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies: Ms. Jocelyn P. Cruz Subject TeacherDocument29 pagesEmpowerment Technologies: Ms. Jocelyn P. Cruz Subject TeacherJocelyn CruzNo ratings yet
- Wood 2Document26 pagesWood 2Ameya KhangarNo ratings yet
- CSS Color Module Level 3Document47 pagesCSS Color Module Level 3Crina PopaNo ratings yet
- LAS 2 - Week2 - Arts6 - Print Making Silk ScreenDocument8 pagesLAS 2 - Week2 - Arts6 - Print Making Silk ScreenJade LuiNo ratings yet
- PHOTOPRINTDocument5 pagesPHOTOPRINTMohammad yusufmNo ratings yet
- Foc Colour Code Data SheetDocument3 pagesFoc Colour Code Data Sheetpari84No ratings yet
- History of Photography ModuleDocument5 pagesHistory of Photography ModuleJemwel CalindongNo ratings yet
- CigüeñaDocument7 pagesCigüeñaBrittany RamirezNo ratings yet
- Maths Symmetry Post TestDocument3 pagesMaths Symmetry Post Testapi-2483359410% (1)
- Gato LlaveroDocument20 pagesGato LlaveroAngelica SalasNo ratings yet
- Theory of Colour Harmony and Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesTheory of Colour Harmony and Its ApplicationMarvin AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Gyroid Pattern ENGDocument8 pagesGyroid Pattern ENGSailor Lily100% (1)
- Printmaking Art Curriculum MapDocument19 pagesPrintmaking Art Curriculum MapMill ValleyNo ratings yet
- Washing CapacityDocument4 pagesWashing CapacityReazus SalehinNo ratings yet
- Expert Guide ColorDocument61 pagesExpert Guide ColorJason RobertsNo ratings yet
- Light Painting PhotographyDocument14 pagesLight Painting Photographylucy baikNo ratings yet
- Happy Easter Mouse Printable Pack - A Little Pinch of PerfectDocument20 pagesHappy Easter Mouse Printable Pack - A Little Pinch of PerfectSerban VioletaNo ratings yet
- Loka - Mata Pricelist 2022 - r1Document18 pagesLoka - Mata Pricelist 2022 - r1OpenData Bandung20No ratings yet
- Introduction To Colour ConceptsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Colour ConceptsGuido JonesNo ratings yet
- LightQualityCRI by Haroon JDocument3 pagesLightQualityCRI by Haroon JLighthouse IlluminationsNo ratings yet
- Marcare SOD-80 DiodesDocument2 pagesMarcare SOD-80 DiodesisosicaNo ratings yet
- IA 6 - Enhancing and Decorating Wood ProductsDocument23 pagesIA 6 - Enhancing and Decorating Wood ProductsVICTORIANO DONOSONo ratings yet
- Color Theory Cheat Sheet For BeginnersDocument13 pagesColor Theory Cheat Sheet For BeginnersCharlie Brown71% (7)
- Search For Salt Colors: Ed BowmanDocument4 pagesSearch For Salt Colors: Ed BowmanEdward Pitts100% (2)